这里我们运用vcpkg去下载安装gRPC,进入vcpkg目录后,执行命令:.\vcpkg.exe install grpc:x64-windows
grpc在vcpkg里面安装完成后,我们就来使用grpc做一个简单的例子。
gRPC顾名思义,就是google的RPC方案,基于protobuf数据传输,其中proto文件的定义约定了服务器端和客户端的服务接口协议。
这里我们就用加法和乘法作为服务器端提供的服务,让客户端去调用(RPC),我们建立三个文件夹CPP_Server, CPP_Client, proto 来分别存储服务器端代码,客户端代码,以及proto文件。项目配置选用cmakelist.txt和cmake来管理。
1. 服务器端和客户端的proto定义(calculation.proto文件):
syntax = "proto3";
package data_handler;service CalculationInterface{
// Add operation
rpc Add(AddRequest) returns (AddReply){}
// Multiply operation
rpc Multiply(MultiplyRequest) returns (MultiplyReply){}
}message AddReply{
int32 result = 1;
}message AddRequest{
int32 param1 = 1;
int32 param2 = 2;
}message MultiplyReply{
int32 result = 1;
}message MultiplyRequest{
int32 param1 = 1;
int32 param2 = 2;
}
2. 服务器端代码
在服务器端,我们要在cmakelist里面进行proto文件的解析执行成相应的.pb.cc,.pb.h,.grpc.pb.cc,.grpc.pb.h文件,同时对项目文件的配置。
那么我们必然要先找到grpc, protobuf库和执行文件。这时候就需要用到vcpkg这套包管理器,
而下面这句话就是让vcpkg的包管理起作用的关键:
set(CMAKE_TOOLCHAIN_FILE "$ENV{VCPKG_ROOT}/scripts/buildsystems/vcpkg.cmake" CACHE STRING "Vcpkg toolchain file")
注意这句话一定要在定义project名字之前,本例子是:project(CalculationInGrpcServer)
这样子后面的find_package, find_program, target_link_libraries等都会去vckpg里面找到。
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.20)
# Note: 8 target(s) were omitted.
message("--------" $ENV{VCPKG_ROOT})set(CMAKE_TOOLCHAIN_FILE "$ENV{VCPKG_ROOT}/scripts/buildsystems/vcpkg.cmake" CACHE STRING "Vcpkg toolchain file")
project(CalculationInGrpcServer)set(_GRPC_GRPCPP gRPC::grpc++)
set(_PROTOBUF_LIBPROTOBUF protobuf::libprotobuf)
set(_REFLECTION gRPC::grpc++_reflection)set(_PROTOBUF_LIBPROTOBUF_D libprotobufd)
find_package(gRPC CONFIG REQUIRED)
find_program(_PROTOBUF_PROTOC protoc REQUIRED)
find_program(_GRPC_CPP_PLUGIN_EXECUTABLE grpc_cpp_plugin REQUIRED)# Generated proto sources
get_filename_component(proto "../proto/calculation.proto" ABSOLUTE)
get_filename_component(proto_name "../proto/calculation.proto" NAME_WE)
get_filename_component(proto_path "${proto}" PATH)set(proto_srcs "${proto_path}/${proto_name}.pb.cc")
set(proto_hdrs "${proto_path}/${proto_name}.pb.h")
set(grpc_srcs "${proto_path}/${proto_name}.grpc.pb.cc")
set(grpc_hdrs "${proto_path}/${proto_name}.grpc.pb.h")
message("------------------------------------------------")
message(${_PROTOBUF_PROTOC})
message(${_GRPC_CPP_PLUGIN_EXECUTABLE})
message(${proto_path})message("-------------------------------------------------")
add_custom_command(
OUTPUT "${proto_srcs}" "${proto_hdrs}" "${grpc_srcs}" "${grpc_hdrs}"
COMMAND ${_PROTOBUF_PROTOC}
ARGS --grpc_out "${proto_path}"
--cpp_out "${proto_path}"
-I "${proto_path}"
--plugin=protoc-gen-grpc="${_GRPC_CPP_PLUGIN_EXECUTABLE}"
"${proto}"
DEPENDS "${proto}")# Include generated *.pb.h files
include_directories(
"${proto_path}"
)file(GLOB PUBLIC_HEADER ${CMAKE_CURRENT_BINARY_DIR}/*.h
${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/../proto/*.h)
add_executable(${PROJECT_NAME} CalculationServer.cc ${proto_srcs} ${grpc_srcs})
target_link_libraries(${PROJECT_NAME} PRIVATE gRPC::gpr gRPC::upb gRPC::grpc gRPC::grpc++)message("protobuf libs are:")
message(${_PROTOBUF_LIBPROTOBUF_D})
在我们的服务器端代码里面着重用到的是::data_handler::CalculationInterface::Service,这个是proto解释器帮我们对proto文件解析成cc文件后,里面的一个Service接口,我们代码里面最主要是去实现这个接口,来看看吧:
#include <grpcpp/grpcpp.h>
#include <grpcpp/security/server_credentials.h>
#include <grpcpp/server.h>
#include <grpcpp/server_builder.h>
#include <grpcpp/server_context.h>
#include <calculation.grpc.pb.h>
#include <calculation.pb.h>
#include <thread>
using grpc::Server;
using grpc::ServerBuilder;
using ::grpc::ServerContext;
using grpc::ServerReader;
using grpc::ServerReaderWriter;
using grpc::ServerWriter;
using grpc::Status;
class CalculationInGrpcServerImpl final
: public ::data_handler::CalculationInterface::Service {
public:
virtual ~CalculationInGrpcServerImpl(){};
// Add operation
::grpc::Status Add(::grpc::ServerContext* context,
const ::data_handler::AddRequest* request,
::data_handler::AddReply* response) override;
// Multiply operation
::grpc::Status Multiply(
::grpc::ServerContext* context,
const ::data_handler::MultiplyRequest* request,
::data_handler::MultiplyReply* response) override;
};
::grpc::Status CalculationInGrpcServerImpl::Add(
::grpc::ServerContext* context,
const ::data_handler::AddRequest* request,
::data_handler::AddReply* response) {
if (!context || !request || !response) {
return ::grpc::Status::CANCELLED;
}
int32_t a = request->param1();
int32_t b = request->param2();
int32_t result = a + b;
response->set_result(result);
std::cout << "Add operation: " << a << " + " << b << std::endl;
std::cout << "The result is: " << result << std::endl;
return ::grpc::Status::OK;
}
::grpc::Status CalculationInGrpcServerImpl::Multiply(
::grpc::ServerContext* context,
const ::data_handler::MultiplyRequest* request,
::data_handler::MultiplyReply* response) {
if (!context || !request || !response) {
return ::grpc::Status::CANCELLED;
}
int32_t a = request->param1();
int32_t b = request->param2();
int32_t result = a * b;
response->set_result(result);
std::cout << "Multiply operation: " << a << " * " << b << std::endl;
std::cout << "The result is: " << result << std::endl;
return ::grpc::Status::OK;
}
// define the gRPC server
std::unique_ptr<Server> server_ptr;
CalculationInGrpcServerImpl service;
void RunServer(const std::string& server_address) {
ServerBuilder builder;
builder.AddListeningPort(server_address, grpc::InsecureServerCredentials());
builder.RegisterService(&service);
server_ptr = builder.BuildAndStart();
std::cout << "Server(" << server_address << ") is listening on ..." << std::endl;
std::cout << "Press 'q' to exit the server" << std::endl;
server_ptr->Wait();
}
int main() {
std::string server_address("0.0.0.0:50051");
std::thread server_thread(RunServer, server_address);
bool running = true;
while (running) {
char c = getchar();
if (c == '\n' || c == EOF) continue;
if (c == 'q') {
// reset running flag and shutdown server
running = false;
server_ptr->Shutdown();
}
}
server_thread.join();
return 0;
}大家有可能看到了main函数,本人偷懒,将其一起写在一个文件里了,最好还是将main函数实现放到另外的文件。当然我们重点是将grpc的运用,大家可以借鉴一下里面server是怎样绑定IP和port口,运行起来server的。
生成一下,看看是不是和预想的一样啊?
3. 客户端代码
客户端代码主要是调用服务器端的接口,就是上面写的接口,grpc通过一个stub代理来实现,这样我们就象调用本地的函数一样去远程调用函数接口了,从而达到访问服务的目的。
客户端的cmakelist.txt和服务器端的有点类似,我贴出来,大家看看就行:
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.20)
# Note: 8 target(s) were omitted.
message("--------" $ENV{VCPKG_ROOT})set(CMAKE_TOOLCHAIN_FILE "$ENV{VCPKG_ROOT}/scripts/buildsystems/vcpkg.cmake" CACHE STRING "Vcpkg toolchain file")
project(CalculationInGrpcClient)set(_GRPC_GRPCPP gRPC::grpc++)
set(_PROTOBUF_LIBPROTOBUF protobuf::libprotobuf)
set(_REFLECTION gRPC::grpc++_reflection)set(_PROTOBUF_LIBPROTOBUF_D libprotobufd)
find_package(gRPC CONFIG REQUIRED)
find_program(_PROTOBUF_PROTOC protoc REQUIRED)
find_program(_GRPC_CPP_PLUGIN_EXECUTABLE grpc_cpp_plugin REQUIRED)# Generated proto sources
get_filename_component(proto "../proto/calculation.proto" ABSOLUTE)
get_filename_component(proto_name "../proto/calculation.proto" NAME_WE)
get_filename_component(proto_path "${proto}" PATH)set(proto_srcs "${proto_path}/${proto_name}.pb.cc")
set(proto_hdrs "${proto_path}/${proto_name}.pb.h")
set(grpc_srcs "${proto_path}/${proto_name}.grpc.pb.cc")
set(grpc_hdrs "${proto_path}/${proto_name}.grpc.pb.h")
message("------------------------------------------------")
message(${_PROTOBUF_PROTOC})
message(${_GRPC_CPP_PLUGIN_EXECUTABLE})
message(${proto_path})message("-------------------------------------------------")
add_custom_command(
OUTPUT "${proto_srcs}" "${proto_hdrs}" "${grpc_srcs}" "${grpc_hdrs}"
COMMAND ${_PROTOBUF_PROTOC}
ARGS --grpc_out "${proto_path}"
--cpp_out "${proto_path}"
-I "${proto_path}"
--plugin=protoc-gen-grpc="${_GRPC_CPP_PLUGIN_EXECUTABLE}"
"${proto}"
DEPENDS "${proto}")# Include generated *.pb.h files
include_directories(
"${proto_path}"
)file(GLOB PUBLIC_HEADER ${CMAKE_CURRENT_BINARY_DIR}/*.h
${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/../proto/*.h)add_executable(${PROJECT_NAME} CalculationClient.cc ${proto_srcs} ${grpc_srcs})
target_link_libraries(${PROJECT_NAME} PRIVATE gRPC::gpr gRPC::upb gRPC::grpc gRPC::grpc++)message("protobuf libs are:")
message(${_PROTOBUF_LIBPROTOBUF_D})
下面就是要介绍客户端的代码模块了,我这边简单封装了一个客户端类去调用服务,代码如下,
大家看看简单的request/reply调用方式。
#include <grpcpp/grpcpp.h>
#include <grpcpp/security/server_credentials.h>
#include <grpcpp/server.h>
#include <grpcpp/server_builder.h>
#include <grpcpp/server_context.h>
#include <calculation.grpc.pb.h>
#include <calculation.pb.h>
#include <thread>
using grpc::Server;
using grpc::ServerBuilder;
using ::grpc::ServerContext;
using grpc::ServerReader;
using grpc::ServerReaderWriter;
using grpc::ServerWriter;
using grpc::Status;
class CalculationInGrpcClient final {
public:
CalculationInGrpcClient(CalculationInGrpcClient& param) = delete;
CalculationInGrpcClient& operator=(CalculationInGrpcClient& param) = delete;
CalculationInGrpcClient(std::shared_ptr<grpc::Channel> channelPtr);
~CalculationInGrpcClient(){};
bool RequestAddOperation(const int32_t a, const int32_t b, int32_t& result);
bool RequestMultiplyOperation(const int32_t a, const int32_t b, int32_t& result);
private:
std::unique_ptr<data_handler::CalculationInterface::Stub> mStub;
};
CalculationInGrpcClient::CalculationInGrpcClient(
std::shared_ptr<grpc::Channel> channel)
: mStub(data_handler::CalculationInterface::NewStub(channel)) {}
bool CalculationInGrpcClient::RequestAddOperation(int32_t a, int32_t b,
int32_t& result) {
grpc::Status grcpStatus;
grpc::ClientContext context;
data_handler::AddReply reply;
data_handler::AddRequest request;
request.set_param1(a);
request.set_param2(b);
grcpStatus = mStub->Add(&context, request, &reply);
if (grcpStatus.error_code() == ::grpc::StatusCode::OK) {
result = static_cast<int32_t>(reply.result());
std::cout << "After adding operation, the result is: "
<< result
<< std::endl;
return true;
} else {
std::cout << "Server not running..." << std::endl;
}
return false;
}
bool CalculationInGrpcClient::RequestMultiplyOperation(int32_t a, int32_t b,
int32_t& result) {
grpc::Status grcpStatus;
grpc::ClientContext context;
data_handler::MultiplyReply reply;
data_handler::MultiplyRequest request;
request.set_param1(a);
request.set_param2(b);
grcpStatus = mStub->Multiply(&context, request, &reply);
if (grcpStatus.error_code() == ::grpc::StatusCode::OK) {
result = static_cast<int32_t>(reply.result());
std::cout << "After Multiplication operation, the result is: "
<< result
<< std::endl;
return true;
} else {
std::cout << "Server not running..." << std::endl;
}
return false;
}
void showHelp() {
std::cout << "Calculation starts : \r\n\
Press 'q' to exit the calculator. \r\n\
"
<< std::endl;
}
bool FindParamters(const std::string& src, const char operation, int32_t& left, int32_t& right) {
auto it = src.find(operation);
if (it != std::string::npos) {
std::string leftParam = src.substr(0, it);
std::string rightParam = src.substr(it + 1, src.length() - it - 1);
left = atoi(leftParam.c_str());
right = atoi(rightParam.c_str());
return true;
}
return false;
}
int main() {
showHelp();
auto grpcChannel = grpc::CreateChannel("127.0.0.1:50051",
grpc::InsecureChannelCredentials());
if (!grpcChannel) {
printf("Failed to create gRPC channel\n");
return 0;
}
std::unique_ptr<CalculationInGrpcClient> clientPtr =
std::make_unique<CalculationInGrpcClient>(grpcChannel);
bool running = true;
while (running) {
std::string strTmp;
std::getline(std::cin, strTmp);
int32_t a = 0;
int32_t b = 0;
int32_t result = 0;
if (FindParamters(strTmp, '+', a, b)) {
if (clientPtr) {
clientPtr->RequestAddOperation(a, b, result);
}
} else if (FindParamters(strTmp, '*', a, b)) {
if (clientPtr) {
clientPtr->RequestMultiplyOperation(a, b, result);
}
} else {
// reserve
}
if (strTmp.find('q') != std::string::npos) {
// reset running flag and shutdown server
running = false;
}
}
return 0;
}代码里面的request, reply基本上是固定格式:
grpc::Status grcpStatus;
grpc::ClientContext context;
data_handler::MultiplyReply reply;
data_handler::MultiplyRequest request;
request.set_param1(a);
request.set_param2(b);
grcpStatus = mStub->Multiply(&context, request, &reply);
主要是stub去调用服务器端的接口,而前的context, request, reply都是准备工作。
grpc的createChannel绑定了服务器端的IP和port,进行服务器端和客户端通信,grpc都封装好了,固定格式调用就行。
4. 编译生成后,运行服务器端后,在运行客户端
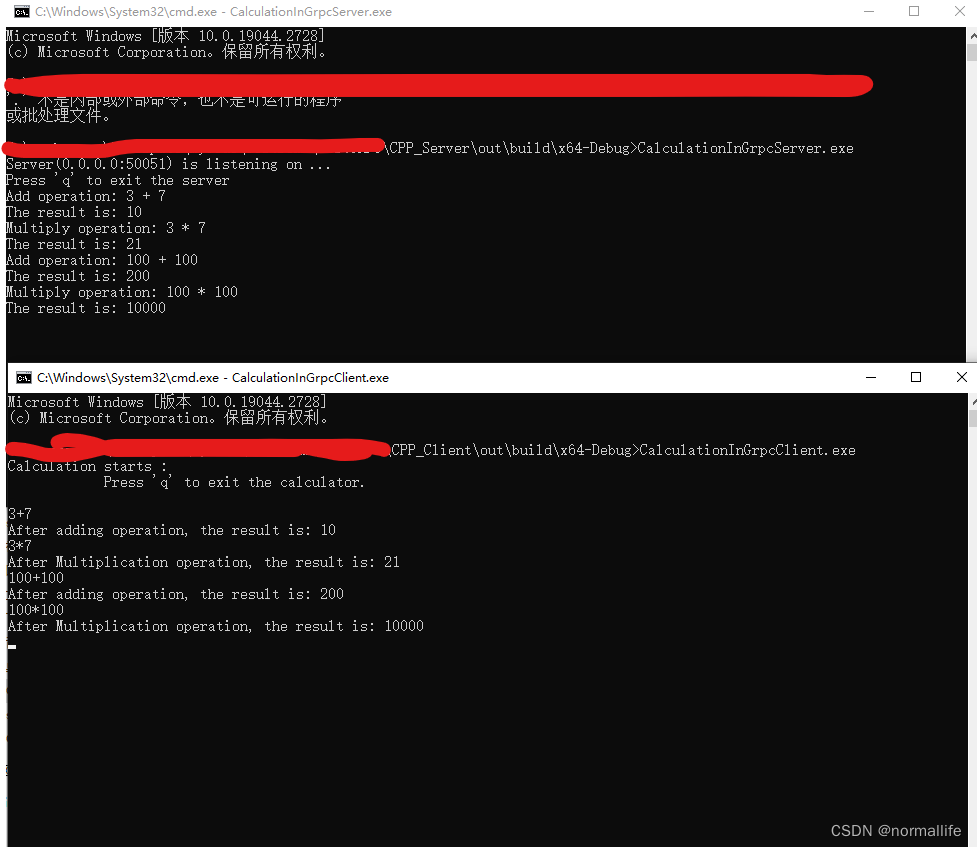
好了,就先到这里吧,代码只是demo,大家看看就行,里面有些不严谨的地方,多多担担!





![[计算机图形学]动画与模拟:关键帧动画、质点弹簧系统、运动学与绑定(前瞻预习/复习回顾)](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/79ea2d973dfc47b59d0f43d376d1fe65.png)




