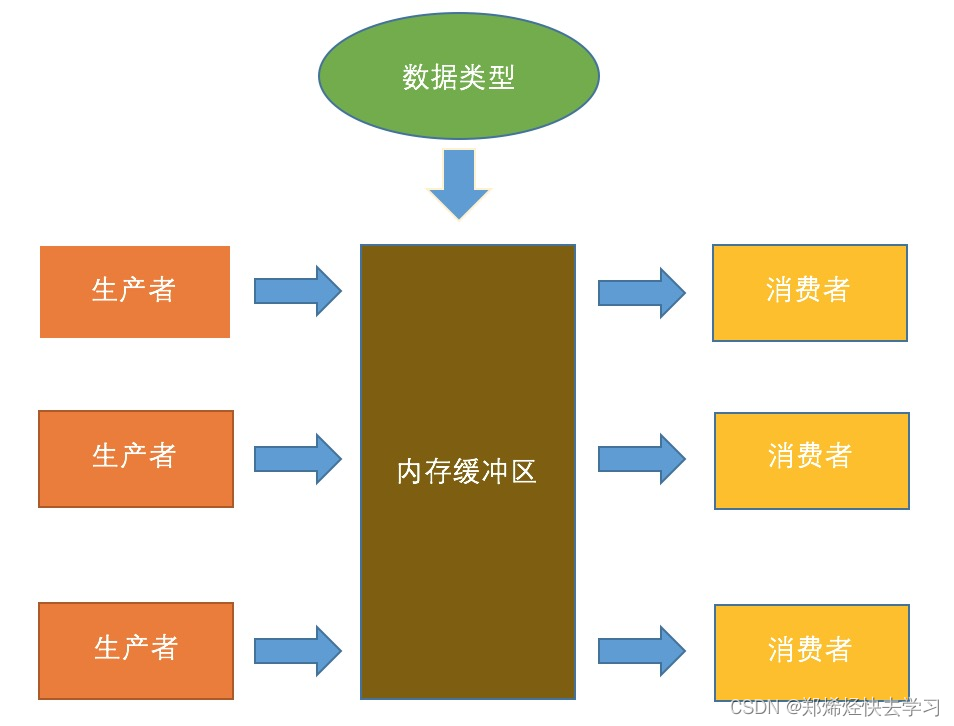
目录
1.一些关于excel的常识
2.使用Apache POI操作excel
3.使用easyexcel操作excel
4.结合mybatis-plus批量导入excel数据到数据库
1.一些关于excel的常识
首先关于excel的文件格式,分为xls和xlsx,分别对应03版本和07以后的版本。
03版本的excel最大行数限制为表格共有65536行,256列;而07版本的excel则无此限制。
关于excel中的单元格格式,一般为以下几类:
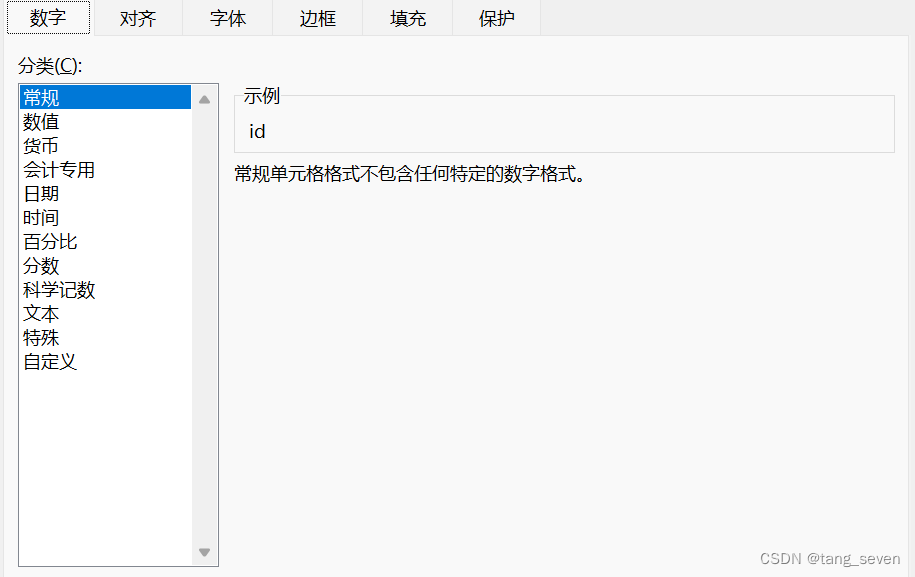
转为java代码时,可以初略地处理为:字符串、数值(普通数字、日期)、公式三类。由于不同的格式对应不同的java数据类型,所以读取时需要进行格式的转换。
2.使用Apache POI操作excel
Apache POI是创建和维护操作各种符合Office Open XML(OOXML)标准和微软的OLE 2复合文档格式(OLE2)的Java API。用它可以使用Java读取和创建,修改EXCEL文件。简单来说Apache POI 提供Java操作Excel进行读写的解决方案。
首先,我们需要知道的是,不同版本的excel对应POI不同版本下的依赖:
<!--xls 03版-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.poi</groupId>
<artifactId>poi</artifactId>
<version>3.9</version>
</dependency>
<!--xlsx 07版-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.poi</groupId>
<artifactId>poi-ooxml</artifactId>
<version>3.9</version>
</dependency>操作excel对象时,也对应不同的类:
//创建工作蒲(03版)
Workbook workbook_03 = new HSSFWorkbook();
//创建工作蒲(07版)
Workbook workbook_07 = new XSSFWorkbook();(1)使用POI实现excel写:
import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFWorkbook;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Cell;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Row;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Sheet;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Workbook;
import org.joda.time.DateTime;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
public class ExcelWriter {
private static final String path = "C:/Users/14125/Desktop/";
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//创建工作蒲(03版)
Workbook workbook = new HSSFWorkbook();
//Workbook workbook_07 = new XSSFWorkbook();
//创建工作表
Sheet sheet = workbook.createSheet();
//创建行/列
Row row1 = sheet.createRow(0);
Cell cell_11 = row1.createCell(0);
cell_11.setCellValue("测试一下");
Cell cell_12 = row1.createCell(1);
cell_12.setCellValue("测试两下");
Row row2 = sheet.createRow(1);
Cell cell_21 = row2.createCell(0);
cell_21.setCellValue(new DateTime().toString("yyyy-MM-dd"));
//生成一张表(IO流)
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(path+"java_excel.xls");
workbook.write(fileOutputStream);
fileOutputStream.close();
}
}逻辑上很简单,创建工作蒲——》创建表——》创建行——》创建列,从而确定一个单元格——》往单元格写入值——》生成表,使用文件流输出——》关闭流。
(1)使用POI实现excel读:
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.*;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFFormulaEvaluator;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFWorkbook;
import org.joda.time.DateTime;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Date;
public class ExcelReader {
private static final String path = "C:/Users/14125/Desktop/";
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//获取文件流
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(path+"test_read.xlsX");
//获取工作蒲对象
Workbook workbook = new XSSFWorkbook(fileInputStream);
Sheet sheet = workbook.getSheetAt(1);
//获取计算公式
FormulaEvaluator formulaEvaluator = new XSSFFormulaEvaluator((XSSFWorkbook) workbook);
Row rowTitle = sheet.getRow(0);
if(rowTitle!=null) {
//获取一行中数据数
int cellCount = rowTitle.getPhysicalNumberOfCells();
//获取标题行
for (int i = 0; i < cellCount; i++) {
Cell cell = rowTitle.getCell(i);
if (cell != null) {
//都为String,直接读取
System.out.print(cell.getStringCellValue()+"| ");
}
}
System.out.println();
//获取行数
int rowCount = sheet.getPhysicalNumberOfRows();
//第二行非标题行开始遍历
for (int i = 1; i < rowCount; i++) {
Row rowData = sheet.getRow(i);
if(rowData!=null){
for (int j = 0; j < cellCount; j++) {
Cell cell = rowData.getCell(j);
if (cell != null) {
//匹配单元格的数据类型
int cellType = cell.getCellType();
switch (cellType) {
//字符串。直接读取
case Cell.CELL_TYPE_STRING:
String StringCellValue = cell.getStringCellValue();
System.out.print(StringCellValue+"| ");
break;
//数字类型,转换
case Cell.CELL_TYPE_NUMERIC:
// 判断是否是日期
if (DateUtil.isCellDateFormatted(cell)) {
Date DateCellValue = cell.getDateCellValue();
//转换日期格式
System.out.print(new DateTime(DateCellValue)
.toString("yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm:ss")+"| ");
}else {
//重新设置单元格的数据类型
cell.setCellType(Cell.CELL_TYPE_STRING);
//转换成字符串获取,防止数字过长
System.out.print(cell.toString()+"| ");
}
break;
//boolean类型
case Cell.CELL_TYPE_BOOLEAN:
boolean booleanCellValue = cell.getBooleanCellValue();
System.out.print(booleanCellValue+"| ");
break;
//公式类型
case Cell.CELL_TYPE_FORMULA:
// //计算
// CellValue evaluate = formulaEvaluator.evaluate(cell);
// //获取计算后的值
// String cellValuate = evaluate.formatAsString();
// System.out.println(cellValuate+"| ");
//重新设置单元格的数据类型
double value = cell.getNumericCellValue();
//转换成字符串获取,防止数字过长
System.out.print(value+"| ");
break;
//空白
case Cell.CELL_TYPE_BLANK:
break;
// 匹配不能转换的错误
case Cell.CELL_TYPE_ERROR:
break;
}
}
}
}
System.out.println();
}
}
//关闭流
fileInputStream.close();
}
}上述代码逻辑如上:创建文件流——》获取excel工作簿——》获取表头行——》 获取有内容单元格行数——》遍历所有行——》在每一行中获取有内容单元格列数——》遍历该行所有单元格——》判断单元格格式,并输出内容——》直到遍历所有单元格内容
上述代码中,核心代码为判断单元格格式,转为可处理的格式并进行输出:
//匹配单元格的数据类型
switch (cellType) {
//字符串。直接读取
case Cell.CELL_TYPE_STRING:
String StringCellValue = cell.getStringCellValue();
System.out.print(StringCellValue+"| ");
break;
//数字类型,转换
case Cell.CELL_TYPE_NUMERIC:
// 判断是否是日期
if (DateUtil.isCellDateFormatted(cell)) {
Date DateCellValue = cell.getDateCellValue();
//转换日期格式
System.out.print(new DateTime(DateCellValue)
.toString("yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm:ss")+"| ");
}else {
//重新设置单元格的数据类型
cell.setCellType(Cell.CELL_TYPE_STRING);
//转换成字符串获取,防止数字过长
System.out.print(cell.toString()+"| ");
}
break;
//boolean类型
case Cell.CELL_TYPE_BOOLEAN:
boolean booleanCellValue = cell.getBooleanCellValue();
System.out.print(booleanCellValue+"| ");
break;
//公式类型
case Cell.CELL_TYPE_FORMULA:
//计算
CellValue evaluate = formulaEvaluator.evaluate(cell);
//获取计算后的值
String cellValuate = evaluate.formatAsString();
System.out.println(cellValuate+"| ");
//重新设置单元格的数据类型
double value = cell.getNumericCellValue();
//转换成字符串获取,防止数字过长
System.out.print(value+"| ");
break;
//空白
case Cell.CELL_TYPE_BLANK:
break;
// 匹配不能转换的错误
case Cell.CELL_TYPE_ERROR:
break;
}
}实际开发中,我们可以将上述代码封装为一个工具类,传入一个excel文件流参数即可进行后续的调用。若在存储数据库,即在 Switch中转换格式后进行存储即可
3.使用easyexcel操作excel
EasyExcel是一个基于Java的、快速、简洁、解决大文件内存溢出的Excel处理工具。可以让你在不用考虑性能、内存的等因素的情况下,快速完成Excel的读、写等功能。
首先引入依赖,而easyexcel中已经包含了Apache poi相关依赖:
<!--easy excel 已包含POI-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>easyexcel</artifactId>
<version>2.2.0-beta2</version>
</dependency>(1)使用easyexcel写:
首先,创建实体类,@ExcelProperty(value="列名称",index = 列坐标);若是包含子标题的复杂标题,使用方法为:@ExcelProperty({"主标题", "字符串标题"})。
@ExcelIgnore 标签可以让实体类写入时,忽略该字段,不进行写入
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public class Student {
@ExcelProperty(index = 0)
private Integer id;
@ExcelProperty(index = 1)
private String age;
@ExcelProperty(index = 2)
private String name;
@ExcelProperty(index = 3)
private String gender;
}easyexecl进行代码如下:
String fileName = TestFileUtil.getPath() + "complexHeadWrite" + System.currentTimeMillis() + ".xlsx";
// 这里 需要指定写用哪个class去写,然后写到第一个sheet,名字为模板 然后文件流会自动关闭
EasyExcel.write(fileName, ComplexHeadData.class).sheet("模板").doWrite(data());4.结合mybatis-plus批量导入excel数据到数据库
(2)使用easyexcel读:
首先,创建实体类:
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
@TableName("student")
public class Student {
@TableId(value = "id",type = IdType.AUTO)
@ExcelProperty(index = 0)
private Integer id;
@ExcelProperty(index = 1)
private String age;
@ExcelProperty(index = 2)
private String name;
@ExcelProperty(index = 3)
private String gender;
}此处,为了简便mybatis-plus和easyexcel使用了同一个实体类,实际中应该为easyexcel封装一个dto,mybatis-plus单使用一个实体类,更为合理。
编写listener代码:
import com.alibaba.excel.context.AnalysisContext;
import com.alibaba.excel.event.AnalysisEventListener;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON;
import com.seven.excel.dao.StudentDao;
import com.seven.excel.entities.Student;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
@Slf4j
public class StudentDataListener extends AnalysisEventListener<Student> {
/**
* 每隔10条存储数据库,然后清理list ,方便内存回收
*/
private static final int BATCH_COUNT = 10;
//缓存数据列表
private List<Student> cachedDataList = new ArrayList<>(BATCH_COUNT);
//不可以用spring管理,需用该方法实例化对象
private StudentDao studentDao;
public StudentDataListener(StudentDao studentDao) {
this.studentDao = studentDao;
}
/**
* 这个每一条数据解析都会来调用
*
* @param data one row value. Is is same as {@link AnalysisContext#readRowHolder()}
* @param context
*/
@Override
public void invoke(Student data, AnalysisContext context) {
log.info("解析到一条数据:{}", JSON.toJSONString(data));
Student student = new Student();
cachedDataList.add(student);
// 达到BATCH_COUNT了,需要去存储一次数据库,防止数据几万条数据在内存,容易OOM
if (cachedDataList.size() >= BATCH_COUNT) {
saveData();
// 存储完成清理 list
cachedDataList = new ArrayList<>(BATCH_COUNT);
}
}
/**
* 所有数据解析完成了 都会来调用
* @param context
*/
@Override
public void doAfterAllAnalysed(AnalysisContext context) {
// 这里也要保存数据,确保最后遗留的数据也存储到数据库
saveData();
log.info("所有数据解析完成!");
}
/**
* 加上存储数据库
*/
private void saveData() {
if(cachedDataList.size()>0){
log.info("{}条数据,开始存储数据库!", cachedDataList.size());
studentDao.insertBatchSomeColumn(cachedDataList);
log.info("存储数据库成功!");
}
}
}此处,使用了mybatis-plus的批量插入,代码如下:
@Component
public class InsertBatchInjector extends DefaultSqlInjector {
@Override
public List<AbstractMethod> getMethodList(Class<?> mapperClass, TableInfo tableInfo){
List<AbstractMethod> methodList = super.getMethodList(mapperClass,tableInfo);
// 过滤Insert语句中的字段
methodList.add(new InsertBatchSomeColumn(t -> !"weekend".equals(t.getColumn())
&& !"position".equals(t.getColumn())
&& !"date".equals(t.getColumn())
)); // 添加InsertBatchSomeColumn方法
return methodList;
}
}其次,在一个新的包下面创建一个EasyBaseMapper继承baseMapper:
public interface EasyBaseMapper<T> extends BaseMapper<T> {
/**
* 批量插入 仅适用于mysql
*
* @param entityList 实体列表
* @return 影响行数
*/
Integer insertBatchSomeColumn(Collection<T> entityList);
}然后,在另一个包下,创建自己的dao继承该 EasyBaseMapper:
@Mapper
public interface StudentDao extends EasyBaseMapper<Student> {
}注意,二者代码不可放在同一个包下!
最后,编写控制类代码,读取excel文件,批量插入:
@RestController
public class StudentController {
private static final String PATH = "C:/Users/14125/Desktop/";
@Resource
private StudentDao studentDao;
@GetMapping("/read")
public void read(@RequestParam("filename") String fileName){
fileName = PATH + fileName;
// 这里 需要指定读用哪个class去读,然后读取第一个sheet 文件流会自动关闭
EasyExcel.read(fileName, Student.class, new StudentDataListener(studentDao)).sheet().doRead();
}
}
![[附源码]计算机毕业设计springboot绿色生鲜](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/a3860d0ab64d4a6dbcb128caf65e98eb.png)

![[附源码]计算机毕业设计JAVA小区宠物管理系统](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/147ef7d82bea4662b695a4a29d7ddbae.png)