文章目录
- 说明
- Day34 图的深度优先遍历
- 1.思路
- 2.代码
- 3.总结
- 1.在广度遍历中借助了队列
- 2.在深度优先遍历借助了栈。
说明
闵老师的文章链接: 日撸 Java 三百行(总述)_minfanphd的博客-CSDN博客
自己也把手敲的代码放在了github上维护:https://github.com/fulisha-ok/sampledata
Day34 图的深度优先遍历
1.思路
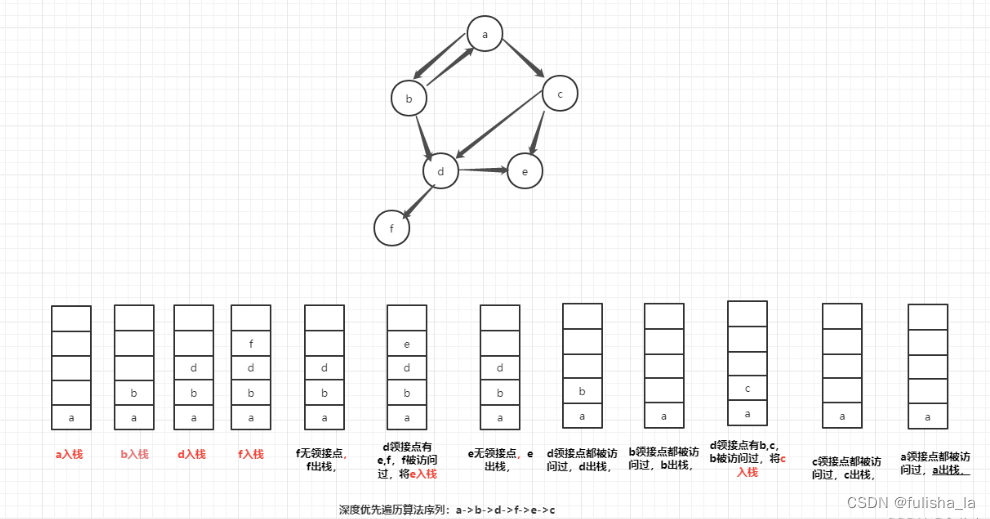
相比于广度优先遍历,深度优先遍历是往深度遍历,深度遍历更像是树的先根遍历。深度遍历借助栈来实现,如下图,从a节点出发,先访问a后再将a入栈,直到访问到f无法再往深度访问则是就往回溯,回溯上一个节点,看他的领接点,再对领接点进行深度遍历,最后将节点都遍历完。
根据上图画出相应的矩阵
Δ
a
b
c
d
e
f
a
0
1
1
0
0
0
b
1
0
0
1
0
0
c
0
0
0
1
1
0
d
0
0
0
0
1
1
e
0
0
0
0
0
0
f
0
0
0
0
0
0
\begin{array}{c} % 总表格 \begin{array}{c|cccc} % 第二行 Delta 值数组 \Delta & a & b & c & d & e & f \\ \hline a & 0 & 1 & 1 & 0 & 0 & 0 \\ b & 1 & 0 & 0 & 1 & 0 & 0 \\ c & 0 & 0 & 0 & 1 & 1 & 0\\ d & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 1 & 1 \\ e & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 \\ f & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 \\ \end{array} % 第二行表格结束 \end{array} % 总表格结束
Δabcdefa010000b100000c100000d011000e001100f000100
假如我们从a点出发,我们初始化栈时,会将a压入栈中。现在a出栈,同时a的领接点b入栈;接下来将b的领节点d入栈;再将d的领节点(e或f)入栈,这里选择f, 发现f没有领结点,则是就开始回溯,f出栈,然后d出栈,判断d的领结点有没有访问过,发现f被访问过,e没有,则将e压入栈中,然后又从e节点开始往下深度找,和上面步骤一样。在这个过程中主要注意有几点:
- 1.何时入栈
当所访问的节点还有邻结点且没有被访问,则继续将孩子节点进行入栈 - 2.何时出栈
当发现访问节点没有孩子节点,自己就需要出栈,且要往回回溯节点。
2.代码
在深度遍历的代码中,while(true)这个循环一定要有退出循环的条件,不然会进入死循环。在循环中的tempNext变量则是往深度找节点的变量,当往最深不能再走,则节点出栈(栈:先进后出)回溯。
- 和day33代码一样,如果有多个连通分量 可能回漏掉结点,所以也加了一个判断,tempVisitedArray,resultString作为成员变量,breadthTraversal和depthTraversal方法是保证所有结点都能访问到,在方法开始前都会重新初始化tempVisitedArray,resultString这两个变量。
代码如下:
package graph;
import datastructure.queue.CircleObjectQueue;
import datastructure.stack.ObjectStack;
import matrix.IntMatrix;
import java.time.Year;
/**
* @author: fulisha
* @date: 2023/4/18 15:43
* @description:
*/
public class Graph {
IntMatrix connectivityMatrix;
/**
* The first constructor.
* @param paraNumNodes The number of nodes in the graph.
*/
public Graph(int paraNumNodes){
connectivityMatrix = new IntMatrix(paraNumNodes, paraNumNodes);
}
/**
* The second constructor.
* @param paraMatrix The data matrix.
*/
public Graph(int[][] paraMatrix){
connectivityMatrix = new IntMatrix(paraMatrix);
}
@Override
public String toString(){
return "This is the connectivity matrix of the graph.\r\n" + connectivityMatrix;
}
/**
* Get the connectivity of the graph.
* @return
*/
public boolean getConnectivity() throws Exception {
// Step 1. Initialize accumulated matrix.
IntMatrix tempConnectivityMatrix = IntMatrix.getIdentityMatrix(connectivityMatrix.getData().length);
//Step 2. Initialize
IntMatrix tempMultipliedMatrix = new IntMatrix(connectivityMatrix);
//Step 3. Determine the actual connectivity.
for (int i = 0; i < connectivityMatrix.getData().length - 1; i++){
// M_a = M_a + M^k
tempConnectivityMatrix.add(tempMultipliedMatrix);
// M^k
tempMultipliedMatrix = IntMatrix.multiply(tempMultipliedMatrix, connectivityMatrix);
}
// Step 4. Check the connectivity.
System.out.println("The connectivity matrix is: " + tempConnectivityMatrix);
int[][] tempData = tempConnectivityMatrix.getData();
for (int i = 0; i < tempData.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < tempData.length; j++){
if (tempData[i][j] == 0){
System.out.println("Node " + i + " cannot reach " + j);
return false;
}
}
}
return true;
}
/**
* Unit test for getConnectivity.
*/
public static void getConnectivityTest(){
int[][] tempMatrix = { { 0, 1, 0 }, { 1, 0, 1 }, { 0, 1, 0 } };
Graph tempGraph2 = new Graph(tempMatrix);
System.out.println(tempGraph2);
boolean tempConnected = false;
try {
tempConnected = tempGraph2.getConnectivity();
} catch (Exception ee) {
System.out.println(ee.getMessage());
}
System.out.println("Is the graph connected? " + tempConnected);
//Test a directed graph. Remove one arc to form a directed graph.
tempGraph2.connectivityMatrix.setValue(1, 0, 0);
tempConnected = false;
try {
tempConnected = tempGraph2.getConnectivity();
} catch (Exception ee) {
System.out.println(ee);
}
System.out.println("Is the graph connected? " + tempConnected);
}
/**
* Breadth first Traversal
* @param paraStartIndex The start index.
* @return The sequence of the visit.
*/
boolean[] tempVisitedArray;
String resultString = "";
public String breadthFirstTraversal(int paraStartIndex) {
CircleObjectQueue tempQueue = new CircleObjectQueue();
int tempNumNodes = connectivityMatrix.getRows();
// Initialize the queue
tempVisitedArray[paraStartIndex] = true;
resultString += paraStartIndex;
tempQueue.enqueue(paraStartIndex);
//Now visit the rest of the graph.
int tempIndex;
Integer tempInteger = (Integer) tempQueue.dequeue();
while (tempInteger != null){
tempIndex = tempInteger.intValue();
//Enqueue all its unvisited neighbors.
for (int i = 0; i < tempNumNodes; i++){
if (tempVisitedArray[i]){
// Already visited.
continue;
}
if (connectivityMatrix.getData()[tempIndex][i] == 0) {
//Not directly connected.
continue;
}
tempVisitedArray[i] = true;
resultString += i;
tempQueue.enqueue(i);
}
//Take out one from the head.
tempInteger = (Integer)tempQueue.dequeue();
}
return resultString;
}
/**
* Judge connectivity
* @param
* @return
*/
public boolean breadthTraversal(int paraStartIndex) {
int tempNumNodes = connectivityMatrix.getRows();
tempVisitedArray = new boolean[tempNumNodes];
resultString = "";
breadthFirstTraversal(paraStartIndex);
for (int i = 0; i < tempNumNodes; i++){
if (!tempVisitedArray[i]){
breadthFirstTraversal(i);
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
public String depthFirstTraversal(int paraStartIndex) {
ObjectStack tempStack = new ObjectStack();
int tempNumNodes = connectivityMatrix.getRows();
tempVisitedArray = new boolean[tempNumNodes];
tempVisitedArray[paraStartIndex] = true;
resultString += paraStartIndex;
tempStack.push(new Integer(paraStartIndex));
System.out.println("Push " + paraStartIndex);
System.out.println("Visited " + resultString);
int tempIndex = paraStartIndex;
int tempNext;
Integer tempInteger;
while (true) {
tempNext = -1;
// Find an unvisited neighbor and push
for (int i = 0; i < tempNumNodes; i++) {
if (tempVisitedArray[i]) {
continue; //Already visited.
}
if (connectivityMatrix.getData()[tempIndex][i] == 0) {
continue; //Not directly connected.
}
tempVisitedArray[i] = true;
resultString += i;
tempStack.push(new Integer(i));
System.out.println("Push " + i);
tempNext = i;
break;
}
if (tempNext == -1) {
//there is no neighbor node, pop
tempInteger = (Integer) tempStack.pop();
System.out.println("Pop " + tempInteger);
if (tempStack.isEmpty()) {
//No unvisited neighbor。Backtracking to the last one stored in the stack
break;
}else {
tempInteger = (Integer) tempStack.pop();
tempIndex = tempInteger.intValue();
tempStack.push(tempInteger);
}
} else {
tempIndex = tempNext;
}
}
return resultString;
}
public boolean depthTraversal(int paraStartIndex){
int tempNumNodes = connectivityMatrix.getRows();
tempVisitedArray = new boolean[tempNumNodes];
resultString = "";
depthFirstTraversal(paraStartIndex);
for (int i = 0; i < tempNumNodes; i++){
if (!tempVisitedArray[i]){
depthFirstTraversal(i);
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
public static void depthFirstTraversalTest() {
// Test an undirected graph.
//int[][] tempMatrix = { { 0, 1, 1, 0 }, { 1, 0, 0, 1 }, { 1, 0, 0, 0}, { 0, 1, 0, 0} };
int[][] tempMatrix = { { 0, 1, 1, 0 , 0}, { 1, 0, 0, 1, 0 }, { 1, 0, 0, 1, 0}, { 0, 1, 1, 0, 0}, { 0, 0, 0, 0, 0} };
Graph tempGraph = new Graph(tempMatrix);
System.out.println(tempGraph);
String tempSequence = "";
try {
//tempSequence = tempGraph.depthFirstTraversal(0);
tempGraph.depthTraversal(2);
} catch (Exception ee) {
System.out.println(ee);
} // Of try.
System.out.println("The depth first order of visit: " + tempGraph.resultString);
}
public static void breadthFirstTraversalTest() {
// Test an undirected graph.
//int[][] tempMatrix = { { 0, 1, 1, 0 }, { 1, 0, 0, 1 }, { 1, 0, 0, 1}, { 0, 1, 1, 0} };
//int[][] tempMatrix = { { 0, 1, 1, 0 , 0}, { 1, 0, 0, 1, 0 }, { 1, 0, 0, 1, 0}, { 0, 1, 1, 0, 0}, { 0, 0, 0, 0, 0} };
int[][] tempMatrix = { { 0, 1, 1, 0 , 0, 0, 0}, { 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0 }, { 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0}, { 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0}, { 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1}, { 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0}, { 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0} };
Graph tempGraph = new Graph(tempMatrix);
System.out.println(tempGraph);
String tempSequence = "";
try {
tempGraph.breadthTraversal(2);
//tempSequence = tempGraph.breadthFirstTraversal(2);
} catch (Exception ee) {
System.out.println(ee.getMessage());
return;
}
System.out.println("The breadth first order of visit: " + tempGraph.resultString);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Hello!");
Graph tempGraph = new Graph(3);
System.out.println(tempGraph);
// Unit test.
getConnectivityTest();
breadthFirstTraversalTest();
depthFirstTraversalTest();
}
}
-
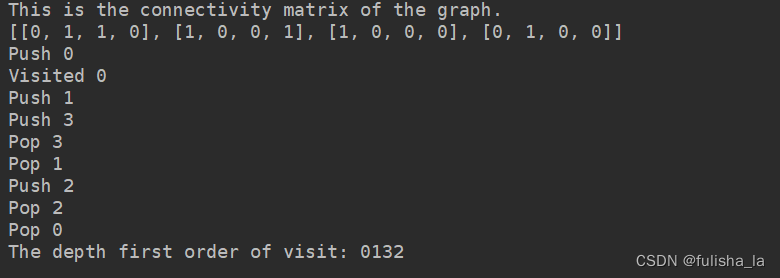
单元测试1(文章中给出的例子)
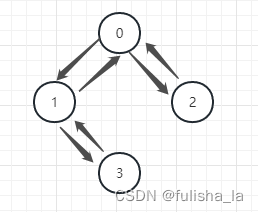
从0开始出发:
-
单元测试2

从0开始出发:
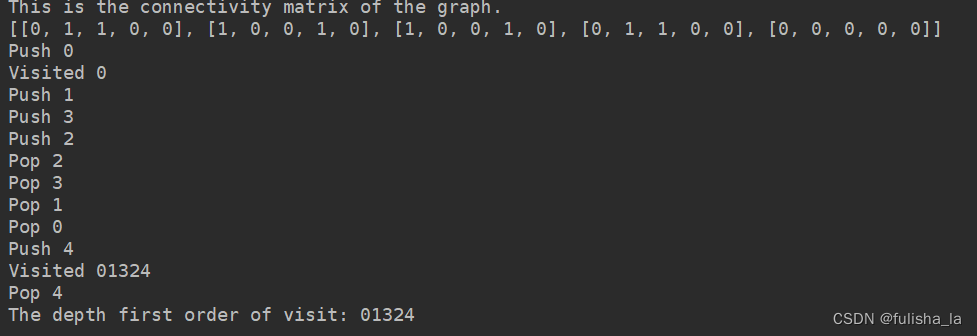
-
单元测试3
从0开始:

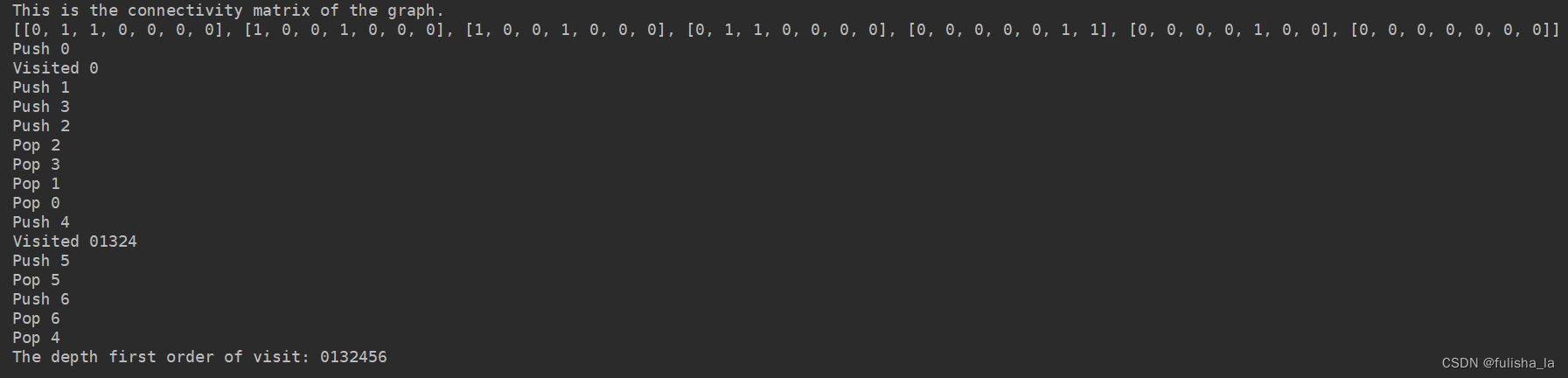
3.总结
在对树或图遍历的时候,根据他们的结构,我们都需要保存访问的节点。
1.在广度遍历中借助了队列
在进行图的广度遍历可以结合树的层次遍历,先说树的层次遍历,它需要一层一层的遍历节点当第一层节点遍历完了,如何找到第二层节点?第二层是上一层的孩子节点,所以第一层访问后将要将节点保存起来,选择存储的结构可以是栈或队列。队列(先进先出)出栈是从左到右的顺序,这更符合我们的读写顺序,用栈(先进后出)来实现则出栈顺序就会很混乱,所以层次遍历使用队列。进一步,在对图的广度遍历,我们更愿意借助队列来实现遍历。
2.在深度优先遍历借助了栈。
在对树进行先序遍历时,我们访问完节点后,需要把节点保存,存储我们也可以选择栈和队列,若使用队列,因为队列特点先进先出,进队列顺序可以,但是在出队列时需要的结点在队尾。因此队列无法达到遍历的要求,但是栈先进后出更适合。进一步我们图的深度遍历会更先弄考虑的是栈。
列和栈特点可以在很多地方应用,例如逆向打印数据,顺序输入数据进入栈在输出时可以逆序打印。(例如Day26:: 二叉树深度遍历的栈实现 (前序和后序))