目录
- 1.简述
- 2.踩坑记录
- 3.LoginController
- 4.LoginService
- 5.LoginLogService
- 5.1 @Async实现异步
- 5.2 自定义线程池实现异步
- 1)自定义线程池
- 2)复制上下文请求
- 3)自定义线程池实现异步
- 6.补充:LoginService 手动提交事务
背景: 模块调用之后,记录模块的相关日志,看似简单,其实暗藏玄机。
1.简述
模块日志的实现方式大致有三种:
- AOP + 自定义注解实现
- 输出指定格式日志 + 日志扫描实现
- 在接口中通过代码侵入的方式,在业务逻辑处理之后,调用方法记录日志。
这里我们主要讨论下第3种实现方式。
假设我们需要实现一个用户登录之后记录登录日志的操作。
调用关系如下:
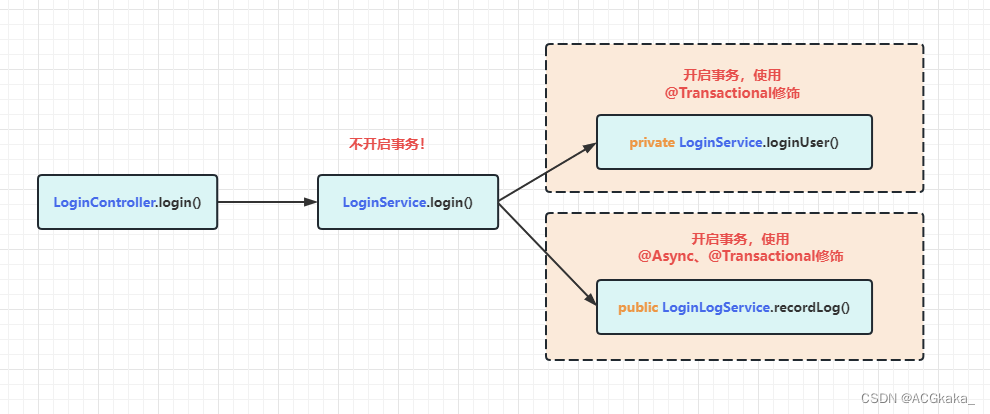
2.踩坑记录
这里之所以不能在 LoginService.login() 方法中开启事务,是为了在日志处理中方便单独开启事务。
如果在 LoginService.login() 方法中开启了事务,日志处理的方法做异步和做新事务都会有问题:
做异步:由于主事务可能没有执行完毕,导致可能读取不到主事务中新增或修改的数据信息;做新事务:可以通过Propagation.REQUIRES_NEW事务传播行为来创建新事务,在新事务中执行记录日志的操作,可能会导致如下问题:- 由于数据库默认事务隔离级别是可重复读,意味着事物之间读取不到未提交的内容,所以也会导致读取不到主事务中新增或修改的数据信息;
- 如果开启的新事务和之前的事务操作了同一个表,就会导致锁表。
什么都不做,直接同步调用:问题最多,可能导致如下几个问题:- 不捕获异常,直接导致接口所有操作回滚;
- 捕获异常,部分数据库,如:PostgreSQL,同一事务中,只要有一次执行失败,就算捕获异常,剩余的数据库操作也会全部失败,抛出异常;
- 日志记录耗时增加接口响应时间,影响用户体验。
3.LoginController
@RestController
public class LoginController {
@Autowired
private LoginService loginService;
@RequestMapping("/login")
public String login(String username, String pwd) {
loginService.login(username, pwd);
return "succeed";
}
}
4.LoginService
@Service
public class LoginService {
@Autowired
private LoginLogService loginLogService;
/** 登录 */
public void login(String username, String pwd) {
// 用户登录
loginUser(username, pwd);
// 记录日志
loginLogService.recordLog(username);
}
/** 用户登录 */
@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)
private void loginUser(String username, String pwd) {
// TODO: 实现登录逻辑..
}
}
5.LoginLogService
5.1 @Async实现异步
@Service
public class LoginLogService {
/** 记录日志 */
@Async
@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)
public void recordLog(String username) {
// TODO: 实现记录日志逻辑...
}
}
注意:@Async 需要配合 @EnableAsync 使用,@EnableAsync 添加到启动类、配置类、自定义线程池类上均可。
补充:由于 @Async 注解会动态创建一个继承类来扩展方法的实现,所以可能会导致当前类注入Bean容器失败 BeanCurrentlyInCreationException,可以使用如下方式:自定义线程池 + @Autowired
5.2 自定义线程池实现异步
1)自定义线程池
import com.demo.async.ContextCopyingDecorator;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.core.task.TaskExecutor;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.EnableAsync;
import org.springframework.scheduling.concurrent.ThreadPoolTaskExecutor;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor;
/**
* <p> @Title AsyncTaskExecutorConfig
* <p> @Description 异步线程池配置
*
* @author ACGkaka
* @date 2023/4/24 19:48
*/
@EnableAsync
@Configuration
public class AsyncTaskExecutorConfig {
/**
* 核心线程数(线程池维护线程的最小数量)
*/
private int corePoolSize = 10;
/**
* 最大线程数(线程池维护线程的最大数量)
*/
private int maxPoolSize = 200;
/**
* 队列最大长度
*/
private int queueCapacity = 10;
@Bean
public TaskExecutor taskExecutor() {
ThreadPoolTaskExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolTaskExecutor();
executor.setCorePoolSize(corePoolSize);
executor.setMaxPoolSize(maxPoolSize);
executor.setQueueCapacity(queueCapacity);
executor.setThreadNamePrefix("MyExecutor-");
// for passing in request scope context 转换请求范围的上下文
executor.setTaskDecorator(new ContextCopyingDecorator());
// rejection-policy:当pool已经达到max size的时候,如何处理新任务
// CALLER_RUNS:不在新线程中执行任务,而是有调用者所在的线程来执行
executor.setRejectedExecutionHandler(new ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy());
executor.setWaitForTasksToCompleteOnShutdown(true);
executor.initialize();
return executor;
}
}
2)复制上下文请求
import org.slf4j.MDC;
import org.springframework.core.task.TaskDecorator;
import org.springframework.security.core.context.SecurityContext;
import org.springframework.security.core.context.SecurityContextHolder;
import org.springframework.web.context.request.RequestAttributes;
import org.springframework.web.context.request.RequestContextHolder;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* <p> @Title ContextCopyingDecorator
* <p> @Description 上下文拷贝装饰者模式
*
* @author ACGkaka
* @date 2023/4/24 20:20
*/
public class ContextCopyingDecorator implements TaskDecorator {
@Override
public Runnable decorate(Runnable runnable) {
try {
// 从父线程中获取上下文,然后应用到子线程中
RequestAttributes requestAttributes = RequestContextHolder.currentRequestAttributes();
Map<String, String> previous = MDC.getCopyOfContextMap();
SecurityContext securityContext = SecurityContextHolder.getContext();
return () -> {
try {
if (previous == null) {
MDC.clear();
} else {
MDC.setContextMap(previous);
}
RequestContextHolder.setRequestAttributes(requestAttributes);
SecurityContextHolder.setContext(securityContext);
runnable.run();
} finally {
// 清除请求数据
MDC.clear();
RequestContextHolder.resetRequestAttributes();
SecurityContextHolder.clearContext();
}
};
} catch (IllegalStateException e) {
return runnable;
}
}
}
3)自定义线程池实现异步
@Service
public class LoginLogService {
@Qualifier("taskExecutor")
@Autowired
private TaskExecutor taskExecutor;
/** 记录日志 */
@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)
public void recordLog(String username) {
taskExecutor.execute(() -> {
// TODO: 实现记录日志逻辑...
});
}
}
6.补充:LoginService 手动提交事务
如果是已经开发好的项目,不好将核心逻辑单独抽离出来,可以通过手动提交事务的方式来实现,代码如下:
import org.springframework.transaction.PlatformTransactionManager;
import org.springframework.transaction.TransactionStatus;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
import org.springframework.transaction.interceptor.TransactionAspectSupport;
@Service
public class LoginService {
@Autowired
private LoginLogService loginLogService;
@Autowired
private PlatformTransactionManager transactionManager;
/** 登录 */
@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)
public void login(String username, String pwd) {
// 用户登录
// TODO: 实现登录逻辑..
// 手动提交事务
TransactionStatus status = TransactionAspectSupport.currentTransactionStatus();
if (status.isNewTransaction()) {
transactionManager.commit(status);
}
// 记录日志
loginLogService.recordLog(username);
}
}
日志记录虽然小,坑是真的多,这里记录的只是目前遇到的问题。
大家有遇到其他坑的欢迎评论补充。
整理完毕,完结撒花~ 🌻
参考地址:
1.SpringBoot 关于异步与事务一起使用的问题,https://blog.csdn.net/qq_19922839/article/details/126322800