一、常用shell命令
1、管道命令
(1)命令格式
(2)案例演示
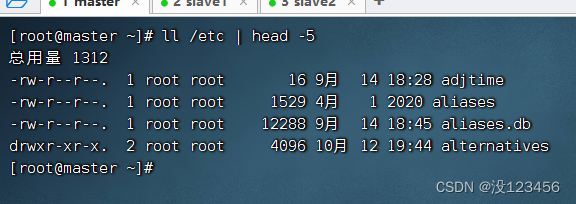
任务1、查看/etc目录信息前5行信息
执行命令:ll /etc | head -5
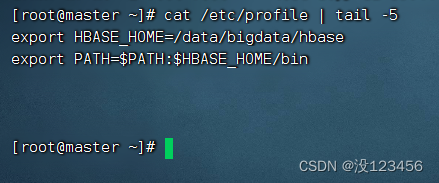
任务2、查看/etc/profile文件后5行信息
执行命令:cat /etc/profile | tail -5
2、grep命令
(1)命令格式
grep [选项参数] 文件
(2)案例演示
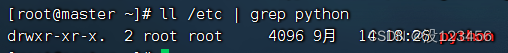
任务1、抓取/etc目录下的python信息
执行命令:ll /etc | grep python
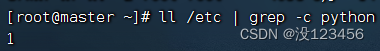
执行命令:ll /etc | grep -c python
任务2、抓取/etc/profile文件里的dev信息
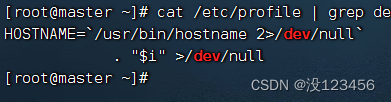
执行命令:cat /etc/profile | grep dev
任务3、抓取用户数据文件中以how打头的信息
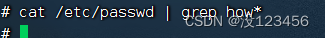
执行命令:cat /etc/passwd | grep how*
任务4、显示所有以d开头的文件中包含hi的行
执行命令:grep hi d*
任务5、显示两个文件匹配某个字符串的行
执行命令:grep ‘hadoop’ demo.txt demo1.txt
任务6、显示文件中至少有n个连续小写字符的行
执行命令:grep ‘[a-z]{7}’ demo.txt
执行命令:grep ‘[a-z]{6}’ demo.txt
3、find命令
(1)命令格式
find 路径 [选项参数]
(2)案例演示
任务1、按类型查找
执行命令:find /etc/sysconfig -type ‘d’
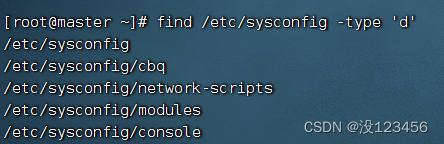
检查是否查找成功
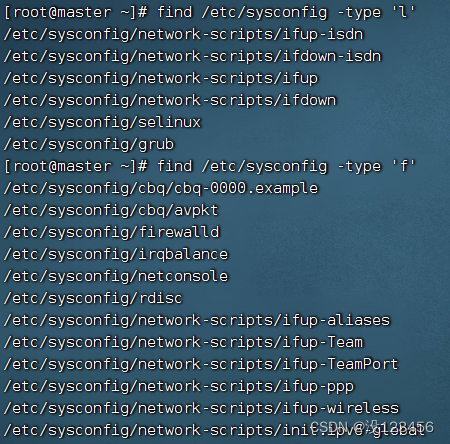
执行命令:find /etc/sysconfig -type ‘l’
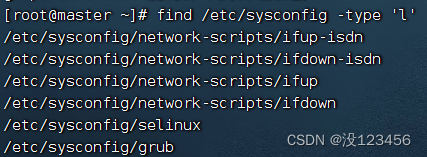
执行命令:find /etc/sysconfig -type ‘f’
任务2、按名称查找
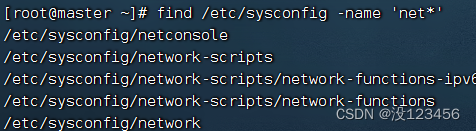
执行命令:find /etc/sysconfig -name ‘network’
执行命令:find /etc/sysconfig -name ‘net*’ (可使用通配符)
任务3、按大小查找
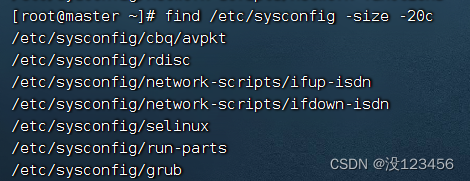
执行命令:find /etc/sysconfig -size 15c(等于15字节)
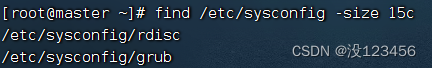
执行命令:find /etc/sysconfig -size +10k(大于10240个字节)
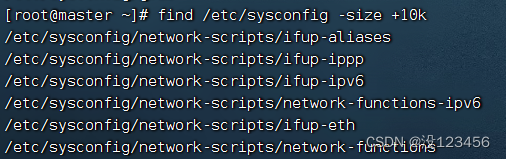
执行命令:find /etc/sysconfig -size -20c (小于20个字节)
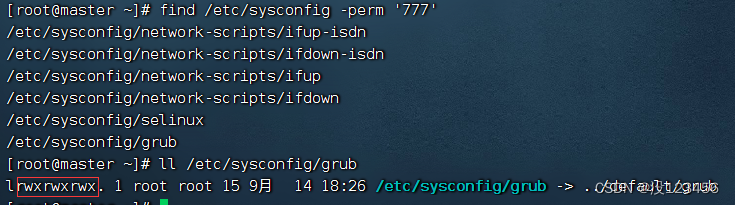
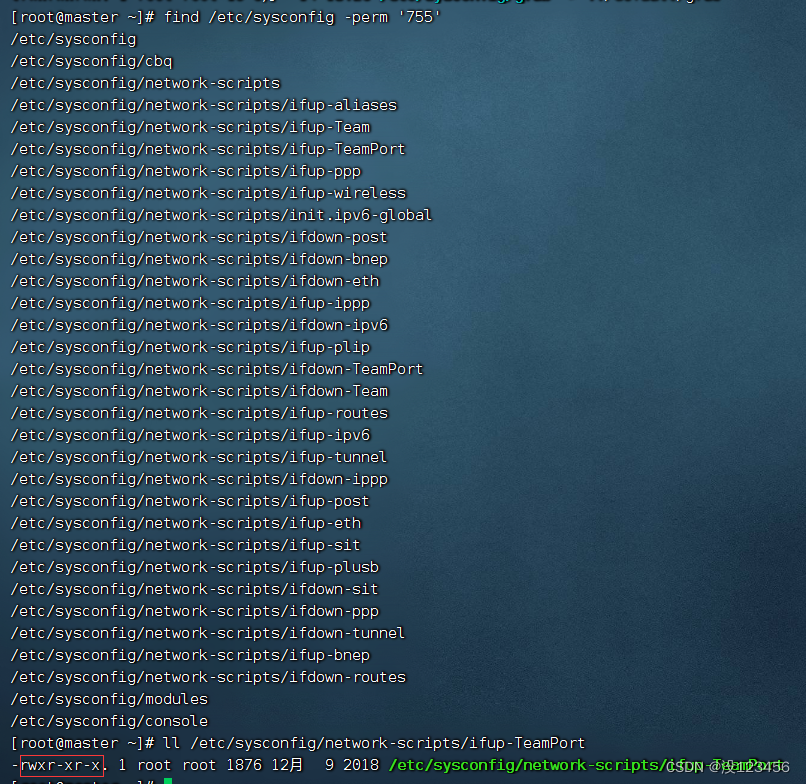
任务4、按权限查找
执行命令:find /etc/sysconfig -perm ‘777’ (权限字符串:rwxrwxrwx)
执行命令:find /etc/sysconfig -perm ‘755’ (权限字符串:rwxr-xr-x)
4、sed命令
(1)命令格式
sed “[action]” [filename]
(2)案例演示
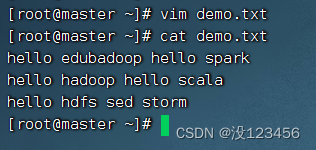
预备工作:创建demo.txt
1)替换操作(s - substitute)
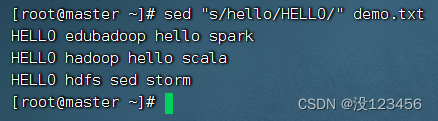
任务1、将所有行的第一个hello替换成HELLO
执行命令:sed “s/hello/HELLO/” demo.txt
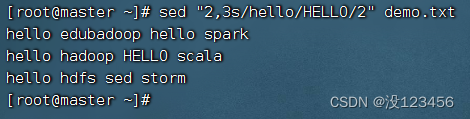
任务2、将第2行到第3行的第2个hello替换成HELLO
执行命令:sed “2,3s/hello/HELLO/2” demo.txt
任务3、将第2行的hello全部替换成HELLO
执行命令:sed “2s/hello/HELLO/g” demo.txt
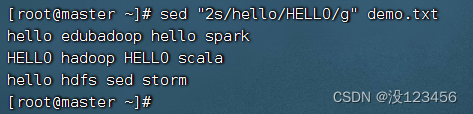
任务4、将全部的hello替换成HELLO后生成新文件
执行命令:sed “s/hello/HELLO/g” demo.txt > demo1.txt
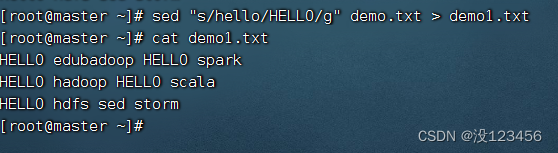
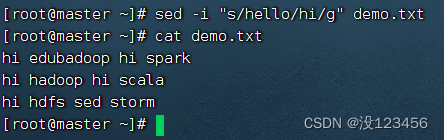
任务5、将全部的hello替换成hi,要求修改原文件
执行命令: sed -i “s/hello/hi/g” demo.txt
2)插入操作(i - insert, a - append)
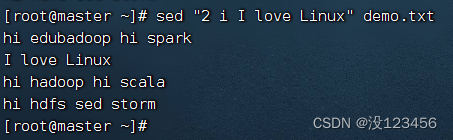
任务1、在第2行之前插入一行新内容
执行命令:sed “2 i I love Linux” demo.txt
任务2、在第2行之后插入一行新内容
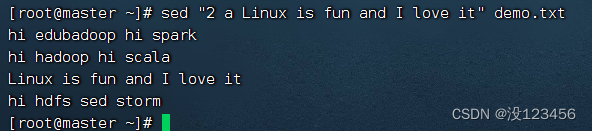
执行命令:sed “2 a Linux is fun and I love it” demo.txt
3)删除操作(d - delete)
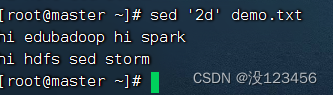
任务1、删除第2行
执行命令:sed ‘2d’ demo.txt
任务2、删除第2行到第3行
执行命令: sed ‘2,3d’ demo.txt

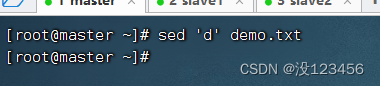
任务3、删除文件所有行
执行命令:sed ‘d’ demo.txt
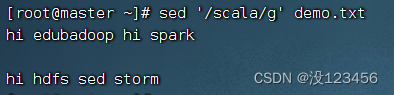
任务4、删除包含指定字符串的行
执行命令:sed ‘/scala/g’ demo.txt
5、tail命令
(1)命令格式
tail [选项参数] 文件名
(2)案例演示
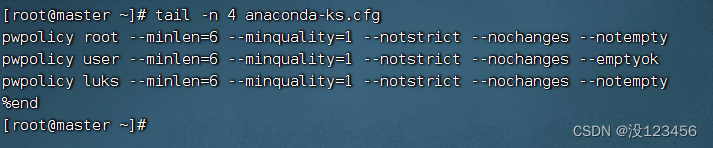
任务1、显示文件最后4行内容
执行命令:tail -n 4 anaconda-ks.cfg
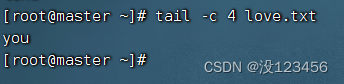
任务2、显示文件最后4个字符内容
执行命令:tail -c 4 love.txt
6、sort命令
(1)命令格式
sort [选项参数] 文件
(2)案例演示
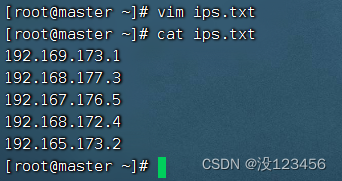
预备工作:创建ips.txt文件
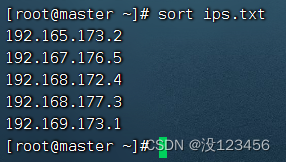
任务1、对文件按行排序
执行命令:sort ips.txt,按字典排序法升序排列
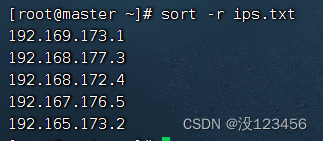
执行命令:sort -r ips.txt,按字典排序法降序排列
任务2、对文件按第4节排序
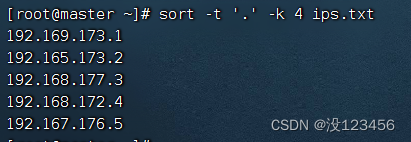
执行命令:sort -t ‘.’ -k 4 ips.txt,升序排列
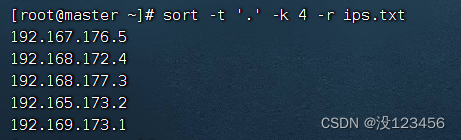
执行命令:sort -t ‘.’ -k 4 -r ips.txt,降序排列
7、cut命令
(1)命令格式
cut [选项参数] 文件名
(2)案例演示
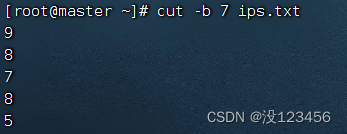
任务1、提取ips.txt文件第7列字符
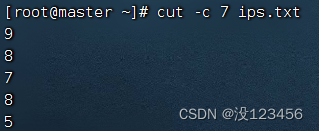
执行命令:cut -c 7 ips.txt
执行命令:cut -b 7 ips.txt
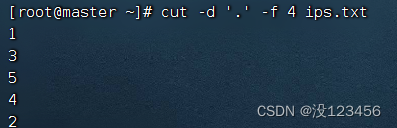
任务2、提取ips.txt文件第4节内容
执行命令:cut -d ‘.’ -f 4 ips.txt,提取第4节内容
执行命令:cut -d ‘.’ -f 2 ips.txt,提取第2节内容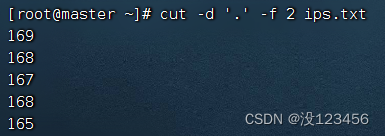
8、history命令
(1)命令格式
history [选项参数]
(2)案例演示
任务1、查看历史操作记录
执行命令:history
任务2、查看最近10条历史命令
执行命令:history 10 (写成history -n 10也是一样效果)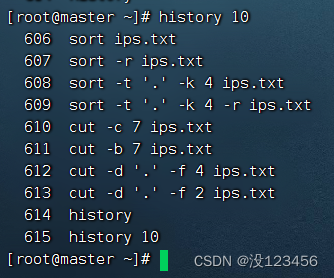
任务3、查看最开始10条历史命令
执行命令:history | head -10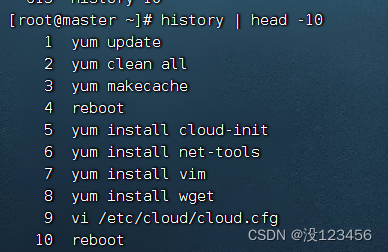
任务4、曾多少次使用vim编辑文本文件?
执行命令:history | grep vim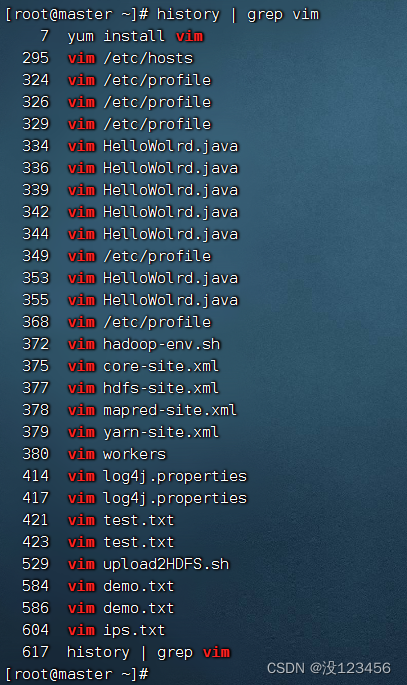
任务5、执行历史第5条命令
查看历史第5条命令
执行命令:!5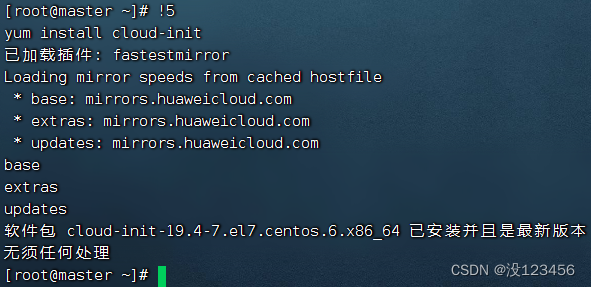
任务6、执行上一条命令
执行命令:!!
任务7、执行最后一次以his开头的命令
执行命令:!his
任务8、将当前历史命令缓冲区命令写入历史命令文件中
执行命令:history -w myhis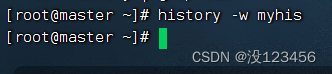
执行命令:cat myhis | tail -5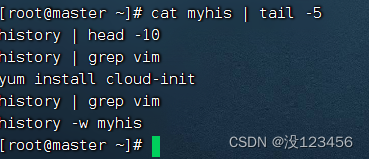
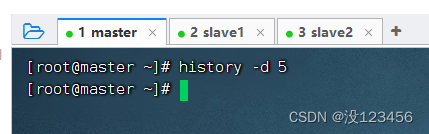
任务9、 清除第5条历史命令
查看第5条历史明令
执行命令:history -d 5
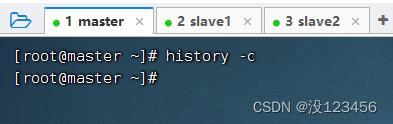
任务10、清除所有历史命令
执行命令:history -c
任务11、将历史命令文件中的命令读入当前历史命令缓冲区
执行命令:history -r myhis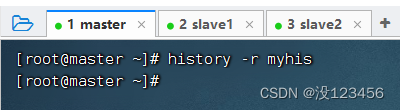
执行命令:history | head -10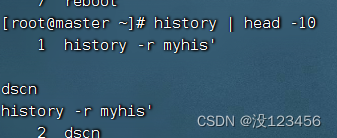
二、shell脚本
1、执行shell脚本
创建脚本文件,执行命令:vim /home/shell.sh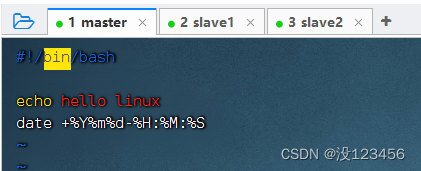
此时,shell.sh对于所有者而言,只有读和写的权限,并不是可执行的脚本

(1)直接执行脚本
shell.sh文件必须具备可读与可执行(rx) 的权限
增加shell.sh的写权限,执行命令:chmod u+x /home/shell.sh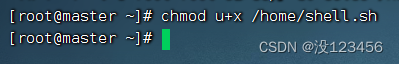

绝对路径方式执行脚本
执行命令:/home/shell.sh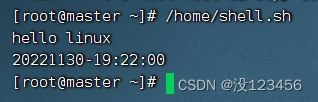
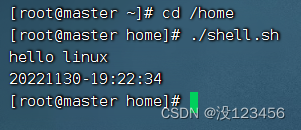
相对路径方式执行脚本
执行命令:cd /home
执行命令:./shell.sh (.表示当前目录)
(2)利用source命令执行脚本
执行命令:source shell.sh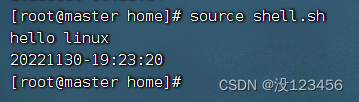
(3)利用bash或sh命令执行脚本
执行命令:bash shell.sh
执行命令: sh shell.sh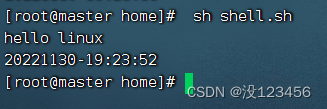
2、shell脚本实战
任务1、显示当前用户主目录
1)编写脚本
执行命令:vim shell01.sh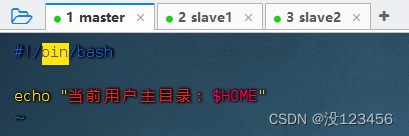
2)设置权限
执行命令:chmod u+x shell01.sh,增加可执行权限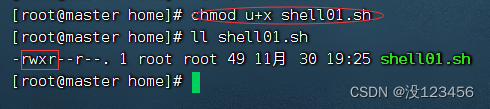
3)执行脚本
执行命令:./shell01.sh
任务2、编程实现两个数相乘
1)编写脚本
执行命令:vim shell02.sh
2)设置权限
执行命令:chmod u+x shell02.sh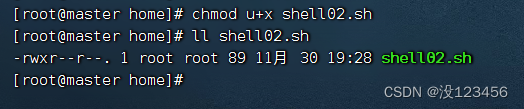
3)执行脚本
执行命令:./shell02.sh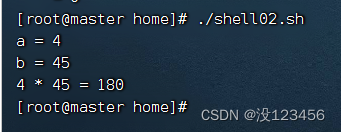


![[附源码]Python计算机毕业设计SSM流浪动物管理系统(程序+LW)](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/68e663b1e61c4014a0742ddb2c392f53.png)

![[附源码]Python计算机毕业设计SSM浪漫烘焙屋(程序+LW)](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/eed66e8b4d9242ed9fcc69d3bed281d4.png)
![[附源码]Python计算机毕业设计Django的桌游信息管理系统](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/df73f78571b64ffb93e5bae450d041ba.png)