目录
一、前言
二、摄像机空间
2.1 摄像机位置
2.2 摄像机方向
2.3 右轴
2.4 上轴
2.5 LookAt观察矩阵
三、视觉移动
3.1 自由移动
3.2 移动速度
3.3 视觉移动
3.4 缩放
四、摄像机类
一、前言
之前3D物体已经有了,如何在观察空间中随意移动去“游览”3D物体,需要使用到摄像机,也就是把场景中的所有物体往相反的方向移动模拟出摄像机,产生一种移动场景的效果。

二、摄像机空间
摄像机空间也叫观察空间,需要定义以摄像机的视角作为场景原点时,场景中所有顶点坐标。
观察矩阵把所有世界坐标变换为相对于摄像机位置与方向的观察坐标。
摄像机定义:在世界空间中位置、观察方向、指向右侧向量、指向上方的向量。
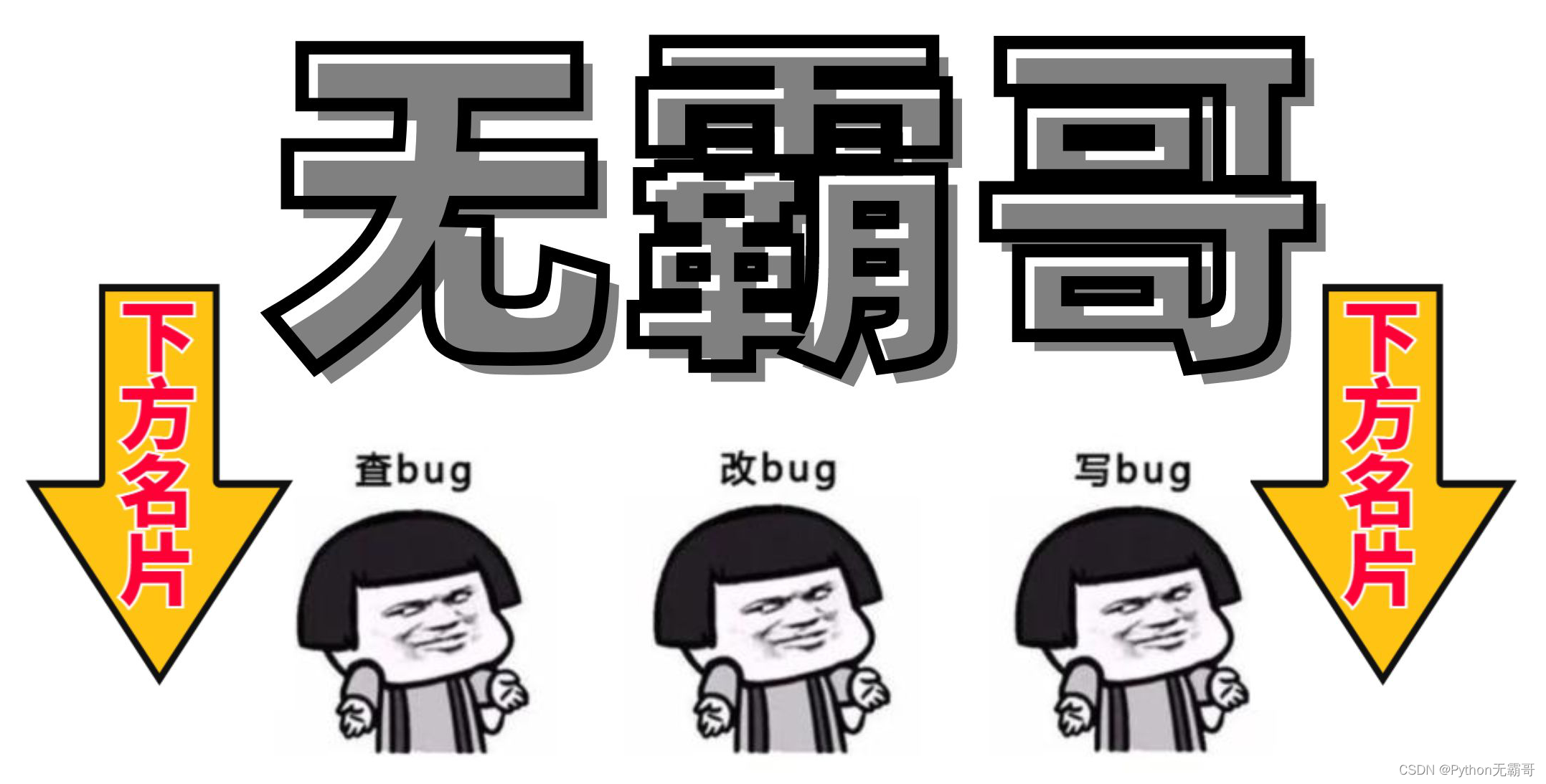
2.1 摄像机位置
摄像机位置是在世界空间中一个指向摄像机位置的向量。右手坐标系:大拇指指向正x轴方向,食指指向正y轴方向,中指指向正z轴方向,z正轴从屏幕指向自己。
glm::vec3 cameraPos = glm::vec3(0.0f, 0.0f, 3.0f);2.2 摄像机方向
摄像机方向是摄像机指向场景原点(0,0,0),用场景原点向量减去摄像机位置向量的结果就是摄像机的指向向量。由原点指向摄像机位置(终点)的方向,方向向量指向摄像机Z轴正方向。
方向向量(Direction Vector)实际上指向从它到目标向量的相反方向。
glm::vec3 cameraTarget = glm::vec3(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f);
glm::vec3 cameraDirection = glm::normalize(cameraPos - cameraTarget);2.3 右轴
右向量表示摄像机空间x轴正方向。先定义一个上向量,然后和摄像机方向向量叉乘得到x轴向量。
glm::vec3 up = glm::vec3(0.0,1.0,0.0);
glm::vec3 cameraRight = glm::normalize(glm::cross(up,cameraDirection));2.4 上轴
上轴表示y轴正方向,x轴向量和z轴向量的叉乘。
glm::vec3 cameraUp = glm::cross(cameraDirection,cameraRight);2.5 LookAt观察矩阵
如果已知3个相互垂直的轴定义了一个坐标空间,再外加一个平移向量创建的矩阵叫做Look At矩阵。LookAt矩阵乘以任何向量就可以变换到摄像机坐标空间中。
下面左侧是摄像机的右向量R,上向量U,方向向量D;右侧P是摄像机位置向量,由于希望把世界平移方向与我们自身移动方向相反,所以位置向量是相反的。

LookAt观察矩阵可以很高效的蒋所有世界坐标变换到观察空间中。
lookAt函数输入摄像机位置、目标位置、表示世界空间中的上向量;
glm::mat4 view = glm::mat4(1.0f);
view = glm::lookAt(glm::vec3(0.0f, 0.0f, 3.0f),
glm::vec3(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f),
glm::vec3(0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f));
/*glm::mat4 glm::lookAt(glm::vec3 const& eye, glm::vec3 const& center, glm::vec3
const& up);
eye:视觉位置,也就是摄像机位置
center:摄像机注视目标方向
up:上向量
*/创建旋转的视角,仅需改变摄像机观察位置即可,改变x和z坐标。
float radius = 10.0f;
float camX = sin(glfwGetTime()) * radius;
float camZ = cos(glfwGetTime()) * radius;
glm::mat4 view;
view = glm::lookAt(glm::vec3(camX, 0.0, camZ), glm::vec3(0.0, 0.0, 0.0), glm::vec3(0.0, 1.0, 0.0)); 
三、视觉移动
3.1 自由移动
上节摄像机围绕场景转动,如何移动摄像机,首先定义摄像机系统。
定义摄像机变量:
//设置摄像机相关参数
glm::vec3 cameraPos = glm::vec3(0.0f, 0.0f, 3.0f);
glm::vec3 cameraFront = glm::vec3(0.0f, 0.0f, -1.0f);//向前向量
glm::vec3 cameraUp = glm::vec3(0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f);
//lookAt
view = glm::lookAt(cameraPos, cameraPos + cameraFront, cameraUp);
//添加键盘输入
void processInput(GLFWwindow *window)
{
...
float cameraSpeed = 0.05f; // adjust accordingly
if (glfwGetKey(window, GLFW_KEY_W) == GLFW_PRESS)
cameraPos += cameraSpeed * cameraFront;
if (glfwGetKey(window, GLFW_KEY_S) == GLFW_PRESS)
cameraPos -= cameraSpeed * cameraFront;
if (glfwGetKey(window, GLFW_KEY_A) == GLFW_PRESS)
cameraPos -= glm::normalize(glm::cross(cameraFront, cameraUp)) * cameraSpeed;
if (glfwGetKey(window, GLFW_KEY_D) == GLFW_PRESS)
cameraPos += glm::normalize(glm::cross(cameraFront, cameraUp)) * cameraSpeed;
}3.2 移动速度
图形程序和游戏通常会跟踪时间差变量,它存储渲染上一帧所用时间,把速度乘以时间差值。结果是如果时间差值大,说明上一次渲染花费的时间长,所以这一帧速度需要变得更高来平衡渲染花去的时间。
//定义全局变量
float deltaTime = 0.0f; // 当前帧与上一帧的时间差
float lastFrame = 0.0f; // 上一帧的时间
//更新时间
float currentFrame = glfwGetTime();
deltaTime = currentFrame - lastFrame;
lastFrame = currentFrame;
//更新速度
void processInput(GLFWwindow *window)
{
float cameraSpeed = 2.5f * deltaTime;
...
}
3.3 视觉移动
使用鼠标改变中心方向cameraFront向量,根据鼠标移动改变方向向量。
(1)欧拉角:可以表示3D空间中任何旋转的3个值,是欧拉在18世纪提出,有3中欧拉角,俯仰pitch,偏航yaw,翻滚roll。
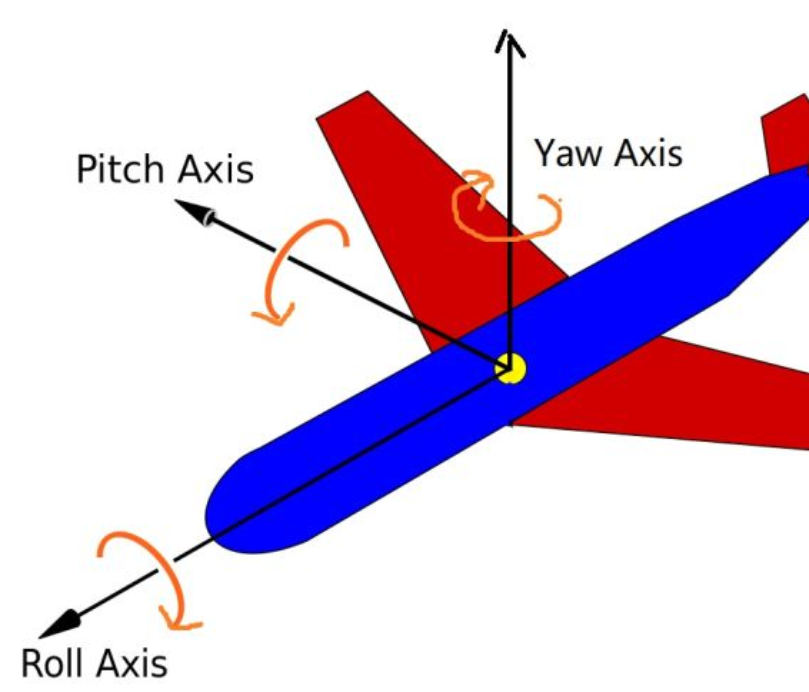

摄像机系统不会翻滚,只关心俯仰角(前后)和偏航角(左右)。给定一个俯仰角和偏航角,可以把它们转换为一个新的方向3D向量。
(2)俯仰角Pitch:
将斜边边长定义为1,如下所示:
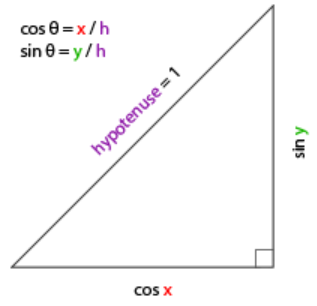
这样我们获得了能够得到x和y方向长度的通用公式,它们取决于所给的角度。我们使用它来计算方向向量的分量。

direction.y = sin(glm::radians(pitch)); // 注意我们先把角度转为弧度
direction.x = cos(glm::radians(pitch));
direction.z = cos(glm::radians(pitch));(3)偏航角yaw:
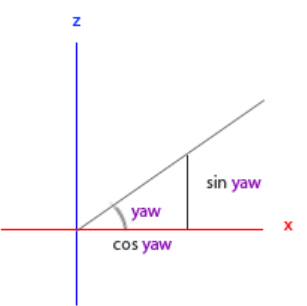
x分量取决于cos(yaw),z值分量取决于sin(yaw),因此结合俯仰角得到最终的方向向量为
direction.x = cos(glm::radians(pitch)) * cos(glm::radians(yaw)); // 译注:direction代表摄像机的前轴(Front),这个前轴是和本文第一幅图片的第二个摄像机的方向向量是相反的
direction.y = sin(glm::radians(pitch));
direction.z = cos(glm::radians(pitch)) * sin(glm::radians(yaw));(4)鼠标输入
鼠标水平移动影响偏航角,竖直的移动影响俯仰角。原理是储存上一帧鼠标位置,当前帧计算与上一帧相差多少。如果水平/竖直差别越大,俯仰角或偏航角就改变越大,也就是摄像机需要移动更多的距离。
配置鼠标:
//1.0设置GLFW隐藏光标,并捕捉光标,也不会离开窗口
glfwSetInputMode(window, GLFW_CURSOR, GLFW_CURSOR_DISABLED);
//2.0设置全局变量,计算偏移量
float lastX = 400, lastY = 300;
//3.0监听鼠标移动事件
void mouse_callback(GLFWwindow* window, double xpos, double ypos);
{
//仿止第一次进入窗口,鼠标位置较远,产生跳变
if(firstMouse) // 这个bool变量初始时是设定为true的
{
lastX = xpos;
lastY = ypos;
firstMouse = false;
}
float xoffset = xpos - lastX;
float yoffset = lastY - ypos; // 注意这里是相反的,因为y坐标是从底部往顶部依次增大的
lastX = xpos;
lastY = ypos;
float sensitivity = 0.05f;
xoffset *= sensitivity;
yoffset *= sensitivity;
//把偏移量加到全局变量pitch和yaw上
yaw += xoffset;
pitch += yoffset;
//俯仰角添加限制,高于89度天空,小于-89度脚下
if(pitch > 89.0f)
pitch = 89.0f;
if(pitch < -89.0f)
pitch = -89.0f;
//通过俯仰角和偏航角来计算以得到真正的方向向量
glm::vec3 front;
front.x = cos(glm::radians(pitch)) * cos(glm::radians(yaw));
front.y = sin(glm::radians(pitch));
front.z = cos(glm::radians(pitch)) * sin(glm::radians(yaw));
cameraFront = glm::normalize(front);
}
//4.0注册回调
glfwSetCursorPosCallback(window, mouse_callback);
这样,鼠标可以自由在3D场景中移动了
3.4 缩放
在前面定义透视投影矩阵时,定义了视野FOV(Field Of View),表示场景中的范围,当视野变小,场景投影的空间就会减小,产生放大Zoom in感觉。
设置鼠标滚轮回调函数:
//定义滚轮回调函数
void scroll_callback(GLFWwindow* window, double xoffset, double yoffset)
{
if(fov >= 1.0f && fov <= 45.0f)
fov -= yoffset;
if(fov <= 1.0f)
fov = 1.0f;
if(fov >= 45.0f)
fov = 45.0f;
}
//注册回调函数
glfwSetScrollCallback(window, scroll_callback);
//调用FOV
projection = glm::perspective(glm::radians(fov), 800.0f / 600.0f, 0.1f, 100.0f);四、摄像机类
将对键盘wasd和鼠标的操作进行抽象,然后封装成摄像机类。
Camera .h
#ifndef CAMERA_H
#define CAMERA_H
#include "glad.h"
#include <glm/glm.hpp>
#include <glm/gtc/matrix_transform.hpp>
#include <vector>
// 宏定义相机移动方式
enum Camera_Movement {
FORWARD,
BACKWARD,
LEFT,
RIGHT
};
//默认相机参数
const float YAW = -90.0f;
const float PITCH = 0.0f;
const float SPEED = 2.5f;
const float SENSITIVITY = 0.1f;
const float ZOOM = 45.0f;
//处理输入、计算对应的欧拉角、向量、矩阵
class Camera
{
public:
// 摄像机属性
glm::vec3 Position;
glm::vec3 Front;
glm::vec3 Up;
glm::vec3 Right;
glm::vec3 WorldUp;
// 欧拉角
float Yaw;
float Pitch;
// 相机操作参数
float MovementSpeed;
float MouseSensitivity;
float Zoom;
//构造函数——向量
Camera(glm::vec3 position = glm::vec3(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f), glm::vec3 up = glm::vec3(0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f), float yaw = YAW, float pitch = PITCH) : Front(glm::vec3(0.0f, 0.0f, -1.0f)), MovementSpeed(SPEED), MouseSensitivity(SENSITIVITY), Zoom(ZOOM)
{
Position = position;
WorldUp = up;
Yaw = yaw;
Pitch = pitch;
updateCameraVectors();
}
// 构造函数——缩放
Camera(float posX, float posY, float posZ, float upX, float upY, float upZ, float yaw, float pitch) : Front(glm::vec3(0.0f, 0.0f, -1.0f)), MovementSpeed(SPEED), MouseSensitivity(SENSITIVITY), Zoom(ZOOM)
{
Position = glm::vec3(posX, posY, posZ);
WorldUp = glm::vec3(upX, upY, upZ);
Yaw = yaw;
Pitch = pitch;
updateCameraVectors();
}
//观察矩阵计算
glm::mat4 GetViewMatrix()
{
return glm::lookAt(Position, Position + Front, Up);
}
// 处理类似键盘输入,移动摄像机位置
void ProcessKeyboard(Camera_Movement direction, float deltaTime)
{
float velocity = MovementSpeed * deltaTime;
if (direction == FORWARD)
Position += Front * velocity;
if (direction == BACKWARD)
Position -= Front * velocity;
if (direction == LEFT)
Position -= Right * velocity;
if (direction == RIGHT)
Position += Right * velocity;
}
// 处理类似鼠标输入,期望俯仰角、横摆角移动 ,x y移动
void ProcessMouseMovement(float xoffset, float yoffset, GLboolean constrainPitch = true)
{
xoffset *= MouseSensitivity;
yoffset *= MouseSensitivity;
Yaw += xoffset;
Pitch += yoffset;
// 确保pitch俯仰角不会超出范围,屏幕不会颠倒
if (constrainPitch)
{
if (Pitch > 89.0f)
Pitch = 89.0f;
if (Pitch < -89.0f)
Pitch = -89.0f;
}
// 更新摄像机视角矩阵, Front, Right and Up Vectors
updateCameraVectors();
}
// 处理类似鼠标滚轮输入事件,缩放
void ProcessMouseScroll(float yoffset)
{
Zoom -= (float)yoffset;
if (Zoom < 1.0f)
Zoom = 1.0f;
if (Zoom > 45.0f)
Zoom = 45.0f;
}
private:
//从摄像机欧拉角 计算 前向量、右向量、上向量
void updateCameraVectors()
{
// calculate the new Front vector
glm::vec3 front;
front.x = cos(glm::radians(Yaw)) * cos(glm::radians(Pitch));
front.y = sin(glm::radians(Pitch));
front.z = sin(glm::radians(Yaw)) * cos(glm::radians(Pitch));
Front = glm::normalize(front);
// also re-calculate the Right and Up vector
Right = glm::normalize(glm::cross(Front, WorldUp)); // normalize the vectors, because their length gets closer to 0 the more you look up or down which results in slower movement.
Up = glm::normalize(glm::cross(Right, Front));
}
};
#endifmain.cpp调用摄像机类
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include "glad.h"
#include "GL/glfw3.h"
#define STB_IMAGE_IMPLEMENTATION
#include "stb_image.h"
#include <glm/glm.hpp>
#include <glm/gtc/matrix_transform.hpp>
#include <glm/gtc/type_ptr.hpp>
#include "Shader.h"
#include "Camera.h"
// settings
const unsigned int SCR_WIDTH = 800;
const unsigned int SCR_HEIGHT = 600;
glm::vec3 cameraPos = glm::vec3(0.0f, 0.0f, 3.0f);
glm::vec3 cameraFront = glm::vec3(0.0f, 0.0f, -1.0f);
glm::vec3 cameraUp = glm::vec3(0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f);
float deltaTime = 0.0f; // 当前帧与上一帧的时间差
float lastFrame = 0.0f; // 上一帧的时间
Camera myCamera(cameraPos.x, cameraPos.y, cameraPos.z, cameraUp.x, cameraUp.y,cameraUp.z,0,0);
// process all input: query GLFW whether relevant keys are pressed/released this frame and react accordingly
// ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
void processInput(GLFWwindow* window)
{
if (glfwGetKey(window, GLFW_KEY_ESCAPE) == GLFW_PRESS)
glfwSetWindowShouldClose(window, true);
//float cameraSpeed = 0.05f; // adjust accordingly
float cameraSpeed = 2.5f * deltaTime;
if (glfwGetKey(window, GLFW_KEY_W) == GLFW_PRESS)
myCamera.ProcessKeyboard(FORWARD, deltaTime);
//cameraPos += cameraSpeed * cameraFront;
if (glfwGetKey(window, GLFW_KEY_S) == GLFW_PRESS)
myCamera.ProcessKeyboard(BACKWARD, deltaTime);
//cameraPos -= cameraSpeed * cameraFront;
if (glfwGetKey(window, GLFW_KEY_A) == GLFW_PRESS)
myCamera.ProcessKeyboard(LEFT, deltaTime);
//cameraPos -= glm::normalize(glm::cross(cameraFront, cameraUp)) * cameraSpeed;
if (glfwGetKey(window, GLFW_KEY_D) == GLFW_PRESS)
myCamera.ProcessKeyboard(LEFT, RIGHT);
//cameraPos += glm::normalize(glm::cross(cameraFront, cameraUp)) * cameraSpeed;
}
// glfw: whenever the window size changed (by OS or user resize) this callback function executes
// ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
void framebuffer_size_callback(GLFWwindow* window, int width, int height)
{
// make sure the viewport matches the new window dimensions; note that width and
// height will be significantly larger than specified on retina displays.
glViewport(0, 0, width, height);
}
//2.0设置全局变量,计算偏移量
float lastX = 400, lastY = 300;
float yaw = 0, pitch = 0 ,fov = 45;
bool firstMouse = true;
//3.0监听鼠标移动事件
void mouse_callback(GLFWwindow* window, double xpos, double ypos)
{
//仿止第一次进入窗口,鼠标位置较远,产生跳变
if (firstMouse) // 这个bool变量初始时是设定为true的
{
lastX = xpos;
lastY = ypos;
firstMouse = false;
}
float xoffset = xpos - lastX;
float yoffset = lastY - ypos; // 注意这里是相反的,因为y坐标是从底部往顶部依次增大的
lastX = xpos;
lastY = ypos;
myCamera.ProcessMouseMovement(xoffset, yoffset);
#if 0
float sensitivity = 0.05f;
xoffset *= sensitivity;
yoffset *= sensitivity;
//把偏移量加到全局变量pitch和yaw上
yaw += xoffset;
pitch += yoffset;
//俯仰角添加限制,高于89度天空,小于-89度脚下
if (pitch > 89.0f)
pitch = 89.0f;
if (pitch < -89.0f)
pitch = -89.0f;
//通过俯仰角和偏航角来计算以得到真正的方向向量
glm::vec3 front;
front.x = cos(glm::radians(pitch)) * cos(glm::radians(yaw));
front.y = sin(glm::radians(pitch));
front.z = cos(glm::radians(pitch)) * sin(glm::radians(yaw));
cameraFront = glm::normalize(front);
#endif
}
//鼠标回调函数
void scroll_callback(GLFWwindow* window, double xoffset, double yoffset)
{
myCamera.ProcessMouseScroll(static_cast<float>(yoffset));
#if 0
if (fov >= 1.0f && fov <= 45.0f)
fov -= yoffset;
if (fov <= 1.0f)
fov = 1.0f;
if (fov >= 45.0f)
fov = 45.0f;
#endif
}
int main()
{
// glfw: 初始化、配置
// ------------------------------
glfwInit();
glfwWindowHint(GLFW_CONTEXT_VERSION_MAJOR, 3);
glfwWindowHint(GLFW_CONTEXT_VERSION_MINOR, 3);
glfwWindowHint(GLFW_OPENGL_PROFILE, GLFW_OPENGL_CORE_PROFILE);
#ifdef __APPLE__
glfwWindowHint(GLFW_OPENGL_FORWARD_COMPAT, GL_TRUE);
#endif
// glfw: 创建窗口、绑定回调
// --------------------
GLFWwindow* window = glfwCreateWindow(SCR_WIDTH, SCR_HEIGHT, "LearnOpenGL", NULL, NULL);
if (window == NULL)
{
std::cout << "Failed to create GLFW window" << std::endl;
glfwTerminate();
return -1;
}
//1.0设置GLFW隐藏光标,并捕捉光标,也不会离开窗口
glfwSetInputMode(window, GLFW_CURSOR, GLFW_CURSOR_DISABLED);
glfwMakeContextCurrent(window);
glfwSetFramebufferSizeCallback(window, framebuffer_size_callback);
//4.0注册回调
glfwSetCursorPosCallback(window, mouse_callback);
//注册回调函数
glfwSetScrollCallback(window, scroll_callback);
// glad: 加载OpenGL相关函数指针
// ---------------------------------------
if (!gladLoadGLLoader((GLADloadproc)glfwGetProcAddress))
{
std::cout << "Failed to initialize GLAD" << std::endl;
return -1;
}
// 构建、编译着色器
// ------------------------------------
Shader ourShader("vertexTexture.vs", "fragmentTexture.fms");
// 顶点数据
// ------------------------------------------------------------------
/*float vertices[] = {
// 位置 // 纹理坐标
0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, // top right
0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, // bottom right
-0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, // bottom left
-0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f // top left
};
unsigned int indices[] = {
0, 1, 3, // 第一个三角形
1, 2, 3 // 第二个三角形
};*/
float vertices[] = {
-0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f,
0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f, 1.0f, 0.0f,
0.5f, 0.5f, -0.5f, 1.0f, 1.0f,
0.5f, 0.5f, -0.5f, 1.0f, 1.0f,
-0.5f, 0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, 1.0f,
-0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f,
-0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f,
0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f, 1.0f, 0.0f,
0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f, 1.0f, 1.0f,
0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f, 1.0f, 1.0f,
-0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, 1.0f,
-0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f,
-0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f, 1.0f, 0.0f,
-0.5f, 0.5f, -0.5f, 1.0f, 1.0f,
-0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, 1.0f,
-0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, 1.0f,
-0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f,
-0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f, 1.0f, 0.0f,
0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f, 1.0f, 0.0f,
0.5f, 0.5f, -0.5f, 1.0f, 1.0f,
0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, 1.0f,
0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, 1.0f,
0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f,
0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f, 1.0f, 0.0f,
-0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, 1.0f,
0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f, 1.0f, 1.0f,
0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f, 1.0f, 0.0f,
0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f, 1.0f, 0.0f,
-0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f,
-0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, 1.0f,
-0.5f, 0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, 1.0f,
0.5f, 0.5f, -0.5f, 1.0f, 1.0f,
0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f, 1.0f, 0.0f,
0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f, 1.0f, 0.0f,
-0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f,
-0.5f, 0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, 1.0f
};
glm::vec3 cubePositions[] = {
glm::vec3(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f),
glm::vec3(2.0f, 5.0f, -15.0f),
glm::vec3(-1.5f, -2.2f, -2.5f),
glm::vec3(-3.8f, -2.0f, -12.3f),
glm::vec3(2.4f, -0.4f, -3.5f),
glm::vec3(-1.7f, 3.0f, -7.5f),
glm::vec3(1.3f, -2.0f, -2.5f),
glm::vec3(1.5f, 2.0f, -2.5f),
glm::vec3(1.5f, 0.2f, -1.5f),
glm::vec3(-1.3f, 1.0f, -1.5f)
};
//创建顶点对象
unsigned int VAO, VBO, EBO;
glGenVertexArrays(1, &VAO);//顶点数组
glGenBuffers(1, &VBO);//数据缓存
//glGenBuffers(1, &EBO);//数据缓存
//绑定数据
glBindVertexArray(VAO);
glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, VBO);
glBufferData(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, sizeof(vertices), vertices, GL_STATIC_DRAW);
//glBindBuffer(GL_ELEMENT_ARRAY_BUFFER, EBO);
//glBufferData(GL_ELEMENT_ARRAY_BUFFER, sizeof(indices), indices, GL_STATIC_DRAW);
//解释数据
glVertexAttribPointer(0, 3, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, 5 * sizeof(float), (void*)0);//位置
glEnableVertexAttribArray(0);
glVertexAttribPointer(1, 2, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, 5 * sizeof(float), (void*)(3 * sizeof(float)));//纹理
glEnableVertexAttribArray(1);
//创建纹理对象1
unsigned int texture1;
glGenTextures(1, &texture1);
glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, texture1);
//设置纹理环绕方式
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_S, GL_REPEAT);
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_T, GL_REPEAT);
//设置纹理过滤方式
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MIN_FILTER, GL_LINEAR_MIPMAP_LINEAR);
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MAG_FILTER, GL_LINEAR);
//加载图片1到纹理数据
int width, height, nrChannels;
unsigned char* data = stbi_load(std::string("container.jpg").c_str(), &width, &height, &nrChannels, 0);
if (data)
{
//加载数据,生成OpenGL纹理图
glTexImage2D(GL_TEXTURE_2D, 0, GL_RGB, width, height, 0, GL_RGB, GL_UNSIGNED_BYTE, data);
//多级渐远纹理
glGenerateMipmap(GL_TEXTURE_2D);
}
else
{
std::cout << "Failed to load texture" << std::endl;
}
//释放内存
stbi_image_free(data);
//创建纹理对象2
unsigned int texture2;
// texture 2
// ---------
glGenTextures(1, &texture2);
glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, texture2);
// set the texture wrapping parameters
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_S, GL_REPEAT); // set texture wrapping to GL_REPEAT (default wrapping method)
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_T, GL_REPEAT);
// set texture filtering parameters
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MIN_FILTER, GL_LINEAR);
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MAG_FILTER, GL_LINEAR);
// load image, create texture and generate mipmaps
stbi_set_flip_vertically_on_load(true);
data = stbi_load(std::string("awesomeface.png").c_str(), &width, &height, &nrChannels, 0);
if (data)
{
// note that the awesomeface.png has transparency and thus an alpha channel, so make sure to tell OpenGL the data type is of GL_RGBA
glTexImage2D(GL_TEXTURE_2D, 0, GL_RGBA, width, height, 0, GL_RGBA, GL_UNSIGNED_BYTE, data);
glGenerateMipmap(GL_TEXTURE_2D);
}
else
{
std::cout << "Failed to load texture" << std::endl;
}
stbi_image_free(data);
//OpenGL解释纹理单元的编号
ourShader.use();
ourShader.setInt("textur1", 0);
ourShader.setInt("textur2", 1);
glEnable(GL_DEPTH_TEST);
//旋转90度,缩放0.5倍
//glm::mat4 trans = glm::mat4(1.0f);
// trans = glm::rotate(trans, glm::radians(90.0f), glm::vec3(0, 0, 1.0));
//trans = glm::scale(trans, glm::vec3(0.5, 0.5, 0.5));
//渲染
while (!glfwWindowShouldClose(window))
{
processInput(window);
//背景颜色
glClearColor(0.2f, 0.3f, 0.3f, 1.0f);
glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT|GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT);
//绑定对应的纹理
glActiveTexture(GL_TEXTURE0);
glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, texture1);
glActiveTexture(GL_TEXTURE1);
glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, texture2);
//glm::mat4 modelMat = glm::mat4(1.0f);
glm::mat4 viewMat = glm::mat4(1.0f);
//viewMat = glm::translate(viewMat, glm::vec3(0.0f, 0.0f, -10.0f));//view matrix
float radius = 10.0f;
float camX = sin(glfwGetTime()) * radius;
float camZ = cos(glfwGetTime()) * radius;
//viewMat = glm::lookAt(glm::vec3(camX, 0.0, camZ), glm::vec3(0.0, 0.0, 0.0), glm::vec3(0.0, 1.0, 0.0));
glm::mat4 projectionMat = glm::mat4(1.0f);
//modelMat = glm::rotate(modelMat, glm::radians(-55.0f), glm::vec3(1.0, 0.0, 0.0));//model matrix
//modelMat = glm::rotate(modelMat, (float)glfwGetTime(), glm::vec3(0.5f, 1.0f, 0.0f));
//viewMat = glm::lookAt(cameraPos, cameraPos + cameraFront, cameraUp);
viewMat = myCamera.GetViewMatrix();
projectionMat = glm::perspective(glm::radians(myCamera.Zoom), (float)(SCR_WIDTH / SCR_HEIGHT), 0.1f, 100.0f);//projection matrix
//着色器引用
ourShader.use();
//unsigned int modelLoc = glGetUniformLocation(ourShader.ID, "model");
//glUniformMatrix4fv(modelLoc, 1, GL_FALSE, glm::value_ptr(modelMat));
unsigned int viewlLoc = glGetUniformLocation(ourShader.ID, "view");
glUniformMatrix4fv(viewlLoc, 1, GL_FALSE, glm::value_ptr(viewMat));
unsigned int projectionlLoc = glGetUniformLocation(ourShader.ID, "projection");
glUniformMatrix4fv(projectionlLoc, 1, GL_FALSE, glm::value_ptr(projectionMat));
//绘图
glBindVertexArray(VAO);
//glDrawArrays(GL_TRIANGLES, 0, 36);
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
glm::mat4 modelMat = glm::mat4(1.0f);
modelMat = glm::translate(modelMat, cubePositions[i]);
modelMat = glm::rotate(modelMat, (float)glfwGetTime(), glm::vec3(1.0f, 0.3f, 0.5f));
ourShader.setMat4("model", modelMat);
glDrawArrays(GL_TRIANGLES, 0, 36);
}
//glDrawElements(GL_TRIANGLES, 6, GL_UNSIGNED_INT, 0);
/*
*
void glDrawElements( GLenum mode,
GLsizei count,
GLenum type,
const GLvoid * indices);
*/
//刷新
glfwSwapBuffers(window);
glfwPollEvents();
//更新时间
float currentFrame = glfwGetTime();
deltaTime = currentFrame - lastFrame;
lastFrame = currentFrame;
}
//释放缓存资源
glDeleteVertexArrays(1, &VAO);
glDeleteBuffers(1, &VBO);
glDeleteBuffers(1, &EBO);
//释放glfw资源
glfwTerminate();
return 0;
}
参考:
摄像机 - LearnOpenGL CN (learnopengl-cn.github.io)