需要源码请点赞关注收藏后评论区留言私信~~~
不管是绘画还是摄影,都是把三维的物体投影到平面上,其实仍旧呈现二维的模拟画面。 随着科技的发展,传统的成像手段越来越凸显出局限性,缘由在于人们需要一种更逼真更接近现实的技术,从而更好地显示三维世界的环境信息,这便催生了增强现实AR和虚拟现实VR。 传统的摄影只能拍摄90度左右的风景,而新型的全景相机能够拍摄360度乃至720度(连同头顶和脚底在内)的场景,这种360/720度的相片即为全景照片。
一、需求描述
传统的照片只是某个视角观测到的平面截图,无法看到视角以外的场景。 现在有了VR技术,只要把全景相机拍摄的全景照片发到手机上,无论在哪里都能及时通过手机浏览全景照片,从而方便掌握最新的现场情况。 全景照片看似一张矩形图片,其实前后左右上下的景色全都囊括在内,但用户每次只能观看某个角度的截图。要想观看其它方向上的图画,就得想办法让全景照片转起来。
二、功能分析
全景照片之于观察者,便是将全景图贴在球体内侧,由此可见,二者的不同之处在于人是在球外还是球内
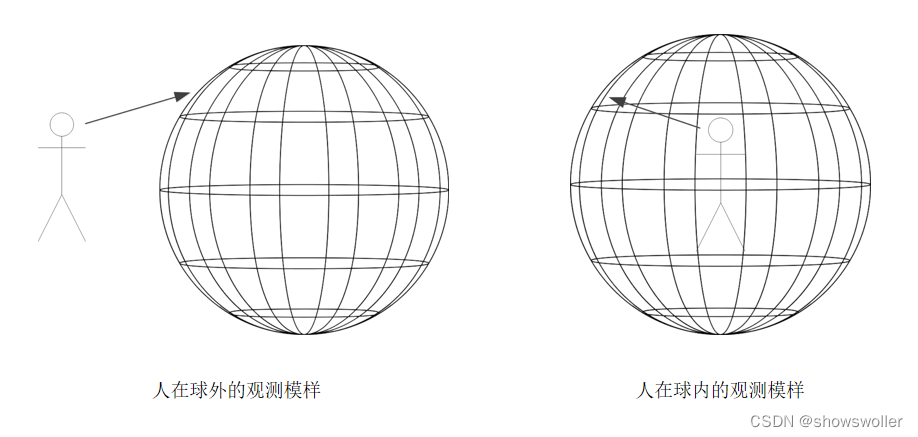
浏览全景照片用到的技术
(1)通过手势的触摸与滑动,把全景照片相应地挪动观测角度。
(2)利用OpenGL ES 库,把平面的全景照片转换为曲面的实景快照。
(3)根据手势滑动在水平方向和垂直方向分别产生的角度变化,实时调整全景图的快照范围。
下面介绍主要代码模块之间的关系
(1)PanoramaActivity.java:这是全景相册的浏览器页面。
(2)PanoramaView.java:这是自定义全景视图的实现代码。
(3)PanoramaRender.java:这是全景图形的三维渲染器代码。
(4)PanoramaUtil.java:这是全景图片的顶点坐标工具类,用于计算全景图片的顶点列表,以及全景图片的纹理列表。
具体到编码过程,主要有以下三项处理
1:实现全景照片的渲染器
2:计算手势触摸引发的角度变更
3:在活动页面加载全景照片的渲染器
三、效果展示
演示视频如下 可以在下拉框中选择不同的相册进行展示,可以放缩或旋转 真正实现了身临其境的感觉
虚拟现实的全景相册
效果图如下


四、代码
部分代码如下 全部源码请点赞关注收藏后评论区留言~
package com.example.threed;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.WindowManager;
import android.widget.AdapterView;
import android.widget.ArrayAdapter;
import android.widget.Spinner;
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;
import com.example.threed.panorama.PanoramaView;
public class PanoramaActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private final static String TAG = "PanoramaActivity";
private PanoramaView pv_content; // 声明一个全景视图对象
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_panorama);
getWindow().addFlags(WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_KEEP_SCREEN_ON); // 保持屏幕常亮
pv_content = findViewById(R.id.pv_content);
pv_content.initRender(resArray[0]); // 设置全景视图的全景图片
initExampleSpinner(); // 初始化样例下拉框
}
// 初始化样例下拉框
private void initExampleSpinner() {
ArrayAdapter<String> exampleAdapter = new ArrayAdapter<>(this,
R.layout.item_select, exampleArray);
Spinner sp_example = findViewById(R.id.sp_example);
sp_example.setPrompt("请选择全景照片例子");
sp_example.setAdapter(exampleAdapter);
sp_example.setOnItemSelectedListener(new ExampleSelectedListener());
sp_example.setSelection(0);
}
private String[] exampleArray = {"现代客厅", "中式客厅", "故宫风光", "城市街景",
"鸟瞰城市", "俯拍高校", "私人会所", "酒店大堂"};
private int[] resArray = {R.drawable.panorama01, R.drawable.panorama02, R.drawable.panorama03, R.drawable.panorama04,
R.drawable.panorama05, R.drawable.panorama06, R.drawable.panorama07, R.drawable.panorama08};
class ExampleSelectedListener implements AdapterView.OnItemSelectedListener {
public void onItemSelected(AdapterView<?> arg0, View arg1, final int arg2, long arg3) {
pv_content.setDrawableId(resArray[arg2]); // 传入全景图片的资源编号
}
public void onNothingSelected(AdapterView<?> arg0) {}
}
}
util类
package com.example.threed.util;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class PanoramaUtil {
// 获取全景图片的顶点列表
public static List<Float> getPanoramaVertexList(int perVertex, double perRadius) {
List<Float> vertexList = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < perVertex; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < perVertex; j++) {
float x1 = (float) (Math.sin(i * perRadius / 2) * Math.cos(j * perRadius));
float z1 = (float) (Math.sin(i * perRadius / 2) * Math.sin(j * perRadius));
float y1 = (float) Math.cos(i * perRadius / 2);
float x2 = (float) (Math.sin((i + 1) * perRadius / 2) * Math.cos(j * perRadius));
float z2 = (float) (Math.sin((i + 1) * perRadius / 2) * Math.sin(j * perRadius));
float y2 = (float) Math.cos((i + 1) * perRadius / 2);
float x3 = (float) (Math.sin((i + 1) * perRadius / 2) * Math.cos((j + 1) * perRadius));
float z3 = (float) (Math.sin((i + 1) * perRadius / 2) * Math.sin((j + 1) * perRadius));
float y3 = (float) Math.cos((i + 1) * perRadius / 2);
float x4 = (float) (Math.sin(i * perRadius / 2) * Math.cos((j + 1) * perRadius));
float z4 = (float) (Math.sin(i * perRadius / 2) * Math.sin((j + 1) * perRadius));
float y4 = (float) Math.cos(i * perRadius / 2);
vertexList.add(x1);
vertexList.add(y1);
vertexList.add(z1);
vertexList.add(x2);
vertexList.add(y2);
vertexList.add(z2);
vertexList.add(x3);
vertexList.add(y3);
vertexList.add(z3);
vertexList.add(x3);
vertexList.add(y3);
vertexList.add(z3);
vertexList.add(x4);
vertexList.add(y4);
vertexList.add(z4);
vertexList.add(x1);
vertexList.add(y1);
vertexList.add(z1);
}
}
return vertexList;
}
// 获取全景图片的纹理列表
public static List<Float> getPanoramaTextureList(int perVertex) {
List<Float> textureList = new ArrayList<>();
double perW = 1 / (float) perVertex;
double perH = 1 / (float) (perVertex);
for (int i = 0; i < perVertex; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < perVertex; j++) {
float w1 = (float) (i * perH);
float h1 = (float) (j * perW);
float w2 = (float) ((i + 1) * perH);
float h2 = (float) (j * perW);
float w3 = (float) ((i + 1) * perH);
float h3 = (float) ((j + 1) * perW);
float w4 = (float) (i * perH);
float h4 = (float) ((j + 1) * perW);
textureList.add(h1);
textureList.add(w1);
textureList.add(h2);
textureList.add(w2);
textureList.add(h3);
textureList.add(w3);
textureList.add(h3);
textureList.add(w3);
textureList.add(h4);
textureList.add(w4);
textureList.add(h1);
textureList.add(w1);
}
}
return textureList;
}
}
XML文件
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="horizontal" >
<TextView
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:gravity="right"
android:text="全景照片例子:"
android:textColor="@color/black"
android:textSize="17sp" />
<Spinner
android:id="@+id/sp_example"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:spinnerMode="dialog" />
</LinearLayout>
<com.example.threed.panorama.PanoramaView
android:id="@+id/pv_content"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_weight="1" />
</LinearLayout>创作不易 觉得有帮助请点赞关注收藏~~~

![[附源码]Python计算机毕业设计Django茶叶销售微信小程序](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/2b44805bc4964ff1bd16bcf6dec08f3f.png)






![[附源码]计算机毕业设计springboot车险销售管理系统论文](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/1789cd835d764ab4af7d7a575e31e784.png)
![[附源码]计算机毕业设计springboot房屋租赁信息系统](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/c2d0a4181baa488aa28e44e30014726f.png)