模拟发送post请求
发送post请求的基础知识dumps和loads
代码示例:
# 发送post请求
import requests,json
# 发送post请求的基础知识dumps和loads
str_dict ={'name':'xiaoming','age':'20','sex':'男'}
print(type(str_dict))
str1 = json.dumps(str_dict) # 1,json.dumps 是把字典、json对象转换为字符串
print(type(str1))
print(str1)
str2 = '{"name":"tom","age":"22","sex":"男"}' # 注意 这里是字符串,里面必须用双引号
str_json = json.loads(str2) # 2,json.loads 是将字符串转成字典,json对象
print(type(str_json))
print(str_json['name'],str_json.get('age'))
以微信开放平台举例
发送post请求
# 1,获取token
url = 'https://api.weixin.qq.com/cgi-bin/token'
data = {'grant_type':'client_credential',
'appid':'wxf14419077f707',
'secret':'92a113bd4b5ffdc72144740dc7123'}
response = requests.get(url=url,params=data)
# 响应是str类型 ,所以我们需要将响应转换成json
json_obj = response.json()
token = json_obj['access_token']
print(token)
# 2,新建用户标签
tag_url = 'https://api.weixin.qq.com/cgi-bin/tags/create'
tag_data = {'access_token':token}
tag_json_body = {"tag":{"name" :"长沙01"} }
headers = {"content-type":"application/json"} # 发送json 数据必须带有头部信息 content-type
# post请求中body中的参数通过data,json 传递
# 如果body中的数据为json格式,在发送时可以直接使用json=body值
# response = requests.post(url=tag_url,params=tag_data,headers=headers,json=tag_json_body)
# 如果body中的数据为json格式,在发送时使用data=json.dumps(body值)
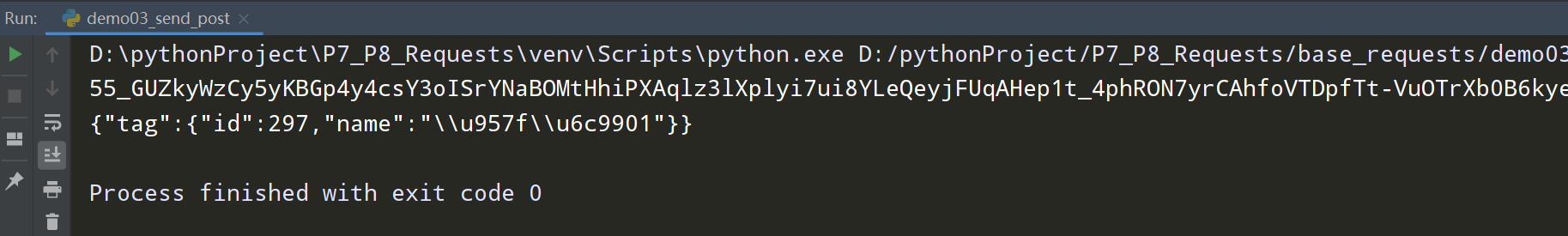
response = requests.post(url=tag_url,params=tag_data,headers=headers,data=json.dumps(tag_json_body))
print(response.content.decode("utf-8"))
查看执行结果:
上传文件
import requests
# 1,获取token
url = 'https://api.weixin.qq.com/cgi-bin/token'
data = {'grant_type':'client_credential',
'appid':'wxf14419077f707856',
'secret':'92a113bd4b5ffdc72144740dc7123c99'}
response = requests.get(url=url,params=data)
# 响应是str类型 ,所以我们需要将响应转换成json
json_obj = response.json()
token = json_obj['access_token']
print(token)
# 上传文件
wx_url = "https://api.weixin.qq.com/cgi-bin/media/upload"
wx_data = {"access_token":token,"type":"image"}
file = {"files":open("E:/12345.png","rb")} # 注意:必须要用字典的方式open
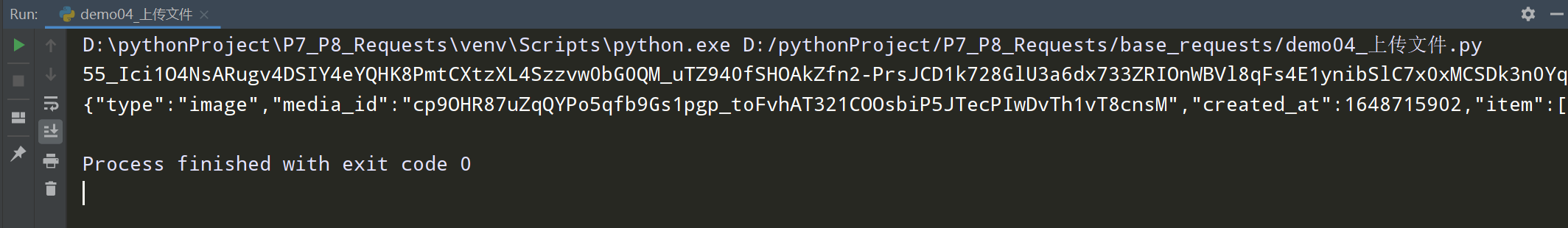
res = requests.post(url=wx_url,params=wx_data,files=file)
print(res.content.decode("utf-8"))
查看执行结果
封装post请求
代码示例:
# 封装post方法
def send_post(url,data,json_info):
headers = {"content-type": "application/json"}
response = requests.post(url=url,params=data,json=json_info,headers=headers)
return response
print(send_post(url=tag_url,data=tag_data,json_info=tag_json).content.decode("utf-8"))
封装main方法
代码示例:
# 封装main方法
def run_main(method,url,data=None,json_info=None):
response = None
if method == "GET":
response = send_get(url,data)
elif method == "POST":
response = send_post(url,data,json_info)
else:
print("参数错误")
response = None
return response
print(run_main("GET","https://www.jd.com/").content.decode("utf-8"))
封装测试类
示例代码:
# 将写好的get、post、run_mian方法做成类
import requests
class run_test:
session_obj = requests.session()
def __init__(self,method,url,params=None,data=None,headers=None):
self.method = method
self.url = url
self.params = params
self.data = data
self.headers = headers
def send_get(self):
res = run_test.session_obj.get(url=self.url,params=self.params,headers=self.headers)
return res
def send_post(self):
res = run_test.session_obj.post(url=self.url,params=self.params,
data=self.data,headers=self.headers)
return res
def run_main(self):
if self.method == "GET":
res = self.send_get()
elif self.method == "POST":
res = self.send_post()
else:
print("请求方式错误,请检查!")
res = None
return res
if __name__ == "__main__":
method = "GET"
url = "https://www.jd.com"
headers = {"User-Agent":"Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/90.0.4430.212 Safari/537.36"}
test_obj = run_test(method=method,url=url,headers=headers)
response = test_obj.run_main()
print(response.content.decode("utf-8"))
实战案例
光学理论是没用的,要学会跟着一起敲,要动手实操,才能将自己的所学运用到实际当中去,这时候可以搞点实战案例来学习。

如果对你有帮助的话,点个赞收个藏,给作者一个鼓励。也方便你下次能够快速查找。
如有不懂还要咨询下方小卡片,博主也希望和志同道合的测试人员一起学习进步
在适当的年龄,选择适当的岗位,尽量去发挥好自己的优势。
我的自动化测试开发之路,一路走来都离不每个阶段的计划,因为自己喜欢规划和总结,
测试开发视频教程、学习笔记领取传送门!!!

![[源码解析]socket系统调用上](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/7994bde0f3a44fbfb757391af88a2db0.png#pic_center)