NPU 转换部署 YOLO V5 模型
本文以 YOLO v5s 模型为例,详述 ONNX 模型在 V853 平台的转换与部署的流程。
模型的准备
YOLO v5 目前开源于 Github,链接【GitHub - ultralytics/yolov5: YOLOv5 🚀 in PyTorch > ONNX > CoreML > TFLite】
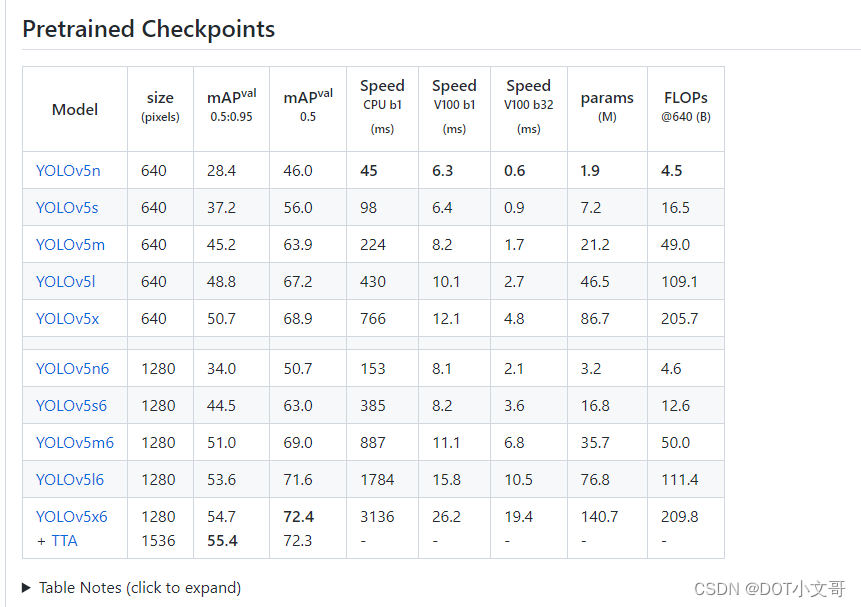
我们可以在 Release 页面找到预先训练好的各式各样的开源 YOLO V5 模型
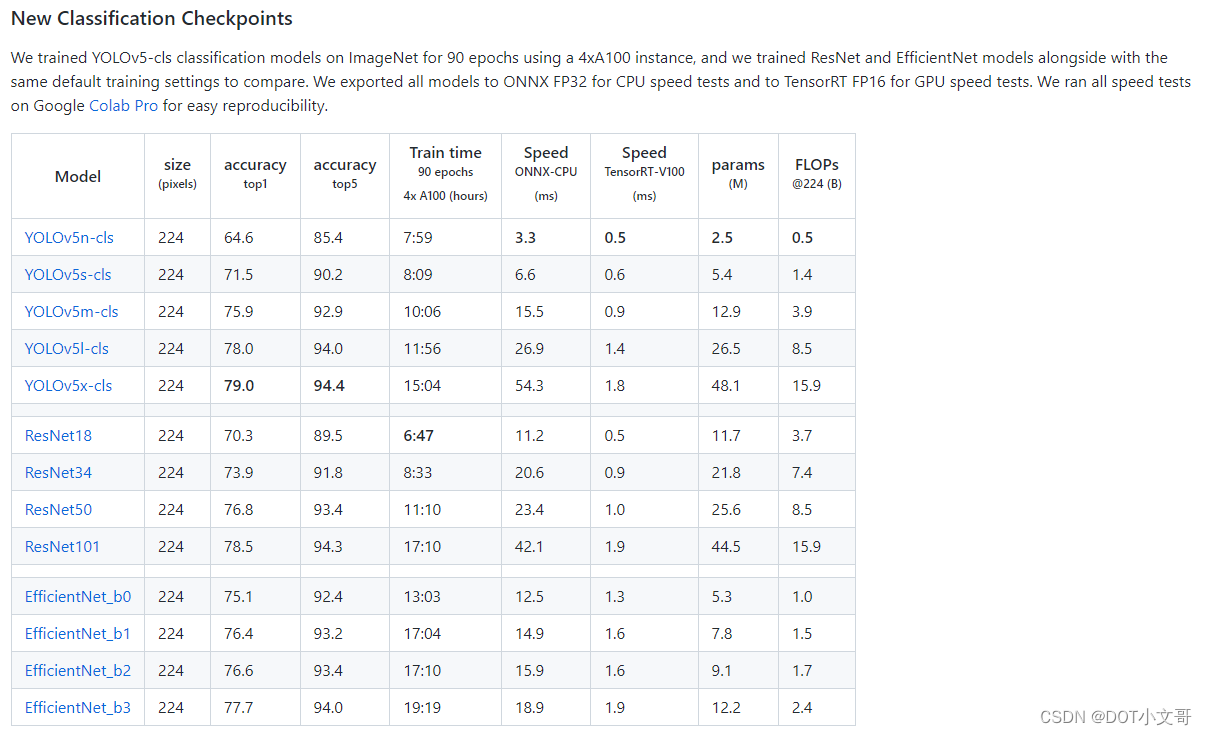
我们选择 v6.0 版本的 yolov5s.onnx 模型作为示例,下载下来。
可以用开源的 Netron 工具打开模型查看模型的结构

模型预处理
由于下载的模型是动态 Shape 的,不限制输入图片的大小,对于 NPU 来说会增加处理工序,所以这里我们需要转换为静态 Shape 的模型。可以先安装 onnxsim 工具,然后使用这条命令转换:
python -m onnxsim yolov5s.onnx yolov5s-sim.onnx --input-shape 1,3,640,640
这里我们将输入固定为了 [1, 3, 640, 640] ,减少了 NPU 的预处理量。转换后的模型可以用 Netron 查看变化
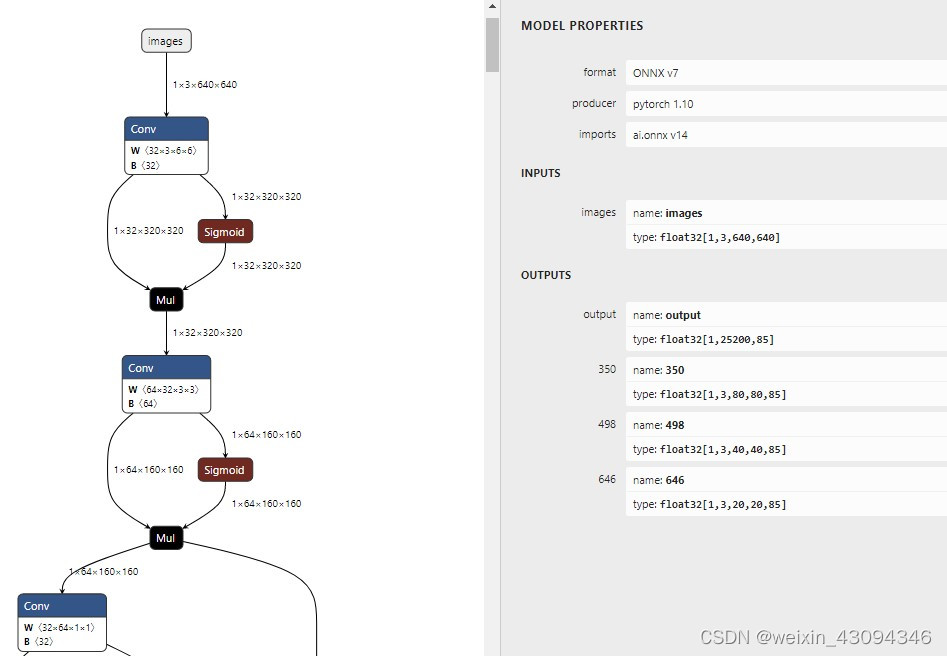
可以看到,输入已经被固定了。
检查预处理情况
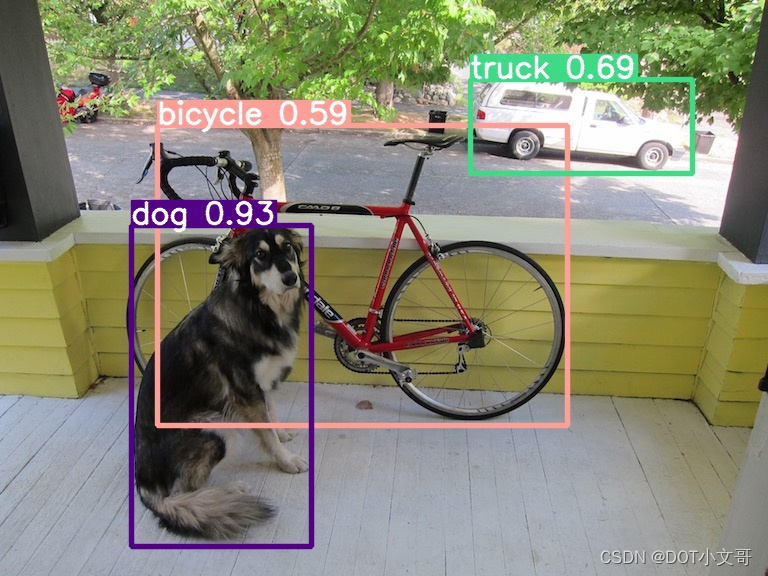
转换后的模型不一定可以用,需要验证一下。这里就使用 YOLOv5 源码提供的 detect.py 测试转换后的 onnx 模型
python detect.py --weights ./yolov5s-sim.onnx --source ./dog.jpg --conf-thres 0.5
可以看到输出结果还是非常精确的,模型确认没有问题。
检查输出节点
我们使用 Netron 打开模型

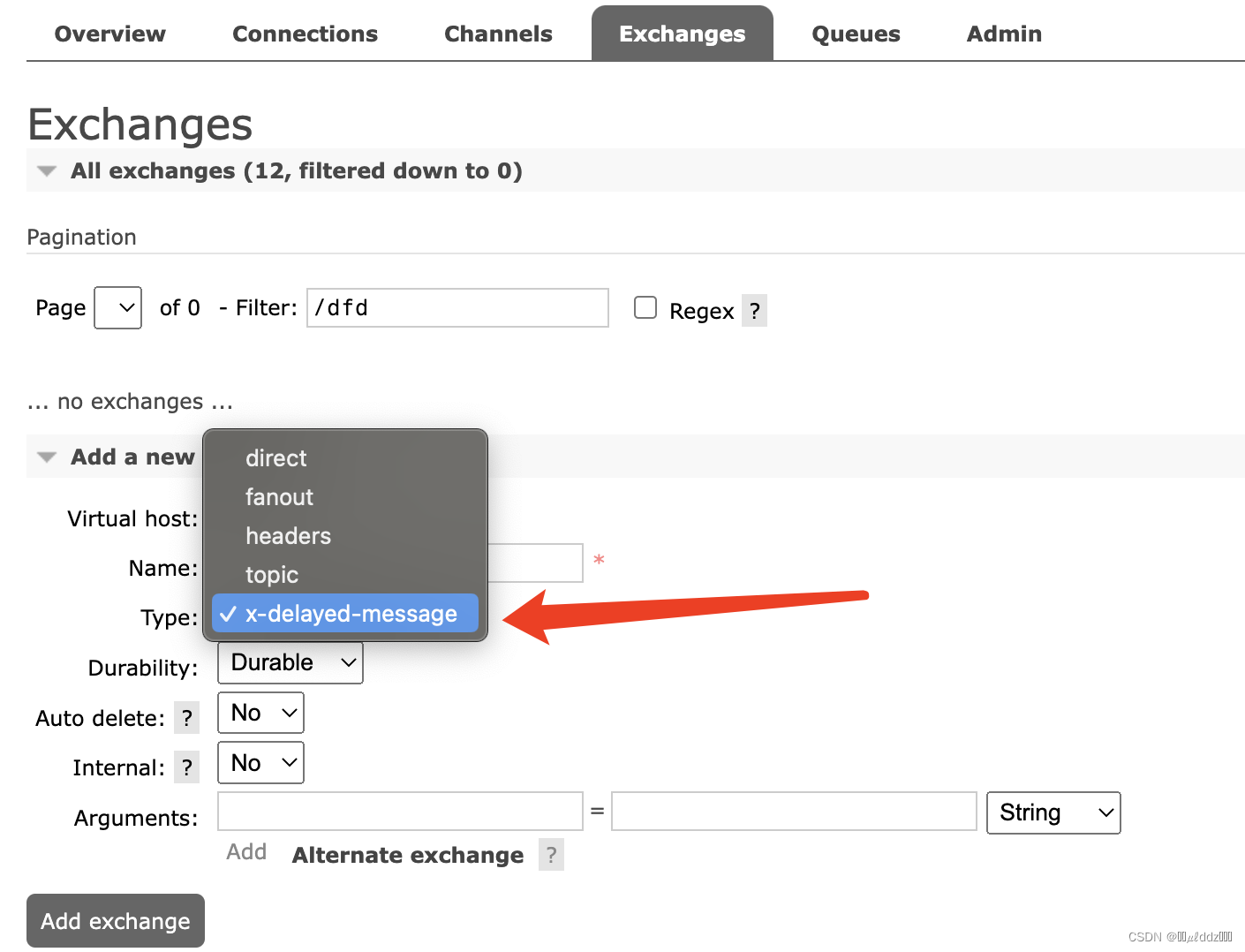
可看到模型有 4 个输出节点,其中 ouput 节点为后处理解析后的节点;在实际测试的过程中,发现 NPU 量化操作后对后处理的运算非常不友好,输出数据偏差较大,所以我们可以将后处理部分放在 CPU 运行;因此保留 350,498, 646 三个后处理解析前的输出节点即可,后文会说明如何修改输出节点。
模型的转换
导入模型
我们先准备下需要的文件,与前文 YOLO v3 的类似,dataset 文件夹存放量化所需要的图片,从训练数据集里拿就ok,一个 dataset.txt 定义图片位置。还有我们的模型。
.
├── dataset
│ ├── COCO_train2014_000000000081.jpg
│ ├── COCO_train2014_000000001569.jpg
│ ├── COCO_train2014_000000002849.jpg
│ ├── COCO_train2014_000000004139.jpg
│ ├── COCO_train2014_000000005933.jpg
│ └── dog.jpg
├── yolov5s-sim.onnx
└── dataset.txt
运行下列命令导入模型,指定输出的节点。
pegasus import onnx --model yolov5s-sim.onnx --output-data yolov5s-sim.data --output-model yolov5s-sim.json --outputs "350 498 646"
导入生成两个文件,分别是是 yolov5s-sim.data 和 yolov5s-sim.json 文件,他们是 YOLO V5 网络对应的芯原内部格式表示文件,data 文件储存权重,cfg 文件储存模型。
生成 YML 文件
与上文一样,生成 YML 配置文件
pegasus generate inputmeta --model yolov5s-sim.json --input-meta-output yolov5s-sim_inputmeta.yml
pegasus generate postprocess-file --model yolov5s-sim.json --postprocess-file-output yolov5s-sim_postprocess_file.yml
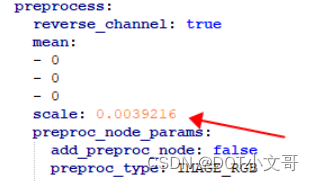
同样的,修改 yolov5s-sim_inputmeta.yml 文件中的的 scale 参数为 0.0039216(1/255),目的是对输入 tensor 进行归一化,和网络进行训练的时候是对应的。
量化
生成量化表文件,使用非对称量化,uint8,修改 --batch-size 参数为你的 dataset.txt 里提供的图片数量。
pegasus quantize --model yolov5s-sim.json --model-data yolov5s-sim.data --batch-size 1 --device CPU --with-input-meta yolov5s-sim_inputmeta.yml --rebuild --model-quantize yolov5s-sim.quantize --quantizer asymmetric_affine --qtype uint8

预推理
利用前文的量化表执行预推理,得到推理 tensor
pegasus inference --model yolov5s-sim.json --model-data yolov5s-sim.data --batch-size 1 --dtype quantized --model-quantize yolov5s-sim.quantize --device CPU --with-input-meta yolov5s-sim_inputmeta.yml --postprocess-file yolov5s-sim_postprocessmeta.yml
输出了三个 tensor,把他拷贝出来,之后上传到开发板部署验证。
验证预推理
可在开发板上将输出 tensor 结合 Python 或 C++ 后处理代码解析出算法输出结果,也可以在 PC 上导入上一步预推理输出的 tensor来验证仿真推理输出是否正确。这里就采用在 Linux PC 端结合 C++ 编写的后处理代码验证仿真的推理输出。
后处理代码如下,使用 C++ 与 OpenCV 编写。这套后处理代码也可以部署到开发板使用。包括了输出的分析,图像的处理,打框打标等操作:
#include <opencv2/core/core.hpp>
#include <opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp>
#include <opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp>
#include <iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
enum Yolov5OutType
{
p8_type = 1,
p16_type = 2,
p32_type = 3,
};
struct Object
{
cv::Rect_<float> rect;
int label;
float prob;
};
int get_tensor_data(string file_path, float *data)
{
int len = 0;
static float *memory = NULL;
static int max_len = 10*1024*1024;
if (memory == NULL)
memory = (float *)malloc(max_len * sizeof(float));
FILE *fp = NULL;
if ((fp = fopen(file_path.c_str(), "r")) == NULL)
{
cout << "open tensor file error ! file name : " << file_path << endl;
exit(-1);
}
int file_len = 0;
while (!feof(fp))
{
fscanf(fp, "%f ", &memory[len++]);
}
memcpy(data, memory, len * sizeof(float));
fclose(fp);
if (len == 0 || data == NULL)
{
cout << "read tensor error happened ! " << "len : " << len << " data address: " << *data << endl;
exit(-1);
}
return len;
}
static inline float sigmoid(float x)
{
return static_cast<float>(1.f / (1.f + exp(-x)));
}
static inline float intersection_area(const Object& a, const Object& b)
{
cv::Rect_<float> inter = a.rect & b.rect;
return inter.area();
}
static void qsort_descent_inplace(std::vector<Object>& faceobjects, int left, int right)
{
int i = left;
int j = right;
float p = faceobjects[(left + right) / 2].prob;
while (i <= j)
{
while (faceobjects[i].prob > p)
i++;
while (faceobjects[j].prob < p)
j--;
if (i <= j)
{
// swap
std::swap(faceobjects[i], faceobjects[j]);
i++;
j--;
}
}
#pragma omp parallel sections
{
#pragma omp section
{
if (left < j) qsort_descent_inplace(faceobjects, left, j);
}
#pragma omp section
{
if (i < right) qsort_descent_inplace(faceobjects, i, right);
}
}
}
static void qsort_descent_inplace(std::vector<Object>& faceobjects)
{
if (faceobjects.empty())
return;
qsort_descent_inplace(faceobjects, 0, faceobjects.size() - 1);
}
static void nms_sorted_bboxes(const std::vector<Object>& faceobjects, std::vector<int>& picked, float nms_threshold)
{
picked.clear();
const int n = faceobjects.size();
std::vector<float> areas(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
areas[i] = faceobjects[i].rect.area();
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
const Object& a = faceobjects[i];
int keep = 1;
for (int j = 0; j < (int)picked.size(); j++)
{
const Object& b = faceobjects[picked[j]];
// intersection over union
float inter_area = intersection_area(a, b);
float union_area = areas[i] + areas[picked[j]] - inter_area;
// float IoU = inter_area / union_area
if (inter_area / union_area > nms_threshold)
keep = 0;
}
if (keep)
picked.push_back(i);
}
}
static void generate_proposals(int stride, const float* feat, float prob_threshold, std::vector<Object>& objects,
int letterbox_cols, int letterbox_rows)
{
static float anchors[18] = {10, 13, 16, 30, 33, 23, 30, 61, 62, 45, 59, 119, 116, 90, 156, 198, 373, 326};
int anchor_num = 3;
int feat_w = letterbox_cols / stride;
int feat_h = letterbox_rows / stride;
int cls_num = 80;
int anchor_group;
if (stride == 8)
anchor_group = 1;
if (stride == 16)
anchor_group = 2;
if (stride == 32)
anchor_group = 3;
for (int h = 0; h <= feat_h - 1; h++)
{
for (int w = 0; w <= feat_w - 1; w++)
{
for (int a = 0; a <= anchor_num - 1; a++)
{
//process cls score
int class_index = 0;
float class_score = -FLT_MAX;
for (int s = 0; s <= cls_num - 1; s++)
{
float score = feat[a * feat_w * feat_h * (cls_num + 5) + h * feat_w * (cls_num + 5) + w * (cls_num + 5) + s + 5];
if (score > class_score)
{
class_index = s;
class_score = score;
}
}
//process box score
float box_score = feat[a * feat_w * feat_h * (cls_num + 5) + (h * feat_w) * (cls_num + 5) + w * (cls_num + 5) + 4];
float final_score = sigmoid(box_score) * sigmoid(class_score);
if (final_score >= prob_threshold)
{
int loc_idx = a * feat_h * feat_w * (cls_num + 5) + h * feat_w * (cls_num + 5) + w * (cls_num + 5);
float dx = sigmoid(feat[loc_idx + 0]);
float dy = sigmoid(feat[loc_idx + 1]);
float dw = sigmoid(feat[loc_idx + 2]);
float dh = sigmoid(feat[loc_idx + 3]);
float pred_cx = (dx * 2.0f - 0.5f + w) * stride;
float pred_cy = (dy * 2.0f - 0.5f + h) * stride;
float anchor_w = anchors[(anchor_group - 1) * 6 + a * 2 + 0];
float anchor_h = anchors[(anchor_group - 1) * 6 + a * 2 + 1];
float pred_w = dw * dw * 4.0f * anchor_w;
float pred_h = dh * dh * 4.0f * anchor_h;
float x0 = pred_cx - pred_w * 0.5f;
float y0 = pred_cy - pred_h * 0.5f;
float x1 = pred_cx + pred_w * 0.5f;
float y1 = pred_cy + pred_h * 0.5f;
Object obj;
obj.rect.x = x0;
obj.rect.y = y0;
obj.rect.width = x1 - x0;
obj.rect.height = y1 - y0;
obj.label = class_index;
obj.prob = final_score;
objects.push_back(obj);
}
}
}
}
}
static int detect_yolov5(const cv::Mat& bgr, std::vector<Object>& objects)
{
std::chrono::steady_clock::time_point Tbegin, Tend;
Tbegin = std::chrono::steady_clock::now();
std::vector<float> p8_data(1*3*80*80*85);
std::vector<float> p16_data(1*3*40*40*85);
std::vector<float> p32_data(1*3*20*50*85);
string tensor_file0 = "../tensor/vip/iter_0_attach_Transpose_Transpose_214_out0_0_out0_1_3_80_80_85.tensor";
string tensor_file1 = "../tensor/vip/iter_0_attach_Transpose_Transpose_326_out0_1_out0_1_3_40_40_85.tensor";
string tensor_file2 = "../tensor/vip/iter_0_attach_Transpose_Transpose_438_out0_2_out0_1_3_20_20_85.tensor";
get_tensor_data(tensor_file0, p8_data.data());
get_tensor_data(tensor_file1, p16_data.data());
get_tensor_data(tensor_file2, p32_data.data());
// set default letterbox size
int letterbox_rows = 640;
int letterbox_cols = 640;
/* postprocess */
const float prob_threshold = 0.5f;
const float nms_threshold = 0.45f;
std::vector<Object> proposals;
std::vector<Object> objects8;
std::vector<Object> objects16;
std::vector<Object> objects32;
generate_proposals(32, p32_data.data(), prob_threshold, objects32, letterbox_cols, letterbox_rows);
proposals.insert(proposals.end(), objects32.begin(), objects32.end());
generate_proposals(16, p16_data.data(), prob_threshold, objects16, letterbox_cols, letterbox_rows);
proposals.insert(proposals.end(), objects16.begin(), objects16.end());
generate_proposals(8, p8_data.data(), prob_threshold, objects8, letterbox_cols, letterbox_rows);
proposals.insert(proposals.end(), objects8.begin(), objects8.end());
qsort_descent_inplace(proposals);
std::vector<int> picked;
nms_sorted_bboxes(proposals, picked, nms_threshold);
/* yolov5 draw the result */
float scale_letterbox;
int resize_rows;
int resize_cols;
if ((letterbox_rows * 1.0 / bgr.rows) < (letterbox_cols * 1.0 / bgr.cols))
{
scale_letterbox = letterbox_rows * 1.0 / bgr.rows;
}
else
{
scale_letterbox = letterbox_cols * 1.0 / bgr.cols;
}
resize_cols = int(scale_letterbox * bgr.cols);
resize_rows = int(scale_letterbox * bgr.rows);
int tmp_h = (letterbox_rows - resize_rows) / 2;
int tmp_w = (letterbox_cols - resize_cols) / 2;
float ratio_x = (float)bgr.rows / resize_rows;
float ratio_y = (float)bgr.cols / resize_cols;
int count = picked.size();
fprintf(stderr, "detection num: %d\n", count);
objects.resize(count);
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++)
{
objects[i] = proposals[picked[i]];
float x0 = (objects[i].rect.x);
float y0 = (objects[i].rect.y);
float x1 = (objects[i].rect.x + objects[i].rect.width);
float y1 = (objects[i].rect.y + objects[i].rect.height);
x0 = (x0 - tmp_w) * ratio_x;
y0 = (y0 - tmp_h) * ratio_y;
x1 = (x1 - tmp_w) * ratio_x;
y1 = (y1 - tmp_h) * ratio_y;
x0 = std::max(std::min(x0, (float)(bgr.cols - 1)), 0.f);
y0 = std::max(std::min(y0, (float)(bgr.rows - 1)), 0.f);
x1 = std::max(std::min(x1, (float)(bgr.cols - 1)), 0.f);
y1 = std::max(std::min(y1, (float)(bgr.rows - 1)), 0.f);
objects[i].rect.x = x0;
objects[i].rect.y = y0;
objects[i].rect.width = x1 - x0;
objects[i].rect.height = y1 - y0;
}
Tend = std::chrono::steady_clock::now();
float f = std::chrono::duration_cast <std::chrono::milliseconds> (Tend - Tbegin).count();
std::cout << "time : " << f/1000.0 << " Sec" << std::endl;
return 0;
}
static void draw_objects(const cv::Mat& bgr, const std::vector<Object>& objects)
{
static const char* class_names[] = {
"person", "bicycle", "car", "motorcycle", "airplane", "bus", "train", "truck", "boat", "traffic light",
"fire hydrant", "stop sign", "parking meter", "bench", "bird", "cat", "dog", "horse", "sheep", "cow",
"elephant", "bear", "zebra", "giraffe", "backpack", "umbrella", "handbag", "tie", "suitcase", "frisbee",
"skis", "snowboard", "sports ball", "kite", "baseball bat", "baseball glove", "skateboard", "surfboard",
"tennis racket", "bottle", "wine glass", "cup", "fork", "knife", "spoon", "bowl", "banana", "apple",
"sandwich", "orange", "broccoli", "carrot", "hot dog", "pizza", "donut", "cake", "chair", "couch",
"potted plant", "bed", "dining table", "toilet", "tv", "laptop", "mouse", "remote", "keyboard", "cell phone",
"microwave", "oven", "toaster", "sink", "refrigerator", "book", "clock", "vase", "scissors", "teddy bear",
"hair drier", "toothbrush"};
cv::Mat image = bgr.clone();
for (size_t i = 0; i < objects.size(); i++)
{
const Object& obj = objects[i];
fprintf(stderr, "%2d: %3.0f%%, [%4.0f, %4.0f, %4.0f, %4.0f], %s\n", obj.label, obj.prob * 100, obj.rect.x,
obj.rect.y, obj.rect.x + obj.rect.width, obj.rect.y + obj.rect.height, class_names[obj.label]);
cv::rectangle(image, obj.rect, cv::Scalar(255, 0, 0));
char text[256];
sprintf(text, "%s %.1f%%", class_names[obj.label], obj.prob * 100);
int baseLine = 0;
cv::Size label_size = cv::getTextSize(text, cv::FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, 1, &baseLine);
int x = obj.rect.x;
int y = obj.rect.y - label_size.height - baseLine;
if (y < 0)
y = 0;
if (x + label_size.width > image.cols)
x = image.cols - label_size.width;
cv::rectangle(image, cv::Rect(cv::Point(x, y), cv::Size(label_size.width, label_size.height + baseLine)),
cv::Scalar(255, 255, 255), -1);
cv::putText(image, text, cv::Point(x, y + label_size.height), cv::FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5,
cv::Scalar(0, 0, 0));
}
cv::imwrite("yolov5_out.png", image);
}
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
if (argc != 2)
{
fprintf(stderr, "Usage: %s [imagepath]\n", argv[0]);
return -1;
}
const char* imagepath = argv[1];
cv::Mat m = cv::imread(imagepath, 1);
if (m.empty())
{
fprintf(stderr, "cv::imread %s failed\n", imagepath);
return -1;
}
std::vector<Object> objects;
detect_yolov5(m, objects);
draw_objects(m, objects);
return 0;
}
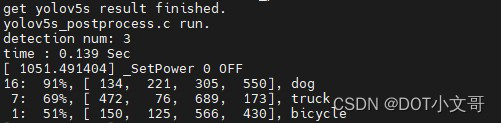
编译运行后结果输出如下:
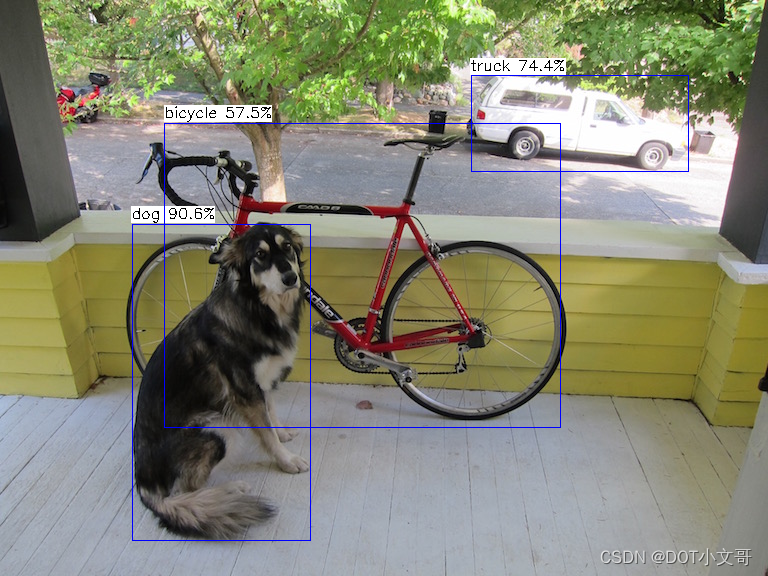
可以看到,量化后精度有所损失,不过大体上没什么问题。
导出模板代码与模型
pegasus export ovxlib --model yolov5s-sim.json --model-data yolov5s-sim.data --dtype quantized --model-quantize yolov5s-sim.quantize --batch-size 1 --save-fused-graph --target-ide-project 'linux64' --with-input-meta yolov5s-sim_inputmeta.yml --output-path ovxilb/yolov5s-sim/yolov5s-simprj --pack-nbg-unify --postprocess-file yolov5s-sim_postprocessmeta.yml --optimize "VIP9000PICO_PID0XEE" --viv-sdk ${VIV_SDK}
输出的模型可以在 ovxilb/yolov5s-sim_nbg_unify 文件夹中找到。
开发板部署测试
测试部署可以参照 【NPU Demo 使用说明 - V853】中提供的 lenet 的方法集成输出的模板代码到 Tina Linux 里,来生成 tensor 文件。
运行结果如下,准确率还是比较高的。
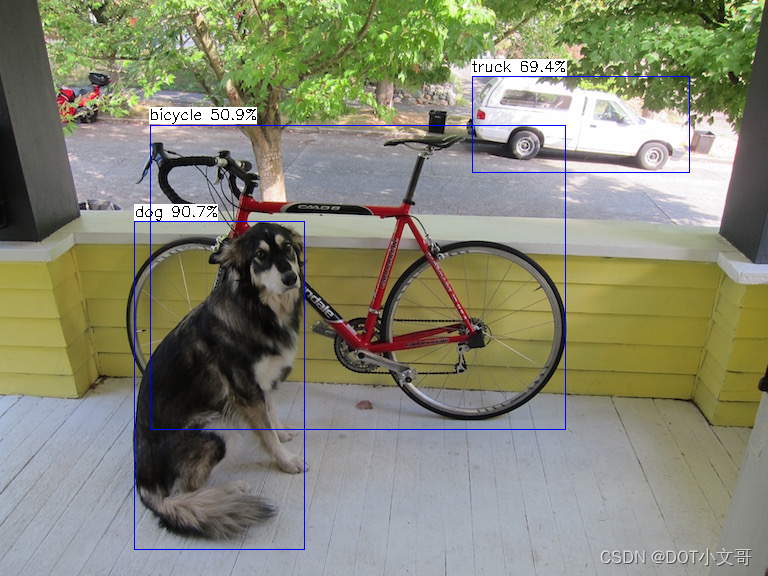
开发板输出打框后图像如下
原贴链接:https://v853.docs.aw-ol.com/npu/npu_yolov5/


![[附源码]Python计算机毕业设计Django茶叶销售微信小程序](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/2b44805bc4964ff1bd16bcf6dec08f3f.png)






![[附源码]计算机毕业设计springboot车险销售管理系统论文](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/1789cd835d764ab4af7d7a575e31e784.png)