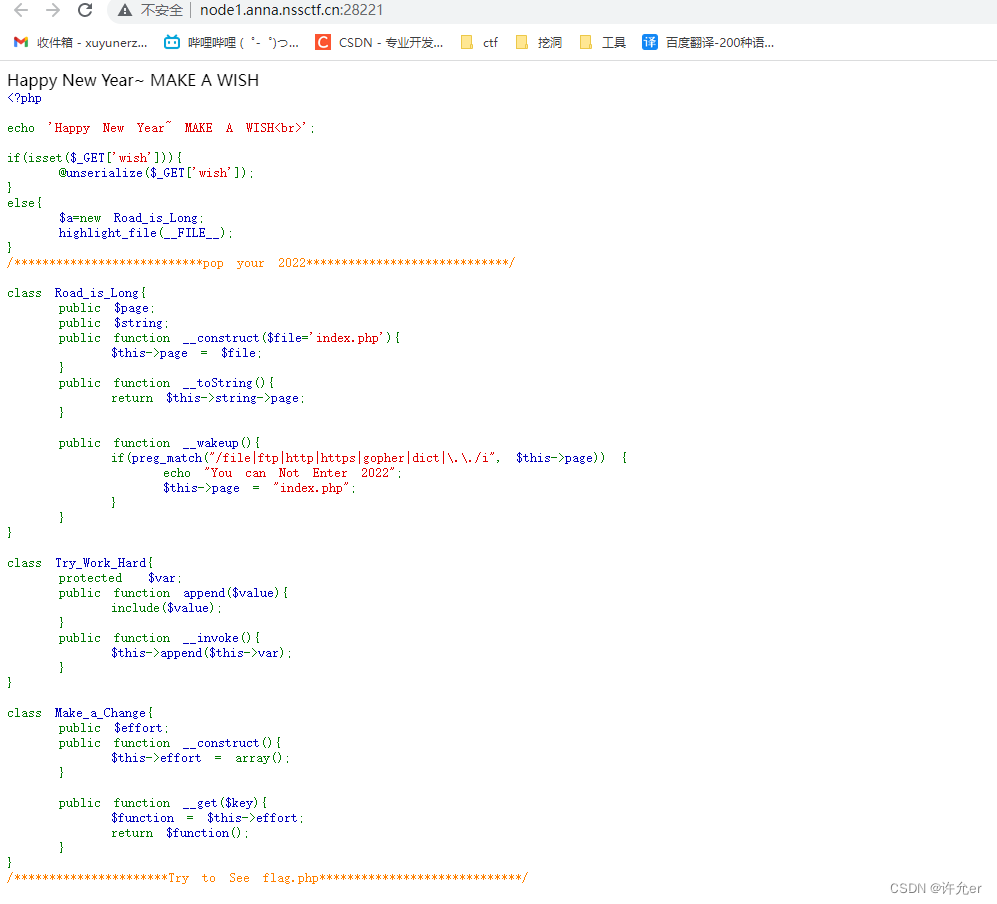
路径视图(PathView)非常强大,但也非常复杂,这个视图由QtQuick提供。它创建了一个可以让子项沿着任意路径移动的视图。沿着相同的路径,使用缩放(scale),透明(opacity)等元素可以更加详细的控制过程。
当使用路径视图(PathView)时,你必须定义一个代理和一个路径。在这些之上,路径视图(PathView)本身也可以自定义一些属性的区间。通常会使用pathItemCount属性,它控制了一次可见的子项总数。preferredHighLightBegin属性控制了高亮区间,preferredHighlightEnd与highlightRangeMode,控制了当前项怎样沿着路径显示。
在关注高亮区间之前,我们必须先看看路径(path)这个属性。路径(path)属性使用一个路径(path)元素来定义路径视图(PathView)内代理的滚动路径。路径使用startx与starty属性来链接路径(path)元素,例如PathLine,PathQuad和PathCubic。这些元素都使用二维数组来构造路径。
当路径定义好之后,可以使用PathPercent和PathAttribute元素来进一步设置。它们被放置在路径元素之间,并且为经过它们的路径和代理提供更加细致的控制。PathPercent提供了如何控制每个元素之间覆盖区域部分的路径,然后反过来控制分布在这条路径上的代理元素,它们被按比例的分布播放。
preferredHightlightBegin与preferredHighlightEnd属性由PathView(路径视图)输入到图片元素中。它们的值在0~1之间。结束值大于等于开始值。例如设置这些属性值为0.5,当前项只会显示当前百分之50的图像在这个路径上。
在Path中,PathAttribute元素也是被放置在元素之间的,就像PathPercent元素。它们可以让你指定属性的值然后插入的路径中去。这些属性与代理绑定可以用来控制任意的属性。

下面这个例子展示了路径视图(PathView)如何创建一个卡片视图,并且用户可以滑动它。我们使用了一些技巧来完成这个例子。路径由PathLine元素组成。使用PathPercent元素,它确保了中间的元素居中,并且给其它的元素提供了足够的空间。使用PathAttribute元素来控制旋转,大小和深度值(z-value)。
在这个路径之上(path),需要设置路径视图(PathView)的pathItemCount属性。它控制了路径的浓密度。路径视图的路径(PathView.onPath)使用preferredHighlightBegin与preferredHighlightEnd来控制可见的代理项。
1.PathView {
2. anchors.fill: parent
3.
4. delegate: flipCardDelegate
5. model: 100
6.
7. path: Path {
8. startX: root.width/2
9. startY: 0
10.
11. PathAttribute { name: "itemZ"; value: 0 }
12. PathAttribute { name: "itemAngle"; value: -90.0; }
13. PathAttribute { name: "itemScale"; value: 0.5; }
14. PathLine { x: root.width/2; y: root.height*0.4; }
15. PathPercent { value: 0.48; }
16. PathLine { x: root.width/2; y: root.height*0.5; }
17. PathAttribute { name: "itemAngle"; value: 0.0; }
18. PathAttribute { name: "itemScale"; value: 1.0; }
19. PathAttribute { name: "itemZ"; value: 100 }
20. PathLine { x: root.width/2; y: root.height*0.6; }
21. PathPercent { value: 0.52; }
22. PathLine { x: root.width/2; y: root.height; }
23. PathAttribute { name: "itemAngle"; value: 90.0; }
24. PathAttribute { name: "itemScale"; value: 0.5; }
25. PathAttribute { name: "itemZ"; value: 0 }
26. }
27.
28. pathItemCount: 16
29.
30. preferredHighlightBegin: 0.5
31. preferredHighlightEnd: 0.5
32. }
代理如下面所示,使用了一些从PathAttribute中链接的属性,itemZ,itemAngle和itemScale。需要注意代理链接的属性只在wrapper中可用。因此,rotxs属性在Rotation元素中定义为可访问值。
另一个需要注意的是路径视图(PathView)链接的PathView.onPath属性的用法。通常对于这个属性都绑定为可见,这样允许路径视图(PathView)缓冲不可见的元素。这不是通过剪裁处理来实现的,因为路径视图(PathView)的代理比其它的视图,例如链表视图(ListView)或者栅格视图(GridView)放置更加随意。
1. Component {
2. id: flipCardDelegate
3.
4. Item {
5. id: wrapper
6.
7. width: 64
8. height: 64
9.
10. visible: PathView.onPath
11.
12. scale: PathView.itemScale
13. z: PathView.itemZ
14.
15. property variant rotX: PathView.itemAngle
16. transform: Rotation { axis { x: 1; y: 0; z: 0 } angle: wrapper.rotX; origin { x: 32; y: 32; } }
17.
18. Rectangle {
19. anchors.fill: parent
20. color: "lightGray"
21. border.color: "black"
22. border.width: 3
23. }
24.
25. Text {
26. anchors.centerIn: parent
27. text: index
28. font.pixelSize: 30
29. }
30. }
31. }当在路径视图(PathView)上使用图像转换或者其它更加复杂的元素时,有一个性能优化的技巧是绑定图像元素(Image)的smooth属性与PathView.view.moving属性。这意味着图像在移动时可能不够完美,但是能够比较平滑的转换。当视图在移动时,对于平滑缩放的处理是没有意义的,因为用户根本看不见这个过程。