文章目录
- 链表
- 1.单链表/双链表的反转
- 2.删除链表中指定的值
- 队列
- 1.数组循环队列的实现
- 2. 双向链表实现双端队列
- 栈
- 1.用数组实现栈
- 栈和队列的面试题
- 1. 实现最小栈
- 2. 两个栈实现一个队列
- 3.两个队列实现一个栈
- 4.用栈实现图的广度优先遍历
- 5.用队列实现图的深度优先遍历
- 递归
- Master公式可以计算递归时间复杂度
链表
1.单链表/双链表的反转
// 单向链表节点
struct Node{
int value;
Node* next;
Node(int data)
: value(data)
, next(nullptr)
{}
};
// 双向链表节点
struct DoubleNode{
int value;
DoubleNode* last;
DoubleNode* next;
};
Node* reverseLinkedList(Node* head)
{
Node* pre=nullptr;
Node* next= nullptr;
while(head!=nullptr)
{
next = head->next;
head->next = pre;
pre = head;
head = next;
}
return pre;
}
DoubleNode* reverseDoubleList(DoubleNode* head)
{
DoubleNode* pre = nullptr;
DoubleNode* next = nullptr;
while(head!=nullptr)
{
next = head->next;
head->next = pre;
head->last = next;
pre = head ;
head = next;
}
return pre;
}
2.删除链表中指定的值
Node* removeValue(Node* head,int num)
{
// 删除的num可能出现在链表头部,我们最后需要返回头节点,
// 因此删除头部元素会导致head野指针。
Node* cur = head;
while(cur!=nullptr)
{
if(cur->value!=num){
break;
}
Node* next = cur->next;
delete cur;
cur = next;
}
head = cur;
Node* pre = head;
while(cur!=nullptr)
{
Node* next = cur->next;
if(next->value == num)
{
pre->next = next;
delete cur;
}
else
{
pre = cur;
}
cur=next;
}
return head;
}
队列
1.数组循环队列的实现
class MyQueue{
private:
vector<int> arr;
int pushi; // 该位置插入元素
int polli; // 该位置拿出元素
int size; // 有效元素个数
public:
MyQueue(int length)
:pushi(0)
,polli(0)
,size(0)
,arr(length){}
int nextIndex(int index)
{
return (index+1) % arr.size();
}
// 插入队列
void push(int value)
{
// 队列满了
if(size==arr.size()){
//扩容 或者 抛异常
}
size++;
arr[pushi] = value;
pushi = nextIndex(pushi);
}
int pop()
{
if(size == 0){
// 队列为空,抛异常
}
size--;
int ans = arr[polli];
polli = nextIndex(polli);
return ans;
}
};
2. 双向链表实现双端队列
栈
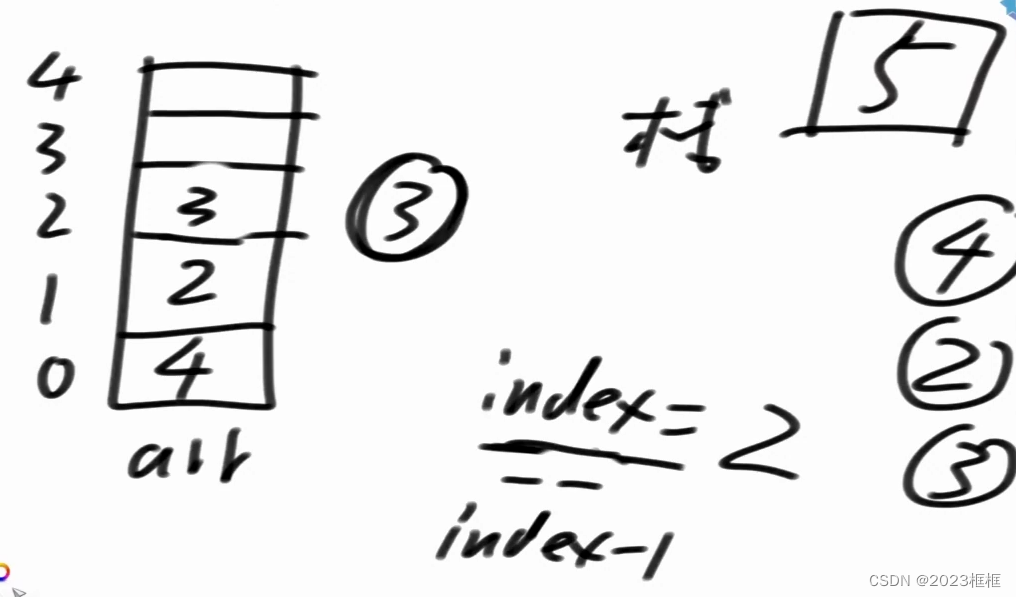
1.用数组实现栈
固定长度的数组(超过下标范围报错, 或者使用动态数组)+index 控制
index: 新进来的数要放的位置
一旦发现 index 超过了下标的范围给用户报错, 标记栈已经满了
栈和队列的面试题
1. 实现最小栈
leetcode
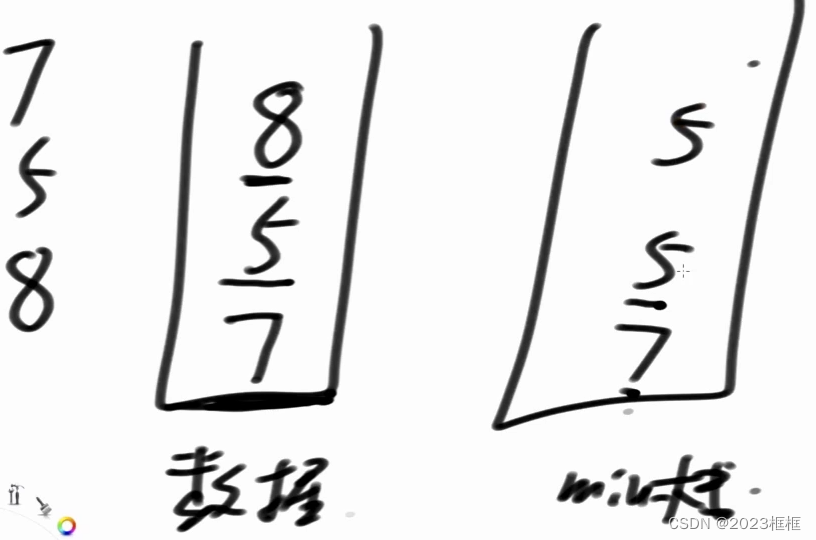
class MinStack {
public:
MinStack() {
}
void push(int val) {
st.push(val);
if(minst.empty()||val<=minst.top())
{
minst.push(val);
}
}
void pop() {
if(!st.empty())
{
if(st.top()==minst.top())
{
minst.pop();
}
st.pop();
}
}
int top() {
return st.top();
}
int getMin() {
return minst.top();
}
private:
stack<int> st;
stack<int> minst;
};
2. 两个栈实现一个队列
leetcode
3.两个队列实现一个栈
leetcode
4.用栈实现图的广度优先遍历
结合第2题
5.用队列实现图的深度优先遍历
结合第3题
递归
Master公式可以计算递归时间复杂度



![K8S[Kubernetes]快速安装组件(Kubectl Kubeadam Kubeinit)](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/d5a107bb133a4833bf0da0718236de3d.png)