self-instruct方式生成语料代码实战
- self-instruct 介绍
- self-instruct 框架
- 生成语料代码实现过程
- Step1 通过模型生成新的指令
- Step2 对模型生成的指令进行判断
- Step3:根据Step2的判断结果,给出不同的输出
- Step4:过滤及后处理
本文对 self-instruct 生成语料的流程进行了分析,并尝试使用该代码生成了一定数量的语料。
self-instruct 介绍
2023年3月14日,斯坦福发布了Stanford Alpaca,该模型是对Meta的LLaMA &B进行了微调,且只花费了不到600美元。
其中,微调过程:在8个80GB A100上训练了3个小时,不到100美元;而微调所用数据是使用OpenAI的API,通过self-instruct方式生成的52K指令数据,花费了500美元。
self-instruct是一种将预训练语言模型与指令对齐的方法。可以通过模型自己来生成数据,而不需要大量的人工标注。
self-instruct论文: https://arxiv.org/abs/2212.10560
self-instruct代码:https://github.com/yizhongw/self-instruct
self-instruct 框架
self-instruct 框架如下图所示:
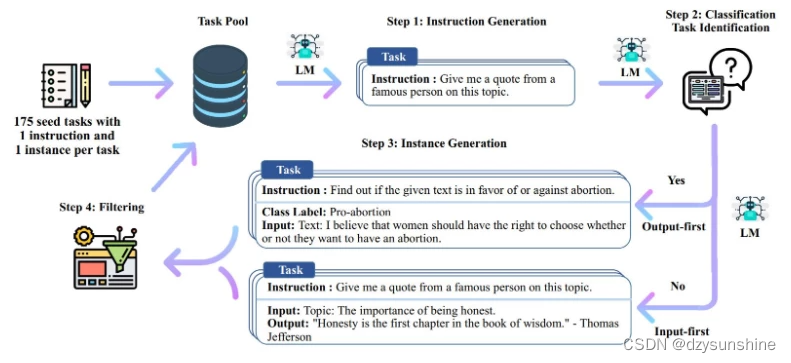
从上图可以看出,整个流程共包含了 4 个步骤。而生成后的数据形式如下:
- instruction: str,描述了模型应该执行的任务,也就是指令描述。
- input: str,任务的可选上下文或输入。
- output: str,由GPT3.5对应的API即 text-davinci-003生成的指令的答案。
Step1:通过模型生成新的指令;
根据人工设计的175个任务,每个任务都有对应的(指令,输入,输出)或(指令,输出);使用模型生成新的指令;
Step2:对模型生成的指令进行判断(指令是否是一个分类任务);
Step3:根据Step2的判断结果,给出不同的输出
如果是分类任务,就通过模型输出 Class_label 和 Input(Output-first);
如果不是分类任务,就通过模型输出 Input 和 Output(Input-first)。
Step4:过滤及后处理
对上述模型生成的数据进行过滤和后处理,将经过过滤和后处理的数据添加到种子池中。
对于以上4个步骤进行不断循环,直到种子池有足够多的数据(通常会设定一个具体的参数,比如:52000),生成过程停止。而对于每一步还需要展开描述下相关细节。
关于 Step1
生成指令时,先从种子池中随机抽取6个人工编写的指令,再随机抽取2个之前步骤中模型生成的指令,总共8个指令。按照指定模版格式组织之后,输入给模型,让模型输出一个新的指令。
需要注意的是,最开始的时候,是没有模型生成的指令,因此是会直接从种子池中随机抽取8条人工编写的指令。
关于 Step2
判断指令是否属于分类任务的操作如下:在种子池中随机挑选12条分类指令和19条非分类指令,然后加上新生成的指令。
关于Step4:过滤及后处理
为了数据的多样性,新生成的指令只有与种子池中的指令的 ROUGE-L 小于0.7时才会添加进入种子池;
排除一些无法被语言模型处理的指令,比如涉及图像、图片、图形的指令;
在给指令生成实例时,会过滤掉输入相同但是输出不同的实例。
生成语料代码实现过程
下面我们从代码部分来看详细的步骤。整个过程是要依次运行 4 个代码文件,对应前文中描述的 4 个步骤。
# 1. Generate instructions from the seed tasks
./scripts/generate_instructions.sh
# 2. Identify whether the instruction represents a classification task or not
./scripts/is_clf_or_not.sh
# 3. Generate instances for each instruction
./scripts/generate_instances.sh
# 4. Filtering, processing, and reformatting
./scripts/prepare_for_finetuning.sh
本次实验在本地的pytorch环境下进行。
1、首先将代码下载到本地,下面两种方式均可。
- 使用 Download 下载zip文件
- git clone https://github.com/yizhongw/self-instruct.git
我这里是在我的windows上操作的,所以无法执行bash命令,我这里直接用python命令运行。
2、进入conda环境(我这里用的pytorch这个环境) ,安装相关的包
cd self-instruct-main
pip install -r requirements.txt
Step1 通过模型生成新的指令
先看下原始人工标注的175种子数据的样式,共包含4个部分,id,name,instruction,is_classification。
{
"id": "seed_task_0",
"name": "breakfast_suggestion",
"instruction": "Is there anything I can eat for a breakfast that doesn't include eggs, yet includes protein, and has roughly 700-1000 calories?", "instances": [{"input": "", "output": "Yes, you can have 1 oatmeal banana protein shake and 4 strips of bacon. The oatmeal banana protein shake may contain 1/2 cup oatmeal, 60 grams whey protein powder, 1/2 medium banana, 1tbsp flaxseed oil and 1/2 cup watter, totalling about 550 calories. The 4 strips of bacon contains about 200 calories."}],
"is_classification": false
}
本次只是实验,故将scripts/generate_instructions.sh中的5000改为100(这样产生的费用也较少)
运行命令如下:
python self_instruct/bootstrap_instructions.py --batch_dir data/ceshi --num_instructions_to_generate 100 --seed_tasks_path data/seed_tasks.jsonl --engine "davinci" --api_key "自己的openai API"
大概需要4分半的时间,生成100条数据。会写入data/ceishi/machine_generated_instructions.jsonl中,最终生成了122条。这些数据是通过LLM生成了与种子任务关联度比较弱的一些任务描述(一些相似度高的就删除了)。
从下面的代码中可以看出,最后写入文件时,一共包含了以下4个部分:instruction,most_similar,avg_similarity_score,metadata,request_idx。
fout.write(json.dumps({
"instruction": inst,
"most_similar": most_similar_instructions,
"avg_similarity_score": float(np.mean(rouge_scores)),
"metadata": metadata,
"request_idx": request_idx
}) + "\n")
生成数据的核心代码如下:
# load the LM-generated instructions,使用生成模型得到新的100条 instruction 提示
machine_instructions = []
# 开始生成 100 条 instruction 提示数据
with open(os.path.join(args.batch_dir, "machine_generated_instructions.jsonl"), "a") as fout:
while len(machine_instructions) < args.num_instructions_to_generate:
batch_inputs = []
# args.request_batch_size为5
for _ in range(args.request_batch_size):
# sample machine instructions from the pool(从生成模型中选,n表示最少的条数。这里为2)
prompt_instructions = sample_machine_instructions(
machine_instructions,
similarities=None,
n=2)
# sample human instructions from the pool
# 从默认的175条中选再选几条,相当于一共选了8条,其中从175条中选6条,使用LLM生成2条(最开始的时候,machine_instructions为空,因此会直接从175条中直接选8条)
prompt_instructions += random.sample(seed_instructions, args.num_prompt_instructions - len(prompt_instructions))
random.shuffle(prompt_instructions)
prompt = encode_prompt(prompt_instructions, classification=args.use_clf_seed_tasks_only)
batch_inputs.append(prompt)
results = make_gpt3_requests(
engine=args.engine,
prompts=batch_inputs,
max_tokens=1024,
temperature=0.7,
top_p=0.5,
frequency_penalty=0,
presence_penalty=2,
stop_sequences=["\n\n", "\n16", "16.", "16 ."],
logprobs=1,
n=1,
best_of=1,
api_key=args.api_key,
organization=args.organization,
)
其中,对不同类型的数据需要构建不同的 prompt 数据(如:是分类数据,不是分类数据),构建方式在函数 encode_prompt中
# 构建prompt数据,针对是否分类分别构建不同的prompt数据,
# 是否是分类任务, 是=>输出优先,否=>输入优先,对应的 prompt_instructions/prompt_instances 不一样
def encode_prompt(prompt_instructions, classification=False):
"""Encode multiple prompt instructions into a single string."""
if classification:
# 源码中prompt
# prompt = "Come up with a series of classification tasks. Try to specify the possible output labels when possible.\n"
prompt = "Referring to a series of classification tasks, generate 8 more new tasks. Try to specify the possible output labels when possible.\n"
else:
# 源码中prompt
# prompt = "Come up with a series of tasks:\n"
prompt = "Referring to these eight tasks, generate 8 more new tasks:\n"
for idx, instruction in enumerate(prompt_instructions):
instruction = re.sub(r"\s+", " ", instruction).strip().rstrip(":")
prompt += f"{idx+1}. {instruction}\n"
prompt += f"{len(prompt_instructions) + 1}."
return prompt
Step2 对模型生成的指令进行判断
3、判断是否是分类任务。
python self_instruct/identify_clf_or_not.py --batch_dir data/ceshi --engine "davinci" --request_batch_size 5 --api_key "自己的openai API"
会写入data/ceishi/is_clf_or_not_davinci_template_1.jsonl中,最终生成了122条。
内容包括:
{"instruction": "Find the largest number in this list.", "is_classification": " Yes"}
{"instruction": "What is the first name of your favorite actor?", "is_classification": " No"}
{"instruction": "Give me the number of distinct elements in this set.", "is_classification": " Yes"}
{"instruction": "Give me the top 5 countries that are exporting tea.", "is_classification": " Yes"}
核心代码如下:
# 执行输出过程
with open(output_path, "w") as fout:
for batch_idx in range(0, len(lines), args.request_batch_size):
batch = [json.loads(line) for line in lines[batch_idx: batch_idx + args.request_batch_size]]
if all(d["instruction"] in existing_requests for d in batch):
for d in batch:
data = existing_requests[d["instruction"]]
data = OrderedDict(
(k, data[k]) for k in \
["instruction", "is_classification"]
)
fout.write(json.dumps(data, ensure_ascii=False) + "\n")
else:
# prefix = compose_prompt_prefix(human_written_tasks, batch[0]["instruction"], 8, 2)
prefix = templates[args.template]
prompts = [prefix + " " + d["instruction"].strip() + "\n" + "Is it classification?" for d in batch]
results = make_gpt3_requests(
engine=args.engine,
prompts=prompts,
max_tokens=3,
temperature=0,
top_p=0,
frequency_penalty=0,
presence_penalty=0,
stop_sequences=["\n", "Task"],
logprobs=1,
n=1,
best_of=1,
api_key=args.api_key,
organization=args.organization)
for i in range(len(batch)):
data = batch[i]
if results[i]["response"] is not None:
data["is_classification"] = results[i]["response"]["choices"][0]["text"]
else:
data["is_classification"] = ""
data = {
"instruction": data["instruction"],
"is_classification": data["is_classification"]
}
data = OrderedDict(
(k, data[k]) for k in \
["instruction", "is_classification"]
)
fout.write(json.dumps(data, ensure_ascii=False) + "\n")
Step3:根据Step2的判断结果,给出不同的输出
python self_instruct/generate_instances.py --batch_dir data/ceshi --input_file machine_generated_instructions.jsonl --output_file machine_generated_instances.jsonl --max_instances_to_gen 5 --engine "davinci" --request_batch_size 5 --api_key "自己的openai API"
如果遇到以下报错:
UnicodeDecodeError: ‘gbk’ codec can’t decode byte 0x9d in position 6169: illegal multibyte sequence
解决方法:
在open函数中添加encoding='utf-8’即可。
运行后会将结果写入 data/ceishi/machine_generated_instances.jsonl中。每条数据包含5部分:“instruction”, “raw_instances”, “instance_metadata”, “instruction_metadata”, “most_similar”, “avg_similarity_score”。
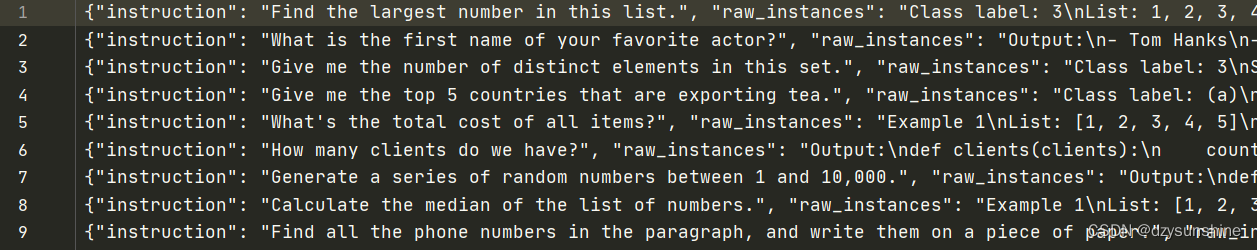
核心代码如下:
with open(output_path, "w", encoding='utf-8') as fout:
for batch_idx in range(0, len(tasks), args.request_batch_size):
batch = tasks[batch_idx: batch_idx + args.request_batch_size]
if all(d["instruction"] in existing_requests for d in batch):
for d in batch:
data = existing_requests[d["instruction"]]
data = OrderedDict(
(k, data[k]) for k in \
["instruction", "raw_instances", "instance_metadata", "instruction_metadata",
"most_similar", "avg_similarity_score"]
)
fout.write(json.dumps(data, ensure_ascii=False) + "\n")
else:
prompts = []
for task in batch:
if task_clf_types[task["instruction"]]:
prompt = output_first_template_for_clf + " " + task["instruction"].strip() + "\n"
prompts.append(prompt)
else:
prompt = input_first_template_for_gen + " " + task["instruction"].strip() + "\n"
prompts.append(prompt)
results = make_gpt3_requests(
engine=args.engine,
prompts=prompts,
# because the clf template is longer, we need to decrease the max_tokens
max_tokens=300 if any(task_clf_types[task["instruction"]] for task in batch) else 350,
temperature=0,
top_p=0,
frequency_penalty=0,
presence_penalty=1.5,
stop_sequences=[f"Example {args.max_instances_to_generate + 1}", "Task:"],
logprobs=1,
n=1,
best_of=1,
api_key=args.api_key,
organization=args.organization)
for i in range(len(batch)):
data = batch[i]
data["instance_metadata"] = results[i]
if results[i]["response"] is not None:
data["raw_instances"] = results[i]["response"]["choices"][0]["text"]
else:
data["raw_instances"] = ""
data = OrderedDict(
(k, data[k]) for k in \
["instruction", "raw_instances", "instance_metadata", "instruction_metadata",
"most_similar", "avg_similarity_score"]
)
fout.write(json.dumps(data, ensure_ascii=False) + "\n")
progress_bar.update(len(batch))
Step4:过滤及后处理
python self_instruct/prepare_for_finetuning.py --instance_files data/ceshi/machine_generated_instances.jsonl --classification_type_files data/ceshi/is_clf_or_not_davinci_template_1.jsonl --output_dir data/ceshi/finetuning_data --include_seed_tasks --seed_tasks_path data/seed_tasks.jsonl
运行后会生成两个数据文件,均在data/ceshi/finetuning_data目录下:
all_generated_instances.jsonl 和 gpt3_finetuning_data_336.jsonl
其中,all_generated_instances.jsonl中包含的是 instruction,input,output
gpt3_finetuning_data_336.jsonl中包含的是prompt,completion。
核心代码如下:
for task in tqdm.tqdm(generated_tasks):
# get instruction
instruction = task["instruction"]
task["is_classification"] = task_clf_types[instruction]
# get the instances
if task["is_classification"]:
task_instances = parse_instances_for_classification_task(task["raw_instances"], instruction, task["instance_metadata"])
else:
task_instances = parse_instances_for_generation_task(task["raw_instances"], instruction, task["instance_metadata"])
# we only allow max 5 instances per task
task_instances = random.sample(task_instances, min(len(task_instances), 5))
if not task_instances:
continue
training_instances += task_instances
# get the prompt and completion for training gpt3
gpt3_instances = []
for instance in training_instances:
# get input and do preprocessing
inst_input = instance[1]
# for some tasks, we check whether the input contains colon, and if so, we remove the part before the colon
if random.random() < 0.5:
colon_words = re.findall(r"(\w+):", inst_input)
# if only one colon is found, we assume the instance only have one input and we remove the field name before the colon
if len(set(colon_words)) == 1:
inst_input = inst_input.split(":", 1)[1].strip()
else:
inst_input = inst_input.strip()
# we also replace two consecutive new lines with one new line half of the time
inst_input = inst_input.replace("\n\n", "\n")
gpt3_instances.append(encode_instance(instance[0], inst_input, instance[2]))
# remove duplicates
filtered_instances = []
prompt_completion_set = set()
for instance in gpt3_instances:
instance_pair = (instance["prompt"], instance["completion"])
if instance_pair not in prompt_completion_set:
prompt_completion_set.add((instance["prompt"], instance["completion"]))
filtered_instances.append(instance)
gpt3_instances = filtered_instances
# shuffle
random.shuffle(gpt3_instances)
with open(os.path.join(args.output_dir, f"gpt3_finetuning_data_{len(gpt3_instances)}.jsonl"), "w") as fout:
for instance in gpt3_instances:
fout.write(json.dumps({
"prompt": instance["prompt"],
"completion": instance["completion"],
}) + "\n")

![[架构之路-176]-《软考-系统分析师》-1-嵌入式系统分析与设计 - 实时性(任务切换时间、中断延迟时间、中断响应时间)、可靠性、功耗、体积、成本](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/4273303146bb413ea9ef10879cd6ede1.png)