文章目录
- 直通滤波
- 降采样
- 使用统计滤波(statisticalOutlierRemoval)移除离群点
- 使用条件滤波(ConditionalRemoval)或 半径滤波(RadiusOutlinerRemoval)移除离群点
在获取点云数据时,由于设备精度,操作者经验环境因素带来的影响,以及电磁波的衍射特性,被测物体表面性质变化和数据拼接配准操作过程的影响,点云数据中将不可避免的出现一些噪声。
几种需要进行点云滤波处理情况如下:
- 点云数据密度不规则需要平滑;
- 因为遮挡等问题造成离群点需要去除;
- 大量数据需要下采样;
- 噪声数据需要去除。
PCL常规滤波手段均进行了很好的封装,对点云的滤波通过调用各个滤波器对象来完成。主要的滤波器有直通滤波器,体素格滤波器,统计滤波器,半径滤波器等。
常用方法如下:
- 使用直通滤波器对点云进行滤波处理
- 使用体素滤波对点云进行下采样
- 使用统计滤波器移除离群点
- 使用条件滤波或半径滤波移除离群点
直通滤波
直通滤波器就是根据点云的属性(属性比如x,y,z,颜色值等),在点的属性上设置范围,对点进行滤波,保留范围内的或保留范围外的。
官网教程——https://pcl.readthedocs.io/projects/tutorials/en/latest/passthrough.html#passthrough
测试案例1(保留z轴范围内0-1m内的点云)
#include <iostream>
#include <pcl/point_types.h>
#include <pcl/filters/passthrough.h>
#include <pcl/visualization/cloud_viewer.h>
typedef pcl::PointXYZ PointT;
int
main(int argc, char **argv) {
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud_filtered(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);
//写入点云
cloud->width = 5;
cloud->height = 1;
cloud->points.resize(cloud->width * cloud->height);
for (size_t i = 0; i < cloud->points.size(); ++i) {
cloud->points[i].x = 1024 * rand() / (RAND_MAX + 1.0f);
cloud->points[i].y = 1024 * rand() / (RAND_MAX + 1.0f);
cloud->points[i].z = 1024 * rand() / (RAND_MAX + 1.0f);
}
std::cerr << "Cloud before filtering: " << std::endl;
for (size_t i = 0; i < cloud->points.size(); ++i)
std::cerr << " " << cloud->points[i].x << " "
<< cloud->points[i].y << " "
<< cloud->points[i].z << std::endl;
// Create the filtering object
pcl::PassThrough<pcl::PointXYZ> pass;
pass.setInputCloud(cloud); // 1. 设置输入源
pass.setFilterFieldName("z"); // 2. 设置过滤域名
pass.setFilterLimits(0.0, 1.0); // 3. 设置过滤范围
// pass.setFilterLimitsNegative(true); // 设置获取Limits之外的内容
pass.filter(*cloud_filtered); // 4. 执行过滤,并将结果输出到cloud_filtered
std::cerr << "Cloud after filtering: " << std::endl;
for (size_t i = 0; i < cloud_filtered->points.size(); ++i)
std::cerr << " " << cloud_filtered->points[i].x << " "
<< cloud_filtered->points[i].y << " "
<< cloud_filtered->points[i].z << std::endl;
pcl::visualization::CloudViewer viewer("Cloud Viewer");
//这里会一直阻塞直到点云被渲染
viewer.showCloud(cloud);
while (!viewer.wasStopped()) {
}
return (0);
}
执行程序之后,会有如下结果
Cloud before filtering:
0.352222 -0.151883 -0.106395
-0.397406 -0.473106 0.292602
-0.731898 0.667105 0.441304
-0.734766 0.854581 -0.0361733
-0.4607 -0.277468 -0.916762
Cloud after filtering:
-0.397406 -0.473106 0.292602
-0.731898 0.667105 0.441304
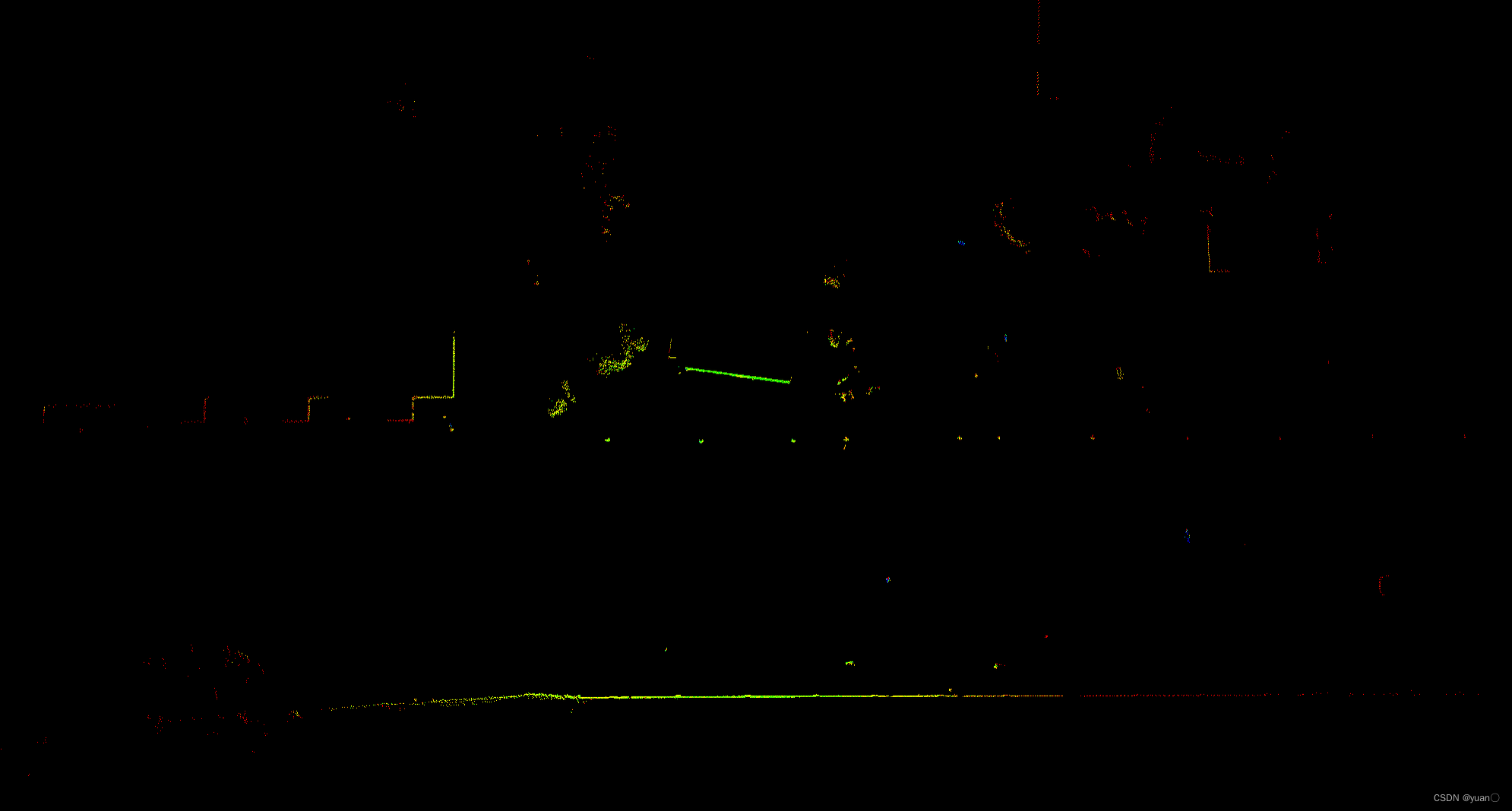
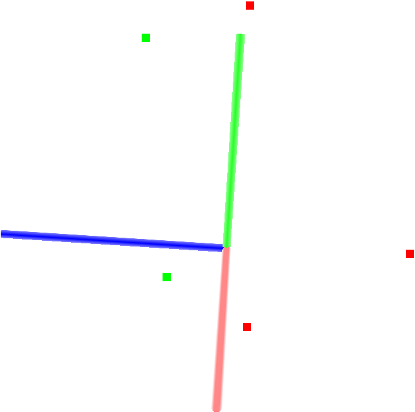
过滤过程的图形显示如下所示,其中坐标系中红色为(x)、绿色为(y)、蓝色为(z)。图中的五个点中绿色的点为被过滤后的点,红色的点为被过滤掉的点。
测试案例2
#include <iostream>
#include <pcl/point_types.h>
#include <pcl/io/io.h>
#include <pcl/io/pcd_io.h>
#include <pcl/filters/passthrough.h>
#include <pcl/visualization/cloud_viewer.h>
int
main(int argc, char **argv) {
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZI>::Ptr cloud(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZI>);
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZI>::Ptr cloud_filtered(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZI>);
// 加载pcd文件到cloud
if (pcl::io::loadPCDFile("../data/result.pcd", *cloud) == -1)
{
std::cout << "Could not load pcd file!" << std::endl;
return -1;
}
// Create the filtering object
pcl::PassThrough<pcl::PointXYZI> pass;
pass.setInputCloud(cloud); // 1. 设置输入源
pass.setFilterFieldName("z"); // 2. 设置过滤域名
pass.setFilterLimits(-1.0, 1.0); // 3. 设置过滤范围
// pass.setFilterLimitsNegative(true); // 设置获取Limits之外的内容
pass.filter(*cloud_filtered); // 4. 执行过滤,并将结果输出到cloud_filtered
pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer viewer_filter("Cloud-Filtered Viewer");
//背景颜色设置
viewer_filter.setBackgroundColor(0, 0, 0);
//按照z字段进行渲染
pcl::visualization::PointCloudColorHandlerGenericField<pcl::PointXYZI> fildColor_filter(cloud_filtered, "intensity");
//显示点云,其中fildColor为颜色显示
viewer_filter.addPointCloud<pcl::PointXYZI>(cloud_filtered, fildColor_filter, "sample");
//设置点云大小
viewer_filter.setPointCloudRenderingProperties(pcl::visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_POINT_SIZE, 1, "sample");
// // 循环判断是否退出
// while (!viewer_filter.wasStopped()) {
// viewer_filter.spinOnce();
// }
pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer viewer("Cloud Viewer");
//背景颜色设置
viewer.setBackgroundColor(0, 0, 0);
//按照z字段进行渲染
pcl::visualization::PointCloudColorHandlerGenericField<pcl::PointXYZI> fildColor(cloud, "intensity");
//显示点云,其中fildColor为颜色显示
viewer.addPointCloud<pcl::PointXYZI>(cloud, fildColor, "sample");
//设置点云大小
viewer.setPointCloudRenderingProperties(pcl::visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_POINT_SIZE, 1, "sample");
// 循环判断是否退出
while (!viewer.wasStopped() && !viewer_filter.wasStopped()) {
viewer_filter.spinOnce();
viewer.spinOnce();
}
return 0;
}
测试效果

降采样
体素法滤波,即减少点的数量,减少点云数据,并同时保持点云的形状特征,在提高配准、曲面重建、形状识别等算法速度中非常实用。
PCL实现的VoxelGrid类通过输入的点云数据创建一个三维体素栅格(可把体素栅格想象为微小的空间三维立方体的集合),然后在每个体素(即三维立方体)内,用体素中所有点的重心来近似显示体素中其他点,这样该体素内所有点就用一个重心点最终表示,对于所有体素处理后得到过滤后的点云。

官方教程—— https://pcl-tutorials.readthedocs.io/en/latest/voxel_grid.html#voxelgrid
#include <iostream>
#include <pcl/io/io.h>
#include <pcl/io/pcd_io.h>
#include <pcl/point_types.h>
#include <pcl/filters/voxel_grid.h>
#include <pcl/visualization/cloud_viewer.h>
int main (int argc, char** argv)
{
pcl::PCLPointCloud2::Ptr cloud (new pcl::PCLPointCloud2 ());
pcl::PCLPointCloud2::Ptr cloud_filtered (new pcl::PCLPointCloud2 ());
// Fill in the cloud data
pcl::PCDReader reader; // 也可以用创建reader的方式来读PCD文件
// Replace the path below with the path where you saved your file
reader.read ("../data/result.pcd", *cloud); // Remember to download the file first!
std::cerr << "PointCloud before filtering: " << cloud->width * cloud->height
<< " data points (" << pcl::getFieldsList (*cloud) << ")." << std::endl;
// Create the filtering object
pcl::VoxelGrid<pcl::PCLPointCloud2> sor;
sor.setInputCloud (cloud);
sor.setLeafSize (0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f);
sor.filter (*cloud_filtered);
std::cerr << "PointCloud after filtering: " << cloud_filtered->width * cloud_filtered->height
<< " data points (" << pcl::getFieldsList (*cloud_filtered) << ")." << std::endl;
pcl::PCDWriter writer;
writer.write ("../data/result_downsampled.pcd", *cloud_filtered,
Eigen::Vector4f::Zero (), Eigen::Quaternionf::Identity (), false);
return (0);
}
PointCloud before filtering: 98322 data points (x y z intensity).
PointCloud after filtering: 11733 data points (x y z intensity).
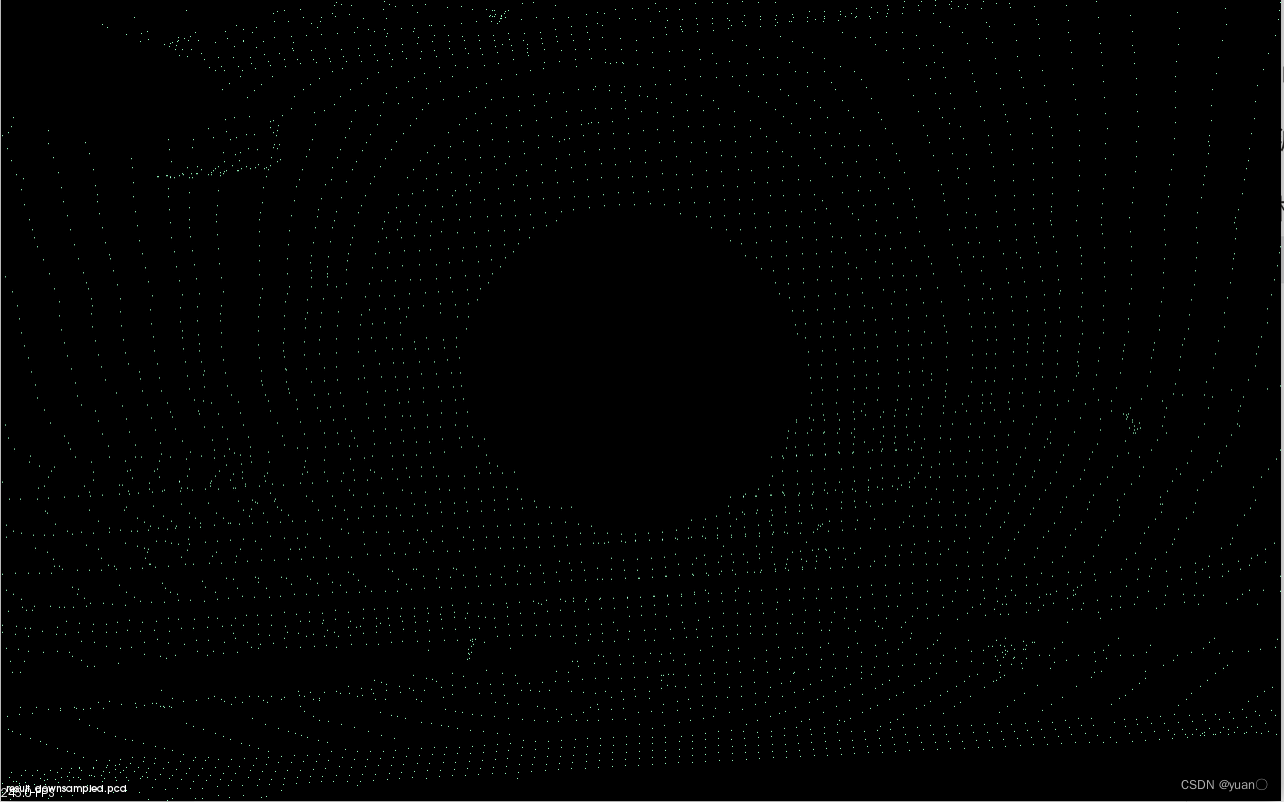
pcl_viewer查看效果,点云数目明显减少。
使用统计滤波(statisticalOutlierRemoval)移除离群点
激光扫描通常会产生密度不均匀的点云数据集,另外测量中的误差也会产生稀疏的离群点,局部点云特征运算(如采样点处法向量或曲率变化率)复杂,容易导致点云配准等后期处理失败。
常用解决思路:每个点的邻域进行一个统计分析,并修剪掉一些不符合一定标准的点。假设得到的结果是一个高斯分布,其形状是由均值和标准差决定,则平均距离在标准范围之外的点,可以被定义为离群点并可从数据中去除。
统计滤波移除离群点的步骤如下:
- 查找每一个点的所有邻域点
- 计算每个点到其邻域点的距离 d i j d_{ij} dij,其中 i = [ 1 , 2 , . . . , m ] i=[1,2,...,m] i=[1,2,...,m]表示共有 m m m个点, j = [ 1 , 2 , . . . , k ] j=[1,2,...,k] j=[1,2,...,k]表示共有 k k k个邻域点
- 根据高斯分布
d
N
(
μ
,
σ
)
d~N(\mu,\sigma)
d N(μ,σ)模型化距离参数,计算所有点与邻域点的
μ
\mu
μ(距离的均值),
σ
\sigma
σ(距离的标准差),如下:
μ
=
1
n
k
∑
i
=
1
m
∑
j
=
1
k
d
i
j
\mu {\rm{ = }}\frac{{\rm{1}}}{{nk}}\sum\limits_{i = 1}^m {\sum\limits_{j = 1}^k {{d_{ij}}} }
μ=nk1i=1∑mj=1∑kdij
σ
=
1
n
k
∑
i
=
1
m
∑
j
=
1
k
(
d
i
j
−
μ
)
2
\sigma {\rm{ = }}\sqrt {\frac{{\rm{1}}}{{nk}}\sum\limits_{i = 1}^m {\sum\limits_{j = 1}^k {{{({d_{ij}} - \mu )}^2}} } }
σ=nk1i=1∑mj=1∑k(dij−μ)2在此步骤时,同时也把每个点与其邻域点的距离均值求出
∑
j
=
1
k
d
i
j
{\sum\limits_{j = 1}^k {{{{d_{ij}} }}} }
j=1∑kdij
遍历所有点,若其距离的均值大于高斯分布的指定置信度,则移除,例如: ∑ j = 1 k d i j > μ + 3 σ o r ∑ j = 1 k d i j < μ − 3 σ \sum\limits_{j = 1}^k {{d_{ij}}} > \mu + 3\sigma or\sum\limits_{j = 1}^k {{d_{ij}}} < \mu - 3\sigma j=1∑kdij>μ+3σorj=1∑kdij<μ−3σ
#include <iostream>
#include <pcl/io/pcd_io.h>
#include <pcl/point_types.h>
#include <pcl/filters/statistical_outlier_removal.h>
int main (int argc, char** argv)
{
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZI>::Ptr cloud (new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZI>);
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZI>::Ptr cloud_filtered (new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZI>);
// 从文件读取点云
// Fill in the cloud data
pcl::PCDReader reader;
// Replace the path below with the path where you saved your file
reader.read<pcl::PointXYZI> ("../data/result.pcd", *cloud);
std::cerr << "Cloud before filtering: " << std::endl;
std::cerr << *cloud << std::endl;
// 创建过滤器,每个点分析计算时考虑的最近邻居个数为50个;
// 设置标准差阈值为1,这意味着所有距离查询点的平均距离的标准偏差均大于1个标准偏差的所有点都将被标记为离群值并删除。
// 计算输出并将其存储在cloud_filtered中
// Create the filtering object
pcl::StatisticalOutlierRemoval<pcl::PointXYZI> sor;
sor.setInputCloud (cloud);
// 设置平均距离估计的最近邻居的数量K
sor.setMeanK (50);
// 设置标准差阈值系数
sor.setStddevMulThresh (1.0);
// 执行过滤
sor.filter (*cloud_filtered);
std::cerr << "Cloud after filtering: " << std::endl;
std::cerr << *cloud_filtered << std::endl;
// 将留下来的点保存到后缀为_inliers.pcd的文件
pcl::PCDWriter writer;
writer.write<pcl::PointXYZI> ("../data/result_inliers.pcd", *cloud_filtered, false);
// 使用个相同的过滤器,但是对输出结果取反,则得到那些被过滤掉的点,保存到_outliers.pcd文件
sor.setNegative (true);
sor.filter (*cloud_filtered);
writer.write<pcl::PointXYZI> ("../data/result_outliers.pcd", *cloud_filtered, false);
return 0;
}
执行程序,输出以下结果
Cloud before filtering:
header: seq: 0 stamp: 0 frame_id:
points[]: 98322
width: 98322
height: 1
is_dense: 1
sensor origin (xyz): [0, 0, 0] / orientation (xyzw): [0, 0, 0, 1]
Cloud after filtering:
header: seq: 0 stamp: 0 frame_id:
points[]: 90637
width: 90637
height: 1
is_dense: 1
sensor origin (xyz): [0, 0, 0] / orientation (xyzw): [0, 0, 0, 1]
用pcl_viwer查看
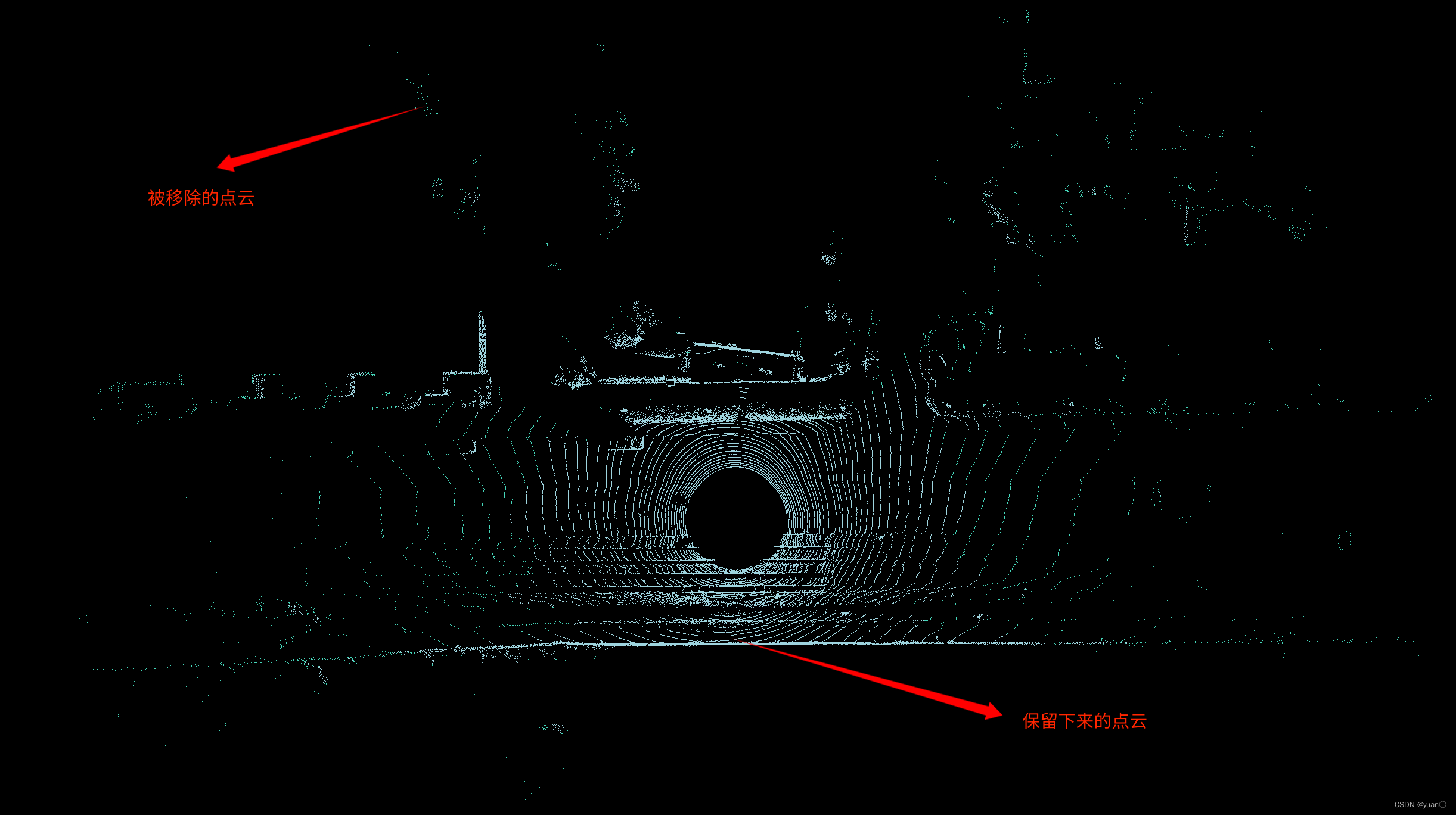
使用条件滤波(ConditionalRemoval)或 半径滤波(RadiusOutlinerRemoval)移除离群点
条件滤波器:通过设定滤波条件进行滤波,有点分段函数的味道,当点云在一定范围则留下,不在则舍弃。
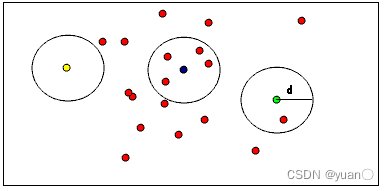
半径滤波器:以某点为中心画一个圆计算落在该圆中点的数量,当数量大于给定值时,则保留该点,数量小于给定值则剔除该点。此算法运行速度快,依序迭代留下的点一定是最密集的,但是圆的半径和圆内点的数目都需要人工指定。
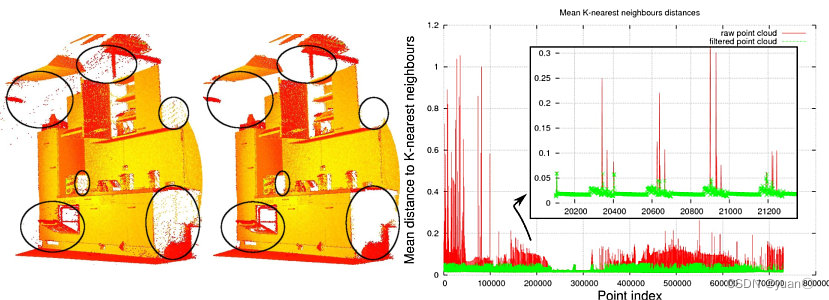
下图有助于可视化RadiusOutlierRemoval过滤器对象的作用。用户指定邻居的个数,要每个点必须在指定半径内具有指定个邻居才能保留在PointCloud中。例如,如果指定了1个邻居,则只会从PointCloud中删除黄点。如果指定了2个邻居,则黄色和绿色的点都将从PointCloud中删除。
#include <iostream>
#include <pcl/io/pcd_io.h>
#include <pcl/point_types.h>
#include <pcl/filters/radius_outlier_removal.h>
#include <pcl/filters/conditional_removal.h>
#include <pcl/visualization/pcl_visualizer.h>
void showPointClouds(const pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZI>::Ptr &cloud){
pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer viewer("Cloud Viewer");
//背景颜色设置
viewer.setBackgroundColor(0, 0, 0);
//按照z字段进行渲染
pcl::visualization::PointCloudColorHandlerGenericField<pcl::PointXYZI> fildColor(cloud, "intensity");
//显示点云,其中fildColor为颜色显示
viewer.addPointCloud<pcl::PointXYZI>(cloud, fildColor, "sample");
//设置点云大小
viewer.setPointCloudRenderingProperties(pcl::visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_POINT_SIZE, 1, "sample");
while (!viewer.wasStopped())
{
viewer.spinOnce();
}
}
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
if (argc != 2)
{
//选择-r为半径滤波;选择-c为条件滤波
std::cerr << "please specify command line arg '-r' or '-c'" << std::endl;
exit(0);
}
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZI>::Ptr cloud(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZI>);
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZI>::Ptr cloud_filtered(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZI>);
// 从文件读取点云
// Fill in the cloud data
pcl::PCDReader reader;
// Replace the path below with the path where you saved your file
reader.read<pcl::PointXYZI> ("../data/result.pcd", *cloud);
if (strcmp(argv[1], "-r") == 0)
{
//半径滤波
pcl::RadiusOutlierRemoval<pcl::PointXYZI> outrem;
// build the filter
outrem.setInputCloud(cloud);
outrem.setRadiusSearch(0.4); //设置半径滤波时圆的半径
outrem.setMinNeighborsInRadius(2); //设置圆内的点数
// apply filter
outrem.filter(*cloud_filtered);
//保存相应pcd文件,以方便后续查看
pcl::PCDWriter writer;
writer.write<pcl::PointXYZI>("../data/result_remove_outliers_r.pcd", *cloud_filtered, false);
}
else if (strcmp(argv[1], "-c") == 0)
{
//条件滤波
// build the condition
// 过滤条件:z轴方向上,大于0.0,小于8.0
pcl::ConditionAnd<pcl::PointXYZI>::Ptr range_cond(new pcl::ConditionAnd<pcl::PointXYZI>());
range_cond->addComparison(pcl::FieldComparison<pcl::PointXYZI>::ConstPtr(
new pcl::FieldComparison<pcl::PointXYZI>("z", pcl::ComparisonOps::GT, 0.0)));
range_cond->addComparison(pcl::FieldComparison<pcl::PointXYZI>::ConstPtr(
new pcl::FieldComparison<pcl::PointXYZI>("z", pcl::ComparisonOps::LT, 0.8)));
// build the filter
pcl::ConditionalRemoval<pcl::PointXYZI> condrem;
condrem.setCondition(range_cond);
condrem.setInputCloud(cloud);
condrem.setKeepOrganized(false);
// apply filter
condrem.filter(*cloud_filtered);
//保存相应pcd文件,以方便后续查看
pcl::PCDWriter writer;
writer.write<pcl::PointXYZI>("../data/result_remove_outliers_c.pcd", *cloud_filtered, false);
}
else
{
std::cerr << "please specify command line arg '-r' or '-c'" << std::endl;
exit(0);
}
std::cerr << "Cloud before filtering: " << std::endl;
std::cerr << *cloud << std::endl;
// display pointcloud after filtering
std::cerr << "Cloud after filtering: " << std::endl;
std::cerr << *cloud_filtered << std::endl;
showPointClouds(cloud_filtered);
return (0);
}
半径滤波
Cloud before filtering:
header: seq: 0 stamp: 0 frame_id:
points[]: 98322
width: 98322
height: 1
is_dense: 1
sensor origin (xyz): [0, 0, 0] / orientation (xyzw): [0, 0, 0, 1]
Cloud after filtering:
header: seq: 0 stamp: 0 frame_id:
points[]: 95967
width: 95967
height: 1
is_dense: 1
sensor origin (xyz): [0, 0, 0] / orientation (xyzw): [0, 0, 0, 1]
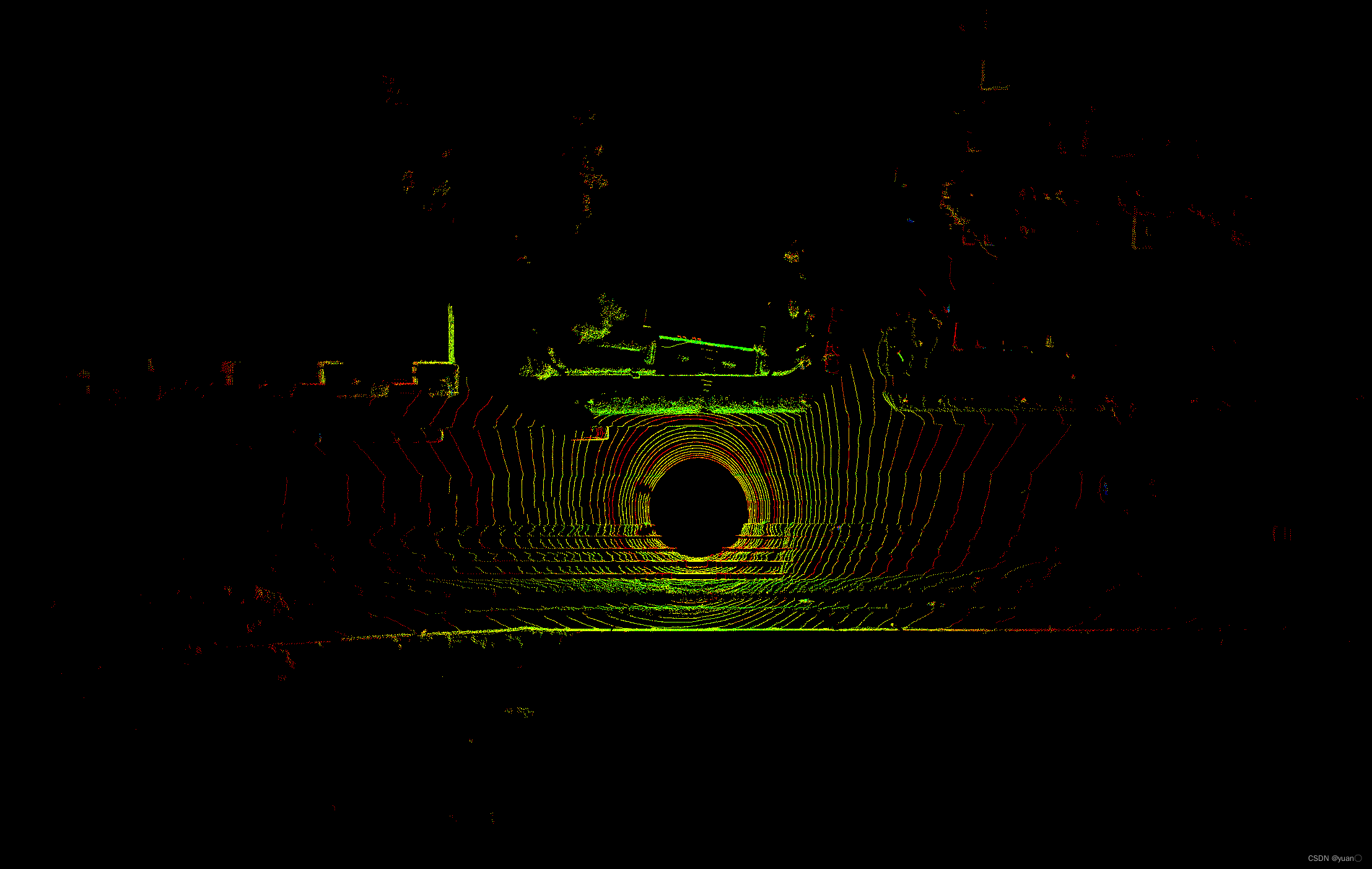
条件滤波
Cloud before filtering:
header: seq: 0 stamp: 0 frame_id:
points[]: 98322
width: 98322
height: 1
is_dense: 1
sensor origin (xyz): [0, 0, 0] / orientation (xyzw): [0, 0, 0, 1]
Cloud after filtering:
header: seq: 0 stamp: 0 frame_id:
points[]: 9904
width: 9904
height: 1
is_dense: 1
sensor origin (xyz): [0, 0, 0] / orientation (xyzw): [0, 0, 0, 1]