目录
💥1 概述
📚2 运行结果
🎉3 参考文献
👨💻4 Matlab代码
💥1 概述
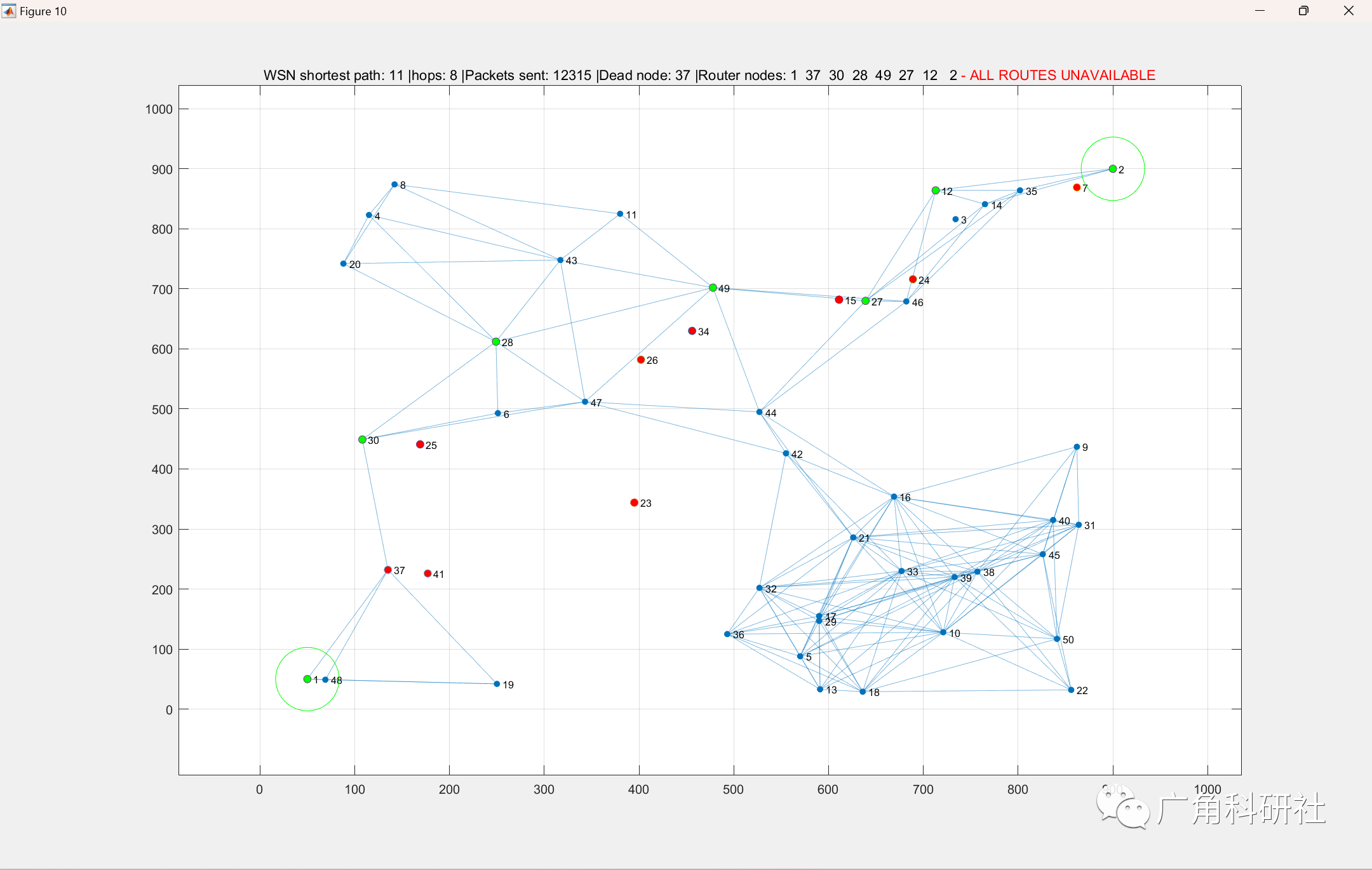
本代码基于无线传感器网络,在两个节点(源节点和目标节点)之间找到最短路径,并开始发送数据,直到路由中涉及的一个节点死亡。一旦一个节点死亡,它就会搜索另一条路径并重新开始发送,直到参与路由的节点因没有能量等原因死亡,直到网络在源节点和目标节点之间不再有连接。
📚2 运行结果









主函数部分代码:
clear all
close all
clc
%% GPU config - if want to run some code block into GPU. (NOT FULLY IMPLEMENTED)
%gpu = gpuDevice;
%gpu(1);
%% Main configuration values for this simulation
dataset.nodeNo = 50; %Number of nodes
dataset.nodePosition(1,:) = [1 50 50]; %(Sender node fixed position)
dataset.nodePosition(2,:) = [2 900 900]; %(Receiver node fixed position)
dataset.NeighborsNo = 5;
dataset.range = 250; %Tolerance distance to became neighbor of one node (Euclidean distance based)
dataset.atenuationFactor = 1.8; %Atenuation factor in freespace - ranges from 1.8 to 4 due environment
dataset.minEnergy = 80; % Mw - Miliwatts (70% energy)
dataset.maxEnergy = 100; % Mw - Miliwatts (Full energy (100%) - 1 mAh charge capacity within 1 Volt energy)
dataset.energyconsumptionperCicle = 0.35;
dataset.energyrecoveryperCicle = 0.2;
dataset.energyfactor = 0.001;
STenergy=10000;
packet=0;
iterationcounter=1;
% Node position sortition
for a = 3 : dataset.nodeNo
dataset.nodeId = a;
garbage.x = randi([1 900]); %Xpos sortition
garbage.y = randi([1 900]); %Ypos sortition
dataset.nodePosition(a,:) = [dataset.nodeId garbage.x garbage.y]; %NodeID, X and Y position into nodePosition table
end
% Euclidean Distance calc from one node to all others
for i = 1 : dataset.nodeNo
for j = 1: dataset.nodeNo
garbage.x1 = dataset.nodePosition(i,2);
garbage.x2 = dataset.nodePosition(j,2);
garbage.y1 = dataset.nodePosition(i,3);
garbage.y2 = dataset.nodePosition(j,3);
dataset.euclidiana(i,j) = sqrt( (garbage.x1 - garbage.x2) ^2 + (garbage.y1 - garbage.y2)^2 );
end
end
% Edges matrix definition due "range" variable value
dataset.weights = lt(dataset.euclidiana,dataset.range);
% Graph construction
G=graph(dataset.weights,'omitselfloops'); %Graph creation based on adjacency matrix (Edges matrix) built above
% Euclidean distance extraction for all existente end-to-end formed by
% "distance tolerance" (range variable value)
for a = 1 : height(G.Edges)
garbage.s = G.Edges.EndNodes(a,1);
garbage.t = G.Edges.EndNodes(a,2);
garbage.Z(a,:) = dataset.euclidiana(garbage.s,garbage.t);
end
G.Edges.Euclidiana = garbage.Z(:,1);
%Initial energy sortition (from 70% to 100% - minEnergy and maxEnergy variable valeu)
[dataset.nodePosition(:,4)] = dataset.maxEnergy -(dataset.maxEnergy-dataset.minEnergy)*rand(dataset.nodeNo,1);
dataset.nodePosition(1:2,4)=STenergy;
%All "G" (Graph object) based nodes degree to use as "node processing
%status overload"
(more connections, busier!)
for a = 1: length(dataset.nodePosition(:,1))
dataset.nodePosition(a,5) = degree(G,dataset.nodePosition(a,1));
end
% Pathloss calc of each Edges based in a freespace (1.8 factor)
[G.Edges.Pathloss] = (10*dataset.atenuationFactor)*log10(G.Edges.Euclidiana);
%End points coordinates and energy migration to G object
for a = 1 : height(G.Edges)
garbage.Sourcenode = G.Edges.EndNodes(a,1);
garbage.Targetnode = G.Edges.EndNodes(a,2);
G.Edges.SourcenodeXpos(a) = dataset.nodePosition(garbage.Sourcenode,2);
G.Edges.SourcenodeYpos(a) = dataset.nodePosition(garbage.Sourcenode,3);
G.Edges.TargetnodeXpos(a) = dataset.nodePosition(garbage.Targetnode,2);
G.Edges.TargetnodeYpos(a) = dataset.nodePosition(garbage.Targetnode,3);
G.Edges.ActiveEdge(a) = 1;
end
🎉3 参考文献
[1]陆政. 基于改进蚁群算法的WSN路由研究[D].安徽理工大学,2018.
部分理论引用网络文献,若有侵权联系博主删除。