文章目录
- B- 树系列
- 定义
- 插入规则
- 代码
- B-树结点定义
- 查找key在结点哪个子树
- 插入+分裂
B- 树系列
定义
B-树是一棵多叉 平衡 搜索树(不是二叉树,B-树中每个结点中可以有多个key,也有多个孩子)
B-树中每个结点在实现时人为规定一个key的上限(KEY_LIMIT = 4)
B-树结点中的key是按照key的顺序进行保存
我们把key的个数记为size,则child的个数—定是size + 1
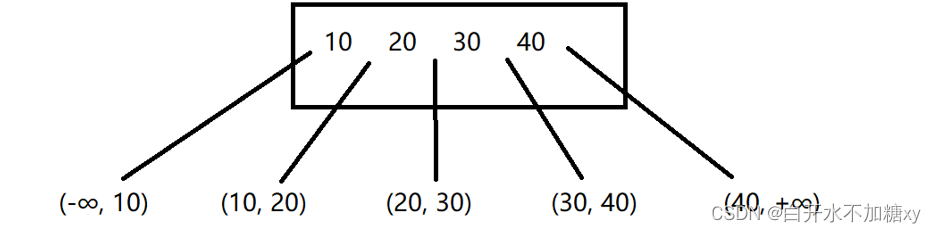
插入规则
1.所有插入过程,只能发生在叶子上,不能发生在非叶子结点上
2.插入时,每个结点的kev的数量是有上限的
(1) 未达上限,插入结束
(2) 达到上限,则进行“结点分裂”过程
3.叶子结点的分裂
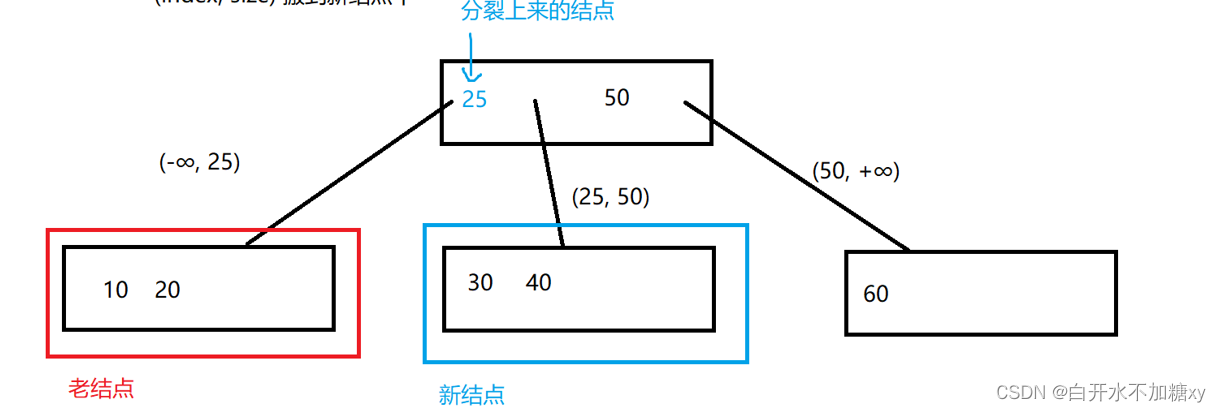
如下情况中,插入25后,结点中key的数量超过上限4,引发分裂,分裂过程如下:
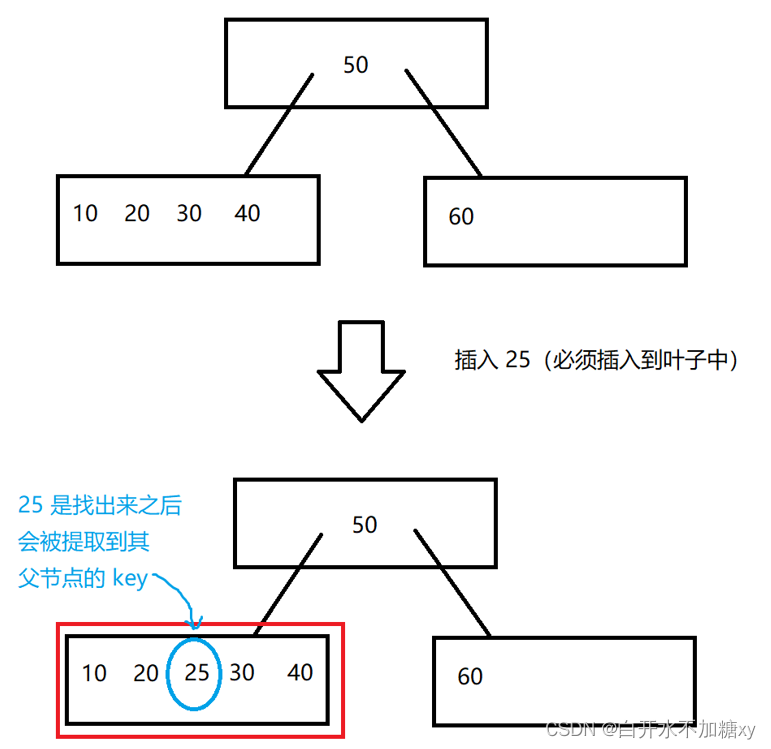
步骤:
1. 找到key的中间值(25)把下标记为index
1)不一定就是新插入的结点
2)偶数的话,前一个或者后一个都可以(一般都实现成奇数的形式)
2. 把当前结点分成两个结点(分家)
[0 , index) key留在当前结点中
[index]提到父结点中
(index, size)搬到新结点中
代码
B-树结点定义
/**
* 暂时只考虑:
* 1. key 模型而不是 key-value 模型
* 2. key 类型定义为 long 类型
* 3. public
*/
public class BTreeNode {
/**
* 先规定,一个 B-树结点中,能存的 key 的数量的上限,要求 size(key) <= KEY_LIMIT
* 在实际的应用中,一般 KEY_LIMIT 都是 1000 数量级以上的
*/
public static final int KEY_LIMIT = 4;
/**
* 去保存结点中所有的 key
* 使用数组(线性结构)进行维护,需要维护 key 与 key 之间的有序性
* 从空间利用率角度考虑,new long[KEY_LIMIT] 就足够了
* 但我们多申请一个空间,方便进行结点分裂代码的编写(用于保存即将分裂状态下的所有 key)
*/
public long[] keyList = new long[KEY_LIMIT + 1];
/**
* 记录目前拥有的 key 的个数
*/
public int size = 0;
/**
* 去维护结点中所有的 child
* 同理,多申请一个空间
* 本来,child 就比 key 多一个
* new BTreeNode[KEY_LIMIT + 2]
*/
public BTreeNode[] childList = new BTreeNode[KEY_LIMIT + 2];
/**
* 我们不维护 child 的个数,因为 其个数一定是 size + 1
*/
/**
* 保存该结点的父结点,null 代表该结点是根结点
*/
public BTreeNode parent = null;
@Override
public String toString() {
return String.format("%d: %s", size, Arrays.toString(Arrays.copyOf(keyList, size)));
}
}
查找key在结点哪个子树
public BTreeNode findKey(long key) {
if (key > keyList[size - 1]) {
// child 比 key 多一个
// keyList 的最后一个元素位于 [size - 1]
// childList 的最后一个元素位于 [size]
return childList[size];
}
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
if (key == keyList[i]) {
// key 就在当前结点中
return this;
} else if (key < keyList[i]) {
// 由于我们是从左向右遍历的
// 所以 keyList[i] 中的元素是 "第一个" 大于 key 的关键字元素
return childList[i];
} else {
// key > keyList[i] 的情况下,我们什么都不需要做,继续遍历查找
// 第一个 大于 key 的元素
}
}
// 我们的代码组织方式使得,理论上,不应该走到这个位置
// 但 java 编译器分析不出来,所以,为了让编译器不报错,我们随便返回一个值
// 这个 return 没有任何执行的意义
return null;
}
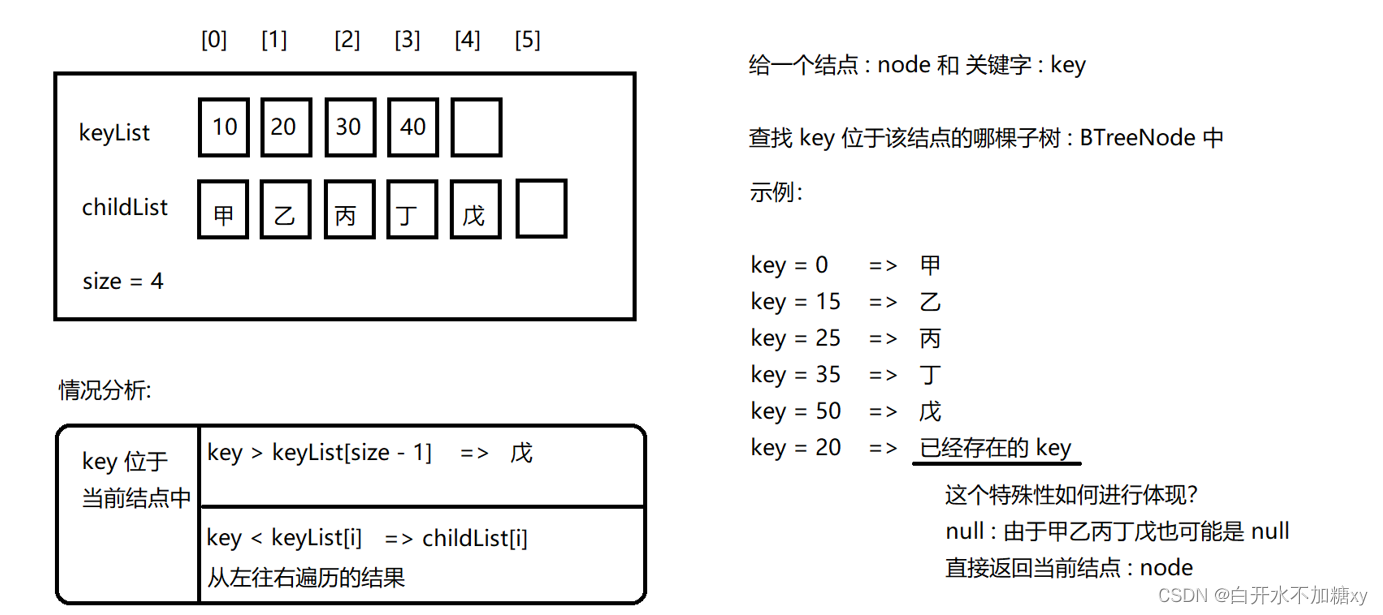
测试查找Key的代码:
包含测试用例分析
public static void testFindKey() {
BTreeNode node = new BTreeNode();
node.keyList[0] = 10;
node.keyList[1] = 20;
node.keyList[2] = 30;
node.keyList[3] = 40;
node.size = 4;
BTreeNode 甲 = new BTreeNode();
BTreeNode 乙 = new BTreeNode();
BTreeNode 丙 = new BTreeNode();
BTreeNode 丁 = new BTreeNode();
BTreeNode 戊 = new BTreeNode();
node.childList[0] = 甲;
node.childList[1] = 乙;
node.childList[2] = 丙;
node.childList[3] = 丁;
node.childList[4] = 戊;
/**
* 测试用例:
* 执行动作 期望结果
* < 10 期望 甲
* == 10 期望 node
* == 20 期望 node
* (10, 20) 期望 乙
* (20, 30) 期望 丙
* (30, 40) 期望 丁
* > 40 期望 戊
* == 40 期望 node
*/
// 引用1 == 引用2: 判断两个引用是否指向同一个对象
System.out.println(node.findKey(3) == 甲);
System.out.println(node.findKey(10) == node);
System.out.println(node.findKey(20) == node);
System.out.println(node.findKey(13) == 乙);
System.out.println(node.findKey(29) == 丙);
System.out.println(node.findKey(31) == 丁);
System.out.println(node.findKey(300) == 戊);
System.out.println(node.findKey(40) == node);
}
插入+分裂
插入步骤:
将key插入结点的keyList中,并且维持有序性 ——类似插入排序的做法

/**
* 用来作为插入的返回值类型的类
*/
public static class InsertResult {
public long key; // 分裂出的 key
public BTreeNode node; // 分裂出的新结点
}
/**
* 将指定关键字 key,插入叶子结点中
* @param key 关键字
* @return
* null: 插入之后不需要分裂
* !null: 发生了分裂
*/
public InsertResult insertKey(long key) {
// 1. 如果 key 按序插入到 keyList 中
insertIntoKeyList(key);
size++;
// 2. 判断是否需要进行分裂
// 3. 如果有必要,进行结点分裂
if (shouldSplit()) {
return splitLeaf();
}
return null;
}
/**
* 将指定关键字 key 和 chid,插入非叶子结点中
* @param key 关键字
* @param child > key 的孩子
* @return
*/
public InsertResult insertKeyWithChild(long key, BTreeNode child) {
// 1. 如果 key 按序插入到 keyList 中
int index = insertIntoKeyList(key);
// 2. 根据 index 进行 child 的插入,暂时没有进行 size 的变动
// child[0, size]
// [0, index] 不动
// [index + 1] 要插入 child 的下标
// [index + 1, size] 搬到 [index + 2, size + 1] 元素个数 size - (index + 1) + 1 == size - index
System.arraycopy(childList, index + 1, childList, index + 2, size - index);
childList[index + 1] = child;
// 这个时候再让 size++
size++;
// 2. 判断是否需要进行分裂
// 3. 如果有必要,进行结点分裂
if (shouldSplit()) {
return splitNotLeaf();
}
return null;
}
public InsertResult splitNotLeaf() {
// 因为一会儿 this.size 在中途会变化,先提前记录
int size = this.size;
InsertResult result = new InsertResult();
BTreeNode node = new BTreeNode();
// 1. 找到 keyList 的中间位置
int index = size / 2;
// 2. 保存需要分裂出的 key
result.key = keyList[index];
/**
* 3. 处理 key 的分裂
* 哪些 key 应该留在当前结点中 [0, index) 一共有 index 个
* 哪个 key 是分裂出的 key [index]
* 哪些 key 应该在新结点中 (index, size) 一共有 size - index - 1
*/
// 先把 (index, size) 位置的 key 搬到新结点中
System.arraycopy(keyList, index + 1, node.keyList, 0, size - index - 1);
node.size = size - index - 1;
// 把 [index, size) 所有 key 重置为默认值 (0),重置 size
Arrays.fill(keyList, index, size, 0);
this.size = index;
/**
* 4. 我们对非叶子结点进行分裂,非叶子结点有孩子,所以也进行分裂
*/
System.arraycopy(this.childList, index + 1, node.childList, 0, size - index);
Arrays.fill(this.childList, index + 1, size + 1, null);
for (int i = 0; i < size - index; i++) {
node.childList[i].parent = node;
}
/**
* 5. 处理分裂的 parent 的问题
* 1) this.parent 不变,分裂不影响父子关系
* 2) node.parent 和 this 是同一个父亲
*/
node.parent = this.parent;
result.node = node;
return result;
}
public InsertResult splitLeaf() {
// 因为一会儿 this.size 在中途会变化,先提前记录
int size = this.size;
InsertResult result = new InsertResult();
BTreeNode node = new BTreeNode();
// 1. 找到 keyList 的中间位置
int index = size / 2;
// 2. 保存需要分裂出的 key
result.key = keyList[index];
/**
* 3. 处理 key 的分裂
* 哪些 key 应该留在当前结点中 [0, index) 一共有 index 个
* 哪个 key 是分裂出的 key [index]
* 哪些 key 应该在新结点中 (index, size) 一共有 size - index - 1
*/
// 先把 (index, size) 位置的 key 搬到新结点中
System.arraycopy(keyList, index + 1, node.keyList, 0, size - index - 1);
node.size = size - index - 1;
// 把 [index, size) 所有 key 重置为默认值 (0),重置 size
Arrays.fill(keyList, index, size, 0);
this.size = index;
/**
* 4. 我们对叶子结点进行分裂,叶子结点没有孩子 childList[...] = null,不需要分裂
*/
/**
* 5. 处理分裂的 parent 的问题
* 1) this.parent 不变,分裂不影响父子关系
* 2) node.parent 和 this 是同一个父亲
*/
node.parent = this.parent;
result.node = node;
return result;
}
public boolean shouldSplit() {
return size > KEY_LIMIT;
}
public int insertIntoKeyList(long key) {
// keyList 中有效的下标范围是 [0, size)
// 从后向前遍历 [size - 1, 0]
int i;
for (i = size - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
if (keyList[i] < key) {
// 第一次碰到了 keyList[i] < key
break;
}
// 没有 keyList[i] == key
// 继续遍历查找,同时将数据向后搬一格
keyList[i + 1] = keyList[i];
}
// 1. i == -1
// 2. keyList[i] < key
// 不管怎么样,key 都应该放在 [i + 1]
keyList[i + 1] = key;
return i + 1;
}
import btree.BTreeNode.InsertResult;
/**
* B-树定义
*/
public class BTree {
/**
* B-树的根结点
*/
public BTreeNode root = null;
/**
* B-树中的 key 的个数
* 备注:和二叉搜索树不同,B-树的 key 的个数 不等于 结点的个数
*/
public int size = 0;
public boolean insert(long key) {
if (insertWithoutSize(key)) {
size++;
return true;
}
return false;
}
public boolean insertWithoutSize(long key) {
// 1. 是否是空树
if (root == null) {
// root = 构建一个包含 key 的结点;
root = new BTreeNode();
root.keyList[0] = key;
root.size = 1;
return true;
}
// 2. 不是空树的情况
BTreeNode current = root;
while (true) {
BTreeNode node = current.findKey(key);
if (node == current) {
// key 就在 current 结点中
// 不运行重复 key 的插入,插入失败
return false;
} else if (node == null) {
// current 就是叶子结点
// current 就是接下来要插入 key 的结点
break;
} else {
// 找到了一个孩子 并且 current 不是叶子
// 规则:插入必须发生在叶子结点上
current = node;
}
}
// 进行 key 的插入
// current 就是我们要进行 key 插入的结点
// current 此时一定是叶子
InsertResult r = current.insertKey(key);
while (true) {
if (r == null) {
// 插入过程中,没有发生结点分裂,直接退出
return true;
}
// 说明发生分裂了
// 需要把新分裂出的 key 和 分裂出的结点,插入到 current.parent 中
BTreeNode parent = current.parent;
if (parent == null) {
// 说明 current 是根结点
// 根结点发生分裂了
// 需要一个新的根结点,来保存分裂出的 key
root = new BTreeNode();
root.keyList[0] = r.key;
root.size = 1;
root.childList[0] = current;
root.childList[1] = r.node;
// 由于原来 current 是根结点,所以其 parent == null
// 自然分裂出的结点,跟着也是 null
// 所以为他们设置新的父结点
current.parent = r.node.parent = root;
return true;
}
// 不是根结点分裂了
r = parent.insertKeyWithChild(r.key, r.node);
current = parent;
}
}
}