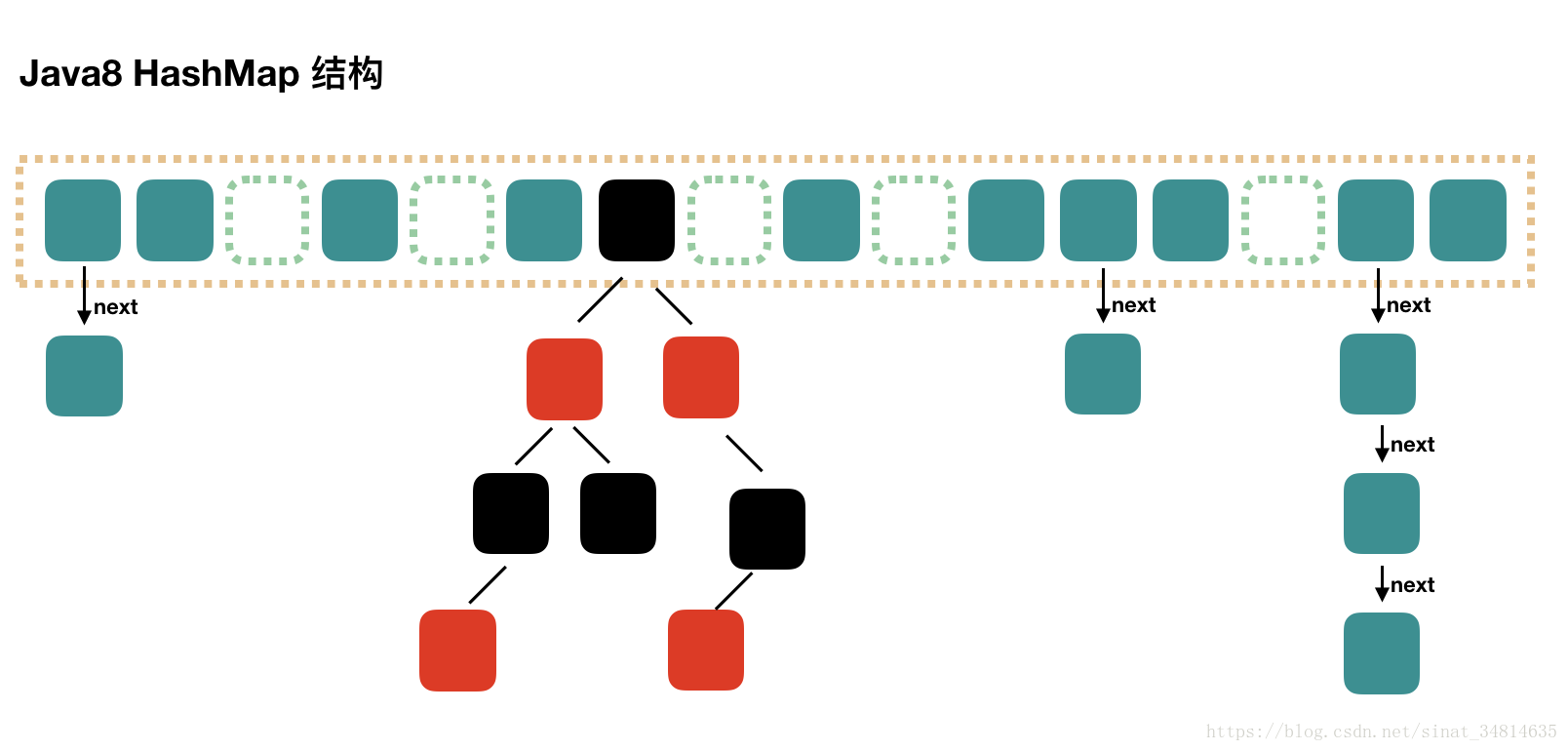
前言
mybatis可以自己带有二级缓存的实现,这里加上redis是想把东西缓存到redis中,而不是mybaits自带的map中。这也就构成了我们看到的springboot + mybatisplus +redis实现二级缓存的题目。
具体步骤如下:
首先加入需要的依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-cache</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
</dependency>
第二步:在application.properties或者yml中配置redis属性和设置开启二级缓存(默认是关闭的)
spring.cache.type=redis
spring.redis.host=192.168.9.82
spring.redis.jedis.pool.max-active=10
spring.redis.jedis.pool.max-idle=10
spring.redis.jedis.pool.max-wait=3000
spring.redis.jedis.pool.min-idle=20
spring.redis.port=6379
spring.redis.timeout=3000
mybatis-plus.configuration.cache-enabled=true #开启二级缓存第三步:编写redis缓存的配置类,大体需要如下三个类,先截图在上代码

ApplicationContextHolder.java类主要用于在另外另个类中可以通过context获取spring容器中注入的redisTemplate来操作redis。代码如下:
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
//@Component
public class ApplicationContextHolder {
private static ApplicationContext applicationContext = null;
public static void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) {
ApplicationContextHolder.applicationContext = applicationContext;
}
public static ApplicationContext getApplicationContext() {
return applicationContext;
}
public static <T> T getBean(String name) {
return (T)applicationContext.getBean(name);
}
public static <T> T getBean(Class clz) {
return (T)applicationContext.getBean(clz);
}
}
MybatisRedisCache.java类实现了Mybatis的Cache接口,这样才能在执行数据库操作前调用缓存。代码如下:
import org.apache.ibatis.cache.Cache;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisCallback;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.ValueOperations;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReadWriteLock;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantReadWriteLock;
public class MybatisRedisCache implements Cache {
private final ReadWriteLock readWriteLock = new ReentrantReadWriteLock();
private final String id; // cache instance id
private RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
private static final long EXPIRE_TIME_IN_MINUTES = 30; // redis过期时间
public MybatisRedisCache(String id) {
if (id == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Cache instances require an ID");
}
this.id = id;
}
@Override
public String getId() {
return id;
}
/**
* Put query result to redis
*
* @param key
* @param value
*/
@Override
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public void putObject(Object key, Object value) {
try {
RedisTemplate redisTemplate = getRedisTemplate();
ValueOperations opsForValue = redisTemplate.opsForValue();
opsForValue.set(key, value, EXPIRE_TIME_IN_MINUTES, TimeUnit.MINUTES);
}
catch (Throwable t) {
t.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* Get cached query result from redis
*
* @param key
* @return
*/
@Override
public Object getObject(Object key) {
try {
RedisTemplate redisTemplate = getRedisTemplate();
ValueOperations opsForValue = redisTemplate.opsForValue();
return opsForValue.get(key);
}
catch (Throwable t) {
return null;
}
}
/**
* Remove cached query result from redis
*
* @param key
* @return
*/
@Override
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public Object removeObject(Object key) {
try {
RedisTemplate redisTemplate = getRedisTemplate();
redisTemplate.delete(key);
}
catch (Throwable t) {
t.getMessage();
}
return null;
}
/**
* Clears this cache instance
*/
@Override
public void clear() {
RedisTemplate redisTemplate = getRedisTemplate();
redisTemplate.execute((RedisCallback) connection -> {
connection.flushDb();
return null;
});
}
/**
* This method is not used
*
* @return
*/
@Override
public int getSize() {
return 0;
}
@Override
public ReadWriteLock getReadWriteLock() {
return readWriteLock;
}
private RedisTemplate getRedisTemplate() {
if (redisTemplate == null) {
// 这里用到了ApplicationContextHolder.java
redisTemplate = ApplicationContextHolder.getBean("redisTemplate");
}
return redisTemplate;
}
}RedisCacheConfig.java类主要用来配置redis的一些属性,里面这里主要配置了reids序列化。代码如下:
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.cache.CacheManager;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CachingConfigurerSupport;
import org.springframework.cache.interceptor.CacheErrorHandler;
import org.springframework.cache.interceptor.CacheResolver;
import org.springframework.cache.interceptor.SimpleCacheErrorHandler;
import org.springframework.cache.interceptor.SimpleCacheResolver;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheConfiguration;
import org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheManager;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisConnectionFactory;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisStandaloneConfiguration;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.lettuce.LettuceConnectionFactory;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.RedisSerializationContext;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.StringRedisSerializer;
import java.time.Duration;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* ignit改redis缓存
* @author lhb
* @since 2022/11/24
*/
@Configuration
public class RedisCacheConfig extends CachingConfigurerSupport {
@Value("${spring.redis.host}")
private String redisHost;
@Value("${spring.redis.port}")
private int redisPort;
@Bean
public RedisTemplate<Object, Object> redisTemplate() {
RedisTemplate<Object, Object> redisTemplate = new RedisTemplate<>();
redisTemplate.setConnectionFactory(redisConnectionFactory());
GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer genericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer = new GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer();
redisTemplate.setKeySerializer(genericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer);
redisTemplate.setValueSerializer(genericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer);
redisTemplate.setHashKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
redisTemplate.setHashValueSerializer(genericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer);
return redisTemplate;
}
@Override
public CacheResolver cacheResolver() {
return new SimpleCacheResolver(cacheManager());
}
@Override
public CacheErrorHandler errorHandler() {
return new SimpleCacheErrorHandler();
}
@Override
public CacheManager cacheManager() {
Map<String, RedisCacheConfiguration> cacheConfigurationMap = generateCacheConfigMap();
RedisCacheConfiguration redisCacheConfiguration = RedisCacheConfiguration.defaultCacheConfig()
.disableCachingNullValues()
.serializeValuesWith(RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair.fromSerializer(new GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer()));
return RedisCacheManager.builder(redisConnectionFactory())
.cacheDefaults(redisCacheConfiguration)
.withInitialCacheConfigurations(cacheConfigurationMap)
.build();
}
public Map<String, RedisCacheConfiguration> generateCacheConfigMap() {
Map<String, RedisCacheConfiguration> initialCacheConfiguration = new HashMap<>();
initialCacheConfiguration.put("hourCache", RedisCacheConfiguration.defaultCacheConfig().entryTtl(Duration.ofHours(1)));//1小时
initialCacheConfiguration.put("minCache", RedisCacheConfiguration.defaultCacheConfig().entryTtl(Duration.ofMinutes(1)));
initialCacheConfiguration.put("dayCache", RedisCacheConfiguration.defaultCacheConfig().entryTtl(Duration.ofDays(1)));
return initialCacheConfiguration;
}
public RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory() {
RedisStandaloneConfiguration configuration = new RedisStandaloneConfiguration();
configuration.setHostName(redisHost);
configuration.setPort(redisPort);
configuration.setDatabase(0);
LettuceConnectionFactory factory = new LettuceConnectionFactory(configuration);
factory.afterPropertiesSet();
return factory;
}
}第四步:在mapper.xml中添加cache标签,来告诉mybtisplus这个mapper中的内容使用二级缓存,这个cache标签放在mapper表中的什么位置都行
<mapper namespace="hisense.HiDevMng.code.hidevConfigManager.web.dao.DevBusRouterelViewDao">
<!-- 开启基于redis的二级缓存 -->
<cache type="hisense.HiDevMng.code.base.config.cache.MybatisRedisCache"/>
<select id="getOrgList" resultType="his.api.dto.OrgDto">
SELECT * from table1
WHERE br.BUSID IN
<foreach collection="ids" index="index" item="item" open="(" separator="," close=")">
#{item}
</foreach>
</select>
</mapper>第五步:在启动类中实现ApplicationContextAware接口,目的是拿到spring容器的context,然后给ApplicationContextHolder,这样我们的redis缓存的配置类中就可以通过applicationContext来得到容器中中的redisTemplate进行redis操作了。添加如下代码:
public class StartApplication extends SpringBootServletInitializer implements ApplicationContextAware {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(StartApplication.class, args);
}
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
//重点在此,通过这个赋值context
ApplicationContextHolder.setApplicationContext(applicationContext);
}
}网上很多帖子给出的方式是自己单独写一个类来实现ApplicationContextAware接口,但是因为我的项目中用到了@PostConstruct注解,那样会导致ApplicationContrext为空,所以我选择了通过上面在启动类给ApplicationContextHolder赋值的方式。
第六步,测试,创建测试类例如
RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest(classes = StartApplication.class, webEnvironment = SpringBootTest.WebEnvironment.DEFINED_PORT)
public class test {
@Autowired
private MyDao dao;
@Test
public void testOne() {
Set<String> ids = new HashSet<>();
ids.add("25191027172915794000");
List<BusOrgDto> busOrgList = dao.getBusOrgList(ids);
System.out.println(busOrgList.size());
System.out.println("====================================================");
List<BusOrgDto> busOrgList1 = dao.getBusOrgList(ids);
System.out.println(busOrgList1.size());
}
}
运行2次查询,但是只出现一次如下图的log,就说明第二次执行使用redis缓存中的数据了
![]()
出现一次Preparing:就说明执行的是数据库查询,没走redis缓存。当我们多次执行都不在显示这个Preparing:了就说明缓存成功了。
总结:
这里就不把代码放git上了,直接从上面把代码都拷贝下来,就可以执行了。关于什么是二级缓存网上可以自行百度。
代码中还存在完善的空间,比如多久后自动从缓存删除等,大家可以自行了解下。这里只是为了给初学者使用,写多了怕容易乱。谢谢支持

![[附源码]SSM计算机毕业设计医院仪器设备管理系统JAVA](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/8a914466953c40bda7057f121eb92829.png)
![[MySQL]-压力测试_TPCC-MySQL](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/92f821b3268a48a79694ea74fcdc1433.png#pic_center)