我们知道,经过网关的业务请求会被路由到后端真实的业务服务上去,假如我们使用的是Spring Cloud Gateway,那么你知道Spring Cloud Gateway是在哪一步去匹配路由的吗?
源码之下无秘密,让我们一起从源码中寻找答案。
入口
Spring Cloud Gateway 的入口为 DispatcherHandler 的 handle 方法,其中主要逻辑有获取Hander 和 执行Handler。
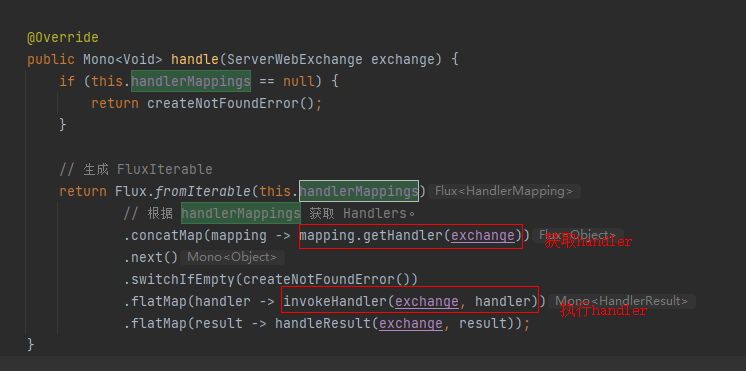
获取Handler
获取 Handler 的时候,handlerMappings 中包含有一个 RoutePredicateHandlerMapping 实例,其获取 Handler 的实现最终会调用到 getHandlerInternal 方法。
org.springframework.cloud.gateway.handler.RoutePredicateHandlerMapping
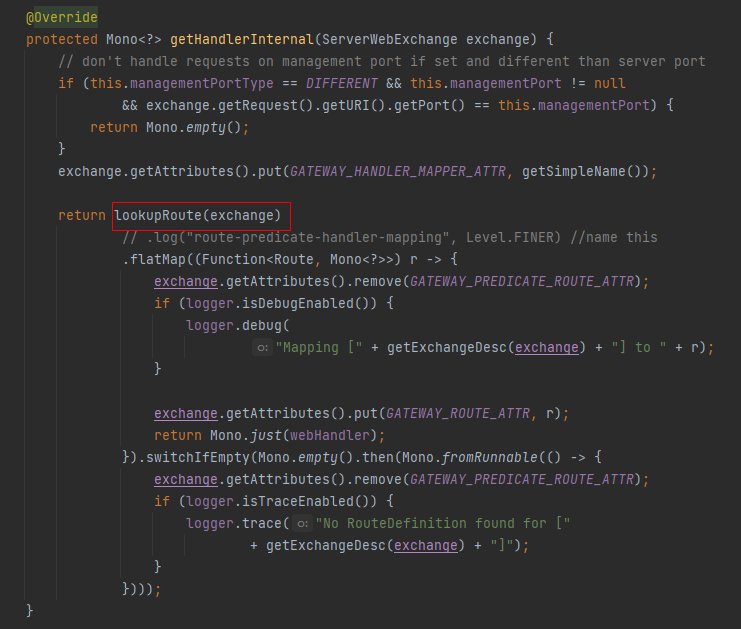
getHandlerInternal 方法会调用了 lookupRoute 方法去获取路由。
其中:
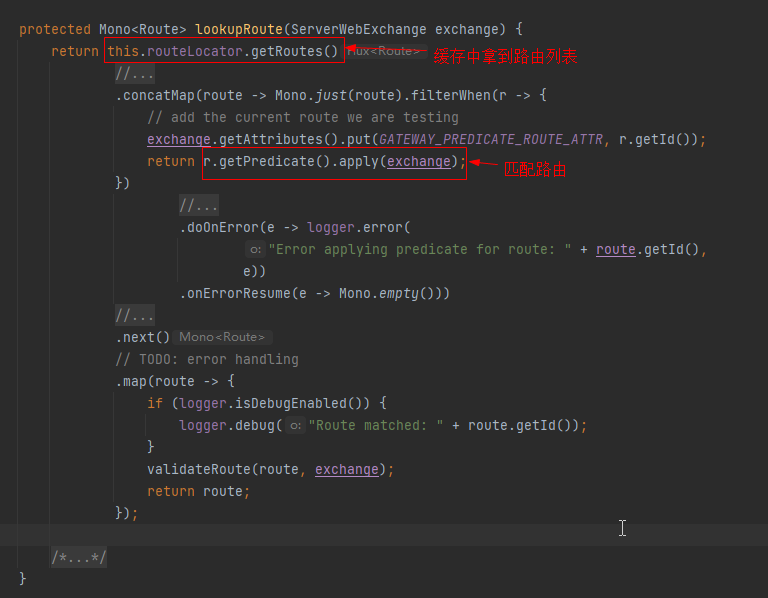
- 第一步是从缓存中获取路由列表,源码解析见:
- 第二步是调用每个路由的断言去匹配当前请求,匹配到就直接返回,忽略后续所有其他路由。
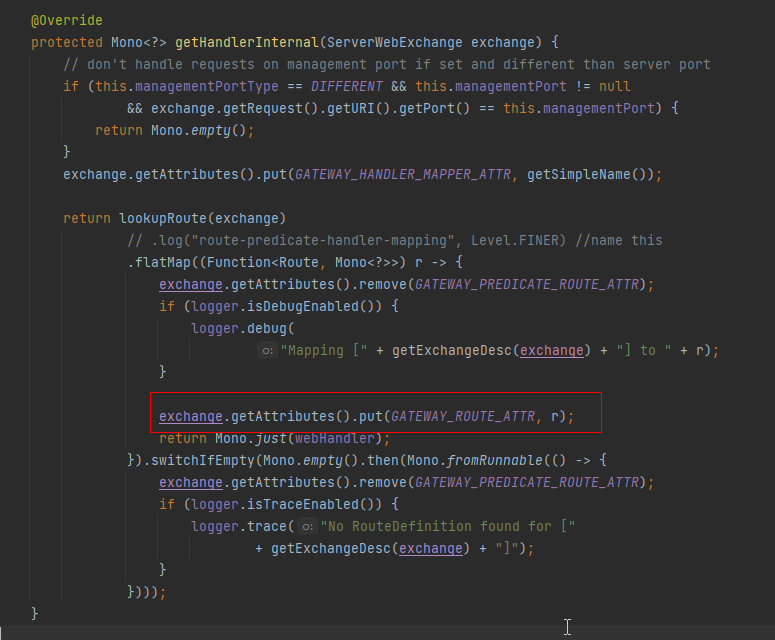
获取到路由后将路由信息设置到 exchange 的 gatewayRoute 属性上,然后返回 Handler。
其中RoutePredicateHandlerMapping 实例是在 GatewayAutoConfiguration 中配置好的。
org.springframework.cloud.gateway.config.GatewayAutoConfiguration
public class GatewayAutoConfiguration {
// ...
@Bean
public RouteLocator routeDefinitionRouteLocator(GatewayProperties properties,
List<GatewayFilterFactory> gatewayFilters,
List<RoutePredicateFactory> predicates,
RouteDefinitionLocator routeDefinitionLocator,
ConfigurationService configurationService) {
return new RouteDefinitionRouteLocator(routeDefinitionLocator, predicates,
gatewayFilters, properties, configurationService);
}
@Bean
@Primary
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(name = "cachedCompositeRouteLocator")
// TODO: property to disable composite?
public RouteLocator cachedCompositeRouteLocator(List<RouteLocator> routeLocators) {
return new CachingRouteLocator(
new CompositeRouteLocator(Flux.fromIterable(routeLocators)));
}
@Bean
public RoutePredicateHandlerMapping routePredicateHandlerMapping(
FilteringWebHandler webHandler, RouteLocator routeLocator,
GlobalCorsProperties globalCorsProperties, Environment environment) {
return new RoutePredicateHandlerMapping(webHandler, routeLocator,
globalCorsProperties, environment);
}
// ...
}
}
结论
综上,Spring Cloud Gateway 的路由匹配是在获取 Handler 的过程中,在 RoutePredicateHandlerMapping 中实现的,具体实现方法为 lookupRoute。最后将匹配到的路由设置到 exchange 的 gatewayRoute 属性上,供后续获取并使用。