来源0x3f:https://space.bilibili.com/206214
文章目录
- 反转链表
- [206. 反转链表](https://leetcode.cn/problems/reverse-linked-list/)
- [92. 反转链表 II](https://leetcode.cn/problems/reverse-linked-list-ii/)
- [25. K 个一组翻转链表](https://leetcode.cn/problems/reverse-nodes-in-k-group/)
- 拓展
- [剑指 Offer 06. 从尾到头打印链表](https://leetcode.cn/problems/cong-wei-dao-tou-da-yin-lian-biao-lcof/)
反转链表
206. 反转链表
难度简单2859
给你单链表的头节点 head ,请你反转链表,并返回反转后的链表。
示例 1:

输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5]
输出:[5,4,3,2,1]
示例 2:

输入:head = [1,2]
输出:[2,1]
示例 3:
输入:head = []
输出:[]
提示:
- 链表中节点的数目范围是
[0, 5000] -5000 <= Node.val <= 5000
**进阶:**链表可以选用迭代或递归方式完成反转。你能否用两种方法解决这道题?
图片来自:https://leetcode.cn/problems/reverse-linked-list/solution/fan-zhuan-lian-biao-shuang-zhi-zhen-di-gui-yao-mo-/
递归
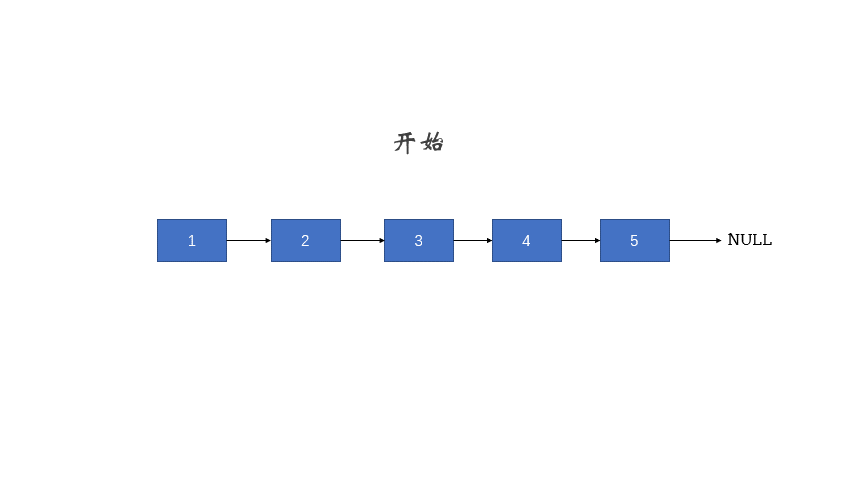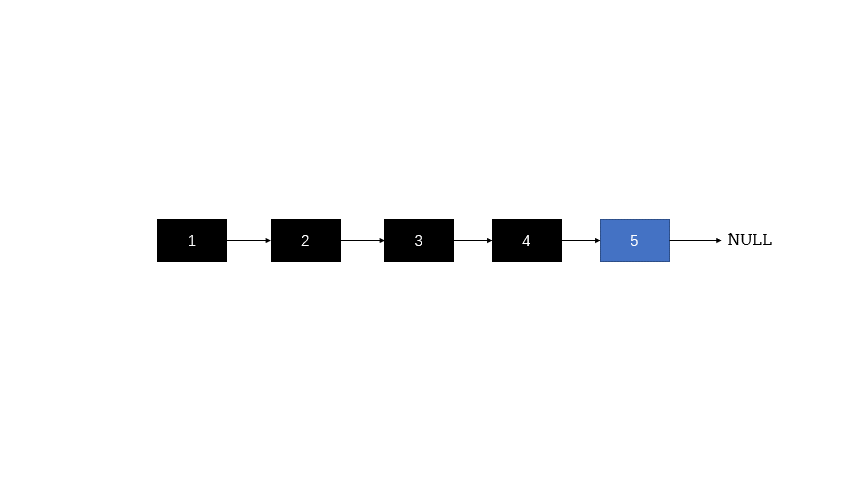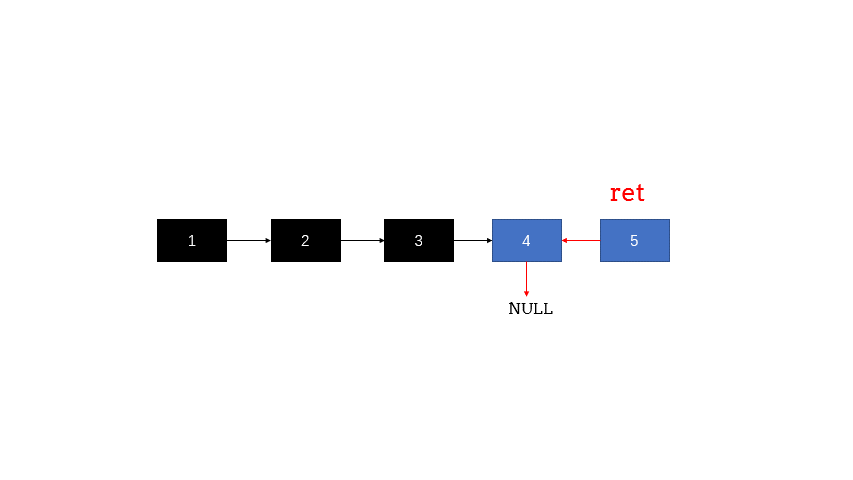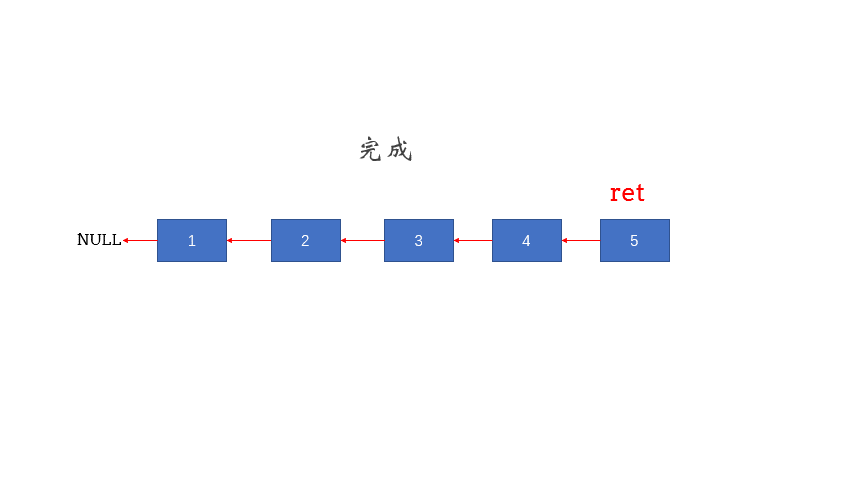
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
if(head == null || head.next == null)
return head;//确保有头结点
ListNode cur = reverseList(head.next);
// 翻转头节点 第二个节点的指向
head.next.next = head;
// 此时的 head 节点为尾节点,next 需要指向 NULL
head.next = null;
return cur;
}
}
迭代
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode pre = null; // 前指针结点
ListNode cur = head; // 当前指针结点
while(cur != null){
ListNode tmp = cur.next; //临时结点保存遍历顺序
cur.next = pre; //将当前节点指向它前面的节点
pre = cur; //前指针后移
cur = tmp; //当前指针后移
}
return pre;
}
}
头插法
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode p = head;
ListNode res = new ListNode(-1, null);
while(p != null){
ListNode tmp = p.next;
p.next = res.next;
res.next = p;
p = tmp;
}
return res.next;
}
}
92. 反转链表 II
难度中等1446
给你单链表的头指针 head 和两个整数 left 和 right ,其中 left <= right 。请你反转从位置 left 到位置 right 的链表节点,返回 反转后的链表 。
示例 1:

输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5], left = 2, right = 4
输出:[1,4,3,2,5]
示例 2:
输入:head = [5], left = 1, right = 1
输出:[5]
提示:
- 链表中节点数目为
n 1 <= n <= 500-500 <= Node.val <= 5001 <= left <= right <= n
进阶: 你可以使用一趟扫描完成反转吗?
性质:反转结束后,从原来的链表上看:
- pre指向反转这一段的末尾
- cur指向反转这一段后续的下一个结点
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseBetween(ListNode head, int left, int right) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1);// 初始化哨兵结点,使得处理第一个结点与第i个结点相同
dummy.next= head;
ListNode p0 = dummy;
// 找到要反转的链表左侧的上一个结点
for(int i = 0; i < left-1; i++){
p0 = p0.next;
}
ListNode pre = null;
ListNode cur = p0.next;
for(int i = 0; i < right-left+1; i++){
ListNode nxt = cur.next;
cur.next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = nxt;
}
p0.next.next = cur;
p0.next = pre;
return dummy.next;
}
}
25. K 个一组翻转链表
难度困难1857
给你链表的头节点 head ,每 k 个节点一组进行翻转,请你返回修改后的链表。
k 是一个正整数,它的值小于或等于链表的长度。如果节点总数不是 k 的整数倍,那么请将最后剩余的节点保持原有顺序。
你不能只是单纯的改变节点内部的值,而是需要实际进行节点交换。
示例 1:
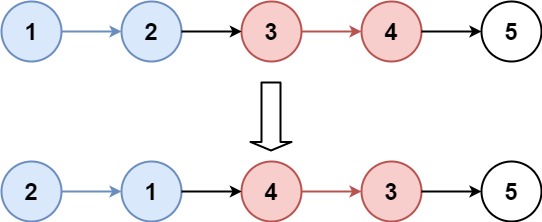
输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5], k = 2
输出:[2,1,4,3,5]
示例 2:

输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5], k = 3
输出:[3,2,1,4,5]
提示:
- 链表中的节点数目为
n 1 <= k <= n <= 50000 <= Node.val <= 1000
**进阶:**你可以设计一个只用 O(1) 额外内存空间的算法解决此问题吗?
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseKGroup(ListNode head, int k) {
//统计一下链表长度
int n = 0;
ListNode cnt = head;
while(cnt != null){
n++;
cnt = cnt.next;
}
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1);// 初始化哨兵结点,使得处理第一个结点与第i个结点相同
dummy.next= head;
ListNode p0 = dummy;
while(n >= k){ // 循环n/k次
n -= k;
ListNode pre = null;
ListNode cur = p0.next;
for(int i = 0; i < k; i++){
ListNode nxt = cur.next;
cur.next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = nxt;
}
ListNode nxt = p0.next;
p0.next.next = cur;
p0.next = pre;
p0 = nxt;
}
return dummy.next;
}
}
拓展
剑指 Offer 06. 从尾到头打印链表
难度简单354
输入一个链表的头节点,从尾到头反过来返回每个节点的值(用数组返回)。
示例 1:
输入:head = [1,3,2]
输出:[2,3,1]
限制:
0 <= 链表长度 <= 10000
从尾到头打印的过程就是递归的过程
class Solution {
List<Integer> tmp = new ArrayList<>();
public int[] reversePrint(ListNode head) {
recur(head);
int[] res = new int[tmp.size()];
for(int i = 0; i < res.length; i++){
res[i] = tmp.get(i);
}
return res;
}
void recur(ListNode head){
if(head == null) return;
recur(head.next);
tmp.add(head.val);
}
}
![[附源码]Python计算机毕业设计Django仓储综合管理系统](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/ca5d6663711547c6b39f28a706b03c90.png)