文章目录
- 二叉树
- 递归法
- 迭代法
- 144. 二叉树的前序遍历 - 力扣(LeetCode)
- 二叉树的递归遍历
- 递归法作图分析
- 代码和思路分析
- 二叉树的迭代遍历
- 前序遍历迭代分析
- 代码及思路分析
- 94. 二叉树的中序遍历
- 递归法
- 作图举例递归流程
- 迭代法
- 代码
- 145. 二叉树的后序遍历 - 力扣(LeetCode)
- 递归法
- 迭代法
- 二叉树的统一迭代法
- 前序遍历统一的迭代法
- 中序遍历统一的迭代法
- 后序遍历统一的迭代法
二叉树

递归法

迭代法
144. 二叉树的前序遍历 - 力扣(LeetCode)
二叉树的递归遍历
递归法作图分析
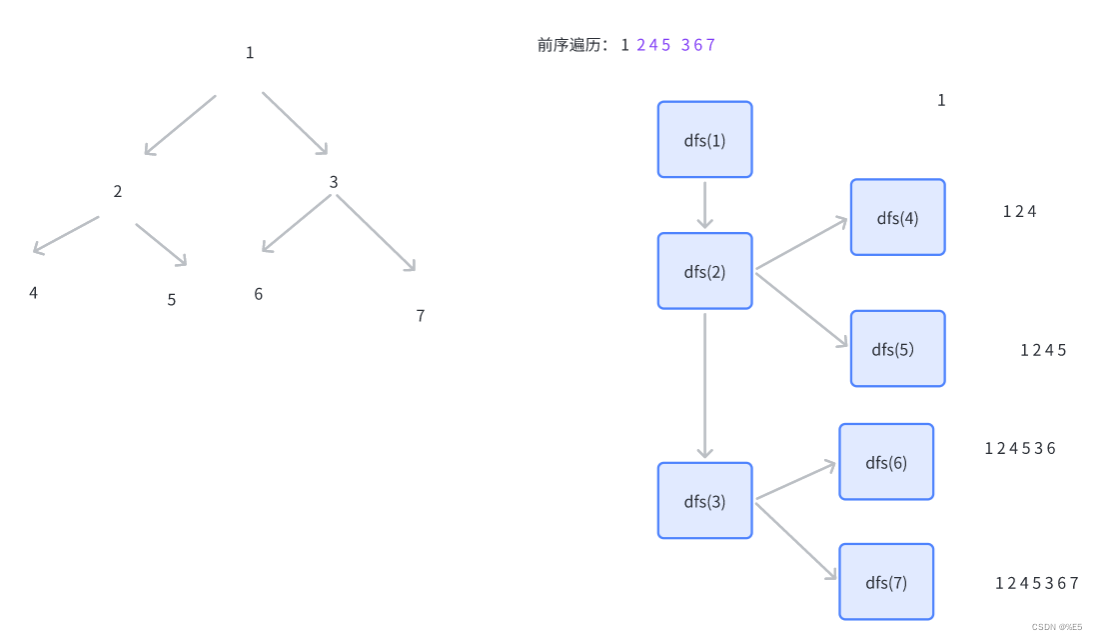
代码和思路分析
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {number[]}
*/
var preorderTraversal = function(root) {
/*
前序遍历:根左右
我们用一个栈存入结果
递归:顺序就是根左右,然后左右又分别是根,再根左右,循环,操作都一致了,可以使用递归
*/
let res = []
const dfs = function(root) {
// 遇到空值,终止执行
if(root === null) return;
// 前序遍历从父节点开始
res.push(root.val)
// 之后会再压入左节点,右节点,然后每个节点的子节点,循环,使用递归
// 左子树递归
dfs(root.left)
// 右子树递归
dfs(root.right)
}
dfs(root)
return res
};
二叉树的遍历除了递归还有迭代
二叉树的迭代遍历
非递归,遍历
用栈也可以实现前中后
前序遍历迭代分析

前序遍历是根左右
我们先让根节点入栈,然后让右节点入栈,再左节点
为什么先右后左?这样出栈的时候就可以达到根左右的效果
入栈:右–>左
出栈:根–>左–>右
代码及思路分析
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {number[]}
*/
var preorderTraversal = function(root) {
let res = []
if(!root) return res
// 把根节点存入栈中
const stack = [root]
let cur = null
// 遍历栈里面的元素
while(stack.length) {
// 最开始出栈的是根节点root
cur = stack.pop()
// 把出栈的节点的值压入res存起来
res.push(cur.val)
// 然后分别把存在的右节点 左节点压入栈,之后循环,弹出左节点,右节点
cur.right && stack.push(cur.right)
cur.left && stack.push(cur.left)
}
return res
};
前序遍历解决了,中序遍历和后序遍历就好解决了
94. 二叉树的中序遍历
递归法
作图举例递归流程
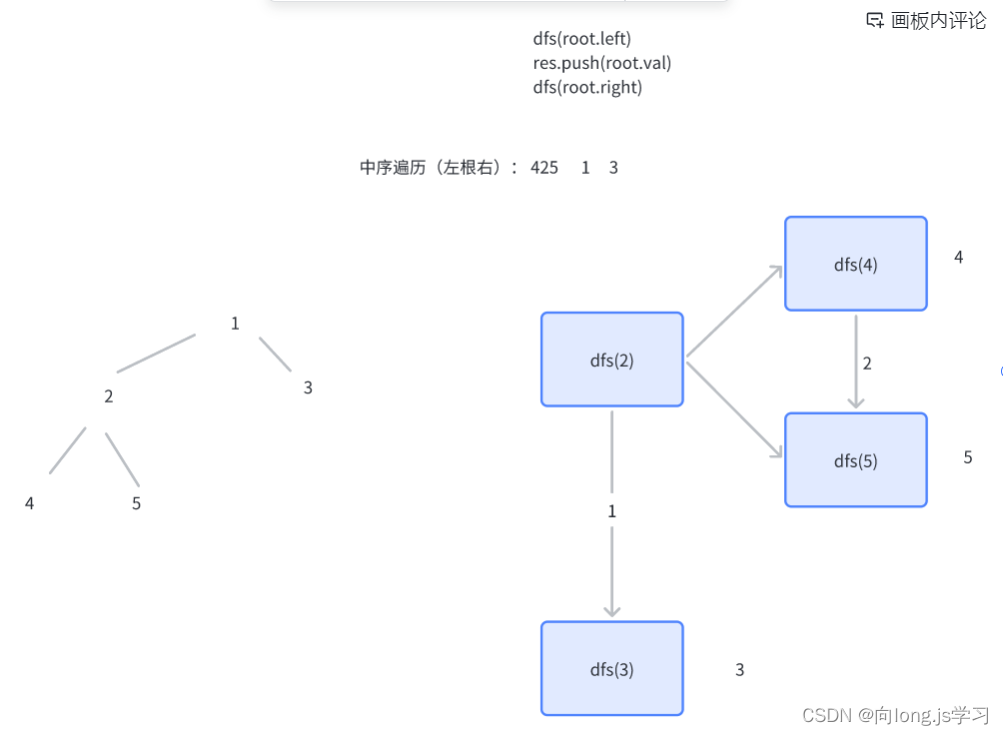
代码
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=94 lang=javascript
*
* [94] 二叉树的中序遍历
*/
// @lc code=start
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {number[]}
*/
var inorderTraversal = function(root) {
/**
* 中序遍历 递归左子树,压入根,递归右子树
*/
let res = []
const dfs = function(root) {
if(root === null) return
dfs(root.left)
res.push(root.val)
dfs(root.right)
}
dfs(root)
return res
};
// @lc code=end
迭代法
迭代法分析

中序遍历:左根右
入栈:左 --> 右
出栈:左 --> 中 --> 右
代码
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {number[]}
*/
var inorderTraversal = function(root) {
let res = []
const stack = []
let cur = root
while(stack.length || cur) {
/*
开始根节点存在,if语句执行,先让根节点入栈,然后让所有的左节点入栈
当没有左节点的时候,执行else,弹出当前的末尾的左节点并且存入res中,再看右节点
*/
if(cur) {
// 根节点入栈
stack.push(cur)
// 左
cur = cur.left
} else {
// 弹出
cur = stack.pop()
res.push(cur.val)
// 右
cur = cur.right
}
}
return res
};
145. 二叉树的后序遍历 - 力扣(LeetCode)
递归法
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=145 lang=javascript
*
* [145] 二叉树的后序遍历
*/
// @lc code=start
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {number[]}
*/
var postorderTraversal = function(root) {
/**
* 后序遍历:左右根 左递归 右递归 压入根
*/
let res = []
const dfs = function(root) {
if(root === null) return
dfs(root.left)
dfs(root.right)
res.push(root.val)
}
dfs(root)
return res
};
// @lc code=end
迭代法
入栈:左 --> 右
出栈: 中 --> 右 --> 左 结果翻转
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {number[]}
*/
var postorderTraversal = function(root) {
let res = []
if(!root) return res
const stack = [root]
let cur = null
do {
cur = stack.pop()
res.push(cur.val)
cur.left && stack.push(cur.left)
cur.right && stack.push(cur.right)
} while(stack.length)
return res.reverse()
};
好多问题画图就可以迎刃而解
算法一遍不熟,大不了就多刷一遍,我都第三遍了
二叉树的统一迭代法
二叉树:一入递归深似海,从此offer是路人
递归至今我还不会?!!
前序遍历统一的迭代法
// 前序遍历:中左右
// 压栈顺序:右左中
var preorderTraversal = function(root, res = []) {
const stack = [];
if (root) stack.push(root);
while(stack.length) {
const node = stack.pop();
if(!node) {
res.push(stack.pop().val);
continue;
}
if (node.right) stack.push(node.right); // 右
if (node.left) stack.push(node.left); // 左
stack.push(node); // 中
stack.push(null);
};
return res;
};
中序遍历统一的迭代法
// 中序遍历:左中右
// 压栈顺序:右中左
var inorderTraversal = function(root, res = []) {
const stack = [];
if (root) stack.push(root);
while(stack.length) {
const node = stack.pop();
if(!node) {
res.push(stack.pop().val);
continue;
}
if (node.right) stack.push(node.right); // 右
stack.push(node); // 中
stack.push(null);
if (node.left) stack.push(node.left); // 左
};
return res;
};
后序遍历统一的迭代法
// 后续遍历:左右中
// 压栈顺序:中右左
var postorderTraversal = function(root, res = []) {
const stack = [];
if (root) stack.push(root);
while(stack.length) {
const node = stack.pop();
if(!node) {
res.push(stack.pop().val);
continue;
}
stack.push(node); // 中
stack.push(null);
if (node.right) stack.push(node.right); // 右
if (node.left) stack.push(node.left); // 左
};
return res;
};