文章目录
- 性质
- 二叉搜索树的遍历
- 遍历伪代码实现
- 二叉搜索树的查找
- 伪代码实现
- 二叉搜索树最大元素
- 伪代码实现
- 二叉搜索树最小元素
- 伪代码实现
- 二叉搜索树的插入
- 伪代码实现
- 二叉搜索树的删除
- 删除叶子节点(对应上面第一种情况):
- 删除度为1的节点(对应上面第二种情况):
- 前驱和后继
- 寻找后继节点
- 删除度为2的节点(对应上面第三种情况):
- 二叉搜索树不平衡
- 通过随机方式构建二叉搜索树
- 完整的Java测试代码:
- BinarySearchTree
- BinaryTreeInfo
- BinaryTrees
- InorderPrinter
- LevelOrderPrinter
- Printer
- Strings
- 总结
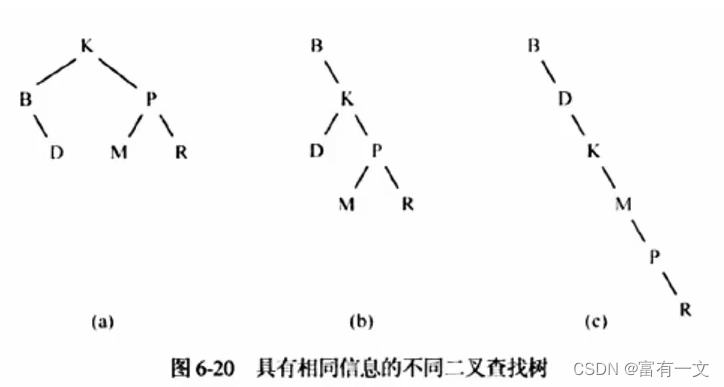
二叉搜索树是一个有序树
性质
- 若它的左子树不空,则左子树上所有结点的值均小于它的根结点的值;
- 若它的右子树不空,则右子树上所有结点的值均大于它的根结点的值;
- 左、右子树也分别为二叉搜索树;
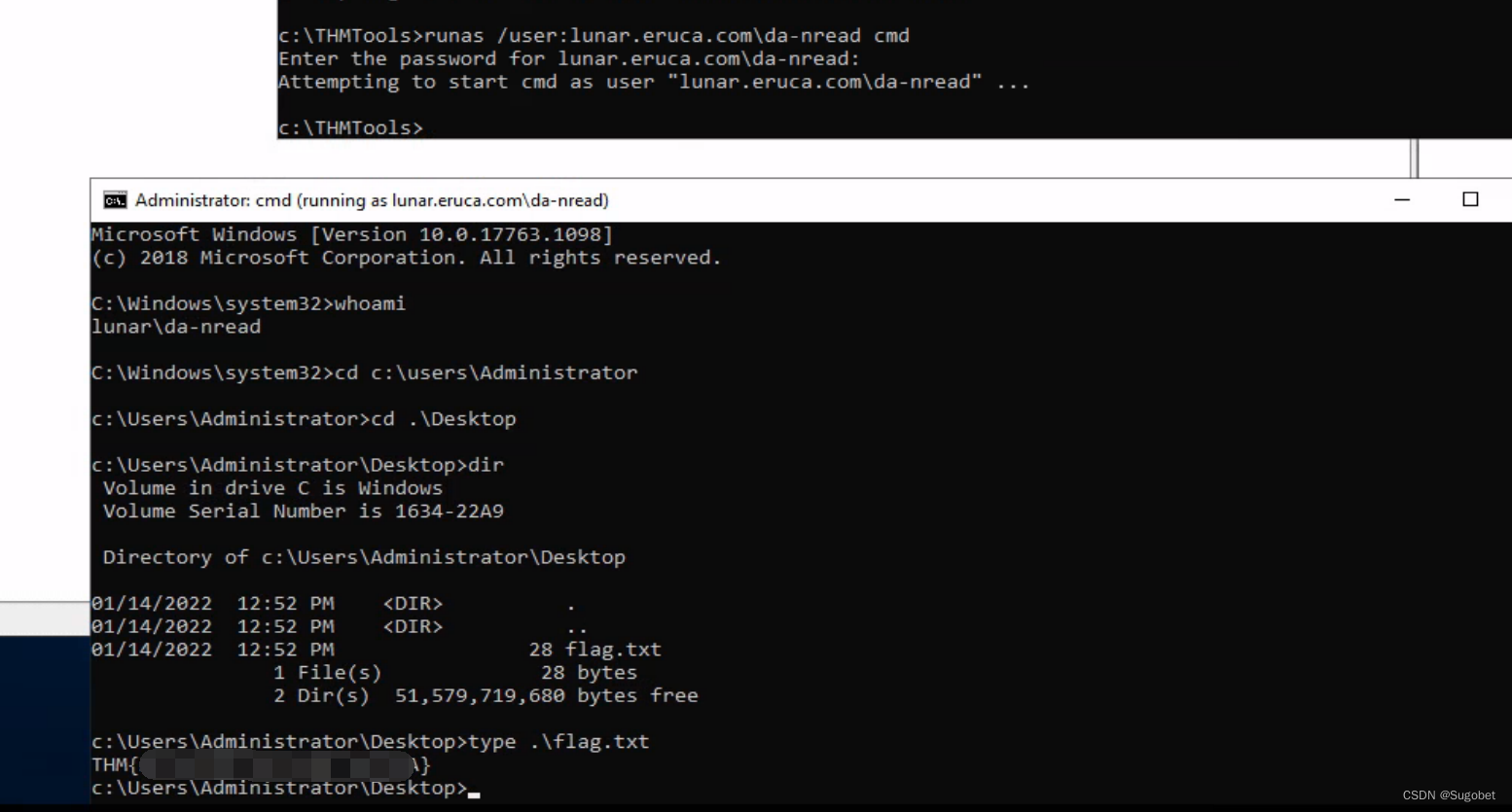
如图所示,两棵都是二叉排序树;
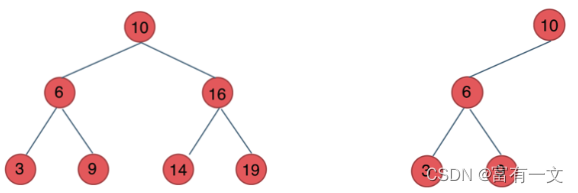
如图所示,左右两棵树都是是二叉搜索树。
二叉搜索树的遍历
二叉搜索树性质允许我们通过一个简单的递归算法来按序输出二叉搜索树中的所有关键字,这种算法称为中序遍历(遍历方法介绍与实现请看二叉树的遍历方式博文)算法。
遍历伪代码实现

二叉搜索树的查找
在一棵二叉搜索树中查找一个具有给定关键字的结点。
输人一个指向树根的指针和一个关键字k,如果这个结点存在,TREE-SEARCH返回一个指向关键字为k的结点的指针;否则返回 Null。
伪代码实现

也可以使用while循环来展开递归去实现,一般情况对于树的问题还是使用递归更简单,但是while循环的效率要高很多,得取舍,如果面试不会做题节约时间可递归简单实现,实际需要专研一下while循环实现。

二叉搜索树最大元素
一路向右查找
伪代码实现

二叉搜索树最小元素
一路向左查找
伪代码实现

二叉搜索树的插入
要将一个新值u插人到一棵二叉搜索树T中,需要调用过程 TREE-INSERT。该过程以结点z作为输人,其中z.key=u,z.left=NIL,z.right=NIL。这个过程要修改 T和z 的某些属性来把z插人到树中的相应位置上。
伪代码实现

二叉搜索树的删除
从一棵二叉搜索树 T中删除一个结点z 的整个策略分为三种基本情况(如下所述),但只有1种情况有点棘手。二叉搜索树要求删除节点后还是一棵二叉搜索树。
- 1、如果z没有孩子结点,那么只是简单地将它删除,并修改它的父结点,用 NIL 作为孩子0来替换 z。
- 2、如果z只有一个孩子,那么将这个孩子提升到树中z的位置上,并修改z的父结点,用z0的孩子来替换 z。
- 3、如果z有两个孩子,那么找z的后继y(一定在z的右子树中),并让y占据树中z 的位置。z的原来右子树部分成为y 的新的右子树,并且 z 的左子树成为y的新的左子树。这种情况稍显麻烦(如下所述),因为还与 y是否为z 的右孩子相关。(这种情况比较麻烦,得注意)
注意:这里可以用z的后继或者是用z的前驱两种方式实现删除。
删除叶子节点(对应上面第一种情况):
这种情况可以直接删除节点,假设要删除的节点为node,则
1、当node.parent == null时,即二叉树只有一个根节点且删除的就是根节点的情况
root = null
2、当node == node.parent.left时,即节点是父节点的左孩子,直接把左孩子置为空
node.parent.left = null
3、当node == node.parent.right时,即节点是父节点的右孩子,直接把右孩子置为空
node.parent.right = null
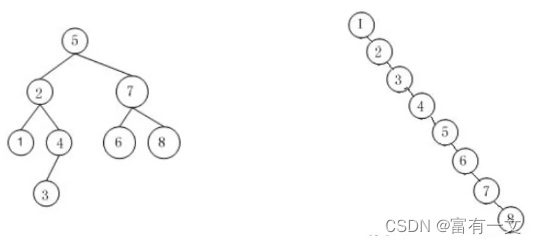
删除度为1的节点(对应上面第二种情况):
用子节点代替原节点的位置,假设node是原节点,son是子节点
1、如果node是根节点
root = son
son.parent = null
如图所示:
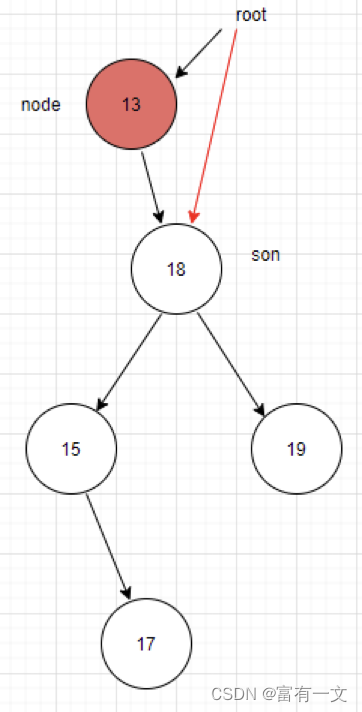
2、如果node是左子节点
son.parent = node.parent
node.parent.left = son
3、如果node是右子节点
son.parent = node.parent
node.parent.right = son
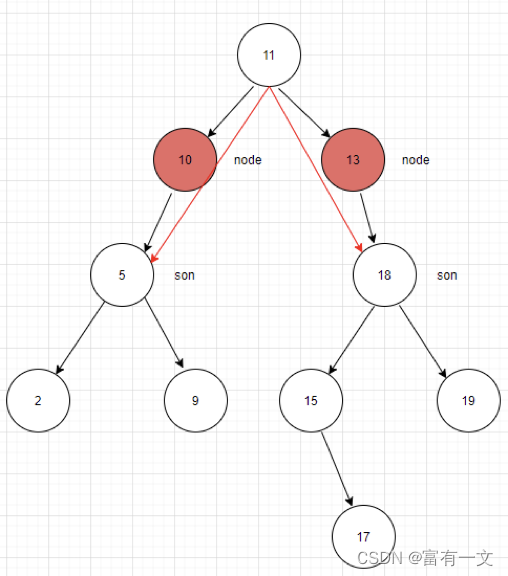
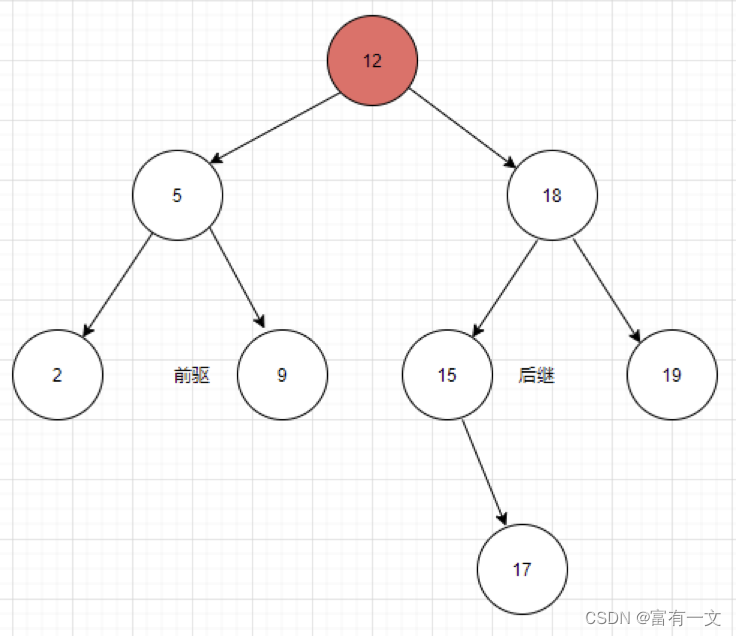
前驱和后继
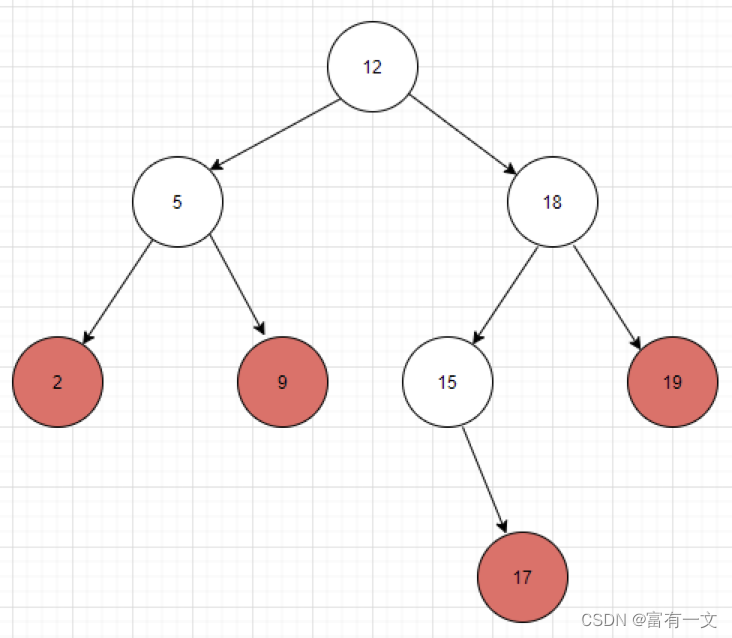
根据中序遍历(左中右)看图说话:
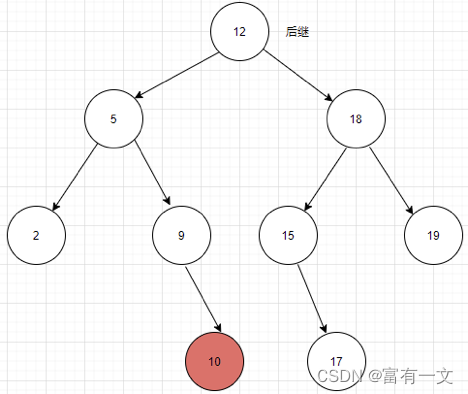
如图中对于节点10而言,后继是12,前驱是9;
再举一个例子:对于9而言,前驱是5,后继是10。
寻找后继节点
如果后继存在,下面的过程将返回一棵二叉搜索树中的结点x的后继;如果x是这棵树中的最大关键字,则返回 NIL.

把上图TREE-SUCCESSOR 的伪代码分为两种情况。如果结点x的右子树非空,那么x的后继恰是x 右子树中的最左结点,通过第2行中的 TREE-MINIMUM(x.right)调用可以找到,即返回右子树的最小值。
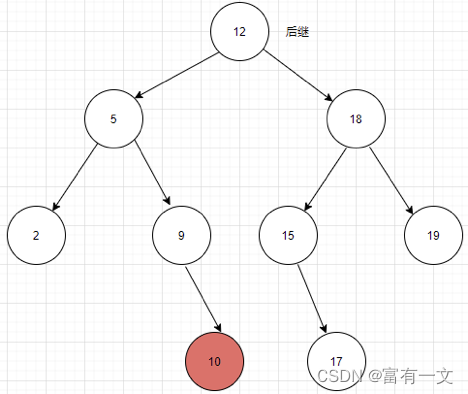
如图12节点的后继就是15;
另一方面,如果结点x的右子树非空并有一个后继y,那么y就是x的有左孩子的最底层祖先,并且它也是x的一个祖先。在上面中,关键字为 10的结点的后继是关键字为12的结点。为了找到 y,只需简单地从x开始沿树而上直到遇到一个其双亲有左孩子的结点。TREE-SUCCESSOR 中的第 3~7 行正是处理这种情况。
说简单一点,10->9->5这个过程中,10一直在右子树上面,当10->9->5->12时,10第一次从挂在右子树变成挂在左子树,所以12就是10的后继。
对19而言,就是后继为空的情况。
前驱的情况就是和后继对称的,掌握一种就可以了。
删除度为2的节点(对应上面第三种情况):
假如要删除节点12
1、先用前驱或者后继节点的值覆盖原节点的值
2、然后删除相应的前驱或者后继节点
如果一个节点的度为2,那么,它的前驱、后继节点的度只可能为1或者0,当前驱、后继节点的度为1时,前驱节点只有左孩子,后继节点只有右孩子。
二叉搜索树不平衡
假如构建二叉搜索树的过程中,数据是高度有序的(包括顺序和逆序),此时构建出的二又搜索树会高度不平衡,甚至退化成链表,增删改查的效率大大降低。
通过随机方式构建二叉搜索树
随机构建二叉搜索树(randomly built binary search tree)为按随机次序插人这些关键字到一棵初始的空树中而生成的树,一棵有n个不同关键字的随机构建二叉搜索树的期望高度为O(lgn)。
完整的Java测试代码:
BinarySearchTree
package binarytree;
/**
* @Author hepingfu
* @Date 2023/05/03/15:37
* @Version 1.0
*/
public class BinarySearchTree implements BinaryTreeInfo {
private Node root;
public Node getRoot() {
return root;
}
public void setRoot(Node root) {
this.root = root;
}
public BinarySearchTree() {
this.root = null;
}
public BinarySearchTree(Node root) {
this.root = root;
}
//前序遍历二叉树
public void preorderTreeWalk(Node x) {
if(x != null) {
System.out.print(x.key + " ");
preorderTreeWalk(x.left);
preorderTreeWalk(x.right);
}
}
//中序遍历二叉树
public void inorderTreeWalk(Node x) {
if(x != null) {
inorderTreeWalk(x.left);
System.out.print(x.key + " ");
inorderTreeWalk(x.right);
}
}
//后序遍历二叉树
public void postorderTreeWalk(Node x) {
if(x != null) {
postorderTreeWalk(x.left);
postorderTreeWalk(x.right);
System.out.print(x.key + " ");
}
}
//在二叉搜索树中查询某个值,递归版本
public Node treeSearch(Node x, Integer k) {
if(x == null || k == x.key) {
return x;
}
if(k < x.key) {
return treeSearch(x.left, k);
} else {
return treeSearch(x.right, k);
}
}
//在二叉搜索树中查询某个值,循环版本
public Node iterativeTreeSearch(Node x, Integer k) {
while(x != null && k != x.key) {
if(k < x.key) {
x = x.left;
} else {
x = x.right;
}
}
return x;
}
//在二叉搜索树中查找包含最小值的节点
public Node treeMinimum(Node x) {
while (x.left != null) {
x = x.left;
}
return x;
}
//在二叉搜索树中查找包含最大值的节点
public Node treeMaximum(Node x) {
while (x.right != null) {
x = x.right;
}
return x;
}
//查找节点x的后继节点
public Node treeSuccessor(Node x) {
if(x.right != null) { //x的右子树不为空,找右子树的最小值
return treeMinimum(x.right);
}
Node y = x.parent;
while(y != null && x == y.right) {
x = y;
y = y.parent;
}
return y;
}
//查找节点x的前驱节点
public Node treePredeceessor(Node x) {
if(x.left != null) {
return treeMaximum(x.left);
}
Node y = x.parent;
while(y != null && x == y.left) {
x = y;
y = y.parent;
}
return y;
}
//二叉搜索树的插入操作
public void treeInsert(BinarySearchTree t, Node z) {
Node y = null;
Node x = t.root;
while(x != null) {
y = x;
if(z.key < x.key) {
x = x.left;
} else {
x = x.right;
}
}
z.parent = y;
if(y == null) { //说明现在是棵空树
t.root = z;
} else if (z.key < y.key) {
y.left = z;
} else {
y.right = z;
}
}
public void transplant(BinarySearchTree t, Node u, Node v) {
if(u.parent == null) {
t.root = v;
} else if(u == u.parent.left) {
u.parent.left = v;
} else {
u.parent.right = v;
}
if(v != null) {
v.parent = u.parent;
}
}
//算法导论书上的删除节点操作
public void treeDelete(BinarySearchTree t, Node z) {
if (z.left == null) {
//z的左孩子为空,用z的右孩子替换z,此时z的右孩子可以为空,也可以不为空
transplant(t, z, z.right);
} else if (z.right == null) {
//z仅有一个孩子且其为左孩子,用z的左孩子替换z
transplant(t, z , z.left);
} else {
//z有两个孩子,找z的后继节点
Node y = treeMinimum(z.right);
//y作为后继节点,只可能有右孩子,不可能有左孩子
if(y.parent != z) {
//用以y的右孩子为根的树代替以y为根的树
transplant(t, y, y.right);
y.right = z.right;
y.right.parent = y;
}
//用以y为根的树代替以z为根的树
transplant(t, z, y);
y.left = z.left;
y.left.parent = y;
}
}
//更容易看懂的删除节点操作
public void remove(Node node) {
if (node == null) return;
if (node.left != null && node.right != null) { // 度为2的节点
// 找到后继节点
Node s = treeSuccessor(node);
// 用后继节点的值覆盖度为2的节点的值
node.key = s.key;
// 为删除后继节点做准备
node = s;
}
// 删除node节点(node的度必然是1或者0)
Node replacement = node.left != null ? node.left : node.right;
if (replacement != null) { // node是度为1的节点
// 更改parent
replacement.parent = node.parent;
// 更改parent的left、right的指向
if (node.parent == null) { // node是度为1的节点并且是根节点
root = replacement;
} else if (node == node.parent.left) {
node.parent.left = replacement;
} else { // node == node.parent.right
node.parent.right = replacement;
}
} else if (node.parent == null) { // node是叶子节点并且是根节点
root = null;
} else { // node是叶子节点,但不是根节点
if (node == node.parent.left) {
node.parent.left = null;
} else { // node == node.parent.right
node.parent.right = null;
}
}
}
//节点类定义
static class Node {
private Integer key; //节点值
private Node parent; //父节点
private Node left; //左孩子
private Node right; //右孩子
public Node() {
}
public Node(Integer key) {
this.key = key;
}
public Node(Integer key, Node parent) {
this.parent = parent;
this.key = key;
}
public Node(Node parent, Node left, Node right, Integer key) {
this.parent = parent;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
this.key = key;
}
public Integer getKey() {
return key;
}
public void setKey(Integer key) {
this.key = key;
}
public Node getParent() {
return parent;
}
public void setParent(Node parent) {
this.parent = parent;
}
public Node getLeft() {
return left;
}
public void setLeft(Node left) {
this.left = left;
}
public Node getRight() {
return right;
}
public void setRight(Node right) {
this.right = right;
}
}
@Override
public Object root() {
return root;
}
@Override
public Object left(Object node) {
return ((Node)node).left;
}
@Override
public Object right(Object node) {
return ((Node)node).right;
}
@Override
public Object string(Object node) {
Node myNode = (Node)node;
return myNode.key + "";
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
BinarySearchTree bst = new BinarySearchTree();
bst.treeInsert(bst, new Node(12));
bst.treeInsert(bst, new Node(5));
bst.treeInsert(bst, new Node(2));
bst.treeInsert(bst, new Node(9));
bst.treeInsert(bst, new Node(18));
bst.treeInsert(bst, new Node(15));
bst.treeInsert(bst, new Node(19));
bst.treeInsert(bst, new Node(17));
bst.inorderTreeWalk(bst.root);
System.out.println();
BinaryTrees.print(bst);
// //两种方式删除根节点12
bst.treeDelete(bst, bst.treeSearch(bst.root, 12));
// bst.remove(bst.treeSearch(bst.root, 12));
// //两种方式删除叶子节点17
// bst.treeDelete(bst, bst.treeSearch(bst.root, 17));
// bst.remove(bst.treeSearch(bst.root, 17));
// //两种方式删除只有一个孩子的节点15
// bst.treeDelete(bst, bst.treeSearch(bst.root, 15));
// bst.remove(bst.treeSearch(bst.root, 15));
System.out.println();
BinaryTrees.print(bst);
}
}
BinaryTreeInfo
package binarytree;
/**
* @Author hepingfu
* @Date 2023/05/03/15:32
* @Version 1.0
*/
public interface BinaryTreeInfo {
/**
* who is the root node
*/
Object root();
/**
* how to get the left child of the node
*/
Object left(Object node);
/**
* how to get the right child of the node
*/
Object right(Object node);
/**
* how to print the node
*/
Object string(Object node);
}
BinaryTrees
package binarytree;
/**
* @Author hepingfu
* @Date 2023/05/03/15:31
* @Version 1.0
*/
public class BinaryTrees {
private BinaryTrees() {
}
public static void print(BinaryTreeInfo tree) {
print(tree, null);
}
public static void println(BinaryTreeInfo tree) {
println(tree, null);
}
public static void print(BinaryTreeInfo tree, PrintStyle style) {
if (tree == null || tree.root() == null) return;
printer(tree, style).print();
}
public static void println(BinaryTreeInfo tree, PrintStyle style) {
if (tree == null || tree.root() == null) return;
printer(tree, style).println();
}
public static String printString(BinaryTreeInfo tree) {
return printString(tree, null);
}
public static String printString(BinaryTreeInfo tree, PrintStyle style) {
if (tree == null || tree.root() == null) return null;
return printer(tree, style).printString();
}
private static Printer printer(BinaryTreeInfo tree, PrintStyle style) {
if (style == PrintStyle.INORDER) return new InorderPrinter(tree);
return new LevelOrderPrinter(tree);
}
public enum PrintStyle {
LEVEL_ORDER, INORDER
}
}
InorderPrinter
package binarytree;
/**
* @Author hepingfu
* @Date 2023/05/03/15:34
* @Version 1.0
*/
/**
┌──800
┌──760
│ └──600
┌──540
│ └──476
│ └──445
┌──410
│ └──394
381
│ ┌──190
│ │ └──146
│ ┌──40
│ │ └──35
└──12
└──9
*/
public class InorderPrinter extends Printer {
private static String rightAppend;
private static String leftAppend;
private static String blankAppend;
private static String lineAppend;
static {
int length = 2;
rightAppend = "┌" + Strings.repeat("─", length);
leftAppend = "└" + Strings.repeat("─", length);
blankAppend = Strings.blank(length + 1);
lineAppend = "│" + Strings.blank(length);
}
public InorderPrinter(BinaryTreeInfo tree) {
super(tree);
}
@Override
public String printString() {
StringBuilder string = new StringBuilder(
printString(tree.root(), "", "", ""));
string.deleteCharAt(string.length() - 1);
return string.toString();
}
/**
* 生成node节点的字符串
* @param nodePrefix node那一行的前缀字符串
* @param leftPrefix node整棵左子树的前缀字符串
* @param rightPrefix node整棵右子树的前缀字符串
* @return
*/
private String printString(
Object node,
String nodePrefix,
String leftPrefix,
String rightPrefix) {
Object left = tree.left(node);
Object right = tree.right(node);
String string = tree.string(node).toString();
int length = string.length();
if (length % 2 == 0) {
length--;
}
length >>= 1;
String nodeString = "";
if (right != null) {
rightPrefix += Strings.blank(length);
nodeString += printString(right,
rightPrefix + rightAppend,
rightPrefix + lineAppend,
rightPrefix + blankAppend);
}
nodeString += nodePrefix + string + "\n";
if (left != null) {
leftPrefix += Strings.blank(length);
nodeString += printString(left,
leftPrefix + leftAppend,
leftPrefix + blankAppend,
leftPrefix + lineAppend);
}
return nodeString;
}
}
LevelOrderPrinter
package binarytree;
/**
* @Author hepingfu
* @Date 2023/05/03/15:36
* @Version 1.0
*/
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Queue;
/**
┌───381────┐
│ │
┌─12─┐ ┌─410─┐
│ │ │ │
9 ┌─40─┐ 394 ┌─540─┐
│ │ │ │
35 ┌─190 ┌─476 ┌─760─┐
│ │ │ │
146 445 600 800
*/
public class LevelOrderPrinter extends Printer {
/**
* 节点之间允许的最小间距(最小只能填1)
*/
private static final int MIN_SPACE = 1;
private Node root;
private int minX;
private int maxWidth;
private List<List<Node>> nodes;
public LevelOrderPrinter(BinaryTreeInfo tree) {
super(tree);
root = new Node(tree.root(), tree);
maxWidth = root.width;
}
@Override
public String printString() {
// nodes用来存放所有的节点
nodes = new ArrayList<>();
fillNodes();
cleanNodes();
compressNodes();
addLineNodes();
int rowCount = nodes.size();
// 构建字符串
StringBuilder string = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < rowCount; i++) {
if (i != 0) {
string.append("\n");
}
List<Node> rowNodes = nodes.get(i);
StringBuilder rowSb = new StringBuilder();
for (Node node : rowNodes) {
int leftSpace = node.x - rowSb.length() - minX;
rowSb.append(Strings.blank(leftSpace));
rowSb.append(node.string);
}
string.append(rowSb);
}
return string.toString();
}
/**
* 添加一个元素节点
*/
private Node addNode(List<Node> nodes, Object btNode) {
Node node = null;
if (btNode != null) {
node = new Node(btNode, tree);
maxWidth = Math.max(maxWidth, node.width);
nodes.add(node);
} else {
nodes.add(null);
}
return node;
}
/**
* 以满二叉树的形式填充节点
*/
private void fillNodes() {
// 第一行
List<Node> firstRowNodes = new ArrayList<>();
firstRowNodes.add(root);
nodes.add(firstRowNodes);
// 其他行
while (true) {
List<Node> preRowNodes = nodes.get(nodes.size() - 1);
List<Node> rowNodes = new ArrayList<>();
boolean notNull = false;
for (Node node : preRowNodes) {
if (node == null) {
rowNodes.add(null);
rowNodes.add(null);
} else {
Node left = addNode(rowNodes, tree.left(node.btNode));
if (left != null) {
node.left = left;
left.parent = node;
notNull = true;
}
Node right = addNode(rowNodes, tree.right(node.btNode));
if (right != null) {
node.right = right;
right.parent = node;
notNull = true;
}
}
}
// 全是null,就退出
if (!notNull) break;
nodes.add(rowNodes);
}
}
/**
* 删除全部null、更新节点的坐标
*/
private void cleanNodes() {
int rowCount = nodes.size();
if (rowCount < 2) return;
// 最后一行的节点数量
int lastRowNodeCount = nodes.get(rowCount - 1).size();
// 每个节点之间的间距
int nodeSpace = maxWidth + 2;
// 最后一行的长度
int lastRowLength = lastRowNodeCount * maxWidth
+ nodeSpace * (lastRowNodeCount - 1);
// 空集合
Collection<Object> nullSet = Collections.singleton(null);
for (int i = 0; i < rowCount; i++) {
List<Node> rowNodes = nodes.get(i);
int rowNodeCount = rowNodes.size();
// 节点左右两边的间距
int allSpace = lastRowLength - (rowNodeCount - 1) * nodeSpace;
int cornerSpace = allSpace / rowNodeCount - maxWidth;
cornerSpace >>= 1;
int rowLength = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < rowNodeCount; j++) {
if (j != 0) {
// 每个节点之间的间距
rowLength += nodeSpace;
}
rowLength += cornerSpace;
Node node = rowNodes.get(j);
if (node != null) {
// 居中(由于奇偶数的问题,可能有1个符号的误差)
int deltaX = (maxWidth - node.width) >> 1;
node.x = rowLength + deltaX;
node.y = i;
}
rowLength += maxWidth;
rowLength += cornerSpace;
}
// 删除所有的null
rowNodes.removeAll(nullSet);
}
}
/**
* 压缩空格
*/
private void compressNodes() {
int rowCount = nodes.size();
if (rowCount < 2) return;
for (int i = rowCount - 2; i >= 0; i--) {
List<Node> rowNodes = nodes.get(i);
for (Node node : rowNodes) {
Node left = node.left;
Node right = node.right;
if (left == null && right == null) continue;
if (left != null && right != null) {
// 让左右节点对称
node.balance(left, right);
// left和right之间可以挪动的最小间距
int leftEmpty = node.leftBoundEmptyLength();
int rightEmpty = node.rightBoundEmptyLength();
int empty = Math.min(leftEmpty, rightEmpty);
empty = Math.min(empty, (right.x - left.rightX()) >> 1);
// left、right的子节点之间可以挪动的最小间距
int space = left.minLevelSpaceToRight(right) - MIN_SPACE;
space = Math.min(space >> 1, empty);
// left、right往中间挪动
if (space > 0) {
left.translateX(space);
right.translateX(-space);
}
// 继续挪动
space = left.minLevelSpaceToRight(right) - MIN_SPACE;
if (space < 1) continue;
// 可以继续挪动的间距
leftEmpty = node.leftBoundEmptyLength();
rightEmpty = node.rightBoundEmptyLength();
if (leftEmpty < 1 && rightEmpty < 1) continue;
if (leftEmpty > rightEmpty) {
left.translateX(Math.min(leftEmpty, space));
} else {
right.translateX(-Math.min(rightEmpty, space));
}
} else if (left != null) {
left.translateX(node.leftBoundEmptyLength());
} else { // right != null
right.translateX(-node.rightBoundEmptyLength());
}
}
}
}
private void addXLineNode(List<Node> curRow, Node parent, int x) {
Node line = new Node("─");
line.x = x;
line.y = parent.y;
curRow.add(line);
}
private Node addLineNode(List<Node> curRow, List<Node> nextRow, Node parent, Node child) {
if (child == null) return null;
Node top = null;
int topX = child.topLineX();
if (child == parent.left) {
top = new Node("┌");
curRow.add(top);
for (int x = topX + 1; x < parent.x; x++) {
addXLineNode(curRow, parent, x);
}
} else {
for (int x = parent.rightX(); x < topX; x++) {
addXLineNode(curRow, parent, x);
}
top = new Node("┐");
curRow.add(top);
}
// 坐标
top.x = topX;
top.y = parent.y;
child.y = parent.y + 2;
minX = Math.min(minX, child.x);
// 竖线
Node bottom = new Node("│");
bottom.x = topX;
bottom.y = parent.y + 1;
nextRow.add(bottom);
return top;
}
private void addLineNodes() {
List<List<Node>> newNodes = new ArrayList<>();
int rowCount = nodes.size();
if (rowCount < 2) return;
minX = root.x;
for (int i = 0; i < rowCount; i++) {
List<Node> rowNodes = nodes.get(i);
if (i == rowCount - 1) {
newNodes.add(rowNodes);
continue;
}
List<Node> newRowNodes = new ArrayList<>();
newNodes.add(newRowNodes);
List<Node> lineNodes = new ArrayList<>();
newNodes.add(lineNodes);
for (Node node : rowNodes) {
addLineNode(newRowNodes, lineNodes, node, node.left);
newRowNodes.add(node);
addLineNode(newRowNodes, lineNodes, node, node.right);
}
}
nodes.clear();
nodes.addAll(newNodes);
}
private static class Node {
/**
* 顶部符号距离父节点的最小距离(最小能填0)
*/
private static final int TOP_LINE_SPACE = 1;
Object btNode;
Node left;
Node right;
Node parent;
/**
* 首字符的位置
*/
int x;
int y;
int treeHeight;
String string;
int width;
private void init(String string) {
string = (string == null) ? "null" : string;
string = string.isEmpty() ? " " : string;
width = string.length();
this.string = string;
}
public Node(String string) {
init(string);
}
public Node(Object btNode, BinaryTreeInfo opetaion) {
init(opetaion.string(btNode).toString());
this.btNode = btNode;
}
/**
* 顶部方向字符的X(极其重要)
*
* @return
*/
private int topLineX() {
// 宽度的一半
int delta = width;
if (delta % 2 == 0) {
delta--;
}
delta >>= 1;
if (parent != null && this == parent.left) {
return rightX() - 1 - delta;
} else {
return x + delta;
}
}
/**
* 右边界的位置(rightX 或者 右子节点topLineX的下一个位置)(极其重要)
*/
private int rightBound() {
if (right == null) return rightX();
return right.topLineX() + 1;
}
/**
* 左边界的位置(x 或者 左子节点topLineX)(极其重要)
*/
private int leftBound() {
if (left == null) return x;
return left.topLineX();
}
/**
* x ~ 左边界之间的长度(包括左边界字符)
*
* @return
*/
private int leftBoundLength() {
return x - leftBound();
}
/**
* rightX ~ 右边界之间的长度(包括右边界字符)
*
* @return
*/
private int rightBoundLength() {
return rightBound() - rightX();
}
/**
* 左边界可以清空的长度
*
* @return
*/
private int leftBoundEmptyLength() {
return leftBoundLength() - 1 - TOP_LINE_SPACE;
}
/**
* 右边界可以清空的长度
*
* @return
*/
private int rightBoundEmptyLength() {
return rightBoundLength() - 1 - TOP_LINE_SPACE;
}
/**
* 让left和right基于this对称
*/
private void balance(Node left, Node right) {
if (left == null || right == null) return;
// 【left的尾字符】与【this的首字符】之间的间距
int deltaLeft = x - left.rightX();
// 【this的尾字符】与【this的首字符】之间的间距
int deltaRight = right.x - rightX();
int delta = Math.max(deltaLeft, deltaRight);
int newRightX = rightX() + delta;
right.translateX(newRightX - right.x);
int newLeftX = x - delta - left.width;
left.translateX(newLeftX - left.x);
}
private int treeHeight(Node node) {
if (node == null) return 0;
if (node.treeHeight != 0) return node.treeHeight;
node.treeHeight = 1 + Math.max(
treeHeight(node.left), treeHeight(node.right));
return node.treeHeight;
}
/**
* 和右节点之间的最小层级距离
*/
private int minLevelSpaceToRight(Node right) {
int thisHeight = treeHeight(this);
int rightHeight = treeHeight(right);
int minSpace = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for (int i = 0; i < thisHeight && i < rightHeight; i++) {
int space = right.levelInfo(i).leftX
- this.levelInfo(i).rightX;
minSpace = Math.min(minSpace, space);
}
return minSpace;
}
private LevelInfo levelInfo(int level) {
if (level < 0) return null;
int levelY = y + level;
if (level >= treeHeight(this)) return null;
List<Node> list = new ArrayList<>();
Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(this);
// 层序遍历找出第level行的所有节点
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
Node node = queue.poll();
if (levelY == node.y) {
list.add(node);
} else if (node.y > levelY) break;
if (node.left != null) {
queue.offer(node.left);
}
if (node.right != null) {
queue.offer(node.right);
}
}
Node left = list.get(0);
Node right = list.get(list.size() - 1);
return new LevelInfo(left, right);
}
/**
* 尾字符的下一个位置
*/
public int rightX() {
return x + width;
}
public void translateX(int deltaX) {
if (deltaX == 0) return;
x += deltaX;
// 如果是LineNode
if (btNode == null) return;
if (left != null) {
left.translateX(deltaX);
}
if (right != null) {
right.translateX(deltaX);
}
}
}
private static class LevelInfo {
int leftX;
int rightX;
public LevelInfo(Node left, Node right) {
this.leftX = left.leftBound();
this.rightX = right.rightBound();
}
}
}
Printer
package binarytree;
/**
* @Author hepingfu
* @Date 2023/05/03/15:35
* @Version 1.0
*/
public abstract class Printer {
/**
* 二叉树的基本信息
*/
protected BinaryTreeInfo tree;
public Printer(BinaryTreeInfo tree) {
this.tree = tree;
}
/**
* 生成打印的字符串
*/
public abstract String printString();
/**
* 打印后换行
*/
public void println() {
print();
System.out.println();
}
/**
* 打印
*/
public void print() {
System.out.print(printString());
}
}
Strings
package binarytree;
/**
* @Author hepingfu
* @Date 2023/05/03/15:36
* @Version 1.0
*/
public class Strings {
public static String repeat(String string, int count) {
if (string == null) return null;
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder();
while (count-- > 0) {
builder.append(string);
}
return builder.toString();
}
public static String blank(int length) {
if (length < 0) return null;
if (length == 0) return "";
return String.format("%" + length + "s", "");
}
}
总结
这个实现过程比较复杂,更多的是在提现一个打印结果的实现,没有必要自己去手敲,可以全部拿下来,去运行,看具体核心实现二叉搜索树对应的那些功能。对于二叉搜索树更细节的去使用,我也还在探索中,之后会更加细节的去记录。
ps:计划每日更新一篇博客,今日2023-05-02,日更第十六天。
昨日更新:(补更)
leetcode100——相同的树