文章目录
- 单调递增的数字
- 题解
- 监控二叉树
- 题解
单调递增的数字
| Category | Difficulty | Likes | Dislikes | ContestSlug | ProblemIndex | Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| algorithms | Medium (50.32%) | 369 | 0 | - | - | 0 |
贪心 | 数学
当且仅当每个相邻位数上的数字 x 和 y 满足 x <= y 时,我们称这个整数是单调递增的。
给定一个整数 n ,返回 小于或等于 n 的最大数字,且数字呈 单调递增 。
示例 1:
输入: n = 10
输出: 9
示例 2:
输入: n = 1234
输出: 1234
示例 3:
输入: n = 332
输出: 299
提示:
0 <= n <= 109
Discussion | Solution
题解
// @lc code=start
class Solution {
public:
int monotoneIncreasingDigits(int n) {
string strNum = to_string(n);
int flag = strNum.size();
for(int i = strNum.size()-1; i> 0;--i) {
if(strNum[i-1] > strNum[i]){
flag = i;
strNum[i-1]--;
}
}
for(int i = flag ;i < strNum.size();i++) {
strNum[i] = '9';
}
return stoi(strNum);
}
};
参考文章:代码随想录 (programmercarl.com)
监控二叉树
| Category | Difficulty | Likes | Dislikes | ContestSlug | ProblemIndex | Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| algorithms | Hard (52.20%) | 583 | 0 | weekly-contest-117 | Q4 | 2124 |
给定一个二叉树,我们在树的节点上安装摄像头。
节点上的每个摄影头都可以监视其父对象、自身及其直接子对象。
计算监控树的所有节点所需的最小摄像头数量。
示例 1:
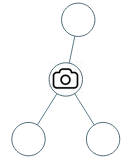
输入:[0,0,null,0,0]
输出:1
解释:如图所示,一台摄像头足以监控所有节点。
示例 2:
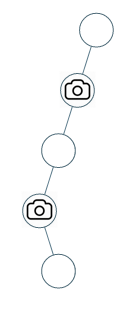
输入:[0,0,null,0,null,0,null,null,0]
输出:2
解释:需要至少两个摄像头来监视树的所有节点。 上图显示了摄像头放置的有效位置之一。
提示:
- 给定树的节点数的范围是
[1, 1000]。 - 每个节点的值都是 0。
Discussion | Solution
题解
#if 0
struct TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode *left;
TreeNode *right;
TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
};
#endif
class Solution {
private:
int result;
int traversal(TreeNode* cur) {
// 空节点,该节点有覆盖
if (cur == NULL) return 2;
int left = traversal(cur->left); // 左
int right = traversal(cur->right); // 右
// 情况1
// 左右节点都有覆盖
if (left == 2 && right == 2) return 0;
// 情况2
// left == 0 && right == 0 左右节点无覆盖
// left == 1 && right == 0 左节点有摄像头,右节点无覆盖
// left == 0 && right == 1 左节点有无覆盖,右节点摄像头
// left == 0 && right == 2 左节点无覆盖,右节点覆盖
// left == 2 && right == 0 左节点覆盖,右节点无覆盖
if (left == 0 || right == 0) {
result++;
return 1;
}
// 情况3
// left == 1 && right == 2 左节点有摄像头,右节点有覆盖
// left == 2 && right == 1 左节点有覆盖,右节点有摄像头
// left == 1 && right == 1 左右节点都有摄像头
// 其他情况前段代码均已覆盖
if (left == 1 || right == 1) return 2;
// 以上代码我没有使用else,主要是为了把各个分支条件展现出来,这样代码有助于读者理解
// 这个 return -1 逻辑不会走到这里。
return -1;
}
public:
int minCameraCover(TreeNode* root) {
result = 0;
// 情况4
if (traversal(root) == 0) { // root 无覆盖
result++;
}
return result;
}
};
r(TreeNode* root) {
result = 0;
// 情况4
if (traversal(root) == 0) { // root 无覆盖
result++;
}
return result;
}
};
参考文章:[代码随想录 (programmercarl.com)](https://programmercarl.com/0968.监控二叉树.html#思路)