本文是看了DeepSORT方法视频之后,关于其中使用的卡尔曼滤波的理解
DeepSORT视频链接
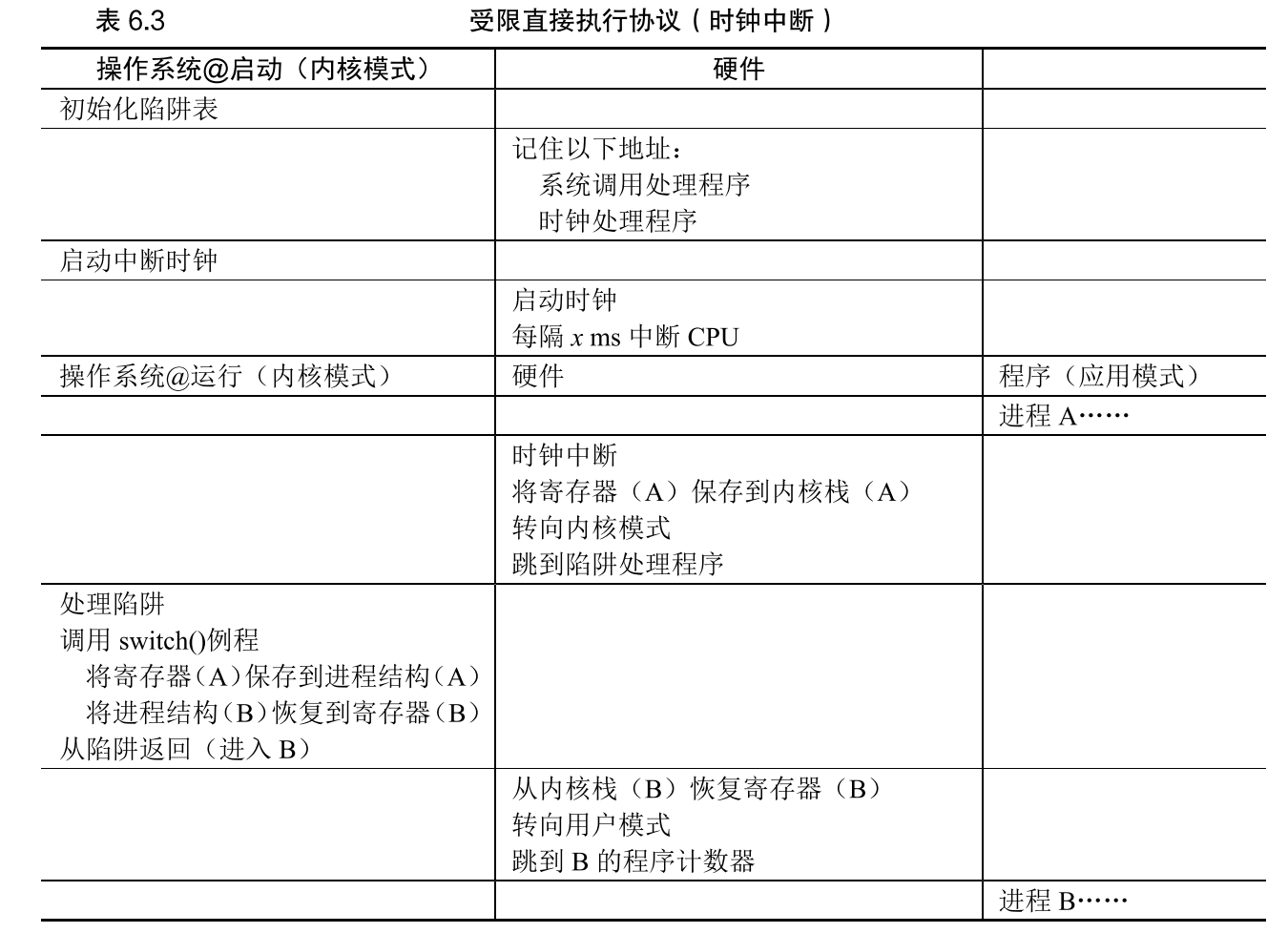
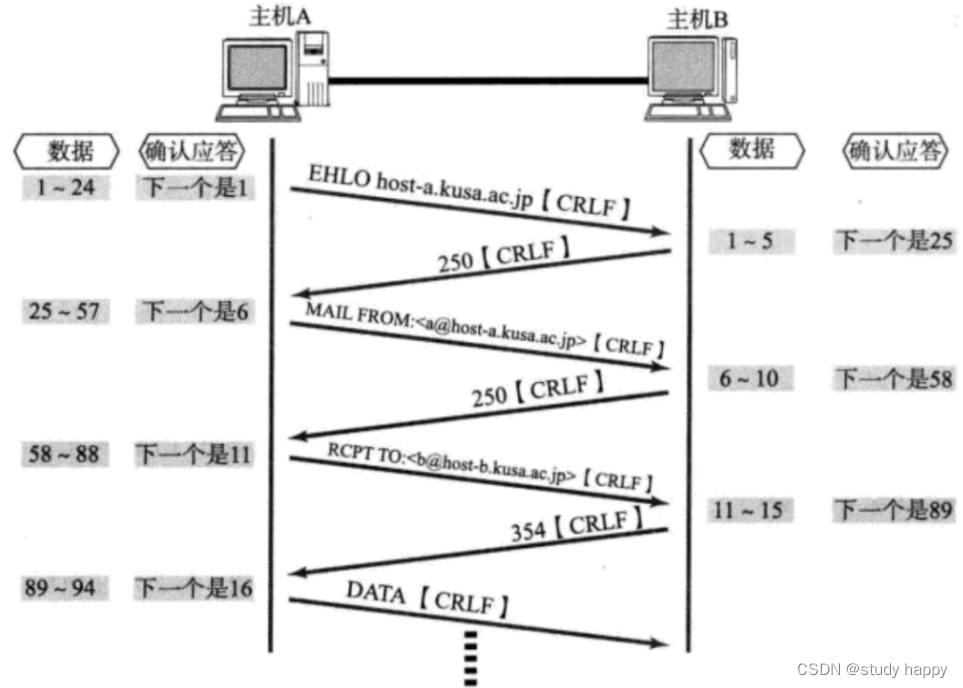
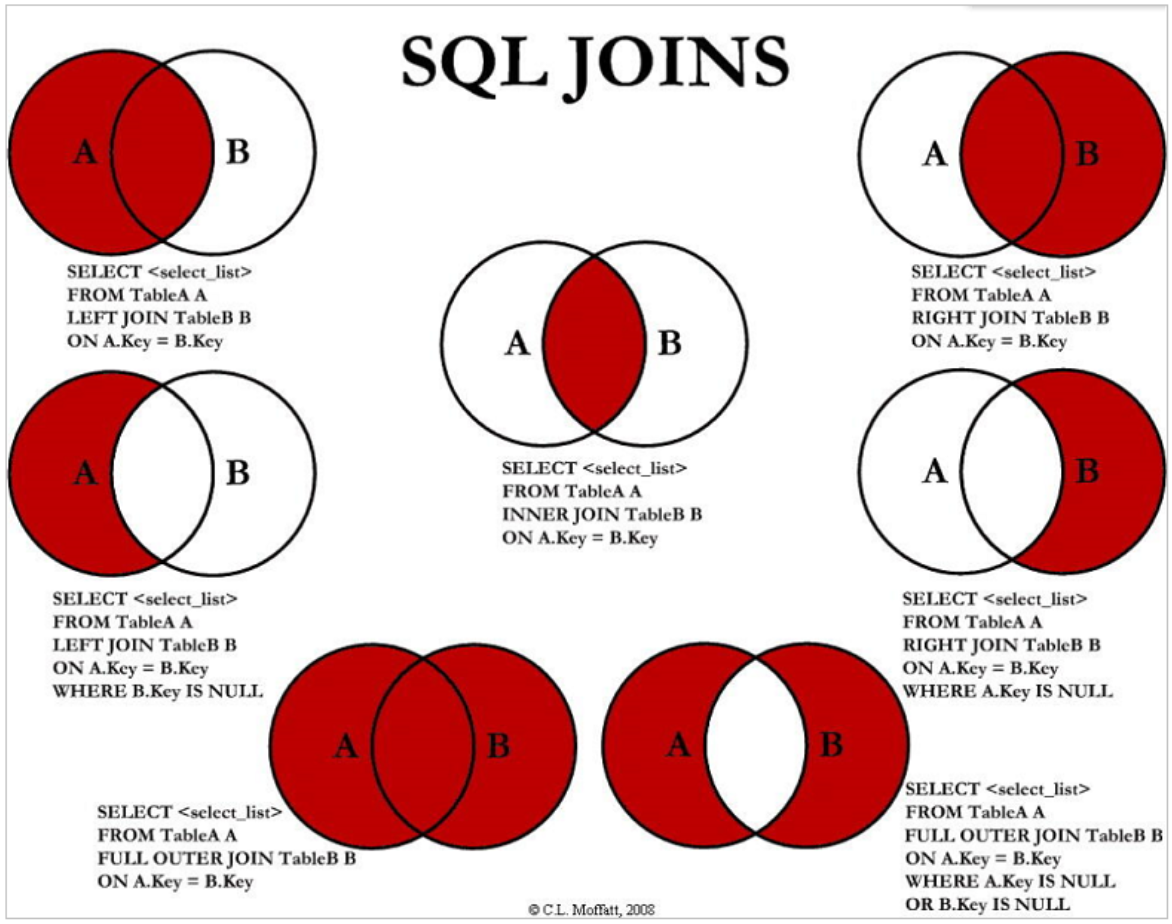
首先是视频中的一张图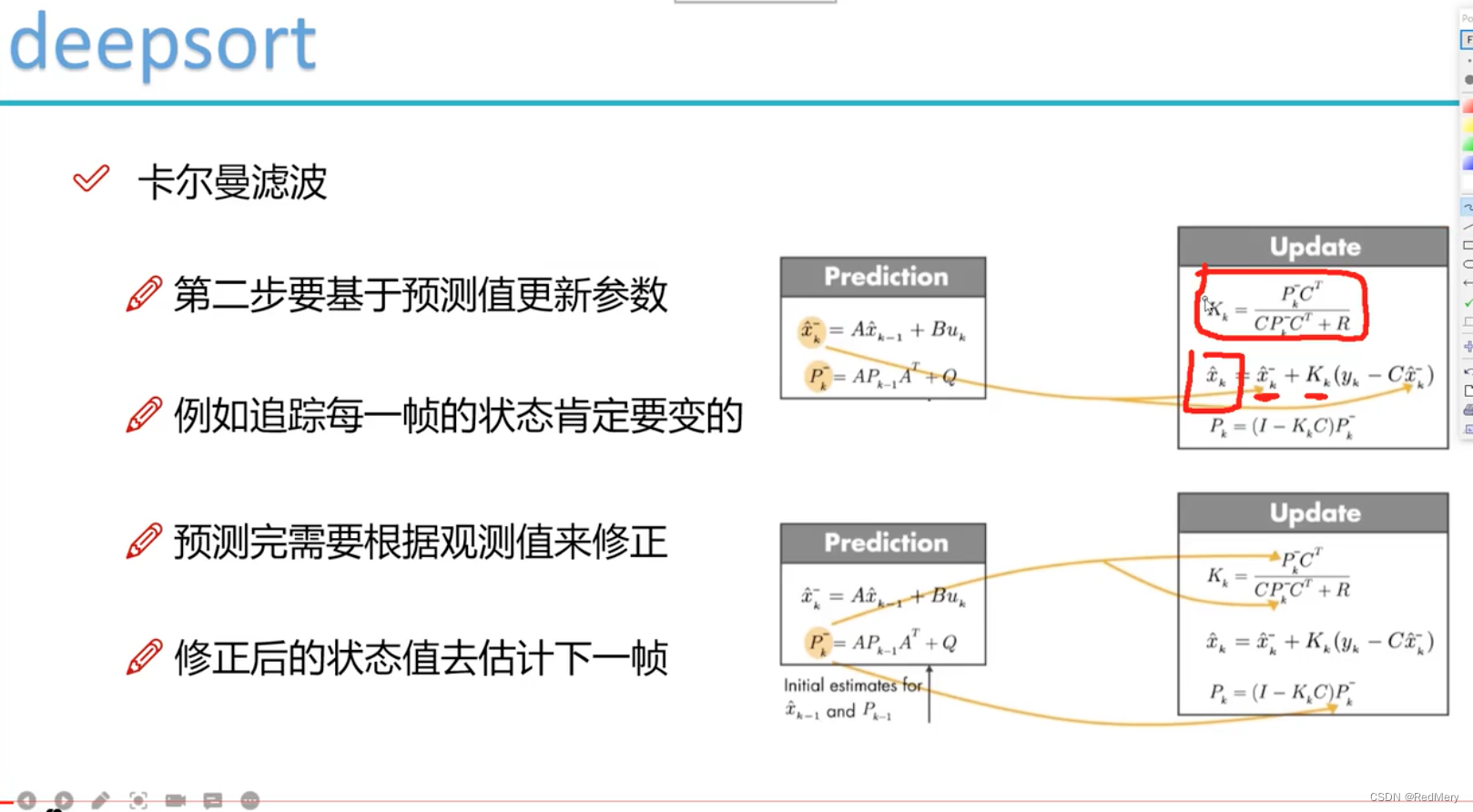
预测阶段
x
^
k
−
=
A
x
^
k
−
1
\hat{x}_k^-=A\hat{x}_{k-1}
x^k−=Ax^k−1
P
k
−
=
A
P
k
−
1
+
Q
,
P
k
−
∈
R
8
,
8
P_k^-=AP_{k-1}+Q, P_k^- \in R^{8,8}
Pk−=APk−1+Q,Pk−∈R8,8
更新阶段
K
k
=
P
k
−
C
T
C
P
k
−
C
T
+
R
,
K
k
∈
R
8
,
4
K_k=\frac{P_k^-C^T}{CP_k^-C^T+R}, K_k\in R^{8,4}
Kk=CPk−CT+RPk−CT,Kk∈R8,4
x
k
^
=
x
^
k
−
+
K
k
(
y
k
−
C
x
^
k
−
)
,
C
∈
R
4
,
8
,
x
^
k
−
∈
R
8
,
1
,
y
k
∈
R
4
,
1
\hat{x_k}=\hat{x}_k^-+K_k(y_k-C\hat{x}_k^-), C\in R^{4,8}, \hat{x}_k^-\in R^{8,1}, y_k\in R^{4,1}
xk^=x^k−+Kk(yk−Cx^k−),C∈R4,8,x^k−∈R8,1,yk∈R4,1
P
k
=
(
I
−
K
k
C
)
P
k
−
P_k=(I-K_kC)P_k^-
Pk=(I−KkC)Pk−
整个过程中,矩阵A和矩阵C保持不变,具体如下所示。C是状态观测矩阵,比如,如果我们现在的观测值是速度,而需要的是位置,那么C就是由速度变化到位置的变换矩阵。而在这里,C是由检测框变换到检测框的变换矩阵,因此C里都是1
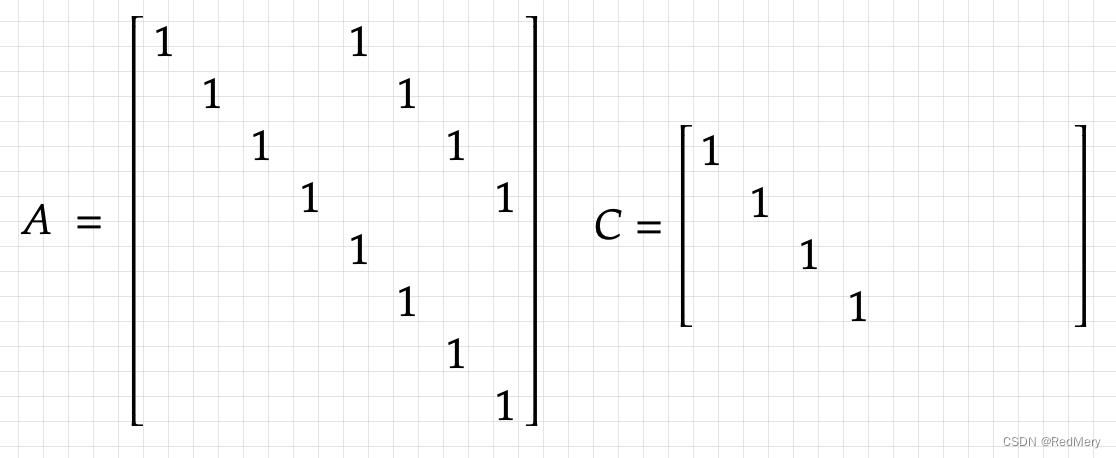 详细步骤:
详细步骤:
1.获得第一帧输出的检测框参数初始化
x
^
k
−
\hat{x}_k^-
x^k−和
P
k
−
P_k^-
Pk−首先被初始化
x
^
0
−
=
[
x
,
y
,
r
,
h
,
0
,
0
,
0
,
0
]
,
∈
R
1
,
8
\hat{x}_0^-=[x,y,r,h,0,0,0,0], \in R^{1,8}
x^0−=[x,y,r,h,0,0,0,0],∈R1,8
P
k
−
P_k^-
Pk−与
x
^
0
−
,
∈
R
8
,
8
\hat{x}_0^-, \in R^{8,8}
x^0−,∈R8,8 有关,差了一个系数,代码如下所示
# self._std_weight_position = 0.05
# self._std_weight_velocity = 0.00625
std = [2 * self._std_weight_position * measurement[3], #
2 * self._std_weight_position * measurement[3],
1e-2,
2 * self._std_weight_position * measurement[3],
10 * self._std_weight_velocity * measurement[3],
10 * self._std_weight_velocity * measurement[3],
1e-5,
10 * self._std_weight_velocity * measurement[3]]
covariance = np.diag(np.square(std))
2.预测下一时刻(第二帧中检测框的位置,图中的Prediction过程)
x
^
k
−
\hat{x}_k^-
x^k−正常计算,
P
k
−
中的
Q
P_k^-中的 Q
Pk−中的Q是一个随机噪声,其为
std_pos = [ self._std_weight_position * mean[3],
self._std_weight_position * mean[3],
1e-2,
self._std_weight_position * mean[3]]
std_vel = [self._std_weight_velocity * mean[3],
self._std_weight_velocity * mean[3],
1e-5,
self._std_weight_velocity * mean[3]]
motion_cov = np.diag(np.square(np.r_[std_pos, std_vel]))
mean = np.dot(self._motion_mat, mean)
covariance = np.linalg.multi_dot(( self._motion_mat, covariance, self._motion_mat.T)) + motion_cov
3.完成配对,给每一个轨迹匹配一个检测框
4.更新过程(Update)
def project(self, mean, covariance):
"""Project state distribution to measurement space.
Parameters
----------
mean : ndarray The state's mean vector (8 dimensional array).
covariance : ndarray The state's covariance matrix (8x8 dimensional).
Returns
-------
(ndarray, ndarray) Returns the projected mean and covariance matrix of the given state estimate.
"""
std = [ self._std_weight_position * mean[3],
self._std_weight_position * mean[3],
1e-1,
self._std_weight_position * mean[3]]
innovation_cov = np.diag(np.square(std))
mean = np.dot(self._update_mat, mean)
covariance = np.linalg.multi_dot(( self._update_mat, covariance, self._update_mat.T))
return mean, covariance + innovation_cov
def update(self, mean, covariance, measurement):
"""Run Kalman filter correction step.
Parameters
----------
mean : ndarray The predicted state's mean vector (8 dimensional). covariance : ndarray The state's covariance matrix (8x8 dimensional).
measurement : ndarray The 4 dimensional measurement vector (x, y, a, h), where (x, y) is the center position, a the aspect ratio, and h the height of the bounding box.
Returns
-------
(ndarray, ndarray)
Returns the measurement-corrected state distribution.
"""
projected_mean, projected_cov = self.project(mean, covariance)
#求解AX=b中的x
chol_factor, lower = scipy.linalg.cho_factor(projected_cov, lower=True, check_finite=False)
kalman_gain = scipy.linalg.cho_solve((chol_factor,lower), np.dot(covariance, self._update_mat.T).T, check_finite=False).T
innovation = measurement - projected_mean
new_mean = mean + np.dot(innovation, kalman_gain.T)
new_covariance = covariance - np.linalg.multi_dot((
kalman_gain, projected_cov, kalman_gain.T))
return new_mean, new_covariance
然后不断的完成上述步骤