目录
一、异常处理机制
一、try-catch-finally
二、throws
二、try-catch 异常处理使用细节
三、try-catch-finally练习
第一题
第二题
第三题
第四题
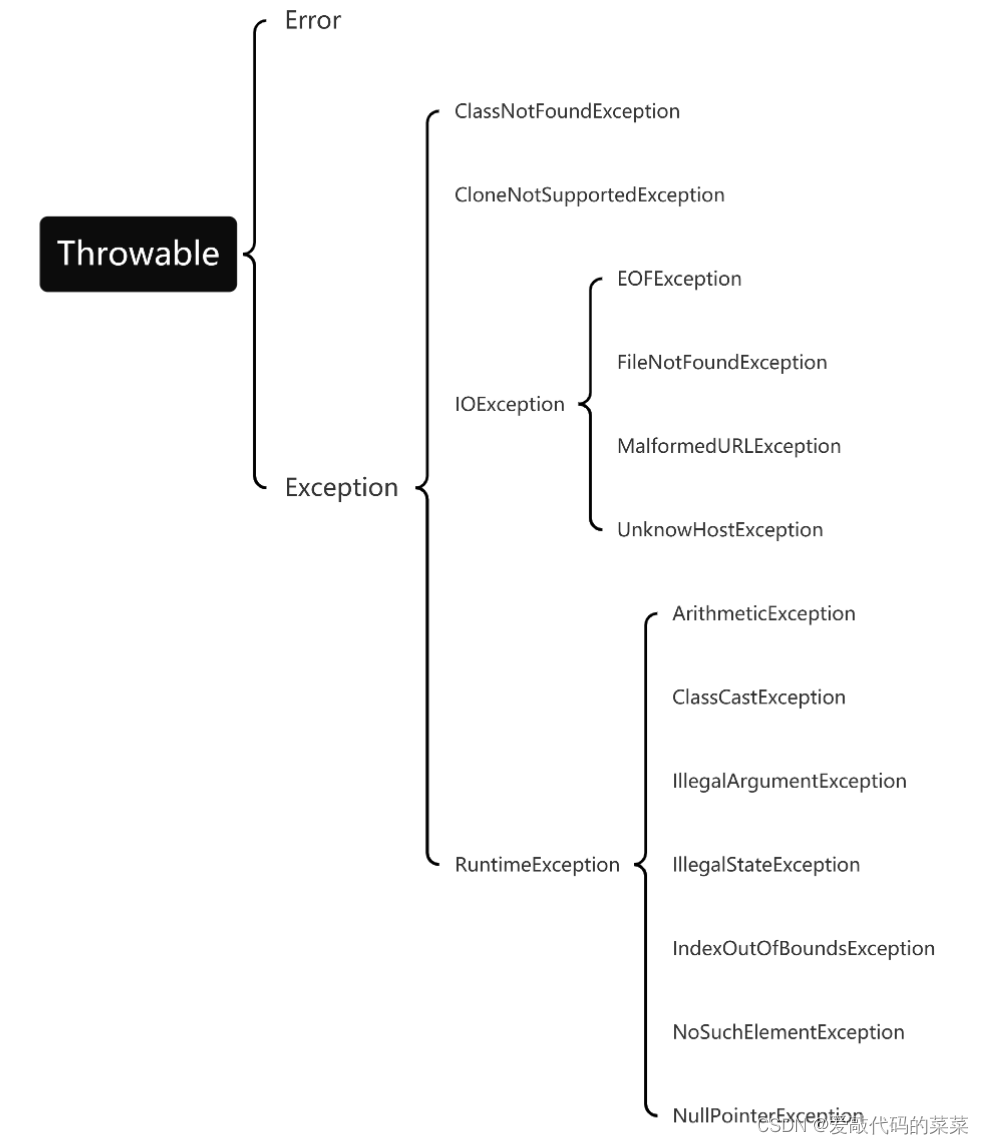
一、异常处理机制
共有两种异常处理机制

一、try-catch-finally
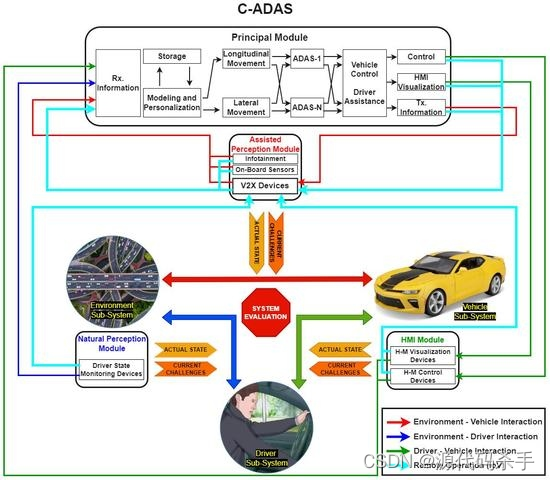
处理机制图示

二、throws
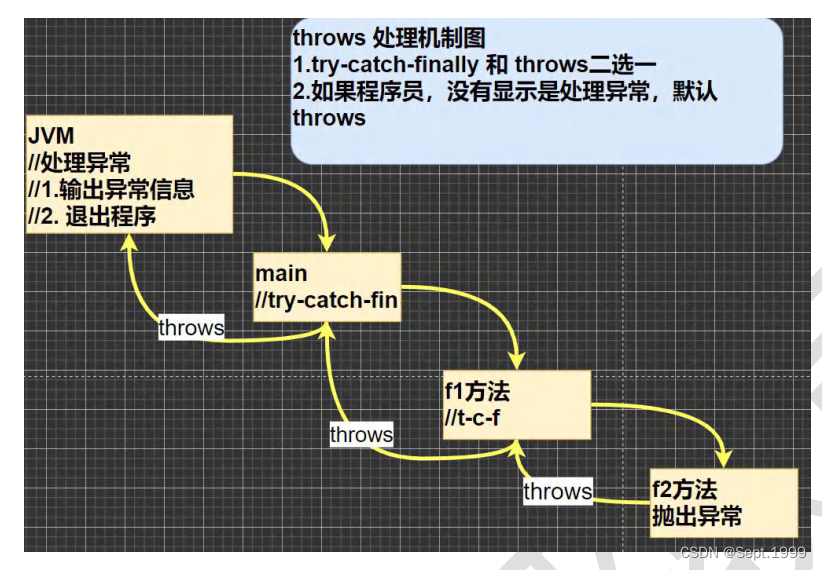
关于第二点,如Exception01.java中所示,就算没有用try-catch处理,直接运行,也是会报错的,因为有默认的 throws Exception
package com.hspedu.exception_;
/**
* @author GQQ
* @version 1.0
*/
public class Exception01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
int num1 = 10;
int num2 = 0;
int res = num1 / num2;
System.out.println("程序继续运行....");
}
}
二、try-catch 异常处理使用细节

package com.hspedu.exception_;
/**
* @author GQQ
* @version 1.0
*/
public class TryCatchDetail {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1. 如果异常发生了, 则异常发生后面的代码不会执行, 直接进入到 catch 块
//2. 如果异常没有发生, 则顺序执行 try 的代码块, 不会进入到 catch
//3. 如果希望不管是否发生异常, 都执行某段代码(比如关闭连接, 释放资源等)则使用如下代码- finally
try {
String str = "java学习";
//String str = "123";
int a = Integer.parseInt(str);
System.out.println("数字" + a);//发生异常后,就不会再执行此输出语句
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
System.out.println("异常信息=" + e.getMessage());
}finally{
System.out.println("代码块被执行...");
}
System.out.println("程序继续...");
}
}

package com.hspedu.exception_;
/**
* @author GQQ
* @version 1.0
*/
public class TryCatchDetail02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.如果 try 代码块有可能有多个异常
//2.可以使用多个 catch 分别捕获不同的异常, 相应处理
//3.要求子类异常写在前面, 父类异常写在后面,如果子类写在后面,会提示 这些异常已经被捕获了
try {
Person person = new Person();
person = null;
System.out.println(person.getName());//NullPointerException
int num1 = 10;
int num2 = 0;
int res = num1 / num2;//ArithmeticException
//分别处理两种异常
} catch (NullPointerException e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
} catch (ArithmeticException e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
} finally {
}
System.out.println(123);
}
}
class Person {
private String name = "jack";
public String getName() {
return name;
}
}

package com.hspedu.exception_;
/**
* @author GQQ
* @version 1.0
*/
public class TryCatchDetail03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try{
int n1 = 10;
int n2 = 0;
System.out.println(n1 / n2);
}finally {
//没有捕捉异常,其实是用了 throws Exception,还是会执行finally里的语句
System.out.println("执行了finally...");
}
System.out.println("程序继续执行...");//当出现异常的时候此语句不会被执行
}
}
三、try-catch-finally练习
第一题
package com.hspedu.exception_;
/**
* @author GQQ
* @version 1.0
*/
public class ExceptionExercise01 {
public static int method() {
try {
String[] names = new String[3];
//names[1]的默认值为null,把null和tom比较会直接报空指针异常
if (names[1].equals("tom")) {
System.out.println(names[1]);
} else {
names[3] = "hspedu";
}
return 1;
} catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
return 2;
} catch (NullPointerException e) {
//空指针异常后会直接return 3,然后跳出整个method方法,但是finally里的语句必须被执行
//所以这里的3不return
return 3;
} finally {
//最后是return 4,也就是说结果是输出4
return 4;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(method());//4
}
}
涉及知识点:
1.String型变量的默认值为null ,当用null进行运算时就会报空指针异常
2.return表示跳出/结束这个方法,但是finally中的语句必须要执行,此时finally的优先级大于return
第二题
package com.hspedu.exception_;
/**
* @author GQQ
* @version 1.0
*/
public class ExceptionExercise02 {
public static int method() {
int i = 1;
try {
i++;
String[] names = new String[3];
if (names[1].equals("tom")) {//names[1]的默认值为null,把null和tom比较会直接报空指针异常
System.out.println(names[1]);
} else {
names[3] = "hspedu";
}
return 1;
} catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
return 2;
} catch (NullPointerException e) {
//空指针异常后会执行return ++i,然后跳出整个method方法,但是finally里的语句必须被执行
//所以这里只是完成 i的自增,并不会return
return ++i;
} finally {
//最后是return 4,也就是说结果是输出4
return ++i;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(method());//4
}
}
知识点:在捕捉到空指针异常的
catch (NullPointerException e) {
//空指针异常后会执行return ++i,然后跳出整个method方法,但是finally里的语句必须被执行
//所以这里只是完成 i的自增,并不会return
return ++i;
}
由于finally的存在,此处虽然不会返回,但是++i的运算还是会执行
第三题
package com.hspedu.exception_;
/**
* @author GQQ
* @version 1.0
*/
public class ExceptionExercise03 {
public static int method() {
int i = 1;
try {
i++;
String[] names = new String[3];
if (names[1].equals("tom")) {//names[1]的默认值为null,把null和tom比较会直接报空指针异常
System.out.println(names[1]);
} else {
names[3] = "hspedu";
}
return 1;
} catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
return 2;
} catch (NullPointerException e) {
//空指针异常后会执行return ++i,然后跳出整个method方法,但是finally里的语句必须被执行
//所以这里只是 return 2, 然后2被临时变量temp保存起来 temp = 2
//然后完成i++, i = 3
return i++;
} finally {
//++i, i = 4;
++i;
System.out.println("i=" + i);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(method());//2和4
}
}
第四题

package com.hspedu.exception_;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* @author GQQ
* @version 1.0
*/
public class ExceptionExercise04 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
while(true){
System.out.print("请输入要判断的数字:");
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
try {
String str = scanner.next();
int num = Integer.parseInt(str);
System.out.println("输入的整数为:" + num);
break;//如果上述输出语句能够执行,说明没有捕捉到异常,结束循环
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
System.out.println("你输入的不是整数,请重新输入");
}
}
}
}