In-Context Learning是最近比较火热的方向,其主要针对超大规模模型(例如1750B参数量的GPT-3模型),在只提供少量标注样本作为提示的前提下,即可以实现很惊艳的效果。本文将元学习引入到In-Context Learning中。
论文PDF:https://doi.org/10.18653/v1/2022.acl-long.53
一、动机
本文提出in-context tuning(ICT)用于few-shot learning
- 目前,向语言模型通过prompting可以在小样本场景下得到很大的成功。例如GPT-3
For example, to coax the model into performing sentiment classification on the target input “This movie is a waste of time”, we prompt the LM with the sequence “I like the movie! Positive review? Yes. Horrible Movie! Positive review? No. This movie is a waste of time. Positive review? ___”, and predict “positive” if the next word is more likely to be “Yes” rather than “No”.
- 然而原始的语言模型在预训练时并没有针对in-context进行优化
raw LMs are not optimized for in-context FSL during pre-training, and exhibit undesirable behavior when used for FSL
- 先前工作发现prompting会过度受到(oversensitive)样本选取以及instruction本身影响
Previous work has also shown that prompting raw LMs is often oversensitive to example choices and instruction wording
二、方法
在训练(fine-tuning)阶段,给定一系列的训练task,每一个task都有相应的instruction,以及该task对应的少量样本(输入/输出对)。在测试阶段,给定一个新的unseen task,以及该task对应的instruction和少量样本(输入/输出对),旨在让模型能够对测试样本预测其类别。如下图,给定一个情感分析task:
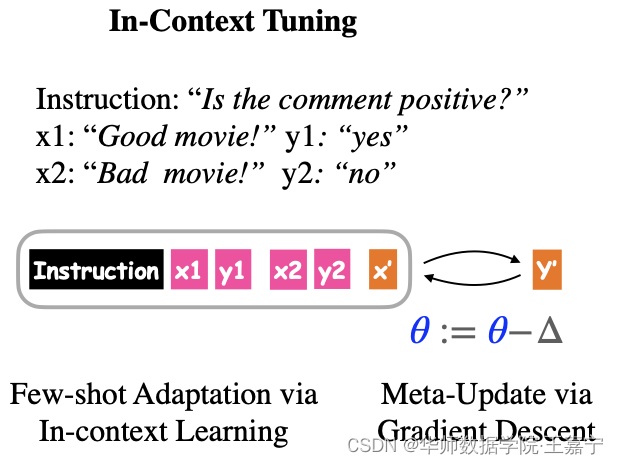
在训练时,直接对instruction I T I_T IT、若干少量标注数据 S T S_T ST 以及target样本 x t a r g e t T x_{target}^T xtargetT 进行拼接,并基于in-context learning训练目标进行优化,预测对应类别 y t a r g e t T y_{target}^T ytargetT:
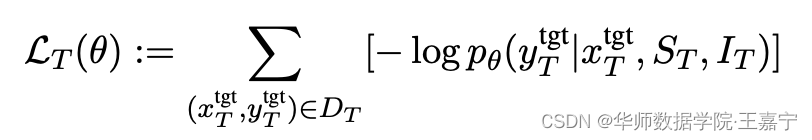
三、实验
(1)baseline模型
Raw In-context Learning
与in-context tuning一样,给定unseen task的instruction、少量标注样本(输入/输出对)和样本输入,直接预测样本的输出。此时没有fine-tuning过程,属于zero-shot learning场景。
Instruction-tuning + Fine-tuning
给定若干种类的task,基于instruction以及样本的输入,用于训练。在fine-tuning阶段,给定unseen task的instruction以及K个样本,进行fine-tuning。
Instruction-tuning
此时只有instruction和样本的输入,属于zero-shot learning场景。
MAML
给定若干task的instruction和一个样本输入,用于训练并预测目标。其与传统的MAML一样,只是训练目标变为instruction tuning
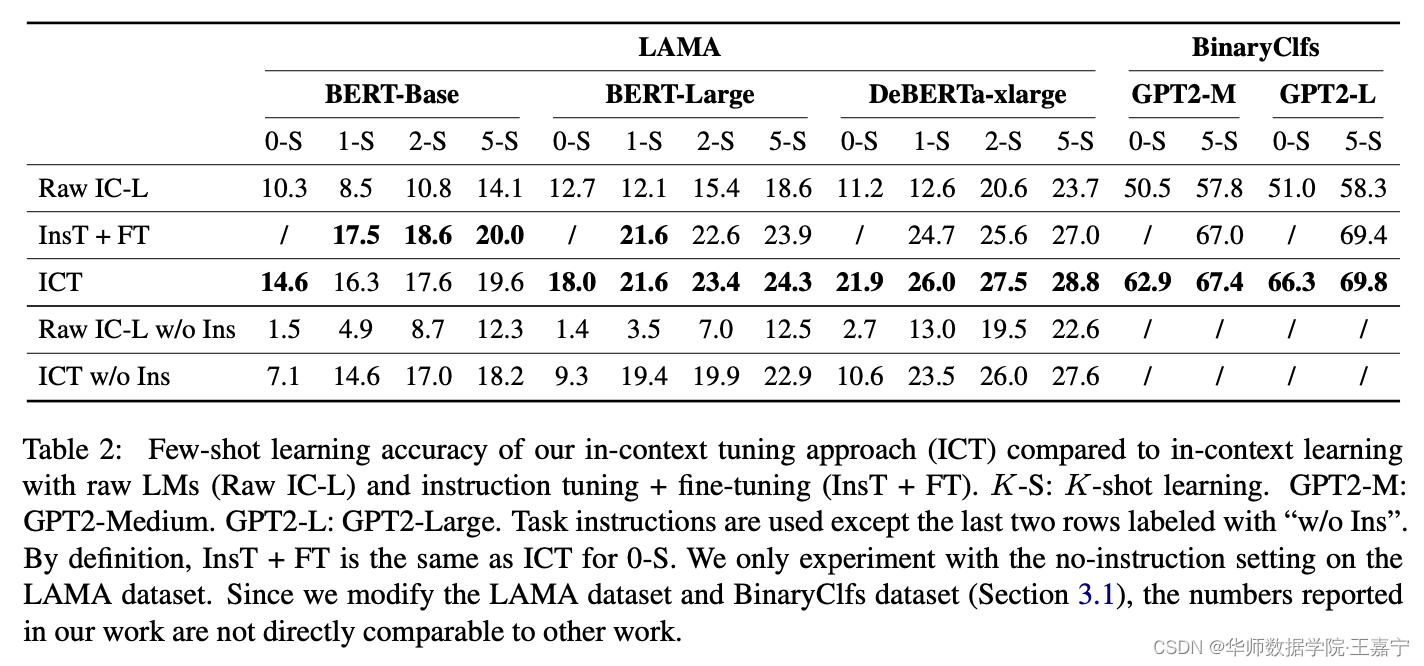
- In-context tuning比原始的in-context learning效果好,说明直接对in-context learning obective进行训练是有效的;
- MAML的效果超越了instruction-tuning,说明MAML是可以充分利用few-shot example来实现task adaptation;而本文提出的方法超越了MAML,则说明in-context tuning可以充分利用预训练语言模型的归纳偏置(inductive bias)

![[附源码]SSM计算机毕业设计闲置物品交易管理系统JAVA](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/47ef026d4b4d46e8b87ede6a764f958b.png)