异步处理

一、线程的实现方式
1. 线程的实现方式
1.1 继承Thread
class ThreadDemo01 extends Thread{
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("当前线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
}
1.2 实现Runnable接口
class ThreadDemo02 implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("当前线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
}
1.3 Callable接口
class MyCallable implements Callable<Integer>{
@Override
public Integer call() throws Exception {
System.out.println("当前线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
return 10;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
System.out.println("main方法执行了...");
ThreadDemo01 t1 = new ThreadDemo01();
t1.start();
ThreadDemo02 t2 = new ThreadDemo02();
new Thread(t2).start();
new Thread(()->{
System.out.println("当前线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
}).start();
// 通过Callable接口来实现 FutureTask 本质上是一个Runnable接口
FutureTask futureTask = new FutureTask(new MyCallable());
Thread t3 = new Thread(futureTask);
t3.start();
// 阻塞等待子线程的执行完成,然后获取线程的返回结果
Object o = futureTask.get();
System.out.println("o = " + o);
System.out.println("main方法结束了...");
}
2.线程池的实现
上面的三种获取线程的方法是直接获取,没有对线程做相关的管理,这时可以通过线程池来更加高效的管理线程对象。
// 定义一个线程池对象
private static ExecutorService service = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);
然后我们就可以通过这个线程池对象来获取对应的线程
service.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("线程池--》当前线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
});
3. 获取线程的区别
通过上面的介绍我们发现获取线程的方式
- 继承Thread对象
- 实现Runnable接口
- 实现Callable接口
- 线程池
继承Thread对象和实现Runnable接口没有办法获取返回结果的,实现Callable接口可以获取线程的返回结果。当然这三种方式都不能控制我们的资源,线程池可以控制资源。
二、线程池的详解
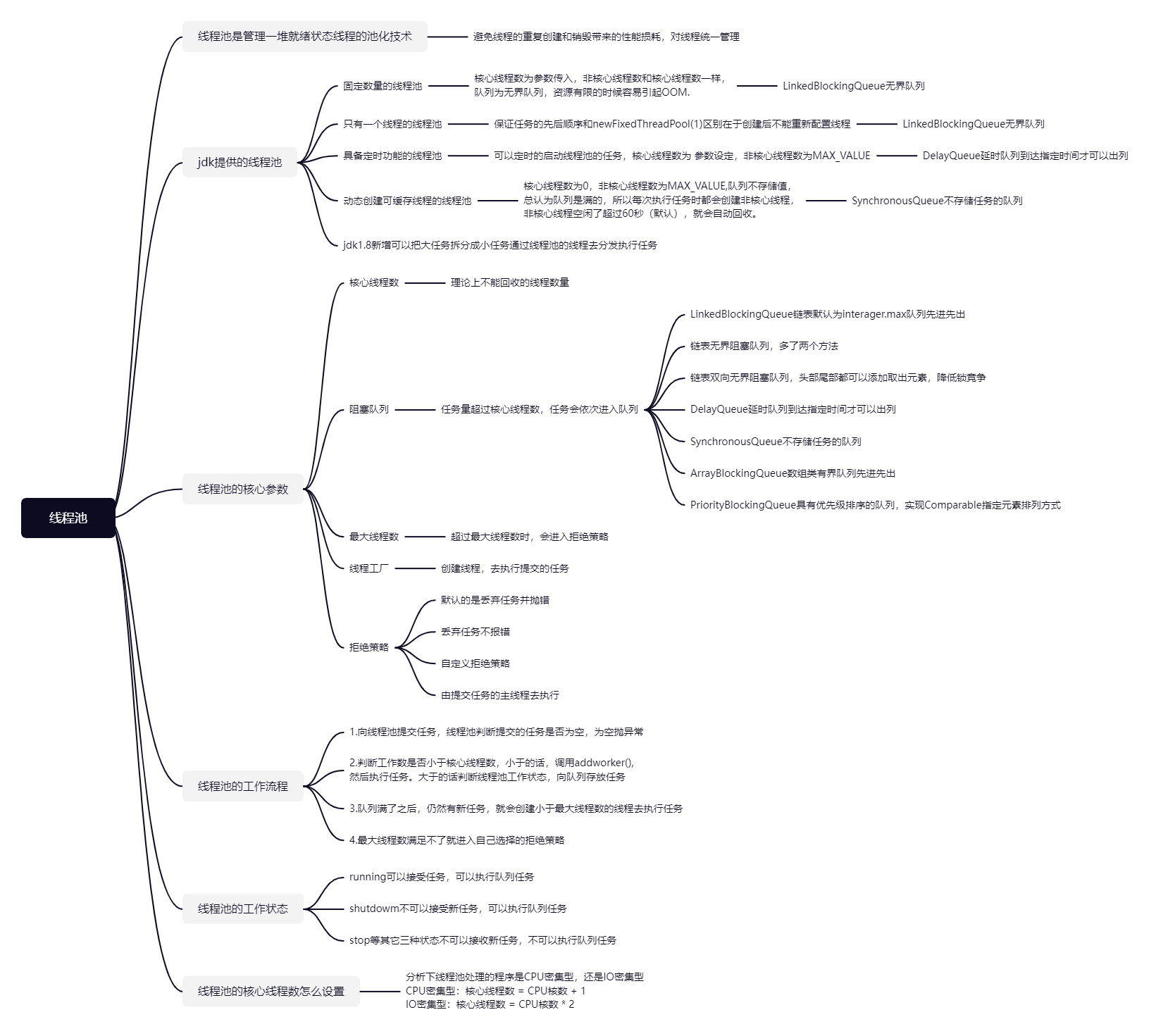
1.线程池的创建方式
- 通过Executors的静态方法
- 通过 new ThreadPoolExecutor方式创建
七大参数的作用
| 参数 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| corePoolSize | 核心线程数,线程池创建好后就准备就绪的线程数量,一直存在 |
| maximumPoolSize | 最大线程数量,控制资源 |
| keepAliveTime | 存活时间,如果当前线程数量如果大于核心线程数量,释放空闲的线程,<br />最大线程-核心数量 |
| unit | 时间单位 |
| BlockingQueue | 阻塞队列,如果任务很多,就会把多的任务放在队列中 |
| threadFactory | 线程的工厂 |
| handler | 如果队列满了,按照指定的拒绝策略执行任务 |
/**
* 线程池详解
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 第一种获取的方式
ExecutorService service = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);
// 第二种方式: 直接new ThreadPoolExecutor()对象,并且手动的指定对应的参数
// corePoolSize:线程池的核心线程数量 线程池创建出来后就会 new Thread() 5个
// maximumPoolSize:最大的线程数量,线程池支持的最大的线程数
// keepAliveTime:存活时间,当线程数大于核心线程,空闲的线程的存活时间 8-5=3
// unit:存活时间的单位
// BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue:阻塞队列 当线程数超过了核心线程数据,那么新的请求到来的时候会加入到阻塞的队列中
// new LinkedBlockingQueue<>() 默认队列的长度是 Integer.MAX 那这个就太大了,所以我们需要指定队列的长度
// threadFactory:创建线程的工厂对象
// RejectedExecutionHandler handler:当线程数大于最大线程数的时候会执行的淘汰策略
ThreadPoolExecutor poolExecutor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(5
, 100
, 10
, TimeUnit.SECONDS
, new LinkedBlockingQueue<>(10000)
, Executors.defaultThreadFactory()
, new ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy()
);
poolExecutor.execute(()->{
System.out.println("----->" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
});
}
2.线程池的执行顺序
线程池创建,准备好core数量的核心线程,准备接收任务
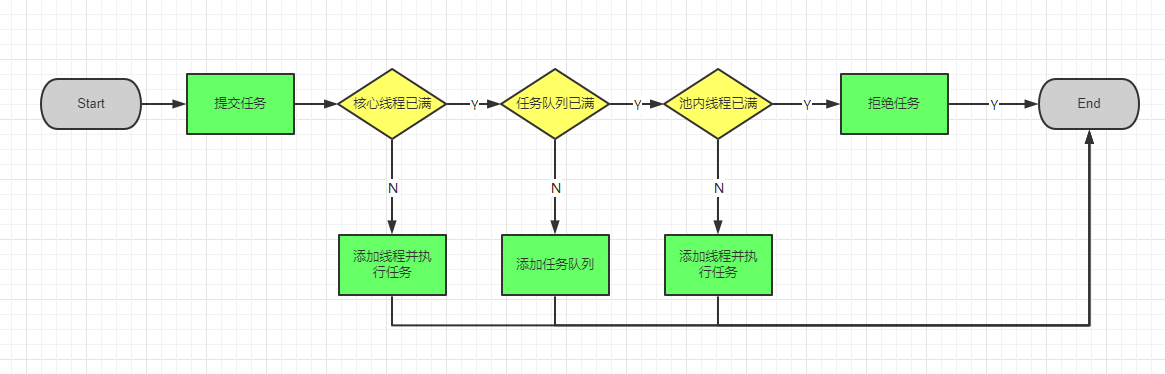
- 1.先判断核心线程是否已满,未满分配线程
- 2.任务队列是否已满,未满放入队列
- 3.是否达到最大的线程数量,未达到创建新的线程
- 4.通过对应的reject指定的拒绝策略进行处理
线程池的面试题:
- 有一个线程池,core:5,max:50,queue:100,如果并发是200,那么线程池是怎么处理的?
- 首先 200个中的前面5个会直接被核心线程处理,然后6个到105个会加入到阻塞队列中,然后106到155的请求在最大线程数中,那么会创建对应的线程来处理这些请求,之后剩下的45个请求会被直接放弃
3.线程池的好处
- 降低资源消耗
- 提高响应速度
- 提高线程的管理
三、CompletableFutrue
一个商品详情页
- 展示SKU的基本信息 0.5s
- 展示SKU的图片信息 0.6s
- 展示SKU的销售信息 1s
- spu的销售属性 1s
- 展示规格参数 1.5s
- spu详情信息 1s
1.ComplatableFuture介绍
Future是Java 5添加的类,用来描述一个异步计算的结果。你可以使用 isDone方法检查计算是否完成,或者使用 get阻塞住调用线程,直到计算完成返回结果,你也可以使用 cancel方法停止任务的执行。
虽然 Future以及相关使用方法提供了异步执行任务的能力,但是对于结果的获取却是很不方便,只能通过阻塞或者轮询的方式得到任务的结果。阻塞的方式显然和我们的异步编程的初衷相违背,轮询的方式又会耗费无谓的CPU资源,而且也不能及时地得到计算结果,为什么不能用观察者设计模式当计算结果完成及时通知监听者呢?
很多语言,比如Node.js,采用回调的方式实现异步编程。Java的一些框架,比如Netty,自己扩展了Java的 Future接口,提供了 addListener等多个扩展方法;Google guava也提供了通用的扩展Future;Scala也提供了简单易用且功能强大的Future/Promise异步编程模式。
作为正统的Java类库,是不是应该做点什么,加强一下自身库的功能呢?
在Java 8中, 新增加了一个包含50个方法左右的类: CompletableFuture,提供了非常强大的Future的扩展功能,可以帮助我们简化异步编程的复杂性,提供了函数式编程的能力,可以通过回调的方式处理计算结果,并且提供了转换和组合CompletableFuture的方法。
CompletableFuture类实现了Future接口,所以你还是可以像以前一样通过 get方法阻塞或者轮询的方式获得结果,但是这种方式不推荐使用。
CompletableFuture和FutureTask同属于Future接口的实现类,都可以获取线程的执行结果。
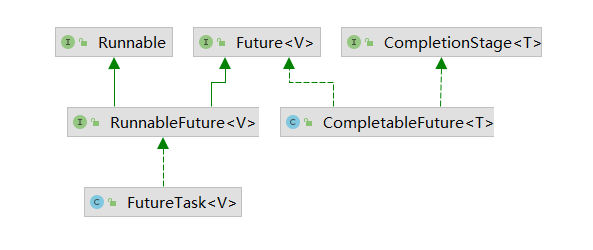
2.创建异步对象
CompletableFuture 提供了四个静态方法来创建一个异步操作。
static CompletableFuture<Void> runAsync(Runnable runnable)
public static CompletableFuture<Void> runAsync(Runnable runnable, Executor executor)
public static <U> CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier)
public static <U> CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier, Executor executor)
方法分为两类:
- runAsync 没有返回结果
- supplyAsync 有返回结果
private static ThreadPoolExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(5
,50
,10
, TimeUnit.SECONDS
,new LinkedBlockingQueue<>(100)
, Executors.defaultThreadFactory()
,new ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy()
);
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
System.out.println("main -- 线程开始了...");
// 获取CompletableFuture对象
CompletableFuture<Void> voidCompletableFuture = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("线程开始了...");
int i = 100/50;
System.out.println("线程结束了...");
},executor);
System.out.println("main -- 线程结束了...");
System.out.println("------------");
CompletableFuture<Integer> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("线程开始了...");
int i = 100 / 50;
System.out.println("线程结束了...");
return i;
}, executor);
System.out.println("获取的线程的返回结果是:" + future.get() );
}
3.whenXXX和handle方法
当CompletableFuture的计算结果完成,或者抛出异常的时候,可以执行特定的Action。主要是下面的方法:
public CompletableFuture<T> whenComplete(BiConsumer<? super T,? super Throwable> action);
public CompletableFuture<T> whenCompleteAsync(BiConsumer<? super T,? super Throwable> action);
public CompletableFuture<T> whenCompleteAsync(BiConsumer<? super T,? super Throwable> action, Executor executor);
public CompletableFuture<T> exceptionally(Function<Throwable,? extends T> fn);
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> handle(BiFunction<? super T, Throwable, ? extends U> fn) ;
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> handleAsync(BiFunction<? super T, Throwable, ? extends U> fn) ;
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> handleAsync(BiFunction<? super T, Throwable, ? extends U> fn, Executor executor) ;
相关方法的说明:
- whenComplete 可以获取异步任务的返回值和抛出的异常信息,但是不能修改返回结果
- execptionlly 当异步任务跑出了异常后会触发的方法,如果没有抛出异常该方法不会执行
- handle 可以获取异步任务的返回值和抛出的异常信息,而且可以显示的修改返回的结果
4.线程串行方法
thenApply 方法:当一个线程依赖另一个线程时,获取上一个任务返回的结果,并返回当前任务的返回值。
thenAccept方法:消费处理结果。接收任务的处理结果,并消费处理,无返回结果。
thenRun方法:只要上面的任务执行完成,就开始执行thenRun,只是处理完任务后,执行 thenRun的后续操作
带有Async默认是异步执行的。这里所谓的异步指的是不在当前线程内执行。
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenApply(Function<? super T,? extends U> fn)
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenApplyAsync(Function<? super T,? extends U> fn)
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenApplyAsync(Function<? super T,? extends U> fn, Executor executor)
public CompletionStage<Void> thenAccept(Consumer<? super T> action);
public CompletionStage<Void> thenAcceptAsync(Consumer<? super T> action);
public CompletionStage<Void> thenAcceptAsync(Consumer<? super T> action,Executor executor);
public CompletionStage<Void> thenRun(Runnable action);
public CompletionStage<Void> thenRunAsync(Runnable action);
public CompletionStage<Void> thenRunAsync(Runnable action,Executor executor);
5.两个都完成
上面介绍的相关方法都是串行的执行,接下来看看需要等待两个任务执行完成后才会触发的几个方法
- thenCombine :可以获取前面两线程的返回结果,本身也有返回结果
- thenAcceptBoth:可以获取前面两线程的返回结果,本身没有返回结果
- runAfterBoth:不可以获取前面两线程的返回结果,本身也没有返回结果
/**
* @param args
* @throws ExecutionException
* @throws InterruptedException
*/
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<Integer> future1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("任务1 线程开始了..." + Thread.currentThread().getName());
int i = 100 / 5;
System.out.println("任务1 线程结束了..." + Thread.currentThread().getName());
return i;
}, executor);
CompletableFuture<Integer> future2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("任务2 线程开始了..." + Thread.currentThread().getName());
int i = 100 /10;
System.out.println("任务2 线程结束了..." + Thread.currentThread().getName());
return i;
}, executor);
// runAfterBothAsync 不能获取前面两个线程的返回结果,本身也没有返回结果
CompletableFuture<Void> voidCompletableFuture = future1.runAfterBothAsync(future2, () -> {
System.out.println("任务3执行了");
},executor);
// thenAcceptBothAsync 可以获取前面两个线程的返回结果,本身没有返回结果
CompletableFuture<Void> voidCompletableFuture1 = future1.thenAcceptBothAsync(future2, (f1, f2) -> {
System.out.println("f1 = " + f1);
System.out.println("f2 = " + f2);
}, executor);
// thenCombineAsync: 既可以获取前面两个线程的返回结果,同时也会返回结果给阻塞的线程
CompletableFuture<String> stringCompletableFuture = future1.thenCombineAsync(future2, (f1, f2) -> {
return f1 + ":" + f2;
}, executor);
// 可以处理异步任务之后的操作
System.out.println("获取的线程的返回结果是:" + stringCompletableFuture.get() );
}
6.两个任务完成一个
在上面5个基础上我们来看看两个任务只要有一个完成就会触发任务3的情况
- runAfterEither:不能获取完成的线程的返回结果,自身也没有返回结果
- acceptEither:可以获取线程的返回结果,自身没有返回结果
- applyToEither:既可以获取线程的返回结果,自身也有返回结果
/**
* @param args
* @throws ExecutionException
* @throws InterruptedException
*/
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<Object> future1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("任务1 线程开始了..." + Thread.currentThread().getName());
int i = 100 / 5;
System.out.println("任务1 线程结束了..." + Thread.currentThread().getName());
return i;
}, executor);
CompletableFuture<Object> future2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("任务2 线程开始了..." + Thread.currentThread().getName());
int i = 100 /10;
try {
Thread.sleep(5000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("任务2 线程结束了..." + Thread.currentThread().getName());
return i+"";
}, executor);
// runAfterEitherAsync 不能获取前面完成的线程的返回结果,自身也没有返回结果
future1.runAfterEitherAsync(future2,()->{
System.out.println("任务3执行了....");
},executor);
// acceptEitherAsync 可以获取前面完成的线程的返回结果 自身没有返回结果
future1.acceptEitherAsync(future2,(res)->{
System.out.println("res = " + res);
},executor);
// applyToEitherAsync 既可以获取完成任务的线程的返回结果 自身也有返回结果
CompletableFuture<String> stringCompletableFuture = future1.applyToEitherAsync(future2, (res) -> {
System.out.println("res = " + res);
return res + "-->OK";
}, executor);
// 可以处理异步任务之后的操作
System.out.println("获取的线程的返回结果是:" + stringCompletableFuture.get() );
}
7.多任务组合
allOf:等待所有任务完成
anyOf:只要有一个任务完成
public static CompletableFuture<Void> allOf(CompletableFuture<?>... cfs);
public static CompletableFuture<Object> anyOf(CompletableFuture<?>... cfs);
/**
* @param args
* @throws ExecutionException
* @throws InterruptedException
*/
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<Object> future1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("任务1 线程开始了..." + Thread.currentThread().getName());
int i = 100 / 5;
System.out.println("任务1 线程结束了..." + Thread.currentThread().getName());
return i;
}, executor);
CompletableFuture<Object> future2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("任务2 线程开始了..." + Thread.currentThread().getName());
int i = 100 /10;
try {
Thread.sleep(5000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("任务2 线程结束了..." + Thread.currentThread().getName());
return i+"";
}, executor);
CompletableFuture<Object> future3 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("任务3 线程开始了..." + Thread.currentThread().getName());
int i = 100 /10;
System.out.println("任务3 线程结束了..." + Thread.currentThread().getName());
return i+"";
}, executor);
CompletableFuture<Object> anyOf = CompletableFuture.anyOf(future1, future2, future3);
anyOf.get();
System.out.println("主任务执行完成..." + anyOf.get());
CompletableFuture<Void> allOf = CompletableFuture.allOf(future1, future2, future3);
allOf.get();// 阻塞在这个位置,等待所有的任务执行完成
System.out.println("主任务执行完成..." + future1.get() + " :" + future2.get() + " :" + future3.get());
}