目录
map
1. 构造、析构和赋值运算符重载
1.1 构造函数
1.2 析构函数
1.3 赋值运算符重载
2. 迭代器
3. 容量
4. 元素访问
5. 修改器
6. 观察者
7. 操作
8. 分配器
map
map是关联容器,它按照特定的顺序存储由关键字值和映射值的组合形成的元素。
在一个map中,关键字值通常用于排序和唯一识别元素,而映射值则存储与此键相关的内容。关键字值和映射值的类型可能不同,在成员类型value_type中被组合在一起,它是一个结合了两者的pair类型:
typedef pair<const Key, T> value_type;在内部,map中的元素总是按照它的关键字进行排序,遵循一个特定的严格的弱排序标准,由其内部的比较对象(类型为Compare)指示。
map容器通常比unordered_map容器按关键字访问单个元素的速度要慢,但是它们允许根据顺序直接迭代子集。
map中的映射值可以使用括号操作符(operator[])直接通过其相应的关键字来访问。
map通常被实现为二叉搜索树。
使用map类型要包含map头文件;map定义在命名空间std中。
1. 构造、析构和赋值运算符重载
1.1 构造函数
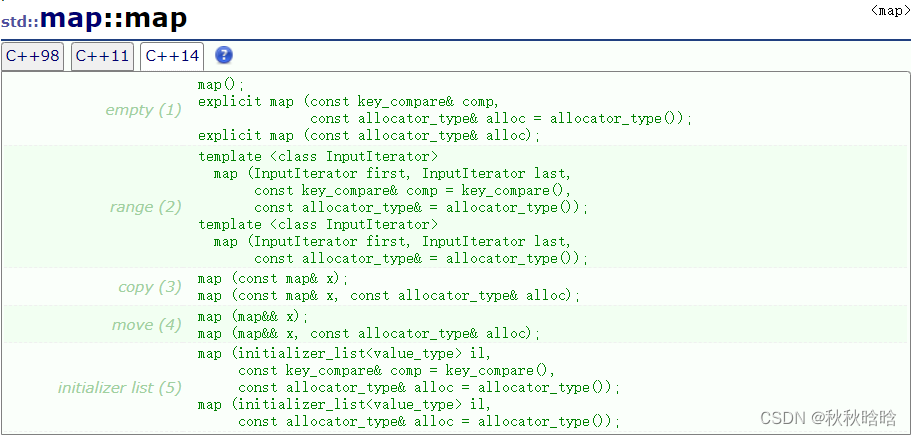
| 重载函数 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| empty | 构造空的map类对象 |
| range | 用迭代器区间[first,last)中的元素构造 |
| copy | 构造一个x的拷贝 |
| move | 移动构造函数 |
| initializer list | 用初始化列表来构造 |
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
map<char, int> m1;//empty
for (auto e : m1)
{
cout << e.first << " " << e.second << endl;
}
//空
//插入
m1.insert({ 'g', 30 });
m1.insert(make_pair('a', 10));
m1.insert(pair<char, int>('f', 50));
m1['b'];
m1['d'] = 20;
for (auto e : m1)
{
cout << e.first << " " << e.second << endl;
}
//a 10
//b 0
//d 20
//f 50
//g 30
map<char, int> m2(++m1.begin(), m1.end());//range
for (auto e : m2)
{
cout << e.first << " " << e.second << endl;
}
//b 0
//d 20
//f 50
//g 30
map<char, int> m3(m2);//copy
//等价于map<char, int> m3 = m2;
for (auto e : m3)
{
cout << e.first << " " << e.second << endl;
}
//b 0
//d 20
//f 50
//g 30
map<string, string> m4{ {"empty","空"},{"range", "范围"},{"copy", "复制"} };
//等价于map<string, string> m4 = { {"empty","空"},{"range", "范围"},{"copy", "复制"} };
for (auto e : m4)
{
cout << e.first << " " << e.second << endl;
}
//copy 复制
//empty 空
//range 范围
return 0;
}1.2 析构函数

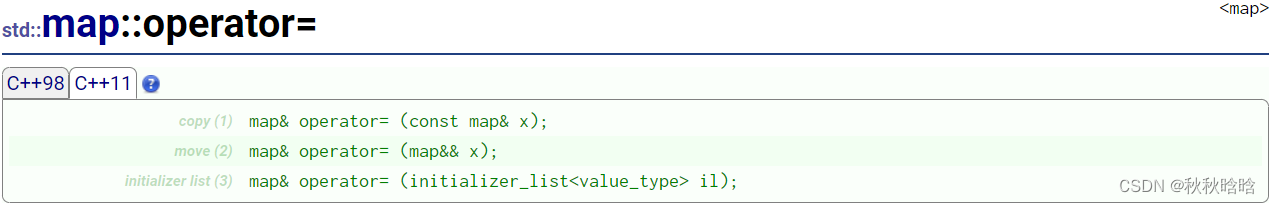
1.3 赋值运算符重载
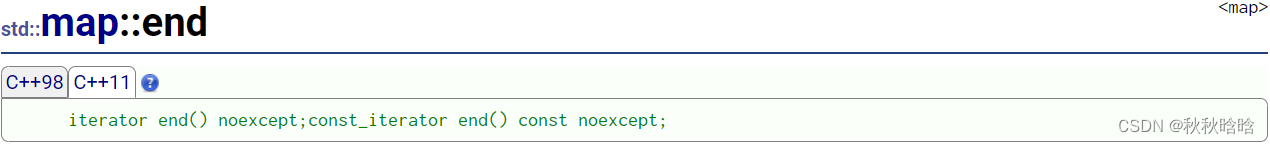
2. 迭代器

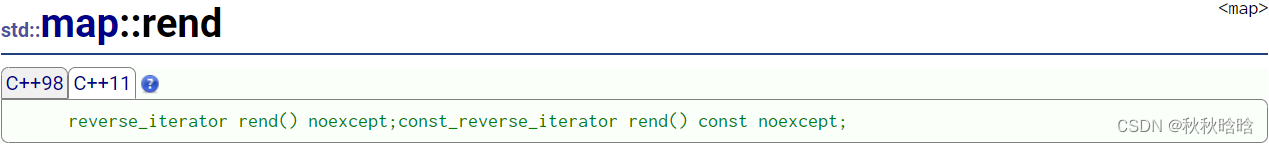




| 函数 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| begin & end | begin返回一个迭代器,指向map对象的第一个元素 end返回一个迭代器,指向map对象的最后一个元素的下一个位置 |
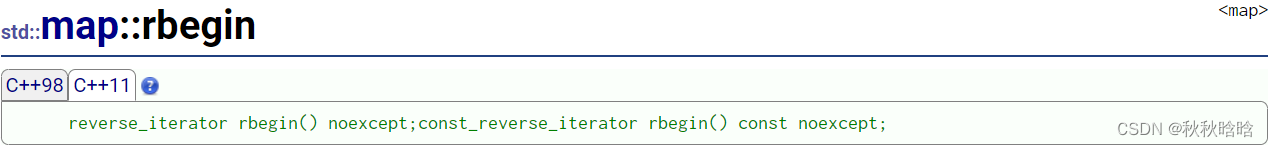
| rbegin & rend | rbegin返回一个反向迭代器,指向map对象的最后一个元素 rend返回一个反向迭代器,指向map对象的第一个元素的上一个位置 |
| cbegin & cend | cbegin返回一个const迭代器,指向map对象的第一个元素 cend返回一个const迭代器,指向map对象的最后一个元素的下一个位置 |
| crbegin & crend | crbegin返回一个const反向迭代器,指向map对象的最后一个元素 crend返回一个const反向迭代器,指向map对象的第一个元素的上一个位置 |
begin&end和rbegin&rend返回的迭代器指向:
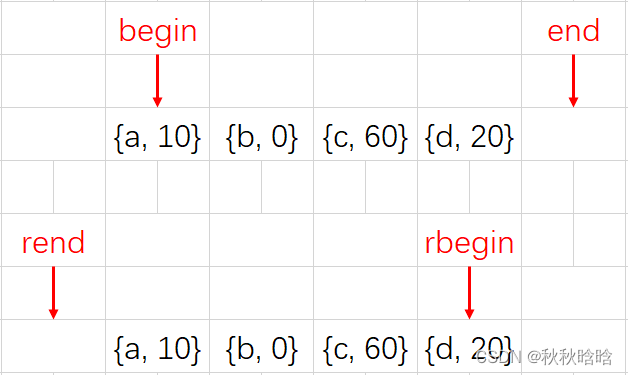
const_iterator是一个指向const内容的迭代器。迭代器本身可以修改,但是它不能被用来修改它所指向的内容。
begin&end/rbegin&rend和cbegin&cend/crbegin&crend的不同:
- begin&end/rbegin&rend的返回类型由对象是否是常量来决定。如果不是常量,返回iterator;如果是常量,返回const_iterator。
- cbegin&cend/crbegin&crend的返回类型是const_iterator,不管对象本身是否是常量。
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
map<string, string> m{ {"iterator", "迭代器"},{"begin","开始"},{"end", "结束"} };
map<string, string>::iterator it = m.begin();
while (it != m.end())
{
cout << it->first << " " << it->second << endl;
//等价于cout << (*it).first << " " << (*it).second << endl;
++it;
}
//begin 开始
//end 结束
//iterator 迭代器
auto rit = m.rbegin();
//map<string, string>::reverse_iterator rit = m.rbegin();
while (rit != m.rend())
{
cout << rit->first << " " << rit->second << endl;
//等价于cout << (*rit).first << " " << (*rit).second << endl;
++rit;
}
//iterator 迭代器
//end 结束
//begin 开始
return 0;
}3. 容量



| 函数 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| empty | 检测set是否为空,是返回true,否则返回false |
| size | 返回set的元素个数 |
| max_size | 返回set所能容纳的最大元素数 |
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
map<string, string> m{ {"iterator", "迭代器"},{"begin","开始"},{"end", "结束"} };
if (m.empty())
cout << "map为空" << endl;
else
cout << "map不为空" << endl;
//map不为空
cout << m.size() << endl;//3
cout << m.max_size() << endl;//59652323
return 0;
}4. 元素访问
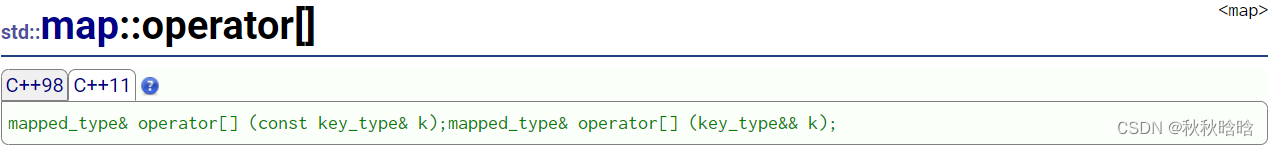

| 函数 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| operator[] | 如果k与某个元素的关键字相匹配,返回对其映射值的引用 如果k与任何元素的关键字不匹配,插入一个关键字为k的新元素,并返回对其映射值的引用 |
| at | 返回vector中n位置的元素的引用 有越界检查,如果越界会抛异常 |
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
map<char, int> m;
m['b']; //插入一个关键字为'b'的元素,但没有对映射值进行初始化
m['d'] = 20;//插入一个关键字为'd'的元素,并将映射值初始化为20
cout << "m['b'] = " << m['b'] << endl;//m['b'] = 0
cout << "m['d'] = " << m['d'] << endl;//m['d'] = 20
m['b'] = 50;//修改关键字为'b'的元素的映射值为50
cout << "m['b'] = " << m['b'] << endl;//m['b'] = 50
cout << "m['d'] = " << m['d'] << endl;//m['d'] = 20
return 0;
}5. 修改器
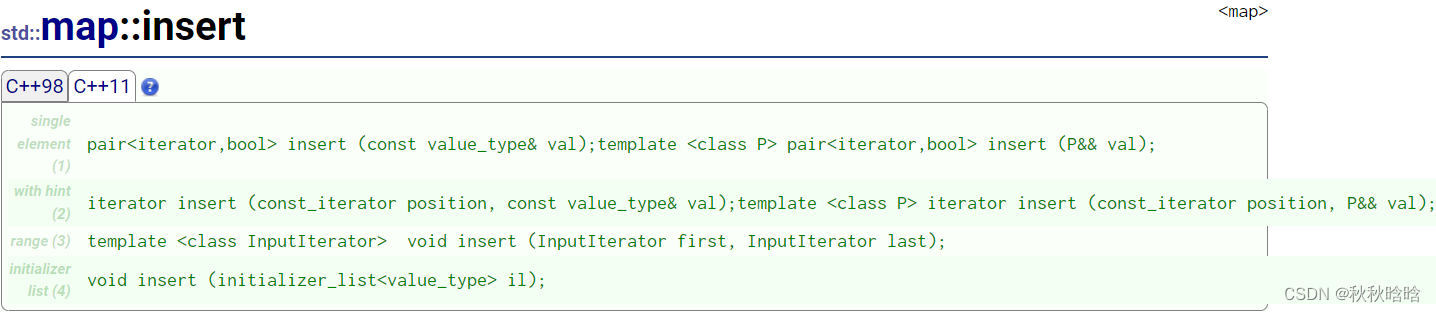
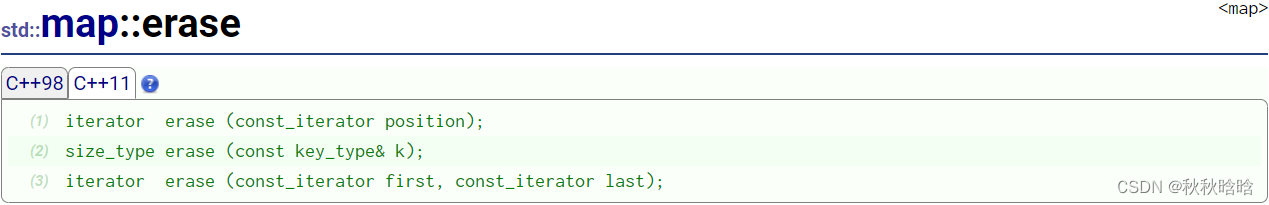




| 函数 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| insert | 插入元素 |
| erase | 删除元素 |
| swap | 交换内容 |
| clear | 清空内容 |
| emplace | 构建和插入元素 |
| emplace_hint | 构建和插入带有提示的元素 |
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
map<char, int> m1;
m1.insert(make_pair('p', 10));
m1.insert(pair<char, int>('f', 50));
m1.insert({ 'g', 30 });
for (auto e : m1)
{
cout << e.first << " " << e.second << endl;
}
//f 50
//g 30
//p 10
m1.erase(--m1.end());
m1.erase('g');
for (auto e : m1)
{
cout << e.first << " " << e.second << endl;
}
//f 50
map<char, int> m2{ {'h', 90},{'d',40},{'a',20} };
m1.swap(m2);
for (auto e : m1)
{
cout << e.first << " " << e.second << endl;
}
//a 20
//d 40
//h 90
m1.clear();
if (m1.empty())
cout << "m1被清空" << endl;
else
cout << "m1没被清空" << endl;
//m1被清空
return 0;
}6. 观察者


| 函数 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| key_comp | 返回比较对象 |
| value_comp | 返回比较对象 |
7. 操作





| 函数 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| find | 获取元素的迭代器 |
| count | 计算特定元素的数量 返回值0或1 |
| lower_bound | 返回指向下限的迭代器 |
| upper_bound | 返回指向上限的迭代器 |
| equal_range | 获取相等元素的范围 范围内有0或1个元素 |
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
map<char, int> m;
m.insert({ 'g', 30 });
m.insert(make_pair('a', 10));
m.insert(pair<char, int>('f', 50));
m['b'];
m['d'] = 20;
auto it = m.find('f');
if (it != m.end())
{
cout << "f在map中" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "f不在map中" << endl;
}
//f在map中
it = m.find('h');
if (it != m.end())
{
cout << "h在map中" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "h不在map中" << endl;
}
//h不在map中
if (m.count('a'))
{
cout << "a在map中" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "a不在map中" << endl;
}
//a在map中
if (m.count('c'))
{
cout << "c在map中" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "c不在map中" << endl;
}
//c不在map中
return 0;
}8. 分配器

| 函数 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| get_allocator | 获取分配器 |




![[Golang] 设计模式以及单例设计模式实例实现](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/290cb82ff7834878aff2daa6c4a0bf4f.gif#pic_center)