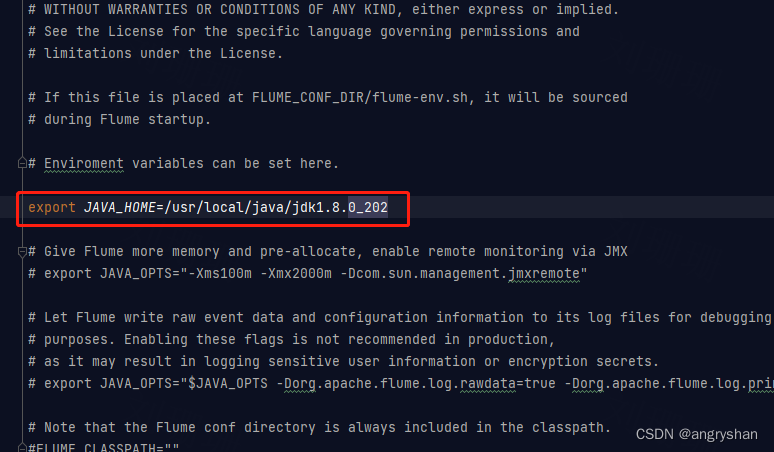
1、对于字符设备驱动而言,当驱动模块加载成功以后需要注册字符设备,同样,卸载驱动模 块的时候也需要注销掉字符设备。字符设备的注册和注销函数原型如下所示
static inline int register_chrdev(unsigned int major, const char *name,
const struct file_operations *fops)
static inline void unregister_chrdev(unsigned int major, const char *name)register_chrdev 函数用于注册字符设备,此函数一共有三个参数
major:主设备号,Linux 下每个设备都有一个设备号,设备号分为主设备号和次设备号两 部分,关于设备号后面会详细讲解。
name:设备名字,指向一串字符串。
fops:结构体 file_operations 类型指针,指向设备的操作函数集合变量。
unregister_chrdev 函数用户注销字符设备,此函数有两个参数
major:要注销的设备对应的主设备号。
name:要注销的设备对应的设备名。
2、一般字符设备的注册在驱动模块的入口函数 xxx_init 中进行,字符设备的注销在驱动模块 的出口函数 xxx_exit 中进行。
1 static struct file_operations test_fops;
2
3 /* 驱动入口函数 */
4 static int __init xxx_init(void)
5 {
6 /* 入口函数具体内容 */
7 int retvalue = 0;
8
9 /* 注册字符设备驱动 */
10 retvalue = register_chrdev(200, "chrtest", &test_fops);
11 if(retvalue < 0){
12 /* 字符设备注册失败,自行处理 */
13 }
14 return 0;
15 }
16
17 /* 驱动出口函数 */
18 static void __exit xxx_exit(void)
19 {
20 /* 注销字符设备驱动 */
21 unregister_chrdev(200, "chrtest");
22 }
23
24 /* 将上面两个函数指定为驱动的入口和出口函数 */
25 module_init(xxx_init);
26 module_exit(xxx_exit);
第 1 行,定义了一个 file_operations 结构体变量 test_fops,test_fops 就是设备的操作函数集 合,只是此时我们还没有初始化 test_fops 中的 open、release 等这些成员变量,所以这个操作函 数集合还是空的。
第 10 行,调用函数 register_chrdev 注册字符设备,主设备号为 200,设备名字为“chrtest”, 设备操作函数集合就是第 1 行定义的 test_fops。要注意的一点就是,选择没有被使用的主设备 号,输入命令“cat /proc/devices”可以查看当前已经被使用掉的设备号

图中可以列出当前系统中所有的字符设备和块设备,其中第 1 列就是设备对应 的主设备号。200 这个主设备号在我的开发板中并没有被使用,所以我这里就用了 200 这个主 设备号。 第 21 行,调用函数 unregister_chrdev 注销主设备号为 200 的这个设备。
3、实现设备的具体操作函数
file_operations 结构体就是设备的具体操作函数,我们定义了 file_operations结构体类型的变量test_fops,但是还没对其进行初始化,也就是初始化其中的open、 release、read 和 write 等具体的设备操作函数。
能够对 chrtest 进行打开和关闭操作
设备打开和关闭是最基本的要求,几乎所有的设备都得提供打开和关闭的功能。因此我们 需要实现 file_operations 中的 open 和 release 这两个函数
对 chrtest 进行读写操作
假设 chrtest 这个设备控制着一段缓冲区(内存),应用程序需要通过 read 和 write 这两个函 数对 chrtest 的缓冲区进行读写操作。所以需要实现 file_operations 中的 read 和 write 这两个函 数。
1 /* 打开设备 */
2 static int chrtest_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *filp)
3 {
4 /* 用户实现具体功能 */
5 return 0;
6 }
7
8 /* 从设备读取 */
9 static ssize_t chrtest_read(struct file *filp, char __user *buf,
size_t cnt, loff_t *offt)
10 {
11 /* 用户实现具体功能 */
12 return 0;
13 }
14
15 /* 向设备写数据 */
16 static ssize_t chrtest_write(struct file *filp,const char __user *buf,
size_t cnt, loff_t *offt)
17 {
18 /* 用户实现具体功能 */
19 return 0;
20 }
21
22 /* 关闭/释放设备 */
23 static int chrtest_release(struct inode *inode, struct file *filp)
24 {
25 /* 用户实现具体功能 */
26 return 0;
27 }
28
29 static struct file_operations test_fops = {
30 .owner = THIS_MODULE,
31 .open = chrtest_open,
32 .read = chrtest_read,
33 .write = chrtest_write,
34 .release = chrtest_release,
35 };
36
37 /* 驱动入口函数 */
38 static int __init xxx_init(void)
39 {
40 /* 入口函数具体内容 */
41 int retvalue = 0;
42
43 /* 注册字符设备驱动 */
44 retvalue = register_chrdev(200, "chrtest", &test_fops);
45 if(retvalue < 0){
46 /* 字符设备注册失败,自行处理 */
47 }
48 return 0;
49 }
50
51 /* 驱动出口函数 */
52 static void __exit xxx_exit(void)
53 {
54 /* 注销字符设备驱动 */
55 unregister_chrdev(200, "chrtest");
56 }
57
58 /* 将上面两个函数指定为驱动的入口和出口函数 */
59 module_init(xxx_init);
60 module_exit(xxx_exit);
我们编写了四个函数:chrtest_open、chrtest_read、chrtest_write 和 chrtest_release。这四个函数就是 chrtest 设备的 open、read、write 和 release 操作函数。第 29 行~35 行初始化 test_fops 的 open、read、write 和 release 这四个成员变量。
4、添加 LICENSE 和作者信息
最后我们需要在驱动中加入 LICENSE 信息和作者信息,其中 LICENSE 是必须添加的,否 则的话编译的时候会报错,作者信息可以添加也可以不添加。LICENSE 和作者信息的添加使用 如下两个函数:
MODULE_LICENSE() //添加模块 LICENSE 信息
MODULE_AUTHOR() //添加模块作者信息
结合上次示例代码 加入 LICENSE 和作者信息,完成以后的内容如下:
1 /* 打开设备 */
2 static int chrtest_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *filp)
3 {
4 /* 用户实现具体功能 */
5 return 0;
6 }
......
57
58 /* 将上面两个函数指定为驱动的入口和出口函数 */
59 module_init(xxx_init);
60 module_exit(xxx_exit);
61
62 MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
63 MODULE_AUTHOR("hsj");第 62 行,LICENSE 采用 GPL 协议。
第 63 行,添加作者名字。 至此,字符设备驱动开发的完整步骤就讲解完了,而且也编写好了一个完整的字符设备驱 动模板,以后字符设备驱动开发都可以在此模板上进行。




![[项目实战] 博客系统实现](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/bd07206fa54f41fc8778981ed7a34584.png)