在之前的博客当中我们已经学习了栈和队列。在本次的博客当中我们就来学习一下怎么将栈和队列进行相互转换。
栈和队列的相互转换其实是两道OJ题。如果在leetcode上面刷过题的小伙伴们可能早就见过这两种数据结构的相互转换。下面我们就来分别讲解一下这两道OJ题目的编写思路。
🌵用队列实现栈
题目详情如下:
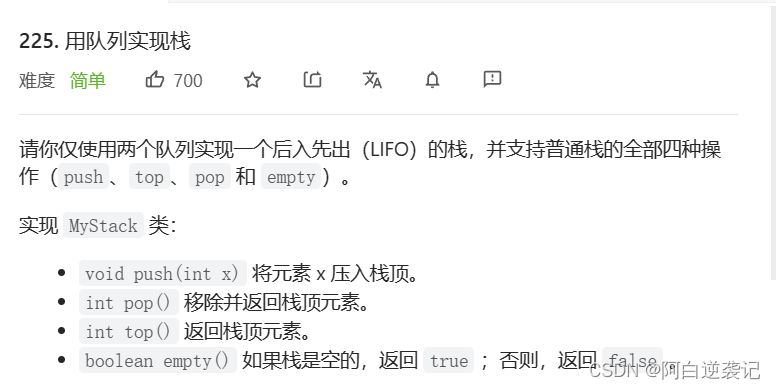 题目中要求我们使用两个队列实现栈的结构。我们在这里重新来梳理一下队列和栈的结构特点。
题目中要求我们使用两个队列实现栈的结构。我们在这里重新来梳理一下队列和栈的结构特点。
⭐队列:队列只能在队尾插入数据,只能从队头输出数据。先进入队列的数据也就会先被读取。
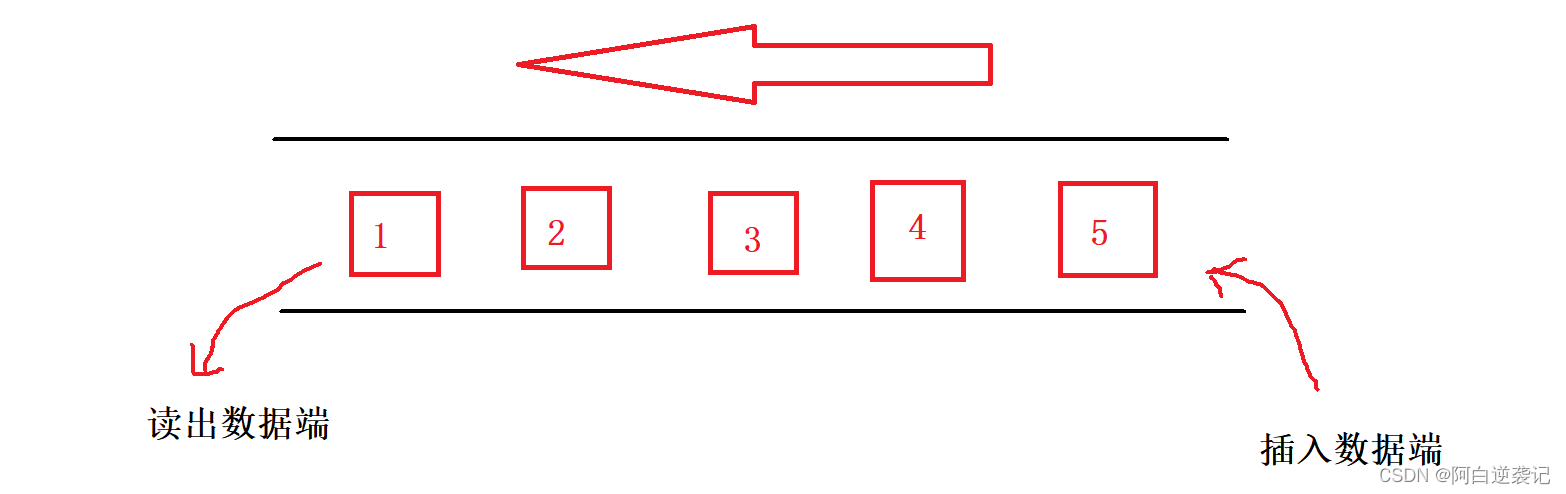 ⭐栈:栈只能从队头插入数据,也只能从对头输出数据。所以在咋还能当中我们只能够取出最近插入的数据。
⭐栈:栈只能从队头插入数据,也只能从对头输出数据。所以在咋还能当中我们只能够取出最近插入的数据。
 在结构上面栈和队列还是有很大的区别的,所以我们需要使用一定的方式进行栈和队列的相互转换。回到我们本题。
在结构上面栈和队列还是有很大的区别的,所以我们需要使用一定的方式进行栈和队列的相互转换。回到我们本题。
使用队列实现栈。也就是利用我们先入先出的数据存储方式实现先入后出的数据存储方式。题目中也给了我们一些相应的思路:使用两个队列。
我们先来构建两个队列:
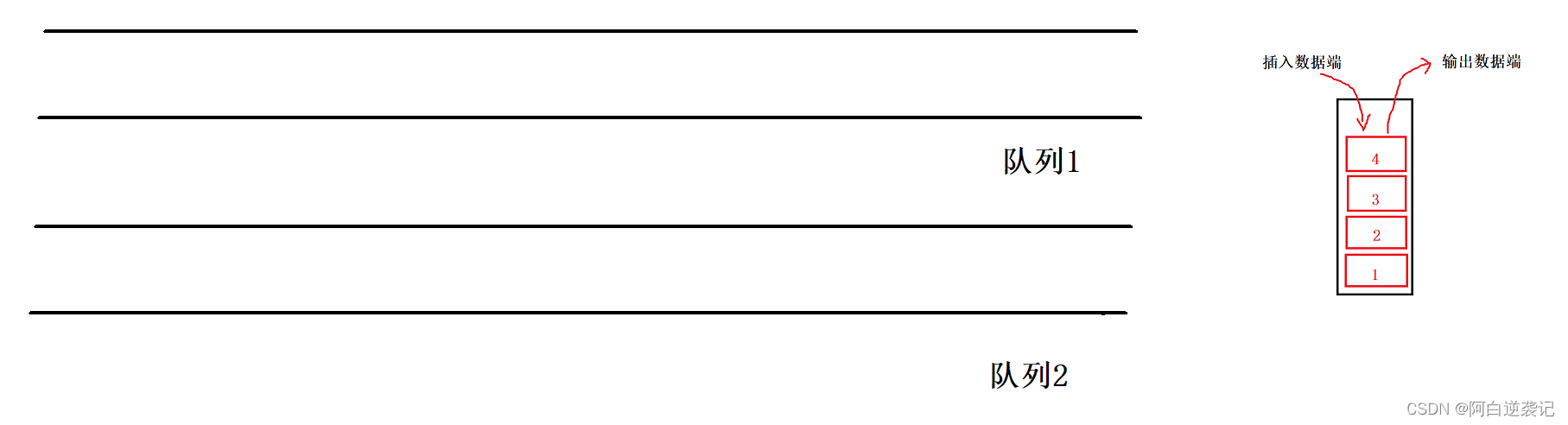 我们直接来说解题思路:我们构建完成两个队列之后可以尝试向一个队列当中插入数据。当我们想要取出数据的时候,根据栈的性质我们需要取得我们队列当中位于队尾的数据。但是又根据队列的性质我们只允许从对头拿出数据,所以我们可以先将队列1当中的数据除了最后一个之外都全部拿到另一个空队列当中。
我们直接来说解题思路:我们构建完成两个队列之后可以尝试向一个队列当中插入数据。当我们想要取出数据的时候,根据栈的性质我们需要取得我们队列当中位于队尾的数据。但是又根据队列的性质我们只允许从对头拿出数据,所以我们可以先将队列1当中的数据除了最后一个之外都全部拿到另一个空队列当中。 当我们的队列当中是剩下最后一个元素的时候,这个元素就是我们队列当中的队尾元素,也就是栈中需要出栈的元素。我们可以所以我们如果想要出栈的话只需要重复上述的操作即可。
当我们的队列当中是剩下最后一个元素的时候,这个元素就是我们队列当中的队尾元素,也就是栈中需要出栈的元素。我们可以所以我们如果想要出栈的话只需要重复上述的操作即可。 所以在队列实现栈的代码的编写当中我们需要实现一个队列的结构,进而构建出两个队列,之后根据上面分析的思路进一步的编写代码。其中我们的队列可以复用以前实现过的队列当中的代码。
所以在队列实现栈的代码的编写当中我们需要实现一个队列的结构,进而构建出两个队列,之后根据上面分析的思路进一步的编写代码。其中我们的队列可以复用以前实现过的队列当中的代码。
typedef int DataType;
typedef struct QNode
{
struct QNode* next;
DataType data;
}QNode;
typedef struct Queue
{
struct QNode* head;
struct QNode* tail;
int size;
}Queue;
//初始化队列
void QueueInit(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;
pq->size = 0;
}
//开辟一个新的节点
QNode* BuyNewNode(DataType x)
{
QNode* ret = (QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode));
if (ret == NULL)
{
perror("malloc");
return NULL;
}
ret->data = x;
ret->next = NULL;
return ret;
}
//向队列当中插入数据
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, DataType x)
{
assert(pq);
QNode* newnode = BuyNewNode(x);
assert(newnode);
if (pq->size == 0)
{
pq->head = newnode;
pq->tail = newnode;
}
else
{
pq->tail->next = newnode;
pq->tail = newnode;
}
pq->size++;
}
//删除队列当中的数据
void QueuePop(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
if (pq->size == 0)
{
printf("队列为空不能进行数据删除。");
return;
}
QNode* ret = pq->head;
pq->head = pq->head->next;
free(ret);
ret = NULL;
pq->size--;
}
//判断队列的大小
DataType QueueSize(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
return pq->size;
}
//队列的判空操作
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
if (pq->size == 0)
{
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
//返回队列的队头元素
DataType QueueFront(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
return pq->head->data;
}
//返回队列的队尾元素
DataType QueueBack(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
return pq->tail->data;
}
//销毁队列
void QueueDestory(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
while (pq->head)
{
QNode* ret = pq->head;
pq->head = pq->head->next;
free(ret);
ret = NULL;
}
}
typedef struct {
Queue s1;
Queue s2;
} MyStack;
MyStack* myStackCreate() {
MyStack*ret=(MyStack*)malloc(sizeof(MyStack));
assert(ret);
QueueInit(&(ret->s1));
QueueInit(&(ret->s2));
return ret;
}
void myStackPush(MyStack* obj, int x)
{
//当第二个队列为空时,向第一个队列当中插入数据
if(QueueEmpty(&obj->s2))
{
QueuePush(&obj->s1,x);
}
//当第二个队列不为空的时候就向第一个队列当中插入数据
else
{
QueuePush(&obj->s2,x);
}
}
int myStackPop(MyStack* obj) {
//将不为空的队列数据除了最后一个全部移到另一个队列当中
if(QueueEmpty(&obj->s1))
{
//判断当前数据是否为最后一个要删除的数据
while(QueueSize(&obj->s2)!=1)
{
DataType ret=QueueFront(&obj->s2);
QueuePush(&obj->s1,ret);
QueuePop(&obj->s2);
}
DataType tmp=QueueFront(&obj->s2);
QueuePop(&obj->s2);
return tmp;
}
else
{
while(QueueSize(&obj->s1)!=1)
{
DataType ret=QueueFront(&obj->s1);
QueuePush(&obj->s2,ret);
QueuePop(&obj->s1);
}
DataType tmp=QueueFront(&obj->s1);
QueuePop(&obj->s1);
return tmp;
}
}
int myStackTop(MyStack* obj)
{
if(QueueEmpty(&obj->s1))
{
//判断当前数据是否为最后一个数据
while(QueueSize(&obj->s2)!=1)
{
DataType ret=QueueFront(&obj->s2);
QueuePush(&obj->s1,ret);
QueuePop(&obj->s2);
}
DataType tmp=QueueFront(&obj->s2);
QueuePush(&obj->s1,tmp);
QueuePop(&obj->s2);
return tmp;
}
else
{
while(QueueSize(&obj->s1)!=1)
{
DataType ret=QueueFront(&obj->s1);
QueuePush(&obj->s2,ret);
QueuePop(&obj->s1);
}
DataType tmp=QueueFront(&obj->s1);
QueuePush(&obj->s2,tmp);
QueuePop(&obj->s1);
return tmp;
}
}
bool myStackEmpty(MyStack* obj)
{
if(QueueEmpty(&obj->s1)&&QueueEmpty(&obj->s2))
{
return true;
}
return false;
}
void myStackFree(MyStack* obj)
{
//当队列1不为空时,释放队列1当中的所有元素
while(!QueueEmpty(&obj->s1))
{
QueuePop(&obj->s1);
}
while(!QueueEmpty(&obj->s2))
{
QueuePop(&obj->s2);
}
}
我们使用队列实现栈的代码的逻辑如上所示。
🌵用栈实现队列
使用队列实现完栈之后就轮到使用栈实现队列了。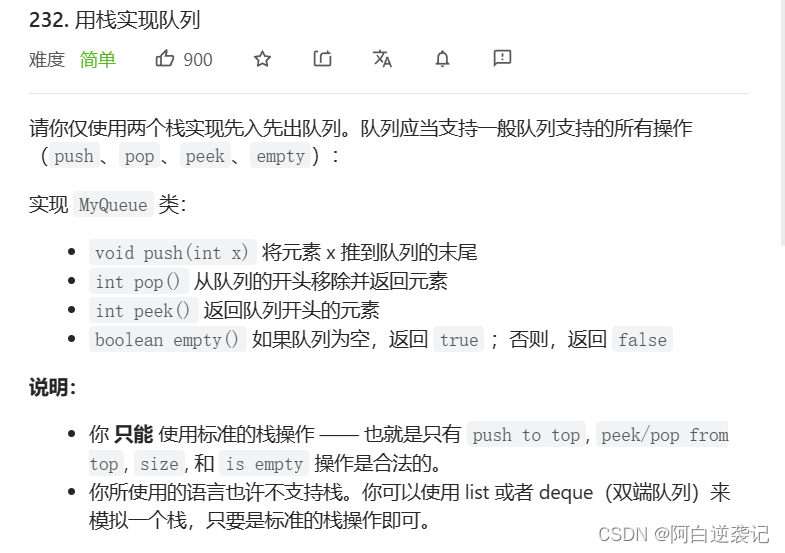
根据题目中的要求我们同样需要构建出两个栈以实现我们队列当中的功能。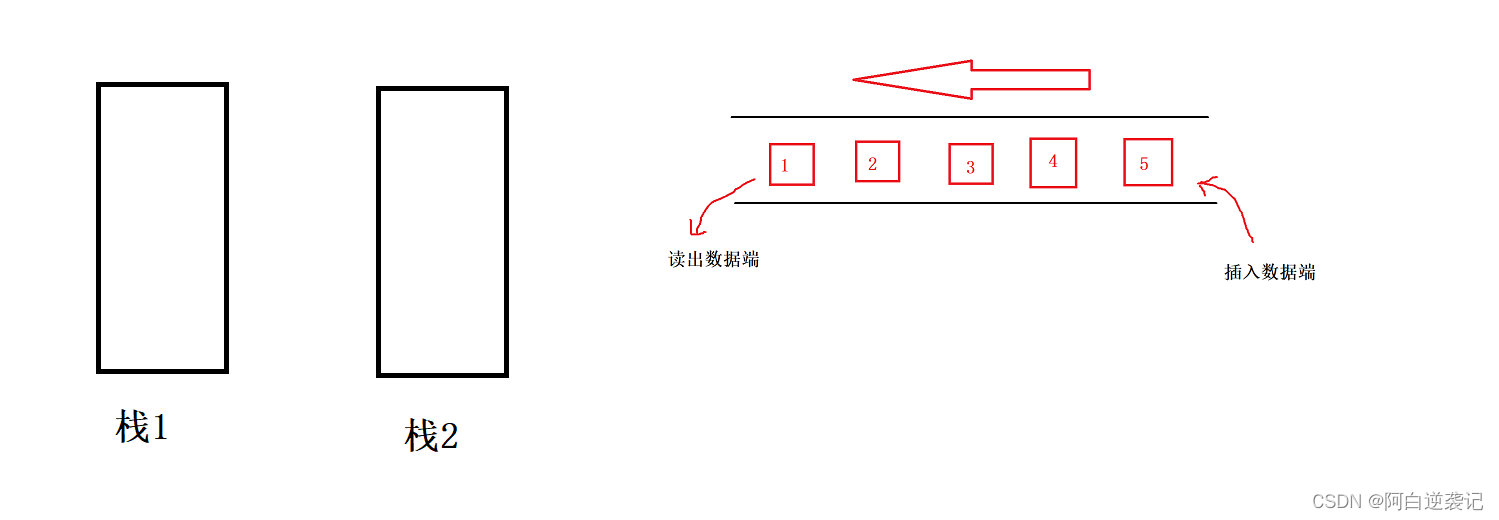 我们的栈每次只能从栈顶插入数据从栈顶拿出数据,当我们想要以队列的形式拿出数据的时候,也就是从栈的底端拿出数据,我们就必须一个一个将数据全部搬运到另一个栈当中。我们剩下的最后一个数据也就是我们以队列的形式想要出的数据。
我们的栈每次只能从栈顶插入数据从栈顶拿出数据,当我们想要以队列的形式拿出数据的时候,也就是从栈的底端拿出数据,我们就必须一个一个将数据全部搬运到另一个栈当中。我们剩下的最后一个数据也就是我们以队列的形式想要出的数据。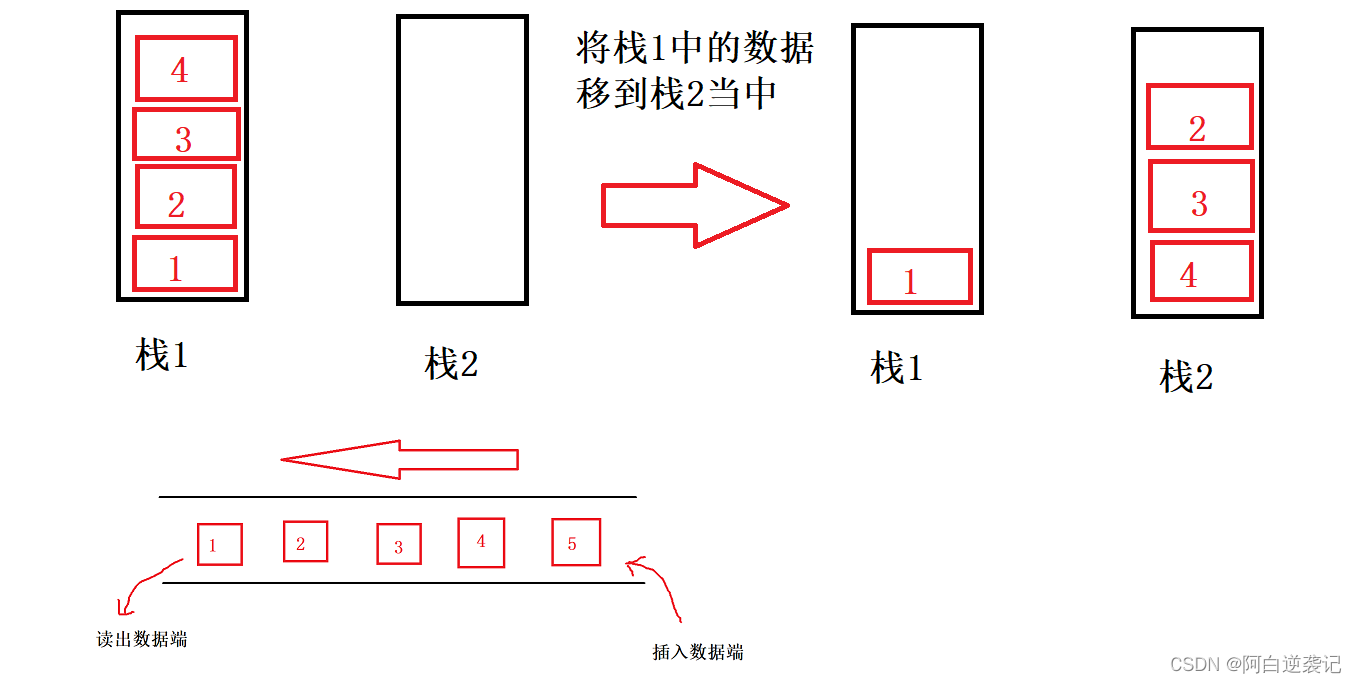 我们会发现我们移入栈2当中的数据全部已经是排好顺序的了,那么我们每次出数据的时候只需要从栈2当中拿出数据得到的就是我们队头的数据。
我们会发现我们移入栈2当中的数据全部已经是排好顺序的了,那么我们每次出数据的时候只需要从栈2当中拿出数据得到的就是我们队头的数据。
但是我们想要继续插入数据应该怎么办呢?如果直接插入栈2当中会是我们栈中元素顺序混乱,那么假如我们将全部数据都转入栈2当中呢?栈1就会为空,之后我们想要输入数据就向栈1当中输入,想要拿出数据据从栈2当中拿,当我们栈2当中的数据全部拿完时,我们再将栈1当中的数据全部转入栈2当中即可。
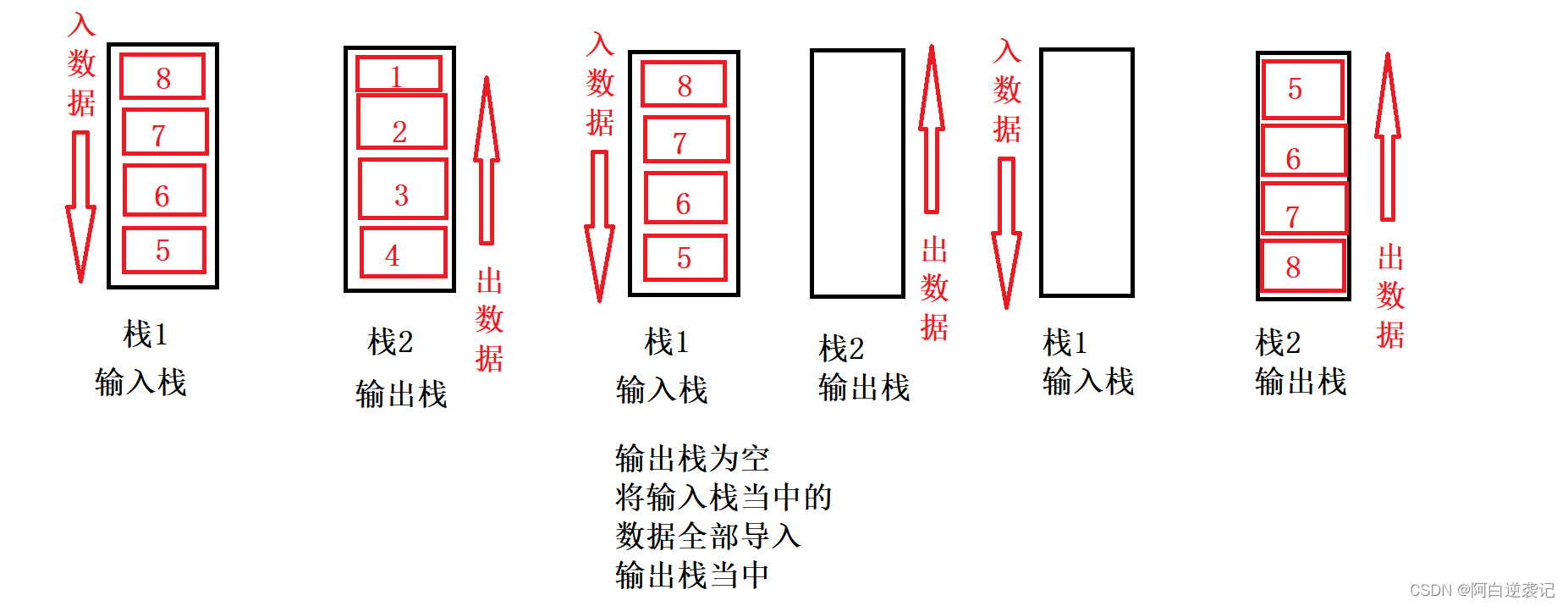 重复上述步骤之后我们就可以使用栈实现一个队列了。具体的代码如下:
重复上述步骤之后我们就可以使用栈实现一个队列了。具体的代码如下:
typedef int DataType;
typedef struct STstack
{
DataType* data;
int top;
int capicity;
}ST;
//栈的初始化
void STInit(ST* s1)
{
assert(s1);
s1->data = (ST*)malloc(sizeof(ST)*4);
s1->capicity = 4;
s1->top = 0;
}
//判断是否需要扩容
void checkcapicity(ST* s1)
{
if (s1->capicity > s1->top)
{
return;
}
else
{
//需要扩容进行扩容
ST*tmp= (ST*)realloc(s1->data,sizeof(ST) * s1->capicity*2);
if (tmp == NULL)
{
perror("malloc");
return;
}
s1->data = tmp;
s1->capicity *= 2;
}
}
//入栈函数
void STPush(ST* s1, DataType x)
{
assert(s1);
//判断是否需要扩容
checkcapicity(s1);
s1->data[s1->top] = x;
s1->top++;
}
//出栈函数
void STPop(ST* s1)
{
assert(s1);
//判断栈中是否存在数据,如果不存在数据就不可以进行删除
if (s1->top == 0)
{
printf("空栈不允许进行删除。");
return;
}
//如果不是空栈就删除栈顶元素
s1->top--;
}
//返回栈顶元素
DataType STTop(ST* s1)
{
assert(s1);
//判断栈中是否存在数据
assert(s1->top);
return s1->data[s1->top-1];
}
//判断栈为空
bool STEmpty(ST* s1)
{
assert(s1);
if (s1->top == 0)
{
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
//返回链表的大小
int STSize(ST* s1)
{
assert(s1);
return s1->top;
}
//销毁栈
void STDestory(ST* s1)
{
assert(s1);
free(s1->data);
s1->data == NULL;
s1->top = 0;
s1->capicity = 0;
}
typedef struct {
ST s1;
ST s2;
} MyQueue;
MyQueue* myQueueCreate()
{
MyQueue*ret=(MyQueue*)malloc(sizeof(MyQueue));
assert(ret);
STInit(&ret->s1);
STInit(&ret->s2);
return ret;
}
void myQueuePush(MyQueue* obj, int x)
{
//两个栈只在左边插入数据
STPush(&obj->s1,x);
}
int myQueuePop(MyQueue* obj)
{
if(STEmpty(&obj->s2))
{
while(!STEmpty(&obj->s1))
{
//将左边栈中数据导入右栈当中
DataType ret=STTop(&obj->s1);
STPop(&obj->s1);
STPush(&obj->s2,ret);
}
}
DataType tmp=STTop(&obj->s2);
STPop(&obj->s2);
return tmp;
}
int myQueuePeek(MyQueue* obj)
{
if(STEmpty(&obj->s2))
{
while(!STEmpty(&obj->s1))
{
//将左边栈中数据导入右栈当中
DataType ret=STTop(&obj->s1);
STPop(&obj->s1);
STPush(&obj->s2,ret);
}
}
DataType tmp=STTop(&obj->s2);
return tmp;
}
bool myQueueEmpty(MyQueue* obj)
{
if(STEmpty(&obj->s1)&&STEmpty(&obj->s2))
{
return true;
}
return false;
}
void myQueueFree(MyQueue* obj)
{
while(!STEmpty(&obj->s1))
{
STDestory(&obj->s1);
}
while(!STEmpty(&obj->s2))
{
STDestory(&obj->s2);
}
}
运行结果:
那么我们栈与队列的相互转换也就实现完毕了,本次博客的内容也就到此结束了。感谢您的观看,再见。