一、Mybatis参数处理
1、数据准备
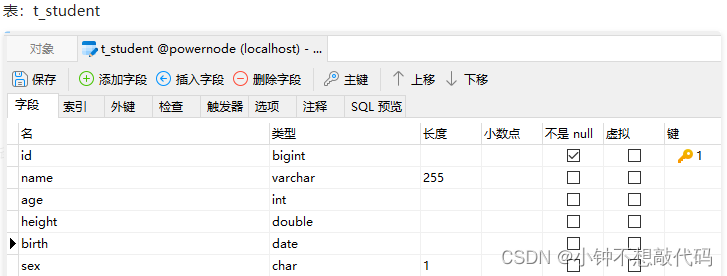
pojo类:
public class Student {
private Long id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
private Double height;
private Character sex;
private Date birth;
// constructor
// setter and getter
// toString
}
2、单个简单类型参数
简单类型包括:
- byte short int long float double char
- Byte Short Integer Long Float Double Character
- String
- java.util.Date
- java.sql.Date
需求:根据name查、根据id查、根据birth查、根据sex查
StudentMapper
package com.powernode.mybatis.mapper;
import com.powernode.mybatis.pojo.Student;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.List;
public interface StudentMapper {
/**
* 根据name查询
* @param name
* @return
*/
List<Student> selectByName(String name);
/**
* 根据id查询
* @param id
* @return
*/
Student selectById(Long id);
/**
* 根据birth查询
* @param birth
* @return
*/
List<Student> selectByBirth(Date birth);
/**
* 根据sex查询
* @param sex
* @return
*/
List<Student> selectBySex(Character sex);
}
StudentMapper.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.powernode.mybatis.mapper.StudentMapper">
<select id="selectByName" resultType="student">
select * from t_student where name = #{name}
</select>
<select id="selectById" resultType="student">
select * from t_student where id = #{id}
</select>
<select id="selectByBirth" resultType="student">
select * from t_student where birth = #{birth}
</select>
<select id="selectBySex" resultType="student">
select * from t_student where sex = #{sex}
</select>
</mapper>
通过测试得知,简单类型对于mybatis来说都是可以自动类型识别的,这里测试程序省略。
其实SQL映射文件中的配置比较完整的写法是:
<select id="selectByName" resultType="student" parameterType="java.lang.String">
select * from t_student where name = #{name, javaType=String, jdbcType=VARCHAR}
</select>
其中sql语句中的javaType,jdbcType,以及select标签中的parameterType属性,都是用来帮助mybatis进行类型确定的。不过这些配置多数是可以省略的。因为mybatis它有强大的自动类型推断机制。
- javaType:可以省略
- jdbcType:可以省略
- parameterType:可以省略
注意:如果参数只有一个的话,#{} 里面的内容就随便写了。对于 ${} 来说,注意加单引号。
3、Map参数
需求:根据name和age查询
StudentMapper接口
/**
* 根据name和age查询
* @param paramMap
* @return
*/
List<Student> selectByParamMap(Map<String,Object> paramMap);
StudentMapper.xml
<select id="selectByParamMap" resultType="student">
select * from t_student where name = #{nameKey} and age = #{ageKey}
</select>
测试程序
@Test
public void testSelectByParamMap(){
// 准备Map
Map<String,Object> paramMap = new HashMap<>();
paramMap.put("nameKey", "张三");
paramMap.put("ageKey", 20);
List<Student> students = mapper.selectByParamMap(paramMap);
students.forEach(student -> System.out.println(student));
}
注意:这种方式是手动封装Map集合,将每个条件以key和value的形式存放到集合中。然后在使用的时候通过#{map集合的key}来取值。
4、实体类参数
需求:插入一条Student数据
StudentMapper接口
/**
* 保存学生数据
* @param student
* @return
*/
int insert(Student student);
StudentMapper.xml
<insert id="insert">
insert into t_student values(null,#{name},#{age},#{height},#{birth},#{sex})
</insert>
测试程序
@Test
public void testInsert(){
Student student = new Student();
student.setName("李四");
student.setAge(30);
student.setHeight(1.70);
student.setSex('男');
student.setBirth(new Date());
int count = mapper.insert(student);
SqlSessionUtil.openSession().commit();
}
这里需要注意的是:#{} 里面写的是属性名字。这个属性名其本质上是:set/get方法名去掉set/get之后的名字。
5、多参数
需求:通过name和sex查询
StudentMapper接口
/**
* 根据name和sex查询
* @param name
* @param sex
* @return
*/
List<Student> selectByNameAndSex(String name, Character sex);
StudentMapper.xml
<select id="selectByNameAndSex" resultType="student">
select * from t_student where name = #{name} and sex = #{sex}
</select>
测试程序
@Test
public void testSelectByNameAndSex(){
List<Student> students = mapper.selectByNameAndSex("张三", '女');
students.forEach(student -> System.out.println(student));
}
执行结果:

异常信息描述了:name参数找不到,可用的参数包括[arg1, arg0, param1, param2]
- arg0 是第一个参数
- param1是第一个参数
- arg1 是第二个参数
- param2是第二个参数
实现原理:实际上在mybatis底层会创建一个map集合,以arg0/param1为key,以方法上的参数为value,例如以下代码:
Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("arg0", name);
map.put("arg1", sex);
map.put("param1", name);
map.put("param2", sex);
// 所以可以这样取值:#{arg0} #{arg1} #{param1} #{param2}
// 其本质就是#{map集合的key}
注意:使用mybatis3.4.2之前的版本时:要用#{0}和#{1}这种形式。
5、@Param注解(命名参数)
可以不用arg0 arg1 param1 param2吗?这个map集合的key我们自定义可以吗?
当然可以。使用@Param注解即可。这样可以增强可读性。
需求:根据name和age查询
StudentMapper接口
/**
* 根据name和age查询
* @param name
* @param age
* @return
*/
List<Student> selectByNameAndAge(@Param(value="name") String name, @Param("age") int age);
StudentMapper.xml
<select id="selectByNameAndAge" resultType="student">
select * from t_student where name = #{name} and age = #{age}
</select>
测试程序
@Test
public void testSelectByNameAndAge(){
List<Student> stus = mapper.selectByNameAndAge("张三", 20);
stus.forEach(student -> System.out.println(student));
}
核心:@Param(“这里填写的其实就是map集合的key”)
二、MyBatis查询语句
返回一个实体类对象和一个装有实体类对象的集合两种方式比较常见,这里不做研究了
1、返回Map
当返回的数据,没有合适的实体类对应的话,可以采用Map集合接收。字段名做key,字段值做value。查询如果可以保证只有一条数据,则返回一个Map集合即可。
CarMapper接口
/**
* 通过id查询一条记录,返回Map集合
* @param id
* @return
*/
Map<String, Object> selectByIdRetMap(Long id);
CarMapper.xml
<select id="selectByIdRetMap" resultType="map">
select id,car_num carNum,brand,guide_price guidePrice,produce_time produceTime,car_type carType from t_car where id = #{id}
</select>
测试程序
@Test
public void testSelectByIdRetMap(){
CarMapper mapper = SqlSessionUtil.openSession().getMapper(CarMapper.class);
Map<String,Object> car = mapper.selectByIdRetMap(35L);
System.out.println(car);
}
当然,如果返回一个Map集合,可以将Map集合放到List集合中吗?当然可以,这里就不再测试了。
反过来,如果返回的不是一条记录,是多条记录的话,只采用单个Map集合接收,这样同样会出现之前的异常:TooManyResultsException
2、返回List<Map>
CarMapper接口
/**
* 查询所有的Car,返回一个List集合。List集合中存储的是Map集合。
* @return
*/
List<Map<String,Object>> selectAllRetListMap();
CarMapper.xml
<select id="selectAllRetListMap" resultType="map">
select id,car_num carNum,brand,guide_price guidePrice,produce_time produceTime,car_type carType from t_car
</select>
测试程序
@Test
public void testSelectAllRetListMap(){
CarMapper mapper = SqlSessionUtil.openSession().getMapper(CarMapper.class);
List<Map<String,Object>> cars = mapper.selectAllRetListMap();
System.out.println(cars);
}
3、resultMap结果映射
查询结果的列名和java对象的属性名对应不上怎么办?
- 第一种方式:as 给列起别名
- 第二种方式:使用resultMap进行结果映射
- 第三种方式:是否开启驼峰命名自动映射(配置settings)
使用resultMap进行结果映射
CarMapper接口
/**
* 查询所有Car,使用resultMap进行结果映射
* @return
*/
List<Car> selectAllByResultMap();
CarMapper.xml
<!--
resultMap:
id:这个结果映射的标识,作为select标签的resultMap属性的值。
type:结果集要映射的类。可以使用别名。
-->
<resultMap id="carResultMap" type="car">
<!--对象的唯一标识,官方解释是:为了提高mybatis的性能。建议写上。-->
<id property="id" column="id"/>
<result property="carNum" column="car_num"/>
<!--当属性名和数据库列名一致时,可以省略。但建议都写上。-->
<!--javaType用来指定属性类型。jdbcType用来指定列类型。一般可以省略。-->
<result property="brand" column="brand" javaType="string" jdbcType="VARCHAR"/>
<result property="guidePrice" column="guide_price"/>
<result property="produceTime" column="produce_time"/>
<result property="carType" column="car_type"/>
</resultMap>
<!--resultMap属性的值必须和resultMap标签中id属性值一致。-->
<select id="selectAllByResultMap" resultMap="carResultMap">
select * from t_car
</select>
是否开启驼峰命名自动映射
使用这种方式的前提是:属性名遵循Java的命名规范,数据库表的列名遵循SQL的命名规范。
Java命名规范:首字母小写,后面每个单词首字母大写,遵循驼峰命名方式。
SQL命名规范:全部小写,单词之间采用下划线分割。
比如以下的对应关系:

如何启用该功能,在mybatis-config.xml文件中进行配置:
<!--放在properties标签后面-->
<settings>
<setting name="mapUnderscoreToCamelCase" value="true"/>
</settings>