📝个人主页:爱吃炫迈
💌系列专栏:数据结构与算法
🧑💻座右铭:道阻且长,行则将至💗
文章目录
- 栈
- 栈的存储
- 栈的基本操作
- 进栈
- 出栈
- 读栈顶元素
- 记录栈内元素个数
- 清除栈内所有元素
- 测试
- 案例
- 💞总结💞
栈
栈是仅限定在表尾进行插入或删除操作的线性表。
- 因此,对线性表来说,表尾端称为栈顶,表头端称为栈底。
栈的示意图
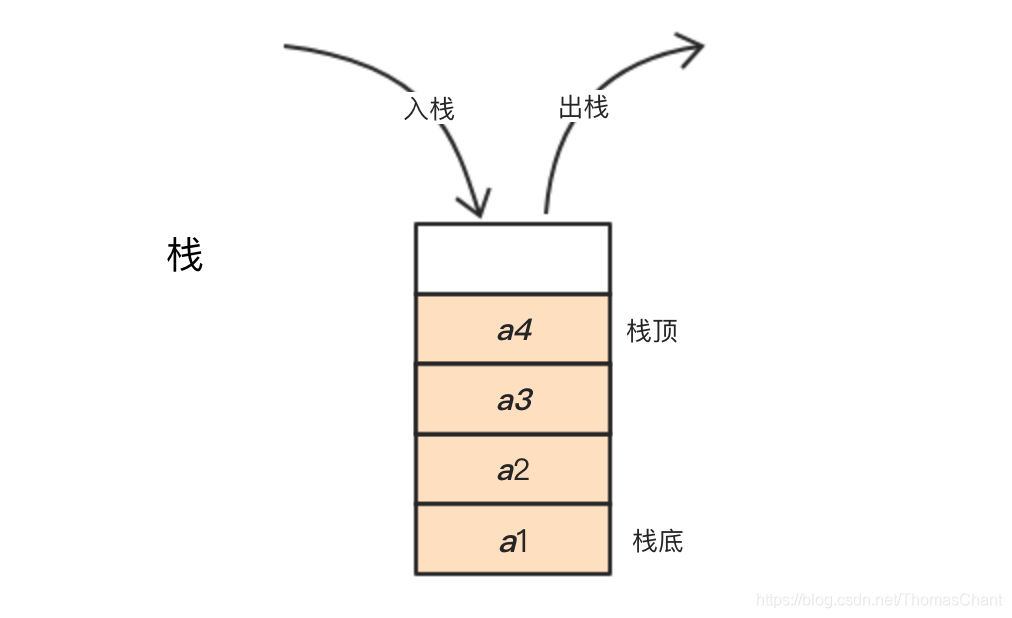
如上图所示,假设某个栈S={a1,a2, a3 ,a4},则a1为栈底元素,a4为栈顶元素。栈中元素进栈顺序为a1,a2, a3 ,a4,出栈顺序为a4,a3 ,a2,a1。换句话说,栈的修改是按后进先出的原则进行的。因此栈又称为是后进先出(简称LIFO结构)的线性表。
栈的存储
和线性表类似,栈也有两种存储表示方法,顺序栈和链栈。
- 采用顺序存储的栈称为顺序栈,它利用一组地址连续的存储单元存放自栈底到栈顶的数据元素,同时附设一个指针(top)指示当前栈顶元素在顺序栈中的位置。
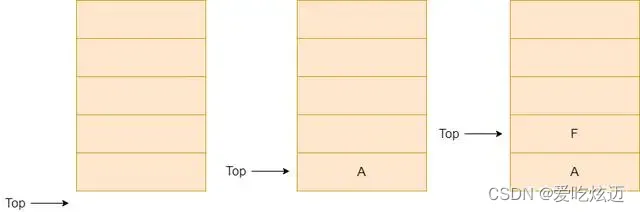
基于JS数组实现
class ArrayStack {
constructor() {
this.stack = [];
}
// 压栈
push(item) {
return this.stack.push(item);
}
// 弹栈
pop() {
return this.stack.pop();
}
// 取栈顶元素
peek() {
if (this.stack.length >= 1)
return this.stack[this.stack.length - 1];
}
// 清空栈
clear() {
this.stack = [];
}
// 判断栈是否为空
isEmpty() {
return this.stack.length === 0;
}
}
基本JS对象实现
class ObjectStack {
constructor() {
this.stack = {};
this.top = -1;
}
// 压栈
push(item) {
return this.stack[++this.top] = item;
}
// 弹栈
pop() {
if (this.top > -1) {
const res = this.stack[this.top];
delete this.stack[this.top--]
return res;
}
return null;
}
// 取栈顶元素
peek() {
if (this.top > -1) {
return this.stack[this.top];
}
return null;
}
// 清空栈
clear() {
this.stack = {};
this.top = -1;
}
// 判断栈是否为空
isEmpty() {
return this.top === -1;
}
}
- 采用链式存储的栈称为链栈,链栈便于多个栈共享存储空间和提高其效率,且不存在栈满上溢的情况。通常采用单链表实现,并且所有操作都是在单链表的表头进行的。
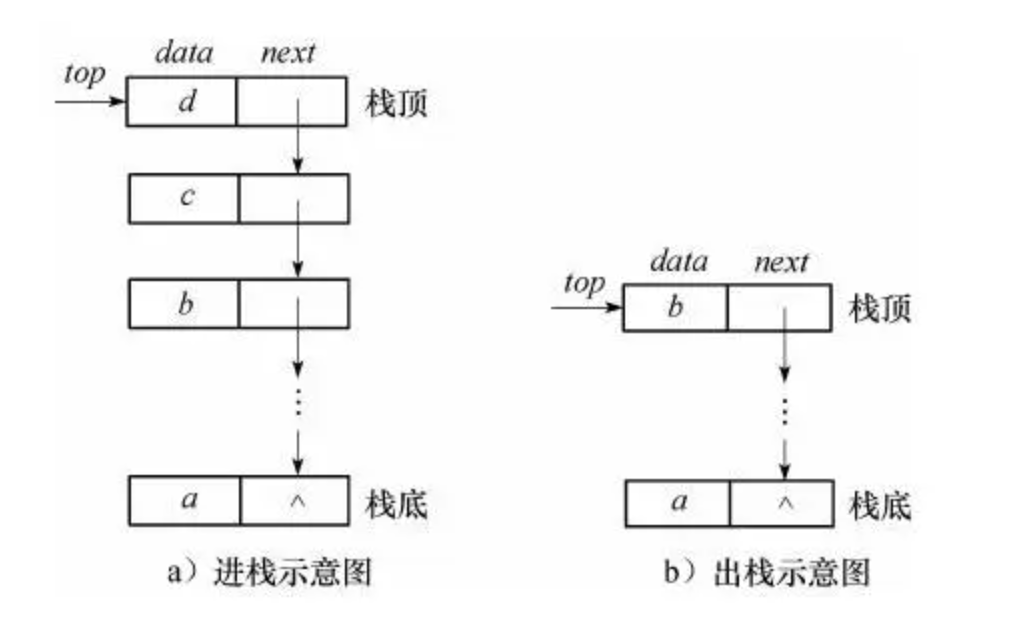
节点结构
数据域:数据域保存数据
指针域:指针域保存指向下一节点的指针。
class Node {
constructor(value) {
this.value = value;
this.next = null;
}
}
完整代码
class LinkStack {
constructor() {
this.top = null;
this.count = 0;
}
// 压栈
push(item) {
const node = new Node(item);
node.next = this.top;
this.top = node;
this.count++;
}
// 弹栈
pop() {
if (this.count > 0) {
const res = this.top.value;
this.top = this.top.next;
this.count--;
return res;
}
return null;
}
// 清空栈
clear() {
this.top = null;
this.count = 0;
}
// 取栈顶元素
peek() {
if (this.count > 0) {
return this.top.value;
}
return null;
}
// 判断栈是否为空
isEmpty() {
return this.count === 0;
}
}
栈的基本操作
实现一个栈,当务之急是决定存储数据结构的底层数据结构,这里采用的是数据。
//定义一个Stack类的构造函数
function Stack(){
this.dataStore = [] //保存栈内元素
this.top = 0; //记录栈顶位置
this.push = push; //元素入栈
this.pop = pop; //元素出栈
this.peek = peek; //预览栈顶元素
this.clear = clear; //清除栈内所有元素
this.length = length; //记录栈内元素个数
}
进栈
function push(element) {
this.dataStore[this.top++] = element;
}
出栈
function pop() {
return this.dataStore[--this.top];
}
读栈顶元素
function peek() {
return this.dataStore[this.top - 1];
}
记录栈内元素个数
function length() {
return this.top;
}
清除栈内所有元素
function clear() {
this.top = 0;
}
测试
let s = new Stack();
s.push("jack");
s.push("kobe");
s.push("Tom");
console.log("length:" + s.length()); //lengeh:3
console.log("top:" + s.top); //top:3
console.log("peek:" + s.peek()); //peek:Tom
let popItem = s.pop();
console.log(popItem); //Tom
s.clear();
console.log("length:" + s.length()); //length:0
s.push("Lily");
console.log(s.peek()); //Lily
案例
题目描述 :有效的括号
解题思路
- 构建栈,遍历字符串s
- 遇到左括号就压入栈中,遇到右括号则判断栈顶左括号是否与右括号相匹配,匹配就把栈顶左括号弹出栈,继续遍历字符串s,不匹配则可以直接返回false
- 遍历结束后,如果栈内没有剩余左括号,返回true
注意:有效字符串的长度一定为偶数,对于长度为奇数的字符串可以直接返回false
代码实现
var isValid = function(s) {
const stack = [];
if(s.length % 2 == 1) {
return false;
}
for(let i = 0; i < s.length; i+=1) {
const c = s[i];
if(c === '{' || c === '(' || c === '[') {
stack.push(c);
} else {
const t = stack[stack.length - 1];
if(
(t === '(' && c === ')') ||
(t === '{' && c === '}') ||
(t === '[' && c === ']')
) {
stack.pop();
} else {
return false ;
}
}
}
return stack.length === 0;
}
💞总结💞
希望我的文章能对你学习栈的知识点有所帮助!

![【题解】P4055 [JSOI2009] 游戏](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/a31d8471dfe94ab7ab7e60302ae563d7.png#pic_center)