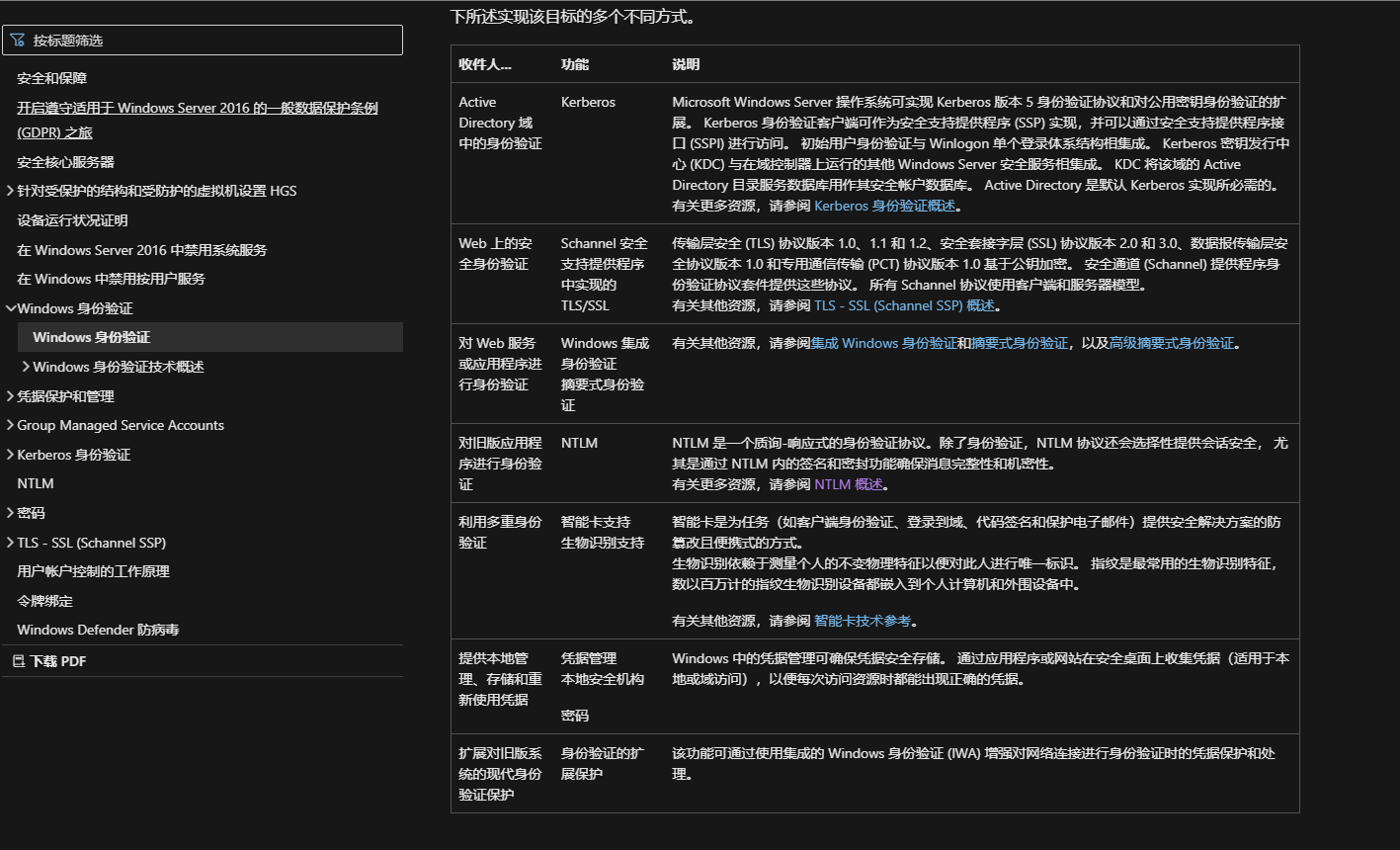
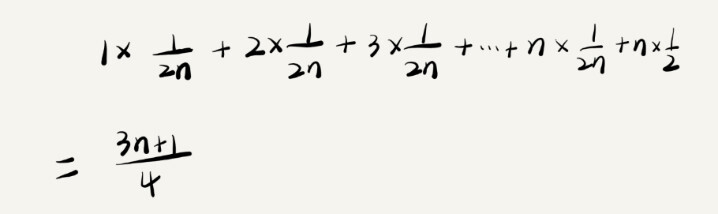Linux Driver 和Device匹配过程分析(2)
- 1 device注册流程
- 2,driver注册匹配过程:
- 2.1 pci_register_driver
- 2.1.1 nvme_init
- 2.1.2 pci_register_driver
- 2.1.3 __pci_register_driver
- 2.1.4 driver_register
- 2.1.5 bus_add_driver
- 2.1.6 driver_attach
- 2.1.7 bus_for_each_dev
- 2.1.8 __driver_attach
- 2.1.9 driver_match_device
- 2.1.10 pci_bus_match
- 2.1.11 pci_match_device
- 2.1.12 pci_match_one_device
- 2.1.13 driver_probe_device
- 2.1.12 __driver_probe_device
- 2.1.14 really_probe
- 2.1.15 call_driver_probe
- 2.1.16 pci_bus_type
- 2.1.17 pci_device_probe
- 2.1.18 __pci_device_probe
- 2.1.19 pci_call_probe
- 2.1.20 local_pci_probe
- 2.1.21 nvme_probe
以linux-5.14.10内核为例来分析总线注册过程:
是基于设备树的处理流程分析的,不过对于bus/dev/drv的模式只是在match函数匹配的过程中稍有差异,其他的流程是一样的。
本篇文章
1,设备注册匹配过程和
2,设备驱动注册匹配过程是介绍的两种不同的设备驱动注册的流程触发的初始化流程来介绍整个总线设备驱动流程关系的。
1 device注册流程
以register_virtio_device为例来介绍,其中register_virtio_device会的注册会使得前期注册的驱动probe函数被调用到。
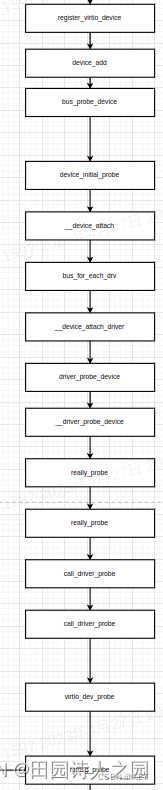
2,driver注册匹配过程:
在该过程中以nvme驱动为例去介绍匹配的过程,nvme是挂载在PCIe总线上的一款设备。
2.1 pci_register_driver
pci_register_driver在注册的时候会去根据注册到PCI总线上的dev_driver和devices去做对应的匹配校验。整个的流程如下所示:
|- nvme_init
|- pci_register_driver
|- __pci_register_driver
|- driver_register
|- bus_add_driver
|- driver_attach
|- bus_for_each_dev
|- __driver_attach
|- driver_match_device
|- pci_bus_match
|- pci_match_device
|- pci_match_one_device
|- driver_probe_device
|- really_probe
|- call_driver_probe
|- pci_device_probe
|- __pci_device_probe
|- pci_call_probe
|- local_pci_probe
|- nvme_probe
2.1.1 nvme_init
nvme设备驱动注册
代码路径:drivers/nvme/host/pci.c
3308 static int __init nvme_init(void)
3309 {
3310 BUILD_BUG_ON(sizeof(struct nvme_create_cq) != 64);
3311 BUILD_BUG_ON(sizeof(struct nvme_create_sq) != 64);
3312 BUILD_BUG_ON(sizeof(struct nvme_delete_queue) != 64);
3313 BUILD_BUG_ON(IRQ_AFFINITY_MAX_SETS < 2);
3314
3315 return pci_register_driver(&nvme_driver);
3316 }
3317
3318 static void __exit nvme_exit(void)
3319 {
3320 pci_unregister_driver(&nvme_driver);
3321 flush_workqueue(nvme_wq);
3322 }
2.1.2 pci_register_driver
代码路径:include/linux/pci.h
1400 /* pci_register_driver() must be a macro so KBUILD_MODNAME can be expanded */
1401 #define pci_register_driver(driver) \
1402 __pci_register_driver(driver, THIS_MODULE, KBUILD_MODNAME)
2.1.3 __pci_register_driver
drv->driver.bus = &pci_bus_type;表示nvme这个设备是挂载在PCI总线上的pci device,而pci_bus_type 的match函数用脚检测挂载在PCI/PCIe总线上的设备和驱动是否匹配。
代码路径:drivers/pci/pci-driver.c
1368 /**
1369 * __pci_register_driver - register a new pci driver
1370 * @drv: the driver structure to register
1371 * @owner: owner module of drv
1372 * @mod_name: module name string
1373 *
1374 * Adds the driver structure to the list of registered drivers.
1375 * Returns a negative value on error, otherwise 0.
1376 * If no error occurred, the driver remains registered even if
1377 * no device was claimed during registration.
1378 */
1379 int __pci_register_driver(struct pci_driver *drv, struct module *owner,
1380 const char *mod_name)
1381 {
1382 /* initialize common driver fields */
1383 drv->driver.name = drv->name;
1384 drv->driver.bus = &pci_bus_type;
1385 drv->driver.owner = owner;
1386 drv->driver.mod_name = mod_name;
1387 drv->driver.groups = drv->groups;
1388 drv->driver.dev_groups = drv->dev_groups;
1389
1390 spin_lock_init(&drv->dynids.lock);
1391 INIT_LIST_HEAD(&drv->dynids.list);
1392
1393 /* register with core */
1394 return driver_register(&drv->driver);
1395 }
1396 EXPORT_SYMBOL(__pci_register_driver);
2.1.4 driver_register
代码路径:drivers/base/driver.c
139 /**
140 * driver_register - register driver with bus
141 * @drv: driver to register
142 *
143 * We pass off most of the work to the bus_add_driver() call,
144 * since most of the things we have to do deal with the bus
145 * structures.
146 */
147 int driver_register(struct device_driver *drv)
148 {
149 int ret;
150 struct device_driver *other;
151
152 if (!drv->bus->p) {
153 pr_err("Driver '%s' was unable to register with bus_type '%s' because the bus was not initialized.\n",
154 drv->name, drv->bus->name);
155 return -EINVAL;
156 }
157
158 if ((drv->bus->probe && drv->probe) ||
159 (drv->bus->remove && drv->remove) ||
160 (drv->bus->shutdown && drv->shutdown))
161 pr_warn("Driver '%s' needs updating - please use "
162 "bus_type methods\n", drv->name);
163
164 other = driver_find(drv->name, drv->bus);
165 if (other) {
166 pr_err("Error: Driver '%s' is already registered, "
167 "aborting...\n", drv->name);
168 return -EBUSY;
169 }
170
171 ret = bus_add_driver(drv);
172 if (ret)
173 return ret;
174 ret = driver_add_groups(drv, drv->groups);
175 if (ret) {
176 bus_remove_driver(drv);
177 return ret;
178 }
179 kobject_uevent(&drv->p->kobj, KOBJ_ADD);
180
181 return ret;
182 }
183 EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(driver_register);
2.1.5 bus_add_driver
代码路径:drivers/base/bus.c
586 /**
587 * bus_add_driver - Add a driver to the bus.
588 * @drv: driver.
589 */
590 int bus_add_driver(struct device_driver *drv)
591 {
592 struct bus_type *bus;
593 struct driver_private *priv;
594 int error = 0;
595
596 bus = bus_get(drv->bus);
597 if (!bus)
598 return -EINVAL;
599
600 pr_debug("bus: '%s': add driver %s\n", bus->name, drv->name);
601
602 priv = kzalloc(sizeof(*priv), GFP_KERNEL);
603 if (!priv) {
604 error = -ENOMEM;
605 goto out_put_bus;
606 }
607 klist_init(&priv->klist_devices, NULL, NULL);
608 priv->driver = drv;
609 drv->p = priv;
610 priv->kobj.kset = bus->p->drivers_kset;
611 error = kobject_init_and_add(&priv->kobj, &driver_ktype, NULL,
612 "%s", drv->name);
613 if (error)
614 goto out_unregister;
615
616 klist_add_tail(&priv->knode_bus, &bus->p->klist_drivers);
617 if (drv->bus->p->drivers_autoprobe) {
618 error = driver_attach(drv);
619 if (error)
620 goto out_unregister;
621 }
622 module_add_driver(drv->owner, drv);
623
624 error = driver_create_file(drv, &driver_attr_uevent);
625 if (error) {
626 printk(KERN_ERR "%s: uevent attr (%s) failed\n",
627 __func__, drv->name);
628 }
629 error = driver_add_groups(drv, bus->drv_groups);
630 if (error) {
631 /* How the hell do we get out of this pickle? Give up */
632 printk(KERN_ERR "%s: driver_add_groups(%s) failed\n",
633 __func__, drv->name);
634 }
635
636 if (!drv->suppress_bind_attrs) {
637 error = add_bind_files(drv);
638 if (error) {
639 /* Ditto */
640 printk(KERN_ERR "%s: add_bind_files(%s) failed\n",
641 __func__, drv->name);
642 }
643 }
644
645 return 0;
646
647 out_unregister:
648 kobject_put(&priv->kobj);
649 /* drv->p is freed in driver_release() */
650 drv->p = NULL;
651 out_put_bus:
652 bus_put(bus);
653 return error;
654 }
2.1.6 driver_attach
代码路径:drivers/base/dd.c
1146 /**
1147 * driver_attach - try to bind driver to devices.
1148 * @drv: driver.
1149 *
1150 * Walk the list of devices that the bus has on it and try to
1151 * match the driver with each one. If driver_probe_device()
1152 * returns 0 and the @dev->driver is set, we've found a
1153 * compatible pair.
1154 */
1155 int driver_attach(struct device_driver *drv)
1156 {
1157 return bus_for_each_dev(drv->bus, NULL, drv, __driver_attach);
1158 }
1159 EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(driver_attach);
2.1.7 bus_for_each_dev
代码路径:drivers/base/bus.c
269 /**
270 * bus_for_each_dev - device iterator.
271 * @bus: bus type.
272 * @start: device to start iterating from.
273 * @data: data for the callback.
274 * @fn: function to be called for each device.
275 *
276 * Iterate over @bus's list of devices, and call @fn for each,
277 * passing it @data. If @start is not NULL, we use that device to
278 * begin iterating from.
279 *
280 * We check the return of @fn each time. If it returns anything
281 * other than 0, we break out and return that value.
282 *
283 * NOTE: The device that returns a non-zero value is not retained
284 * in any way, nor is its refcount incremented. If the caller needs
285 * to retain this data, it should do so, and increment the reference
286 * count in the supplied callback.
287 */
288 int bus_for_each_dev(struct bus_type *bus, struct device *start,
289 void *data, int (*fn)(struct device *, void *))
290 {
291 struct klist_iter i;
292 struct device *dev;
293 int error = 0;
294
295 if (!bus || !bus->p)
296 return -EINVAL;
297
298 klist_iter_init_node(&bus->p->klist_devices, &i,
299 (start ? &start->p->knode_bus : NULL));
300 while (!error && (dev = next_device(&i)))
301 error = fn(dev, data);
302 klist_iter_exit(&i);
303 return error;
304 }
305 EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(bus_for_each_dev);
2.1.8 __driver_attach
代码路径:drivers/base/dd.c
1092 static int __driver_attach(struct device *dev, void *data)
1093 {
1094 struct device_driver *drv = data;
1095 int ret;
1096
1097 /*
1098 * Lock device and try to bind to it. We drop the error
1099 * here and always return 0, because we need to keep trying
1100 * to bind to devices and some drivers will return an error
1101 * simply if it didn't support the device.
1102 *
1103 * driver_probe_device() will spit a warning if there
1104 * is an error.
1105 */
1106
1107 ret = driver_match_device(drv, dev);
1108 if (ret == 0) {
1109 /* no match */
1110 return 0;
1111 } else if (ret == -EPROBE_DEFER) {
1112 dev_dbg(dev, "Device match requests probe deferral\n");
1113 dev->can_match = true;
1114 driver_deferred_probe_add(dev);
1115 } else if (ret < 0) {
1116 dev_dbg(dev, "Bus failed to match device: %d\n", ret);
1117 return ret;
1118 } /* ret > 0 means positive match */
1119
1120 if (driver_allows_async_probing(drv)) {
1121 /*
1122 * Instead of probing the device synchronously we will
1123 * probe it asynchronously to allow for more parallelism.
1124 *
1125 * We only take the device lock here in order to guarantee
1126 * that the dev->driver and async_driver fields are protected
1127 */
1128 dev_dbg(dev, "probing driver %s asynchronously\n", drv->name);
1129 device_lock(dev);
1130 if (!dev->driver) {
1131 get_device(dev);
1132 dev->p->async_driver = drv;
1133 async_schedule_dev(__driver_attach_async_helper, dev);
1134 }
1135 device_unlock(dev);
1136 return 0;
1137 }
1138
1139 __device_driver_lock(dev, dev->parent);
1140 driver_probe_device(drv, dev);
1141 __device_driver_unlock(dev, dev->parent);
1142
1143 return 0;
1144 }
2.1.9 driver_match_device
drv->bus->match(dev, drv)的match函数指向前面注册的pci_bus_type所定义的pci_bus_match函数。
代码路径:drivers/base/base.h
144 static inline int driver_match_device(struct device_driver *drv,
145 struct device *dev)
146 {
147 return drv->bus->match ? drv->bus->match(dev, drv) : 1;
148
2.1.10 pci_bus_match
代码路径:drivers/pci/pci-driver.c
1440 /**
1441 * pci_bus_match - Tell if a PCI device structure has a matching PCI device id structure
1442 * @dev: the PCI device structure to match against
1443 * @drv: the device driver to search for matching PCI device id structures
1444 *
1445 * Used by a driver to check whether a PCI device present in the
1446 * system is in its list of supported devices. Returns the matching
1447 * pci_device_id structure or %NULL if there is no match.
1448 */
1449 static int pci_bus_match(struct device *dev, struct device_driver *drv)
1450 {
1451 struct pci_dev *pci_dev = to_pci_dev(dev);
1452 struct pci_driver *pci_drv;
1453 const struct pci_device_id *found_id;
1454
1455 if (!pci_dev->match_driver)
1456 return 0;
1457
1458 pci_drv = to_pci_driver(drv);
1459 found_id = pci_match_device(pci_drv, pci_dev);
1460 if (found_id)
1461 return 1;
1462
1463 return 0;
1464 }
2.1.11 pci_match_device
代码路径:drivers/pci/pci-driver.c
125 /**
126 * pci_match_device - See if a device matches a driver's list of IDs
127 * @drv: the PCI driver to match against
128 * @dev: the PCI device structure to match against
129 *
130 * Used by a driver to check whether a PCI device is in its list of
131 * supported devices or in the dynids list, which may have been augmented
132 * via the sysfs "new_id" file. Returns the matching pci_device_id
133 * structure or %NULL if there is no match.
134 */
135 static const struct pci_device_id *pci_match_device(struct pci_driver *drv,
136 struct pci_dev *dev)
137 {
138 struct pci_dynid *dynid;
139 const struct pci_device_id *found_id = NULL;
140
141 /* When driver_override is set, only bind to the matching driver */
142 if (dev->driver_override && strcmp(dev->driver_override, drv->name))
143 return NULL;
144
145 /* Look at the dynamic ids first, before the static ones */
146 spin_lock(&drv->dynids.lock);
147 list_for_each_entry(dynid, &drv->dynids.list, node) {
148 if (pci_match_one_device(&dynid->id, dev)) {
149 found_id = &dynid->id;
150 break;
151 }
152 }
153 spin_unlock(&drv->dynids.lock);
154
155 if (!found_id)
156 found_id = pci_match_id(drv->id_table, dev);
157
158 /* driver_override will always match, send a dummy id */
159 if (!found_id && dev->driver_override)
160 found_id = &pci_device_id_any;
161
162 return found_id;
163 }
2.1.12 pci_match_one_device
代码路径:drivers/pci/pci-driver.c
204 /**
205 * pci_match_one_device - Tell if a PCI device structure has a matching
206 * PCI device id structure
207 * @id: single PCI device id structure to match
208 * @dev: the PCI device structure to match against
209 *
210 * Returns the matching pci_device_id structure or %NULL if there is no match.
211 */
212 static inline const struct pci_device_id *
213 pci_match_one_device(const struct pci_device_id *id, const struct pci_dev *dev)
214 {
✗ 215 if ((id->vendor == PCI_ANY_ID || id->vendor == dev->vendor) &&
✗ 216 (id->device == PCI_ANY_ID || id->device == dev->device) &&
✗ 217 (id->subvendor == PCI_ANY_ID || id->subvendor == dev->subsystem_vendor) &&
✗ 218 (id->subdevice == PCI_ANY_ID || id->subdevice == dev->subsystem_device) &&
✗ 219 !((id->class ^ dev->class) & id->class_mask))
✗ 220 return id;
✗ 221 return NULL;
222 }
2.1.13 driver_probe_device
代码路径:drivers/base/dd.c
761 /**
762 * driver_probe_device - attempt to bind device & driver together
763 * @drv: driver to bind a device to
764 * @dev: device to try to bind to the driver
765 *
766 * This function returns -ENODEV if the device is not registered, -EBUSY if it
767 * already has a driver, 0 if the device is bound successfully and a positive
768 * (inverted) error code for failures from the ->probe method.
769 *
770 * This function must be called with @dev lock held. When called for a
771 * USB interface, @dev->parent lock must be held as well.
772 *
773 * If the device has a parent, runtime-resume the parent before driver probing.
774 */
775 static int driver_probe_device(struct device_driver *drv, struct device *dev)
776 {
777 int trigger_count = atomic_read(&deferred_trigger_count);
778 int ret;
779
780 atomic_inc(&probe_count);
781 ret = __driver_probe_device(drv, dev);
782 if (ret == -EPROBE_DEFER || ret == EPROBE_DEFER) {
783 driver_deferred_probe_add(dev);
784
785 /*
786 * Did a trigger occur while probing? Need to re-trigger if yes
787 */
788 if (trigger_count != atomic_read(&deferred_trigger_count) &&
789 !defer_all_probes)
790 driver_deferred_probe_trigger();
791 }
792 atomic_dec(&probe_count);
793 wake_up_all(&probe_waitqueue);
794 return ret;
795 }
2.1.12 __driver_probe_device
代码路径:drivers/base/dd.c
730 static int __driver_probe_device(struct device_driver *drv, struct device *dev)
731 {
732 int ret = 0;
733
734 if (dev->p->dead || !device_is_registered(dev))
735 return -ENODEV;
736 if (dev->driver)
737 return -EBUSY;
738
739 dev->can_match = true;
740 pr_debug("bus: '%s': %s: matched device %s with driver %s\n",
741 drv->bus->name, __func__, dev_name(dev), drv->name);
742
743 pm_runtime_get_suppliers(dev);
744 if (dev->parent)
745 pm_runtime_get_sync(dev->parent);
746
747 pm_runtime_barrier(dev);
748 if (initcall_debug)
749 ret = really_probe_debug(dev, drv);
750 else
751 ret = really_probe(dev, drv);
752 pm_request_idle(dev);
753
754 if (dev->parent)
755 pm_runtime_put(dev->parent);
756
757 pm_runtime_put_suppliers(dev);
758 return ret;
759 }
2.1.14 really_probe
代码路径:drivers/base/dd.c
541 static int really_probe(struct device *dev, struct device_driver *drv)
542 {
543 bool test_remove = IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_DEBUG_TEST_DRIVER_REMOVE) &&
544 !drv->suppress_bind_attrs;
545 int ret;
546
547 if (defer_all_probes) {
548 /*
549 * Value of defer_all_probes can be set only by
550 * device_block_probing() which, in turn, will call
551 * wait_for_device_probe() right after that to avoid any races.
552 */
553 dev_dbg(dev, "Driver %s force probe deferral\n", drv->name);
554 return -EPROBE_DEFER;
555 }
556
557 ret = device_links_check_suppliers(dev);
558 if (ret)
559 return ret;
560
561 pr_debug("bus: '%s': %s: probing driver %s with device %s\n",
562 drv->bus->name, __func__, drv->name, dev_name(dev));
563 if (!list_empty(&dev->devres_head)) {
564 dev_crit(dev, "Resources present before probing\n");
565 ret = -EBUSY;
566 goto done;
567 }
568
569 re_probe:
570 dev->driver = drv;
571
572 /* If using pinctrl, bind pins now before probing */
573 ret = pinctrl_bind_pins(dev);
574 if (ret)
575 goto pinctrl_bind_failed;
576
577 if (dev->bus->dma_configure) {
578 ret = dev->bus->dma_configure(dev);
579 if (ret)
580 goto probe_failed;
581 }
582
583 ret = driver_sysfs_add(dev);
584 if (ret) {
585 pr_err("%s: driver_sysfs_add(%s) failed\n",
586 __func__, dev_name(dev));
587 goto probe_failed;
588 }
589
590 if (dev->pm_domain && dev->pm_domain->activate) {
591 ret = dev->pm_domain->activate(dev);
592 if (ret)
593 goto probe_failed;
594 }
595
596 ret = call_driver_probe(dev, drv);
597 if (ret) {
598 /*
599 * Return probe errors as positive values so that the callers
600 * can distinguish them from other errors.
601 */
602 ret = -ret;
603 goto probe_failed;
604 }
605
606 ret = device_add_groups(dev, drv->dev_groups);
607 if (ret) {
608 dev_err(dev, "device_add_groups() failed\n");
609 goto dev_groups_failed;
610 }
611
612 if (dev_has_sync_state(dev)) {
613 ret = device_create_file(dev, &dev_attr_state_synced);
614 if (ret) {
615 dev_err(dev, "state_synced sysfs add failed\n");
616 goto dev_sysfs_state_synced_failed;
617 }
618 }
619
620 if (test_remove) {
621 test_remove = false;
622
623 device_remove_file(dev, &dev_attr_state_synced);
624 device_remove_groups(dev, drv->dev_groups);
625
626 if (dev->bus->remove)
627 dev->bus->remove(dev);
628 else if (drv->remove)
629 drv->remove(dev);
630
631 devres_release_all(dev);
632 driver_sysfs_remove(dev);
633 dev->driver = NULL;
634 dev_set_drvdata(dev, NULL);
635 if (dev->pm_domain && dev->pm_domain->dismiss)
636 dev->pm_domain->dismiss(dev);
637 pm_runtime_reinit(dev);
638
639 goto re_probe;
640 }
641
642 pinctrl_init_done(dev);
643
644 if (dev->pm_domain && dev->pm_domain->sync)
645 dev->pm_domain->sync(dev);
646
647 driver_bound(dev);
648 pr_debug("bus: '%s': %s: bound device %s to driver %s\n",
649 drv->bus->name, __func__, dev_name(dev), drv->name);
650 goto done;
651
652 dev_sysfs_state_synced_failed:
653 device_remove_groups(dev, drv->dev_groups);
654 dev_groups_failed:
655 if (dev->bus->remove)
656 dev->bus->remove(dev);
657 else if (drv->remove)
658 drv->remove(dev);
659 probe_failed:
660 if (dev->bus)
661 blocking_notifier_call_chain(&dev->bus->p->bus_notifier,
662 BUS_NOTIFY_DRIVER_NOT_BOUND, dev);
663 pinctrl_bind_failed:
664 device_links_no_driver(dev);
665 devres_release_all(dev);
666 arch_teardown_dma_ops(dev);
667 kfree(dev->dma_range_map);
668 dev->dma_range_map = NULL;
669 driver_sysfs_remove(dev);
670 dev->driver = NULL;
671 dev_set_drvdata(dev, NULL);
672 if (dev->pm_domain && dev->pm_domain->dismiss)
673 dev->pm_domain->dismiss(dev);
674 pm_runtime_reinit(dev);
675 dev_pm_set_driver_flags(dev, 0);
676 done:
677 return ret;
678 }
2.1.15 call_driver_probe
对于挂载在PCI/PCIe总线上的设备来说,在调用call_driver_probe 的时候就会通过ret = drv->probe(dev)调用到对应的设备驱动的probe函数。
代码路径:drivers/base/dd.c
510 static int call_driver_probe(struct device *dev, struct device_driver *drv)
511 {
512 int ret = 0;
513
514 if (dev->bus->probe)
515 ret = dev->bus->probe(dev);
516 else if (drv->probe)
517 ret = drv->probe(dev);
518
519 switch (ret) {
520 case 0:
521 break;
522 case -EPROBE_DEFER:
523 /* Driver requested deferred probing */
524 dev_dbg(dev, "Driver %s requests probe deferral\n", drv->name);
525 break;
526 case -ENODEV:
527 case -ENXIO:
528 pr_debug("%s: probe of %s rejects match %d\n",
529 drv->name, dev_name(dev), ret);
530 break;
531 default:
532 /* driver matched but the probe failed */
533 pr_warn("%s: probe of %s failed with error %d\n",
534 drv->name, dev_name(dev), ret);
535 break;
536 }
537
538 return ret;
539 }
2.1.16 pci_bus_type
代码路径:drivers/pci/pci-driver.c
1600 struct bus_type pci_bus_type = {
1601 .name = "pci",
1602 .match = pci_bus_match,
1603 .uevent = pci_uevent,
1604 .probe = pci_device_probe,
1605 .remove = pci_device_remove,
1606 .shutdown = pci_device_shutdown,
1607 .dev_groups = pci_dev_groups,
1608 .bus_groups = pci_bus_groups,
1609 .drv_groups = pci_drv_groups,
1610 .pm = PCI_PM_OPS_PTR,
1611 .num_vf = pci_bus_num_vf,
1612 .dma_configure = pci_dma_configure,
1613 };
1614 EXPORT_SYMBOL(pci_bus_type);
2.1.17 pci_device_probe
pci_device_probe对应着drv->probe(dev),通过pci_device_probe函数会调用到对应的设备驱动的probe函数。
代码路径:drivers/pci/pci-driver.c
418 static int pci_device_probe(struct device *dev)
419 {
420 int error;
421 struct pci_dev *pci_dev = to_pci_dev(dev);
422 struct pci_driver *drv = to_pci_driver(dev->driver);
423
424 if (!pci_device_can_probe(pci_dev))
425 return -ENODEV;
426
427 pci_assign_irq(pci_dev);
428
429 error = pcibios_alloc_irq(pci_dev);
430 if (error < 0)
431 return error;
432
433 pci_dev_get(pci_dev);
434 error = __pci_device_probe(drv, pci_dev);
435 if (error) {
436 pcibios_free_irq(pci_dev);
437 pci_dev_put(pci_dev);
438 }
439
440 return error;
441 }
2.1.18 __pci_device_probe
代码路径:drivers/pci/pci-driver.c
373 /**
374 * __pci_device_probe - check if a driver wants to claim a specific PCI device
375 * @drv: driver to call to check if it wants the PCI device
376 * @pci_dev: PCI device being probed
377 *
378 * returns 0 on success, else error.
379 * side-effect: pci_dev->driver is set to drv when drv claims pci_dev.
380 */
381 static int __pci_device_probe(struct pci_driver *drv, struct pci_dev *pci_dev)
382 {
383 const struct pci_device_id *id;
384 int error = 0;
385
386 if (!pci_dev->driver && drv->probe) {
387 error = -ENODEV;
388
389 id = pci_match_device(drv, pci_dev); -->同2.1.11的代码流程分析
390 if (id)
391 error = pci_call_probe(drv, pci_dev, id);
392 }
393 return error;
394 }
2.1.19 pci_call_probe
代码路径:drivers/pci/pci-driver.c
335 static int pci_call_probe(struct pci_driver *drv, struct pci_dev *dev,
336 const struct pci_device_id *id)
337 {
338 int error, node, cpu;
339 int hk_flags = HK_FLAG_DOMAIN | HK_FLAG_WQ;
340 struct drv_dev_and_id ddi = { drv, dev, id };
341
342 /*
343 * Execute driver initialization on node where the device is
344 * attached. This way the driver likely allocates its local memory
345 * on the right node.
346 */
347 node = dev_to_node(&dev->dev);
348 dev->is_probed = 1;
349
350 cpu_hotplug_disable();
351
352 /*
353 * Prevent nesting work_on_cpu() for the case where a Virtual Function
354 * device is probed from work_on_cpu() of the Physical device.
355 */
356 if (node < 0 || node >= MAX_NUMNODES || !node_online(node) ||
357 pci_physfn_is_probed(dev))
358 cpu = nr_cpu_ids;
359 else
360 cpu = cpumask_any_and(cpumask_of_node(node),
361 housekeeping_cpumask(hk_flags));
362
363 if (cpu < nr_cpu_ids)
364 error = work_on_cpu(cpu, local_pci_probe, &ddi);
365 else
366 error = local_pci_probe(&ddi);
367
368 dev->is_probed = 0;
369 cpu_hotplug_enable();
370 return error;
371 }
2.1.20 local_pci_probe
代码路径:drivers/pci/pci-driver.c
290 static long local_pci_probe(void *_ddi)
291 {
292 struct drv_dev_and_id *ddi = _ddi;
293 struct pci_dev *pci_dev = ddi->dev;
294 struct pci_driver *pci_drv = ddi->drv;
295 struct device *dev = &pci_dev->dev;
296 int rc;
297
298 /*
299 * Unbound PCI devices are always put in D0, regardless of
300 * runtime PM status. During probe, the device is set to
301 * active and the usage count is incremented. If the driver
302 * supports runtime PM, it should call pm_runtime_put_noidle(),
303 * or any other runtime PM helper function decrementing the usage
304 * count, in its probe routine and pm_runtime_get_noresume() in
305 * its remove routine.
306 */
307 pm_runtime_get_sync(dev);
308 pci_dev->driver = pci_drv;
309 rc = pci_drv->probe(pci_dev, ddi->id);
310 if (!rc)
311 return rc;
312 if (rc < 0) {
313 pci_dev->driver = NULL;
314 pm_runtime_put_sync(dev);
315 return rc;
316 }
317 /*
318 * Probe function should return < 0 for failure, 0 for success
319 * Treat values > 0 as success, but warn.
320 */
321 pci_warn(pci_dev, "Driver probe function unexpectedly returned %d\n",
322 rc);
323 return 0;
324 }
2.1.21 nvme_probe
2882 static int nvme_probe(struct pci_dev *pdev, const struct pci_device_id *id)
2883 {
...
2972 }