重新学习Spring很久了,也看了不少的视频,但是没有系统总结,容易忘记,网上寻找相关博客,也没有找到按照路线总结的,只能说不顺我心,所以自己总结一下!!!
从下面五个大点来
概述
在学Sping之前就学过Servlet,学Servlet的时候,就是传统的三层架构,dao层,service层,view层,当时学的时候也没觉得有问题
现在看呢,有两个问题
- 第一个是耦合高,一般是视图层访问业务层,业务层在调用dao层的一些方法,在Servlet中有业务层的对象作为成员变量,业务层又有dao层的对象作为成员变量,这个对象都是我们自己new出来的,这就是耦合性高😛。
- 第二个,如果我们想要对原有代码的功能进行扩展,例如想要在一个方法执行前后加上日志,或者是加上事务,需要去在原有代码上修改,这样可能会对代码的安全造成影响。
而我们的Spring就很好的解决了上面两个问题。
Spring是一个什么样的框架
Spring是一个轻量级非嵌入式框架
为什么说是轻量级的?核心包只有2mb
非嵌入式指的是AOP(Aspect Oriented Programming)面向切面编程,我的理解是提供了动态代理,可以在不修改原有代码的基础上通过注解或者配置对功能进行增强。
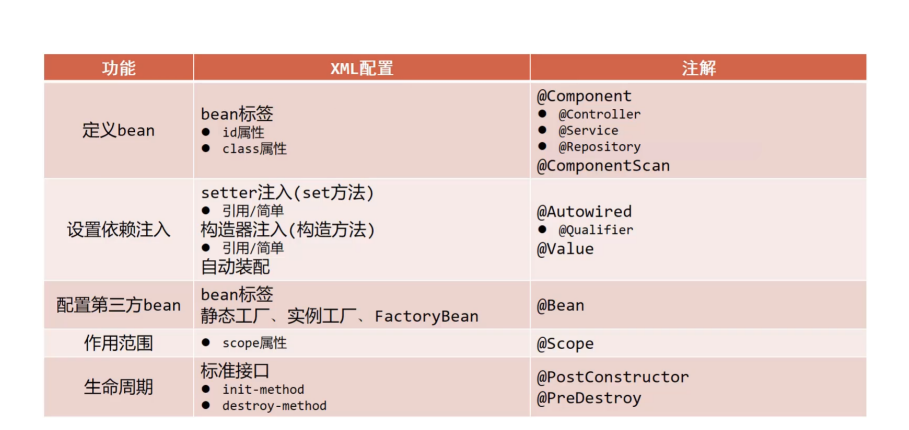
IOC
IOC(Inversion of Control) 意思是控制反转,上面说‘对象都是我们自己new出来的’,IOC则是把创建和管理的这个工作交给了Spring容器。
使用beanFactory
1,首先导入pom文件依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>5.3.7</version>
</dependency>
2,创建两个接口,两个实现类,如下
public interface MyDao {
}
public class MyDaoImpl implements MyDao {
}
public interface MyService {
}
public class MyServiceImpl implements MyService {
private MyDao myDao;
public void init(){
System.out.println("csh");
}
public void destroy(){
System.out.println("xh");
}
private List<String> list;
public void setList(List<String> list) {
this.list = list;
}
private Set<MyDao> myDaoList;
public void setMyDaoList(Set<MyDao> myDaoList) {
this.myDaoList = myDaoList;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "MyServiceImpl{" +
"myDao=" + myDao +
", list=" + list +
", myDaoList=" + myDaoList +
'}';
}
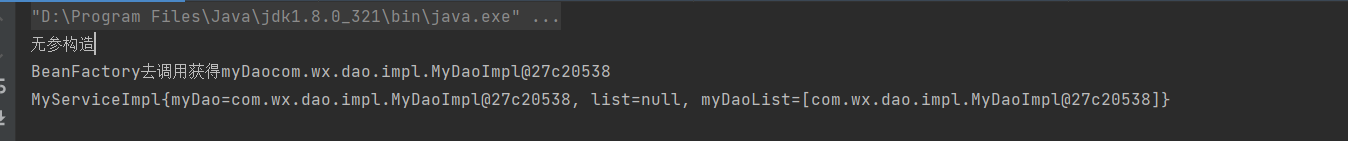
public void setMyDao(MyDao myDao){
this.myDao=myDao;
System.out.println("BeanFactory去调用获得myDao"+myDao);
}
public MyServiceImpl() {
System.out.println("无参构造");
}
public MyServiceImpl(String name) {
System.out.println("有参构造");
}
public void sing(){
System.out.println("正在唱歌");
}
3,测试代码如下
//创建工厂对象
DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = new DefaultListableBeanFactory();
//创建一个读取器(Xml文件的)
XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(beanFactory);
reader.loadBeanDefinitions("beans.xml");
//读取配置文件
Object bean = beanFactory.getBean("myService");
System.out.println(bean);
4,xml配置如下
<bean id="myService" class="com.wx.service.impl.MyServiceImpl" >
<property name="myDao" ref="myDao11"></property>
</bean>
代码输出
使用ApplicationContext
ApplicationContext applicationContext=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml");
MyServiceImpl myService =(MyServiceImpl)applicationContext.getBean("myService");
System.out.println(myService );
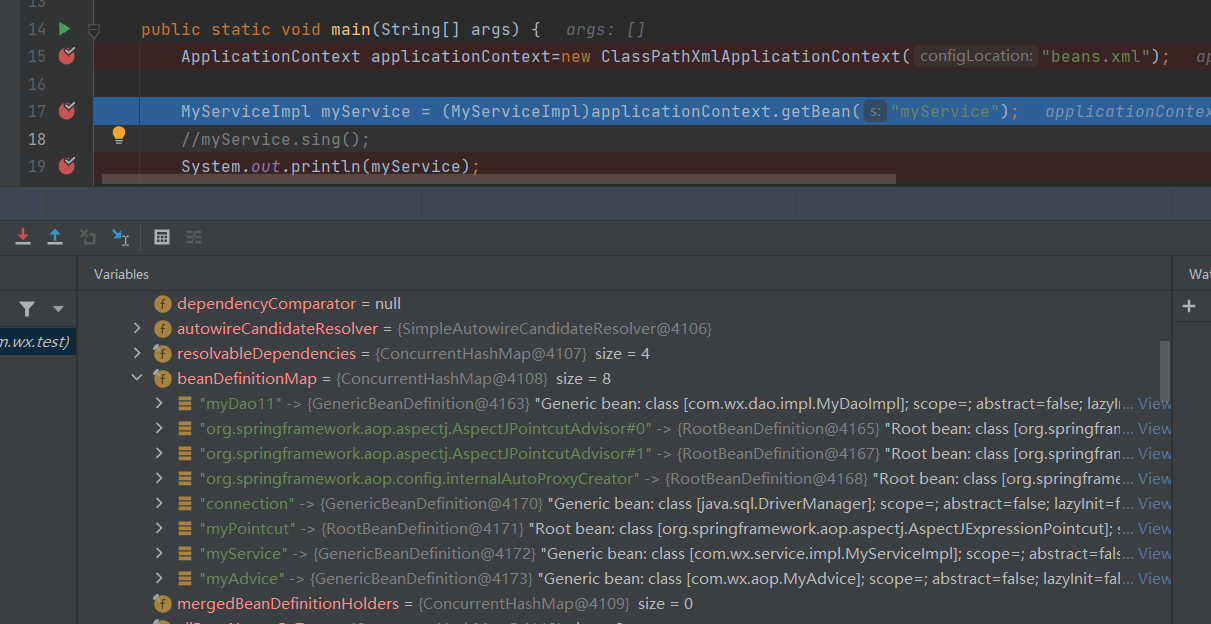
BeanFactory和ApplicationContext的区别,大概是ApplicationContext里面封装了BeanFactory(准确说是继承了BeanFactory,而且里面有BeanFactory的引用),使得ApplicationContext用起来更简单,ApplicationContext是在配置文件加载创建的bean而BeanFactory是第一次getBean时才创建bean(可以打断点去去看beanFactory里面的beanDefinition对象,如下图)。这个BeanFactory叫做bean工厂,ApplicationContext叫做Spring容器。
Xml配置详解
/*
配置bean的id,别名和全限定名,通过别名也能获取到bean
scope:配置bean的作用范围,默认是singleton单例的,还有prototype(原型),request(请求),session(会话)。单例在容器创建的时候就会实例化并存储到单例池中,
prototype容器创建的时候不会创建bena,在getBean的时候每次创建一个
lazy-init:延迟加载,默认是false,设置延迟加载为true,会在第一次getBean的时候创建对象,而不是吃时候的时候。这个配置对于上面的BeanFactory是无效的
init-method="" destroy-method=""初始化和销毁方法,分别在实例化之后和销毁前执行。如果Bean实现InitializingBean接口重写afterPropertiesSet方法
也可以在该方法中执行一些初始化操作,该方法在init方法之前执行,ClassPathXmlApplicationContext的对象.close()可以关闭容器
autowire: 自动注入,可以通过类型(byType,如果存在多个相同的类型的bean,则会报错),名字(name,这个是根据bean中的setXxx方法中的Xxx和bean的id匹配的)等
factory-bean:指定哪个工厂bean的哪个方法完成bean的创建,在下面有例子
*/
<bean id="myService" name="myDao" class="com.wx.service.impl.MyServiceImpl" scope="singleton" lazy-init="true" init-method="" destroy-method="" autowire="byType"
factory-bean="" factory-method="">
bean的实例化方式
第一种:就是我们上面测试的通过构造方法实例化,上面默认找的是无参构造,有参的构造在bean下写子标签<constructor-arg name="name" ref="" value=""></constructor-arg>name是有参构造的变量名,如果String或者基本数据类型通过value去设置,其他的使用ref。注意:这个标签表示是构造bean需要的参数,不一定单指构造方法的参数。
第二种:工厂方式实例化,可以分为三种
- 静态工厂方法实例化
//创建一个工厂类
public class ServiceFactory {
public static MyService ServiceFactory(){
//可以配置一些本来就是通过静态方法获得对象的第三方jar里面的东西
return new MyServiceImpl();
}
}
//xml配置,注意如果这个方法有参数也是通过constructor-arg标签进行配置
<bean id="myService" class="com.wx.service.ServiceFactory" factory-method="ServiceFactory"></bean>
- 实例工厂方法实例化
public class ServiceFactory {
public MyService ServiceFactory(){
System.out.println("实例对象实例化");
return new MyServiceImpl();
}
}
//xml配置,注意如果这个方法有参数也是通过constructor-arg标签进行配置
<bean id="myServiceFactory" class="com.wx.service.ServiceFactory"></bean>
<bean id="myService" factory-bean="myServiceFactory" factory-method="ServiceFactory" ></bean>
- 实现factoryBean规范延迟实例化bean
//写一个工厂类实现FactoryBean,重写getObject方法
public class ServiceFactory implements FactoryBean<MyService> {
@Override
public MyService getObject() throws Exception {
return new MyServiceImpl();
}
@Override
public Class<?> getObjectType() {
return null;
}
}
//xml配置,这个返回的是这个类的getObject方法返回的对象,但是这种方法是在第一次getBean的时候才会实例化对象
<bean id="myService" class="com.wx.service.ServiceFactory"></bean>
属性的注入
- 普通属性:String,还有基本数据类型,使用
<property name="" value="123"></property> - 引用属性:使用
<property name="MyDao" ref="123"></property> - 集合:List,Set(大体上和list相同,只是吧list标签换成set)Map
//private List<String> list; list集合
<property name="list">
<list>
<value>123</value>
<value>123</value>
</list>
</property>
//private List<MyDao> list;包含对象的list
<property name="list">
<list>
<bean class="com.wx.dao.impl.MyDaoImpl"></bean>
<ref bean="myDao"></ref>
</list>
</property>
//map,第一张方式
<property name="map">
<map>
<entry key="12" value="123"></entry>
</map>
</property>
//第二种方式
<property name="map">
<props>
<prop key="123">123</prop>
</props>
</property>
//注意如果是引用数据类型,一般是吧key,value换成key-ref,value-ref
Spring的XML标签
这里我知道个大概,不是很不明白,学懂了再来补充
- 默认标签:不用导入其他命名空间约束的标签,如
<bean>,<alias name="myDao" alias="dao"></alias>,标签
//可以设置不同的开发环境,如果需要获取这个环境下的bean,需要设置
// System.setProperty("spring.profiles.active","dev");
<beans profile="dev"></beans>
//导入其他配置文件
<import resource="beans.xml"></import>
- 自定义标签:需要引入其他命名空间约束,并通过前缀引用的标签
整合第三方框架
分为两种情况
- 不需要自定义命名空间:不需要Spring的文件配置配置第三方框架本身内容,Mybatis
- 需要自定义命名空间:需要Spring的文件配置配置第三方框架本身内容,Dubbo
//整合Mybatis
//1,导入Mybatis以及相关依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring</artifactId>
<version>2.0.5</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-jdbc</artifactId>
<version>5.2.13.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>5.1.49</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis</artifactId>
<version>3.5.5</version>
</dependency>
//编写Mapper和Mapper.xml
//配置SqlSessionFactoryBean和MapperScannerConfigurer
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"></property>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://"></property>
<property name="username" value="root"></property>
<property name="password" value="root"></property>
</bean>
<!-- 配置SqlSessionFactoryBean,将SqlSessionFactory存储到spring容器-->
<bean class="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
</bean>
<!-- 扫描指定的包产生mapper对象存储到spring容器-->
<bean class="org.mybatis.spring.mapper.MapperScannerConfigurer">
<property name="basePackage" value="com.wx.mapper"></property>
</bean>
//测试代码
UserMapper UserMapper =(UserMapper)applicationContext.getBean("userMapper");
System.out.println(UserMapper.findAll());
//原始方式---------------------------------------------------------------
//配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration>
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<transactionManager type="JDBC"/>
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value=""/>
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="root"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
<mappers>
<package name="com.wx.mapper"/>
</mappers>
</configuration>
//测试代码
InputStream in = Resources.getResourceAsStream("mybatis-config.xml");
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder builder = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder();
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = builder.build(in);
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
UserMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
User all = mapper.findAll();
System.out.println(all);
整合dubbo,没学过dubbo,学了再来补充。
SpringBean的实例化流程
实例化的时,在Xml中配置的bean将被封装成一个BeanDefinition对象,放到BeanDefinitionMap的集合中,遍历这个集合,生成真正实例对象放到singletonObject(单例池默认大小256)中。
SpringBean的后处理器
分为下面两种
- BeanFactoryPostPropcessor(bean工厂后处理器):在BeanDefinitionMap填充完成之后,实例化之前执行
使用:只需要实现该接口,然后将实现类交给Spring管理即可。
//将myDao11改成com.wx.service.impl.MyServiceImpl
public class MyBeanFactoryPostProcessor implements BeanFactoryPostProcessor {
@Override
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("beanFactoryPostProcessor回调");
//1,修改beanFactory
BeanDefinition myDao11 = beanFactory.getBeanDefinition("myDao11");
myDao11.setBeanClassName("com.wx.service.impl.MyServiceImpl");
//2,手动注册一个全限定名为hhh的beanDefinition对象
BeanDefinition beanDefinition=new RootBeanDefinition();
beanDefinition.setBeanClassName("hhh");
DefaultListableBeanFactory defaultListableBeanFactory= (DefaultListableBeanFactory)beanFactory;
defaultListableBeanFactory.registerBeanDefinition("hhh",beanDefinition);
}
}
<bean class="com.wx.proccessor.MyBeanFactoryPostProcessor"></bean>
要实现手动的注册beanDefinition到BeanDefinitionMap,BeanFactoryPostPropcessor有一个子接口BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor可以专门用来注册
public class MyBeanFactoryRegistryPostProcessor implements BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor {
@Override
public void postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(BeanDefinitionRegistry beanDefinitionRegistry) throws BeansException {
beanDefinitionRegistry.registerBeanDefinition("hh",null);
}
@Override
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory configurableListableBeanFactory) throws BeansException {
}
}
//注意如果都有是先执行子接口实现类中的方法
- BeanPostProcessor(Bean后处理器):在实例化之后,填充singletonObject之前执行,之间会经过Bean的初始化过程,属性填充,init方法执行等
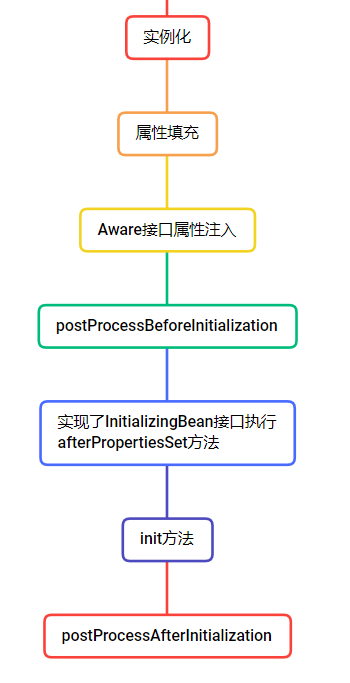
使用:只需要实现该接口,然后将实现类交给Spring管理即可。
public class MyBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor {
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
//在这里给bean设置属性值
if (bean instanceof MyServiceImpl){
((MyServiceImpl) bean).setName("hhhh");
}
return BeanPostProcessor.super.postProcessBeforeInitialization(bean, beanName);
}
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
return BeanPostProcessor.super.postProcessAfterInitialization(bean, beanName);
}
}
Aware接口
Aware接口可以让我们的业务代码在运行期间获取到Spring框架底层的一些api功能
常用的:
- ServletContextAware
- BeanFactoryAware
- BeanNameAware
- ApplicationContextAware
SpringBean的生命周期
可能说的不详细,建议百度具体的过程
- 实例化阶段:Spring判断BeanDefinition对象是否是单例的,是否延迟加载,是不是factoryBean,将一个普通的单例bean通过反射进行实例化
- 初始化阶段:实例化的Bean还是一个半成品,要经历一些属性填充,和一些方法来使他完整。
- 完成阶段:存放当singleton单例池当中
初始化过程如下
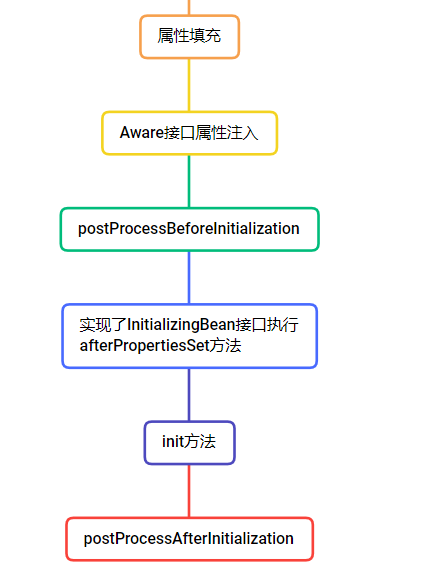
在进行属性填充时会存在几种情况
- String和基本数据类型:直接set方法反射进行设置
- 单向的数据引用:创建被引用的对象,在通过set方法
- 双向数据引用属性:如a中需要注入b,b中需要注入a(Spring提供三级缓存解决这个问题)
Spring的三级缓存
//DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry
//一级缓存,存储已经完成实例化和初始化的bean
private final Map<String, Object> singletonObjects = new ConcurrentHashMap(256);
//三级缓存,单例bean工厂池存储没有初始化完成的bean
private final Map<String, ObjectFactory<?>> singletonFactories = new HashMap(16);
//二级缓存,早期单例池,存储没有初始化完成的bean,但是里面的对象已经被引用了
private final Map<String, Object> earlySingletonObjects = new ConcurrentHashMap(16);
注解开发
Bean的注解开发
//原xml配置方式
<bean id="myService" name="myDao" class="com.wx.service.impl.MyServiceImpl" scope="singleton" lazy-init="true"
init-method="" destroy-method="" autowire="byType"
factory-bean="" factory-method="">
<!--注解扫描,扫描指定包以及字包下面的类,识别使用@Component-->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.wx"></context:component-scan>
//注解
@Component( value = "MyDao")
//我们发现Component注解只有一个属性,而且是value,所以写的时候可以省略value
@Component("MyDao")
@Scope(value ="singleton")
@Lazy(true)
public class MyDaoImpl implements MyDao {
@PostConstruct
public void init(){
System.out.println("初始化方法");
}
@PreDestroy
public void destroy(){
System.out.println("销毁方法");
}
}
//@Component注解源码
@Target({ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Indexed
public @interface Component {
String value() default "";
}
打断点我们可以看到如果不配置@Component的value,则是使用类名第一个字母小写作为beanname
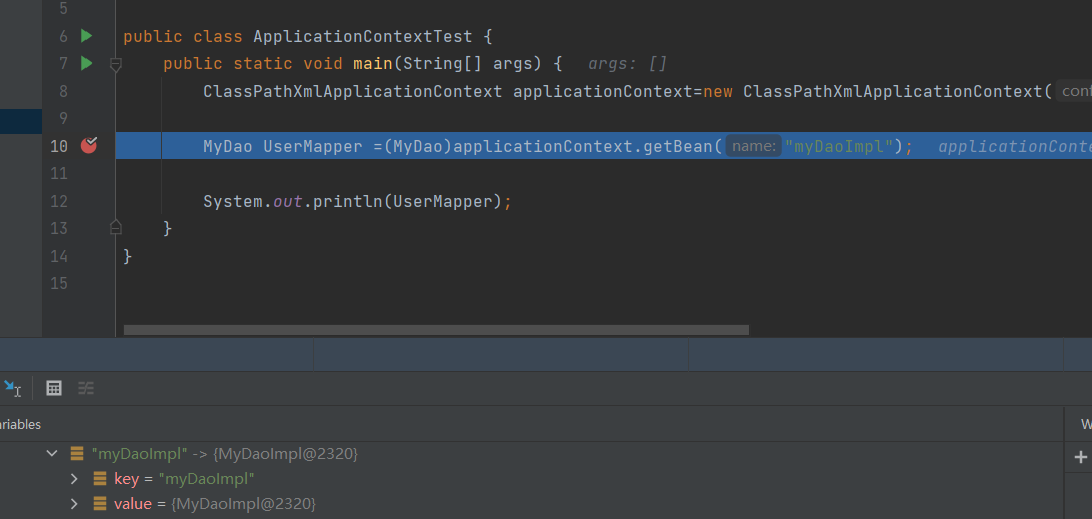 @Primary:提高Bean的优先级
@Primary:提高Bean的优先级
@Profile(“test”):指定环境
@component衍生注解
JavaEE开发是分层,使每层bean语义更加明确,component有三个衍生注解
- @Repository:Dao层使用
- @Service:Service层使用
- @Controller:Web层使用
依赖注入
- @Value:普通属性注入
- @Autowired:自动注入,根据类型(byType),在有多个相同类型的时候,会根据名字进行二次匹配
- @Qualifier:自动注入,根据名字(byType)
- @Resource:自动注入,根据类型或名称(是java自带的,但是Spring会去解析)
//Qualifier用在属性上的时候,必须要配合Autowired使用,单独用Qualifier是注入不了(为空)
@Autowired
@Qualifier("myDao12138")
private MyDao myDao;
//不指定名称根据类型,指定名称根据名称注入
@Resource(name = "myDao12138")
以上四个都可以用在属性或者方法上
非自定义的bean依赖注入
非自定义的bean不能使用@component一样来使用。
需要使用@Bean标签
@Component
public class source {
@Bean("DataSource")
//如果括号里面不写值,那么bean的名字是方法名字
//方法参数有引用的会自动注入,Qualifier可以在这里单独使用
public DataSource dataSource(@Value("234") String password , MyDao myDao){
System.out.println(myDao);
System.out.println(password);
DruidDataSource druidDataSource = new DruidDataSource();
druidDataSource.setDriverClassName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
druidDataSource.setUrl("");
druidDataSource.setUsername("");
druidDataSource.setPassword(password);
return druidDataSource;
}
}
}
配置类
使用注解相对于xml来配置bean方便不少,但是还是需要在配置文件中配置扫描的包等,我们可以使用一个配置类来完成这个功能
//标志当前类是一个配置类(可以代替配置文件)
@Configuration
//相当于<context:component-scan
@ComponentScan(basePackages = {"com.wx"})
//相当于<context:property-placeholder location="jdbc.properties"></context:property-placeholder>
@PropertySource(value = {"jdbc.properties"})
//相当于<import resource="beans.xml"></import>
@Import({OtherSpringConfig.class})
public class SpringConfig {
}
//通过注解方式加载配置类
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig.class);
DataSource UserMapper =(DataSource)applicationContext.getBean("dataSource");
注解整合Mybatis
//标志当前类是一个配置类(可以代替配置文件)
@Configuration
//相当于<context:component-scan
@ComponentScan(basePackages = {"com.wx"})
//相当于<context:property-placeholder location="jdbc.properties"></context:property-placeholder>
@PropertySource("classpath:jdbc.properties")
//Mapper接口扫描
@MapperScan("com.wx.mapper")
public class SpringConfig {
@Bean
public DataSource dataSource(
@Value("${jdbc.driver}") String driver,
@Value("${jdbc.url}") String url,
@Value("${jdbc.userName}") String userName,
@Value("${jdbc.passWord}") String passWord
){
DruidDataSource dataSource = new DruidDataSource();
dataSource.setDriverClassName(driver);
dataSource.setUrl(url);
dataSource.setUsername(userName);
dataSource.setPassword(passWord);
return dataSource;
}
@Bean
public SqlSessionFactoryBean sqlSessionFactoryBean(DataSource dataSource){
SqlSessionFactoryBean sqlSessionFactoryBean = new SqlSessionFactoryBean();
sqlSessionFactoryBean.setDataSource(dataSource);
return sqlSessionFactoryBean;
}
}
//需要注意的是:properties文件值不要加双引号,如下即可
jdbc.driver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
AOP
AOP(Aspect Oriented Programming)面向切面编程,是横向对不同事物的抽象,属性和属性,方法与方法,对象和对象都可以组成一个切面,而面向对象是纵向的对象一个事物的抽象,一个对象包括静态属性信息,方法等
AOP思想实现方案
动态代理技术,在运行期间对目标对象方法进行增强
使用jdk的动态代理模拟实现
//增强类
@Component
public class Advice {
public void beforeAdvice(){
System.out.println("前置增强方法");
}
public void afterAdvice(){
System.out.println("后置增强方法");
}
}
@Component
public class AopServiceImpl implements AopService{
@Override
public void show1() {
System.out.println("show1");
}
@Override
public void show2() {
System.out.println("show2");
}
}
@Component
public class AopPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor , ApplicationContextAware {
ApplicationContext applicationContext;
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
//对AopServiceImpl中show1和show2方法进行增强,增强方法为Advice中方法
if ("aopServiceImpl".equals(beanName)){
Object newProxyInstance = Proxy.newProxyInstance(
bean.getClass().getClassLoader(),
bean.getClass().getInterfaces(),
(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) -> {
Advice advice=(Advice)applicationContext.getBean(Advice.class);
advice.beforeAdvice();
method.invoke(bean,args);
advice.afterAdvice();
return null;
}
);
return newProxyInstance;
}
return bean;
}
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
this.applicationContext=applicationContext;
}
}
//测试代码
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig.class);
AopService aopService =(AopService)applicationContext.getBean("aopServiceImpl");
aopService.show1();
SpringAOP
相关概念
| 概念 | 单词 | 解释 |
|---|---|---|
| 目标对象 | Target | |
| 代理对象 | Proxy | |
| 连接点 | Joinpoint | 目标对象能够被代理的方法 |
| 切入点 | Pointcut | 实际被增强的方法 |
| 通知/切面 | Advice | |
| 切面 | Aspect | |
| 织入 | Weaving |
XML配置AOP
- 配置哪些包哪些类,哪些方法要被增强(一般是通过execute表达式,建议百度学习一下)
- 配置目标方法要被哪些通知方法增强,在目标方法之前还是之后执行增强
1,导入aop的依赖(aop是一种思想,aspectj是Spring采用的一种实现)
<dependency>
<groupId>org.aspectj</groupId>
<artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId>
<version>1.9.6</version>
</dependency>
2,导入aop的命名空间,配置aop
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd
<!-- aop配置-->
<aop:config>
<!-- 配置切点表达式-->
<aop:pointcut id="myPointCut" expression="execution(void com.wx.aop.AopServiceImpl.show1())"/>
<!-- 配置织入,指定哪些切点与哪些通知进行结合-->
<aop:aspect ref="advice" >
<aop:before method="beforeAdvice" pointcut-ref="myPointCut"></aop:before>
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
配置通知的时候,有下面五种通知类型
aop:before:前置通知
aop:after-returning:后置通知,出现异常不会执行
aop:around:环绕通知,出现异常,后置的不会执行
aop:after-throwing:异常通知,抛异常时执行
aop:after:最终通知,不管有没有异常,都会执行
也可以使用<advisor>进行配置
需要通知类型实现Advice的子接口
package org.aopalliance.aop;
public interface Advice {
}
//通知类
@Component
public class MyAdvice implements MethodBeforeAdvice, AfterReturningAdvice {
@Override
public void afterReturning(Object o, Method method, Object[] objects, Object o1) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("MyAdvice前置通知");
}
@Override
public void before(Method method, Object[] objects, Object o) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("MyAdvice后置通知");
}
}
//下面是环绕的
@Component
public class MyAdvice implements MethodInterceptor {
@Override
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation methodInvocation) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("MethodInterceptor前");
Object res = methodInvocation.getMethod().invoke(methodInvocation.getThis(), methodInvocation.getArguments());
System.out.println("MethodInterceptor后");
return res;
}
}
<!-- aop配置-->
<aop:config>
<aop:pointcut id="myPointCut2" expression="execution(void com.wx.aop.AopServiceImpl.show2())"/>
<aop:advisor advice-ref="myAdvice" pointcut-ref="myPointCut2"/>
</aop:config>
原理解析
第一步:根据命名空间找到对应的处理器
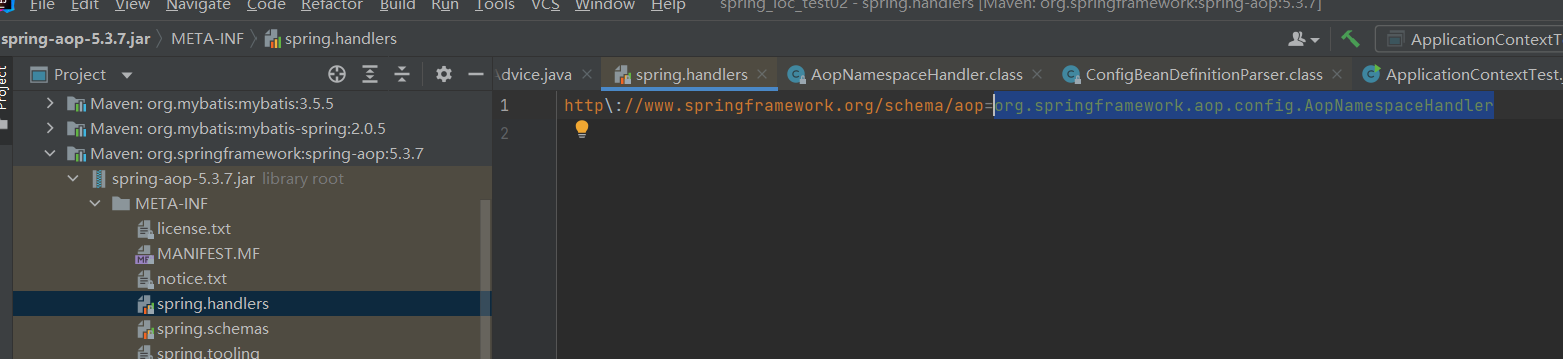 第二步:我们是用的config标签,找到对应的类ConfigBeanDefinitionParser
第二步:我们是用的config标签,找到对应的类ConfigBeanDefinitionParser
第三步:说不下去了,ConfigBeanDefinitionParser大概就是为了向容器中注册一个BeanPostProcessor,这个BeanPostProcessor在after的哪个方法中生成代理对象。
 Spring底层提供了两种方式产生代理对象(默认是JDK动态代理)
Spring底层提供了两种方式产生代理对象(默认是JDK动态代理)<aop:config proxy-target-class="true">这样可以设为Cglib动态代理,当被代理类不是实现接口时,也会使用Cglib
- JDK动态代理:目标类有接口,基于接口动态生成实现类动态代理对象
- Cglib动态代理:目标类无接口且不能使用final修饰,基于被代理对象动态生成子对象为代理对象(下面是Cglib动态代理代码)

使用注解配置AOP
//增强类
@Component
@Aspect
public class Advice {
//<aop:before method="beforeAdvice" pointcut-ref="myPointCut"></aop:before>
@Before("execution(void com.wx.aop.AopServiceImpl.show1())")
@After("execution(void com.wx.aop.AopServiceImpl.show1())")
@AfterReturning("execution(void com.wx.aop.AopServiceImpl.show1())")
@Around("execution(void com.wx.aop.AopServiceImpl.show1())")
@AfterThrowing("execution(void com.wx.aop.AopServiceImpl.show1())")
public void beforeAdvice(){
System.out.println("前置增强方法");
}
public void afterAdvice(){
System.out.println("后置增强方法");
}
}
//开启
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy/>
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy
切点表达式抽取
//增强类
@Component
@Aspect
public class Advice {
//切点表达式抽取
@Pointcut("execution(void com.wx.aop.AopServiceImpl.show1())")
public void myPointCut(){
}
//<aop:before method="beforeAdvice" pointcut-ref="myPointCut"></aop:before>
@Before("Advice.myPointCut()")
public void beforeAdvice(){
System.out.println("前置增强方法");
}
public void afterAdvice(){
System.out.println("后置增强方法");
}
}
AOP的声明式事务控制
编程式事务:Spring提供了事务控制的类和方法,使用编码的方式都业务代码进行事务控制,事务控制代码金额业务代码耦合到一起,开发中基本不用
声明式事务:Spring将事务控制的代码封装,对外提供XML和注解配置,通过配置方式完成事务控制,事务控制和业务操作代码是解耦的。
编程式事务相关的三个类
- PlatformTransactionManager:是一个接口标准,实现类都具备事务提交回滚和获得事务对象的功能,不同持久层有不同的实现方案。
- TransactionDefinition:隔离基本,传播行为,过期时间等属性信息。
- TransactionStatus:存储当前事务的状态信息。
声明式事务Demo
1,创建一张表
create TABLE account(
id INT(11),
name VARCHAR(25),
money DOUBLE
);
 2,mapper接口,实现类方法
2,mapper接口,实现类方法
@Repository
public interface AccountMapper {
@Update("update account set money=money+#{num} where name=#{name}")
public void addMoney(@Param("name") String name , @Param("num") double num);
@Update("update account set money=money-#{num} where name=#{name}")
public void decrMoney(@Param("name") String name , @Param("num") double num);
}
@Service("accountServiceImpl")
public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {
@Autowired
private AccountMapper mapper;
@Override
public void TransferAccounts(String outAccount, String inCount, Double money) {
mapper.decrMoney(outAccount,money);
mapper.addMoney(inCount,money);
}
}
3,测试
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig.class);
AccountService aopService =(AccountService)applicationContext.getBean("accountServiceImpl");
aopService.TransferAccounts("zs","ls",500.0);
//结果是成功的
在service方法减钱和增加钱的方法直接抛一个异常,发现增加钱的方法不执行,所以service的转账方法需要开启事务
再结合Spring的AOP,可以使用AOP对Service的方法进行事务的增强(就是在前开启事务,在后面提交事务)Service中TransferAccounts方法就是切点。使用advisor的方式进行配置。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd
">
<!--注解扫描,扫描指定包以及字包下面的类,识别使用@Component-->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.wx"></context:component-scan>
<context:property-placeholder location=""></context:property-placeholder>
<!-- p配置平台事务管理器-->
<bean id="transactionManager2" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<!-- 数据源-->
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
</bean>
<!-- 配置Spring提供好的Advice-->
<tx:advice id="txAdvice" transaction-manager="transactionManager2">
<tx:attributes>
<!--name方法名称,isolation事务隔离级别,
timeout超时时间,默认为-1,单位是s
read-only是否只读,查询
propagation:事务传播行为,解压业务方法调用业务方法(事务嵌套问题)-->
<tx:method name="TransferAccounts" isolation="DEFAULT" timeout="1" read-only="false" propagation="MANDATORY"/>
</tx:attributes>
</tx:advice>
<aop:config>
<!-- 切点表达式-->
<aop:pointcut id="txPoint" expression="execution(* com.wx.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl.*(..))"/>
<!-- 织入关系,通知是Spring通过的-->
<aop:advisor advice-ref="txAdvice" pointcut-ref="txPoint"></aop:advisor>
</aop:config>
</beans>
DataSourceTransactionManager就是PlatformTransactionManager的一个子类,因为我们dao层用的是Mybatis所以用DataSourceTransactionManager
注解配置声明式事务
//@Transactional写在类和方法上都可以,如果都有则是用方法上的
@Service("accountServiceImpl")
@Transactional(isolation = Isolation.DEFAULT,propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED)
public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {
@Autowired
private AccountMapper mapper;
@Override
@Transactional(isolation = Isolation.DEFAULT,propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED)
public void TransferAccounts(String outAccount, String inCount, Double money) {
mapper.decrMoney(outAccount,money);
//System.out.println(1/0);
mapper.addMoney(inCount,money);
}
}
//下面两个还是要配置的
<!-- 事务的自动代理(注解驱动)-->
<tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="transactionManager"/>
<!-- p配置平台事务管理器-->
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<!-- 数据源-->
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
</bean>
//使用配置类来配置这两个
//标志当前类是一个配置类(可以代替配置文件)
@Configuration
//相当于<context:component-scan
@ComponentScan(basePackages = {"com.wx"})
//相当于<context:property-placeholder location="jdbc.properties"></context:property-placeholder>
@PropertySource("classpath:jdbc.properties")
//Mapper接口扫描
@MapperScan("com.wx.mapper")
//相当于<tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="transactionManager"/>
@EnableTransactionManagement
public class SpringConfig {
@Bean
public DataSource dataSource(
@Value("${jdbc.driver}") String driver,
@Value("${jdbc.url}") String url,
@Value("${jdbc.userName}") String userName,
@Value("${jdbc.passWord}") String passWord
){
DruidDataSource dataSource = new DruidDataSource();
dataSource.setDriverClassName(driver);
dataSource.setUrl(url);
dataSource.setUsername(userName);
dataSource.setPassword(passWord);
return dataSource;
}
@Bean
public SqlSessionFactoryBean sqlSessionFactoryBean(DataSource dataSource){
SqlSessionFactoryBean sqlSessionFactoryBean = new SqlSessionFactoryBean();
sqlSessionFactoryBean.setDataSource(dataSource);
return sqlSessionFactoryBean;
}
@Bean
public DataSourceTransactionManager transactionManager(DataSource dataSource){
DataSourceTransactionManager transactionManager = new DataSourceTransactionManager(dataSource);
return transactionManager;
}
}
整合Web环境
首先javaweb中Servlet,Filter,Listener三种组件都可以在Tomcat组件启动的时候进行初始化,所以Spring整合web的思路可以使用监听器ServletContextListener在tomcat启动的时候将Spring容器放到application域中,这样每个Servlet都可以拿到Spring容器从而拿到Service层的对象。
Spring框架中的spring-web已经帮我们做好了
1,导入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-web</artifactId>
<version>5.3.7</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.servlet-api</artifactId>
<version>4.0.0</version>
</dependency>
2,右键项目,add Framework support 添加Web的环境
3,web.xml中配置
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath:beans.xml</param-value>
</context-param>
<!-- 配置Listener-->
<listener>
<listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class>
4,测试代码
@WebServlet(urlPatterns="/ServletTest")
public class ServletTest extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
ServletContext servletContext = req.getServletContext();
WebApplicationContext applicationContext = WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(servletContext);
AccountService accountServiceImpl = (AccountService)applicationContext.getBean("accountServiceImpl");
accountServiceImpl.TransferAccounts("zs","ls",100.0);
}
}
SpringMVC
是一个基于Spring开发的MVC轻量级框架