今天我们分析seata分布式事务1.4版本TM注册到全流程的源码,这也是事务执行的核心开始:
首先分为客户端TM和服务端TC,业务发起肯定在TM端,接受在TC端。
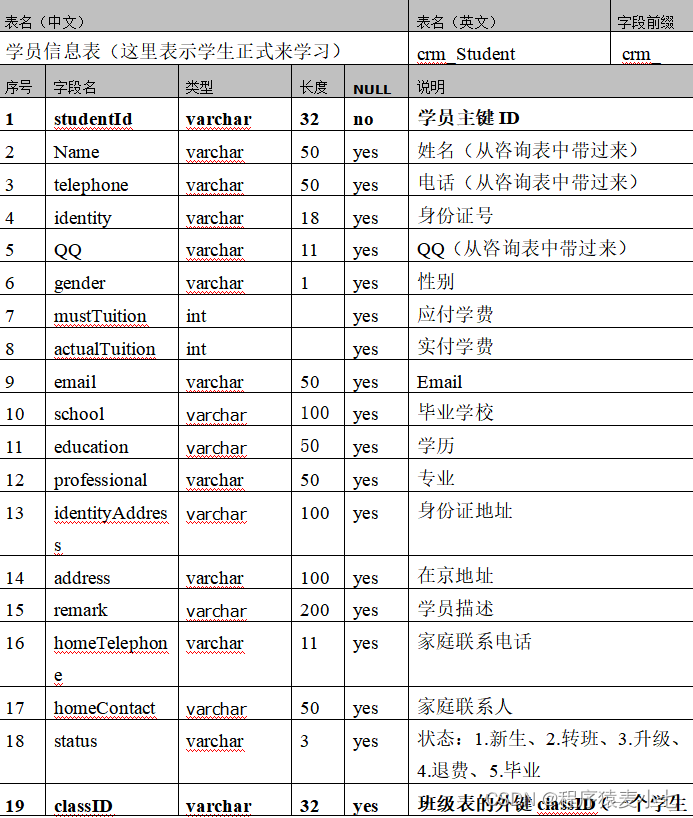
整体类图:
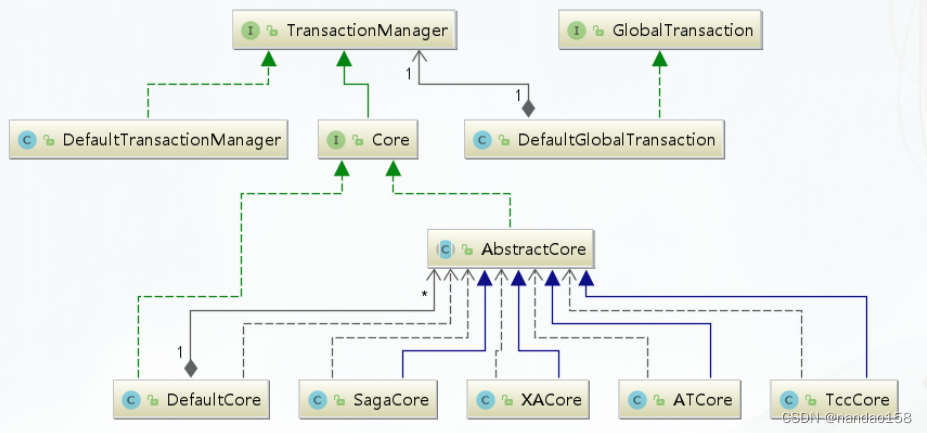
一、业务入口TM端:
1、GlobalTransactionalInterceptor 核心类,业务
怎么流转到此,前几篇已经分享过,此篇重点分析全局事务开启,事务发起:
@Override
public Object invoke(final MethodInvocation methodInvocation) throws Throwable {
Class<?> targetClass =
methodInvocation.getThis() != null ? AopUtils.getTargetClass(methodInvocation.getThis()) : null;
Method specificMethod = ClassUtils.getMostSpecificMethod(methodInvocation.getMethod(), targetClass);
if (specificMethod != null && !specificMethod.getDeclaringClass().equals(Object.class)) {
final Method method = BridgeMethodResolver.findBridgedMethod(specificMethod);
// 获取@GlobalTransactional注解
final GlobalTransactional globalTransactionalAnnotation =
getAnnotation(method, targetClass, GlobalTransactional.class);
// 获取@GlobalLock 注解
final GlobalLock globalLockAnnotation = getAnnotation(method, targetClass, GlobalLock.class);
boolean localDisable = disable || (degradeCheck && degradeNum >= degradeCheckAllowTimes);
if (!localDisable) {
if (globalTransactionalAnnotation != null) {//再次判断是否加注解
//如果方法上面有注解,则会执行到这里,核心方法,进入
return handleGlobalTransaction(methodInvocation, globalTransactionalAnnotation);
} else if (globalLockAnnotation != null) {
return handleGlobalLock(methodInvocation, globalLockAnnotation);// 执行@GlobalLock事务
}
}
}
return methodInvocation.proceed();//如果没有全局事务注解,直接调用目标方法
}
点击:return handleGlobalTransaction(methodInvocation, globalTransactionalAnnotation);
Object handleGlobalTransaction(final MethodInvocation methodInvocation,
final GlobalTransactional globalTrxAnno) throws Throwable {
boolean succeed = true;
try {
/**
* 直接使用内部类创建了一个TransactionalExecutor实例
* TransactionalExecutor实例创建后,它包含了当前事务注解的信息和被代理执行的方法,
* 接着就会调用执行模板TransactionalTemplate的execute方法,该方法是执行全局事务的核心方法,其中包含了AT模式下,两个阶段处理逻辑
*/
return transactionalTemplate.execute(new TransactionalExecutor() {
@Override
public Object execute() throws Throwable {
/**
* 在JDBC 操作数据库时,执行SQL 语句的是PreparedStatement,
* 在Seata 中其代理类为 PreparedStatementProxy,其execute 方法会调用ExecuteTemplate的execute方法。
* 走代理类比较抽象
*/
return methodInvocation.proceed();//核心业务方法
}
// 自定义或者格式化生成事务的名称
public String name() {
String name = globalTrxAnno.name();
if (!StringUtils.isNullOrEmpty(name)) {
return name;
}
return formatMethod(methodInvocation.getMethod());
}
@Override// 将注解封装为成TransactionInfo对象
public TransactionInfo getTransactionInfo() {
// reset the value of timeout 超时时间
int timeout = globalTrxAnno.timeoutMills();
if (timeout <= 0 || timeout == DEFAULT_GLOBAL_TRANSACTION_TIMEOUT) {
timeout = defaultGlobalTransactionTimeout;
}
TransactionInfo transactionInfo = new TransactionInfo();
transactionInfo.setTimeOut(timeout);
transactionInfo.setName(name());//事务名=
transactionInfo.setPropagation(globalTrxAnno.propagation());//传播行为
transactionInfo.setLockRetryInternal(globalTrxAnno.lockRetryInternal());
transactionInfo.setLockRetryTimes(globalTrxAnno.lockRetryTimes());
// 回滚规则
Set<RollbackRule> rollbackRules = new LinkedHashSet<>();
for (Class<?> rbRule : globalTrxAnno.rollbackFor()) {
rollbackRules.add(new RollbackRule(rbRule));
}
for (String rbRule : globalTrxAnno.rollbackForClassName()) {
rollbackRules.add(new RollbackRule(rbRule));
}
for (Class<?> rbRule : globalTrxAnno.noRollbackFor()) {
rollbackRules.add(new NoRollbackRule(rbRule));
}
for (String rbRule : globalTrxAnno.noRollbackForClassName()) {
rollbackRules.add(new NoRollbackRule(rbRule));
}
transactionInfo.setRollbackRules(rollbackRules);
return transactionInfo;
}
});
} catch (TransactionalExecutor.ExecutionException e) {
TransactionalExecutor.Code code = e.getCode();
switch (code) {
case RollbackDone:
throw e.getOriginalException();
case BeginFailure:
succeed = false;
failureHandler.onBeginFailure(e.getTransaction(), e.getCause());
throw e.getCause();
case CommitFailure:
succeed = false;
failureHandler.onCommitFailure(e.getTransaction(), e.getCause());
throw e.getCause();
case RollbackFailure:
failureHandler.onRollbackFailure(e.getTransaction(), e.getOriginalException());
throw e.getOriginalException();
case RollbackRetrying:
failureHandler.onRollbackRetrying(e.getTransaction(), e.getOriginalException());
throw e.getOriginalException();
default:
throw new ShouldNeverHappenException(String.format("Unknown TransactionalExecutor.Code: %s", code));
}
} finally {
if (degradeCheck) {
EVENT_BUS.post(new DegradeCheckEvent(succeed));
}
}
}点击:transactionalTemplate.execute(new TransactionalExecutor(),里面会执行
execute、getTransactionInfo 方法,和普通的get、set一个道理。
2、来到 TransactionalTemplate 类:
public Object execute(TransactionalExecutor business) throws Throwable {
// Get transactionInfo 取事务信息,上一步封装好的,可以去看一下 进入上一步 GlobalTransactionalInterceptor的(handleGlobalTransaction中的)getTransactionInfo()构造方法
TransactionInfo txInfo = business.getTransactionInfo();
if (txInfo == null) {
throw new ShouldNeverHappenException("transactionInfo does not exist");
}
// 1.1 Get current transaction, if not null, the tx role is 'GlobalTransactionRole.Participant'.
// 1. 从RootContext中获取xid,没有则返回NULL,
// 这里是全局事务发起方,所有没有,直接返回NULL
// 如果是被调用方,则会存在传递过来的xid,使用xid创建GlobalTransaction 对象
GlobalTransaction tx = GlobalTransactionContext.getCurrent();//开启事务
// 1.2 Handle the transaction propagation.
// 事务传播行为,默认为REQUIRED
// REQUIRED:如果本来有事务,则加入该事务,如果没有事务,则创建新的事务
Propagation propagation = txInfo.getPropagation();
SuspendedResourcesHolder suspendedResourcesHolder = null;
//事务的传播机制, 根据不同的传播行为,执行不同的逻辑
try {
switch (propagation) {
case NOT_SUPPORTED:
// If transaction is existing, suspend it.
if (existingTransaction(tx)) {
suspendedResourcesHolder = tx.suspend();
}
// Execute without transaction and return.
return business.execute();
case REQUIRES_NEW:
// If transaction is existing, suspend it, and then begin new transaction.
if (existingTransaction(tx)) {
suspendedResourcesHolder = tx.suspend();
tx = GlobalTransactionContext.createNew();//进入
}
// Continue and execute with new transaction
break;
case SUPPORTS:
// If transaction is not existing, execute without transaction.
if (notExistingTransaction(tx)) {
return business.execute();
}
// Continue and execute with new transaction
break;
case REQUIRED://默认的事务类型,如果当前没有事务,则新建事务;如果当前存在事务,则加入当前事务,合并成一个事务
// If current transaction is existing, execute with current transaction,
// else continue and execute with new transaction.
break;
case NEVER:
// If transaction is existing, throw exception.
if (existingTransaction(tx)) {
throw new TransactionException(
String.format("Existing transaction found for transaction marked with propagation 'never', xid = %s"
, tx.getXid()));
} else {
// Execute without transaction and return.
return business.execute();
}
case MANDATORY:
// If transaction is not existing, throw exception.
if (notExistingTransaction(tx)) {
throw new TransactionException("No existing transaction found for transaction marked with propagation 'mandatory'");
}
// Continue and execute with current transaction.
break;
default:
throw new TransactionException("Not Supported Propagation:" + propagation);
}
// 1.3 If null, create new transaction with role 'GlobalTransactionRole.Launcher'.
// 4. 不存在全局事务信息,创建一个
if (tx == null) {
tx = GlobalTransactionContext.createNew();
}
// set current tx config to holder
GlobalLockConfig previousConfig = replaceGlobalLockConfig(txInfo);
try {
// 2. If the tx role is 'GlobalTransactionRole.Launcher', send the request of beginTransaction to TC,
// else do nothing. Of course, the hooks will still be triggered.
beginTransaction(txInfo, tx);//核心代码, 开启全局事务,进去看看
Object rs;
try {
// Do Your Business 调用业务方法,即被代理方法,到 GlobalTransactionalInterceptor
// 里面(handleGlobalTransaction的)TransactionalExecutor实现的方法
rs = business.execute();
} catch (Throwable ex) {
// 3. The needed business exception to rollback.发生异常 二阶段全局回滚 TM 发起回滚
completeTransactionAfterThrowing(txInfo, tx, ex);
throw ex;
}
// 4. everything is fine, commit.如果没有异常,进行二阶段提交,去调用告诉TC端,可以(循环)触发二阶段提交了,
// TC端收到各分支请求后,开始循环二阶段提交,重点!!!
commitTransaction(tx);
return rs;
} finally {
//5. clear 释放资源
resumeGlobalLockConfig(previousConfig);
triggerAfterCompletion();
cleanUp();
}
} finally {
// If the transaction is suspended, resume it.
if (suspendedResourcesHolder != null) {
tx.resume(suspendedResourcesHolder);
}
}
}创建事务对象:tx = GlobalTransactionContext.createNew();
public static GlobalTransaction createNew() {
return new DefaultGlobalTransaction();//直接创建了一个默认的DefaultGlobalTransaction且使用的无参构造函数
}进入:
DefaultGlobalTransaction() {
//创建了一个角色为GlobalTransactionRole.Launcher 事物的发起者的对象,从这里就已经区分出了当前是 TM 还是 RM 角色
this(null, GlobalStatus.UnKnown, GlobalTransactionRole.Launcher);
}进入:TransactionManagerHolder为创建单例TransactionManager的工厂,可以使用EnhancedServiceLoader的spi机制加载用户自定义的类,默认为 DefaultTransactionManager。
DefaultGlobalTransaction(String xid, GlobalStatus status, GlobalTransactionRole role) {
this.transactionManager = TransactionManagerHolder.get();//核心创建
this.xid = xid;
this.status = status;
this.role = role;
}进入:
public static TransactionManager get() {
if (SingletonHolder.INSTANCE == null) {
throw new ShouldNeverHappenException("TransactionManager is NOT ready!");
}
return SingletonHolder.INSTANCE;//实例化对象
}进入:
private static class SingletonHolder {
private static TransactionManager INSTANCE = null;
static {
try {
INSTANCE = EnhancedServiceLoader.load(TransactionManager.class);
LOGGER.info("TransactionManager Singleton {}", INSTANCE);
} catch (Throwable anyEx) {
LOGGER.error("Failed to load TransactionManager Singleton! ", anyEx);
}
}
}验证SPI机制:
3、开启全局事务:beginTransaction(txInfo, tx);//核心代码, 开启全局事务,进去看看
private void beginTransaction(TransactionInfo txInfo, GlobalTransaction tx) throws TransactionalExecutor.ExecutionException {
try {// 开启全局事务之前钩子,可以业务自定义实现
triggerBeforeBegin();
tx.begin(txInfo.getTimeOut(), txInfo.getName());//重要的开始,进入DefaultGlobalTransaction子类
triggerAfterBegin();// 开启全局事务之后钩子,可以业务自定义实现
} catch (TransactionException txe) {
throw new TransactionalExecutor.ExecutionException(tx, txe,
TransactionalExecutor.Code.BeginFailure);
}
}点击:tx.begin(txInfo.getTimeOut(), txInfo.getName())
4、来到其子类DefaultGlobalTransaction:
DefaultGlobalTransaction是GlobalTransaction接口的默认实现,它持有TransactionManager对象,默认开启事务超时时间为60秒,默认名称为default,因为调用者的业务方法可能多重嵌套创建多个GlobalTransaction对象开启事务方法,因此GlobalTransaction有GlobalTransactionRole角色属性,只有Launcher角色的才有开启、提交、回滚事务的权利。

进入 :
@Override
public void begin(int timeout, String name) throws TransactionException {
if (role != GlobalTransactionRole.Launcher) {
assertXIDNotNull();
if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOGGER.debug("Ignore Begin(): just involved in global transaction [{}]", xid);
}
return;
}
assertXIDNull();//全局事务id现在为空,如果不为空报错
String currentXid = RootContext.getXID();
if (currentXid != null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Global transaction already exists," +
" can't begin a new global transaction, currentXid = " + currentXid);
}//创建返回全局事务id(从TC服务端返回),连接服务端开启全局事务,核心代码,进入 DefaultTransactionManager
xid = transactionManager.begin(null, null, name, timeout);
status = GlobalStatus.Begin;
RootContext.bind(xid);//放在本地ThreadLocal中
if (LOGGER.isInfoEnabled()) {
LOGGER.info("Begin new global transaction [{}]", xid);
}
}点击 xid = transactionManager.begin(null, null, name, timeout);
5、来到: DefaultTransactionManager implements TransactionManager
@Override
public String begin(String applicationId, String transactionServiceGroup, String name, int timeout)
throws TransactionException {
/**
* 这里非常重要设置 全局事务开始的类型,return MessageType.TYPE_GLOBAL_BEGIN;
* 对应TC端 AbstractNettyRemotingServer 执行 channelRead 方法时,流转转到 processMessage 方法的
* final Pair<RemotingProcessor, ExecutorService> pair = this.processorTable.get((int) messageTypeAware.getTypeCode());
* 在通过 pair.getFirst().process(ctx, rpcMessage); 获取进入到 ServerOnRequestProcessor
* 为NettyRemotingServer 中这样配置的,如下:
* super.registerProcessor(MessageType.TYPE_GLOBAL_BEGIN, onRequestProcessor, messageExecutor);//全局事务开始
*/
GlobalBeginRequest request = new GlobalBeginRequest();
request.setTransactionName(name);
request.setTimeout(timeout);
//远程调用通知seata服务端,在下游配置中心取服务端相关ip等信息,这里发送请求就是使用的Netty了
GlobalBeginResponse response = (GlobalBeginResponse) syncCall(request);
if (response.getResultCode() == ResultCode.Failed) {
throw new TmTransactionException(TransactionExceptionCode.BeginFailed, response.getMsg());
}
/**
* 到这里大家应该明白了 xid 的生成,那是怎么发送给 RM 的呢?
* 上面再梳理过程的时候提到 Seata 重写了 OpenFeign 客户端,将xid 放入了 header中进行传播,
* 这个重写的客户端就是 SeataFeignClient,这个在 spring-starter-alibaba-seata包中,参考
* https://blog.csdn.net/qq_43692950/article/details/123457812?spm=1001.2101.3001.6661.1&utm_medium=distribute.pc_relevant_t0.none-task-blog-2%7Edefault%7ECTRLIST%7ERate-1-123457812-blog-108329792.pc_relevant_multi_platform_whitelistv6&depth_1-utm_source=distribute.pc_relevant_t0.none-task-blog-2%7Edefault%7ECTRLIST%7ERate-1-123457812-blog-108329792.pc_relevant_multi_platform_whitelistv6&utm_relevant_index=1
* 这样 RPC 进来的请求,如果是全局事物的请求,就会将 全局事物ID xid 存入当前 ThreadLocal 中,这样就和最初的分析所呼应了。
*/
return response.getXid();
}点击: (GlobalBeginResponse) syncCall(request);
private AbstractTransactionResponse syncCall(AbstractTransactionRequest request) throws TransactionException {
try {//客户端向服务端TC发送请求,返回数据。
return (AbstractTransactionResponse) TmNettyRemotingClient.getInstance().sendSyncRequest(request);
} catch (TimeoutException toe) {
throw new TmTransactionException(TransactionExceptionCode.IO, "RPC timeout", toe);
}
}点击 sendSyncRequest(request);
6、来到:AbstractNettyRemotingClient
@Override//TM / RM 发送请求的代码
public Object sendSyncRequest(Object msg) throws TimeoutException {
//通过事务组,负载选择一个服务端实例
String serverAddress = loadBalance(getTransactionServiceGroup(), msg);
int timeoutMillis = NettyClientConfig.getRpcRequestTimeout();//超时时间设置
//组装请求对象,包括请求ID,序列号方式等
RpcMessage rpcMessage = buildRequestMessage(msg, ProtocolConstants.MSGTYPE_RESQUEST_SYNC);
// send batch message
// put message into basketMap, @see MergedSendRunnable
// 如果允许批量发送请求
if (NettyClientConfig.isEnableClientBatchSendRequest()) {
// send batch message is sync request, needs to create messageFuture and put it in futures.
MessageFuture messageFuture = new MessageFuture();
messageFuture.setRequestMessage(rpcMessage);
messageFuture.setTimeout(timeoutMillis);
// 生产MessageFuture放到futures中,key为请求ID
futures.put(rpcMessage.getId(), messageFuture);
// put message into basketMap
// 将请求对象按照server地址放入basketMap中,供MergedSendRunnable任务从basketMap拉取请求,批量发送到server端
BlockingQueue<RpcMessage> basket = CollectionUtils.computeIfAbsent(basketMap, serverAddress,
key -> new LinkedBlockingQueue<>());
if (!basket.offer(rpcMessage)) {
LOGGER.error("put message into basketMap offer failed, serverAddress:{},rpcMessage:{}",
serverAddress, rpcMessage);
return null;
}
if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOGGER.debug("offer message: {}", rpcMessage.getBody());
}
// 生产消费模式,唤醒MergedSendRunnable线程
if (!isSending) {
synchronized (mergeLock) {
mergeLock.notifyAll();
}
}
try {
// TC 服务端返回的响应最终会到ClientOnResponseProcessor进行处理
// 通过ClientOnResponseProcessor关联MessageFuture获取结果
return messageFuture.get(timeoutMillis, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
} catch (Exception exx) {
LOGGER.error("wait response error:{},ip:{},request:{}",
exx.getMessage(), serverAddress, rpcMessage.getBody());
if (exx instanceof TimeoutException) {
throw (TimeoutException) exx;
} else {
throw new RuntimeException(exx);
}
}
} else {
Channel channel = clientChannelManager.acquireChannel(serverAddress);
//正式继续调用
return super.sendSync(channel, rpcMessage, timeoutMillis);
}
}点击 return super.sendSync(channel, rpcMessage, timeoutMillis);
7、进入:AbstractNettyRemoting implements Disposable
protected Object sendSync(Channel channel, RpcMessage rpcMessage, long timeoutMillis) throws TimeoutException {
if (timeoutMillis <= 0) {
throw new FrameworkException("timeout should more than 0ms");
}
if (channel == null) {
LOGGER.warn("sendSync nothing, caused by null channel.");
return null;
}
MessageFuture messageFuture = new MessageFuture();
messageFuture.setRequestMessage(rpcMessage);
messageFuture.setTimeout(timeoutMillis);
futures.put(rpcMessage.getId(), messageFuture);
channelWritableCheck(channel, rpcMessage.getBody());
String remoteAddr = ChannelUtil.getAddressFromChannel(channel);
doBeforeRpcHooks(remoteAddr, rpcMessage);
//正式通过netty的writeAndFlush 标准接口调用,并监听,写入数据;谁实现了ChannelFutureListener 接口,后续详细看看
//跳过源码,下一步是到了 AbstractNettyRemotingServer extends AbstractNettyRemoting implements RemotingServer( channelRead(final ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg))
channel.writeAndFlush(rpcMessage).addListener((ChannelFutureListener) future -> {
if (!future.isSuccess()) {
MessageFuture messageFuture1 = futures.remove(rpcMessage.getId());
if (messageFuture1 != null) {
messageFuture1.setResultMessage(future.cause());
}
destroyChannel(future.channel());
}
});
try {//异步获取调用结果 等待结果,
// TC 服务端返回的响应最终会到ClientOnResponseProcessor进行处理
// 通过ClientOnResponseProcessor关联MessageFuture获取结果
Object result = messageFuture.get(timeoutMillis, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
doAfterRpcHooks(remoteAddr, rpcMessage, result);
return result;
} catch (Exception exx) {
LOGGER.error("wait response error:{},ip:{},request:{}", exx.getMessage(), channel.remoteAddress(),
rpcMessage.getBody());
if (exx instanceof TimeoutException) {
throw (TimeoutException) exx;
} else {
throw new RuntimeException(exx);
}
}
}
二、TC端接收处理:下期详细分析,敬请启动!!!
1、
2、
3、
4、
5、
8、
9、
10、