YOLOv8架构
YOLOv8 是 ultralytics 公司在 2023 年 1月 10 号开源的 YOLOv5 的下一个重大更新版本,目前支持图像分类、物体检测和实例分割任务,鉴于Yolov5的良好表现,Yolov8在还没有开源时就收到了用户的广泛关注。yolov8的整体架构如下:
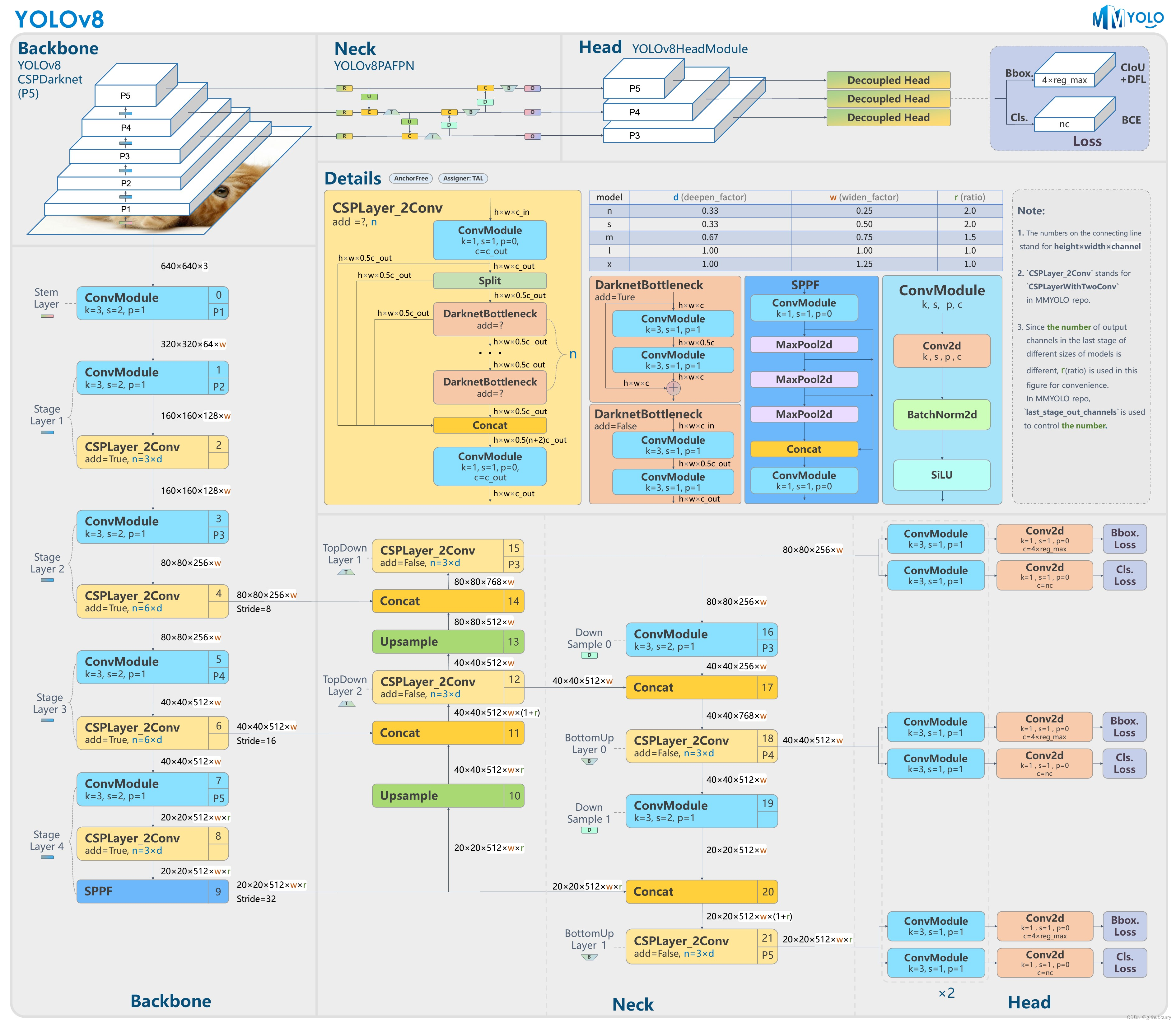
Yolov8的改进之处
- Backbone:使用的依旧是CSP(csp就是为了检测不同大小的目标,分别有大中小的特征提取)的思想,将YOLOv5中的C3模块被替换成了C2f模块,实现了进一步的轻量化,同时YOLOv8依旧使用了YOLOv5等架构中使用的SPPF模块。
- PAN-FPN:YOLOv8依旧使用了PAN的思想,不同的是YOLOv8将YOLOv5中PAN-FPN上采样阶段中的卷积结构删除了,同时也将C3模块替换为了C2f模块。
- Decoupled-Head:这一点源自YOLOX;分类和回归两个任务的head不再共享参数,YoloV8也借鉴了这样的head设计。
- Anchor-Free:YOLOv8抛弃了以往的Anchor-Base,使用了Anchor-Free的思想。
- 损失函数:YOLOv8使用VFL Loss作为分类损失,使用DFL Loss+CIOU Loss作为分类损失。
- 样本匹配:YOLOv8抛弃了以往的IOU匹配或者单边比例的分配方式,而是使用了Task-Aligned Assigner匹配方式。
yolov8是个模型簇,从小到大包括:yolov8n、yolov8s、yolov8m、yolov8l、yolov8x等。模型参数、运行速度、参数量等详见下表:
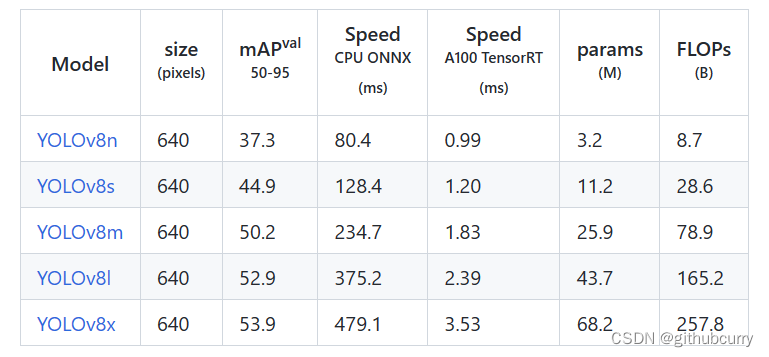
对比v5的效果,如下图:
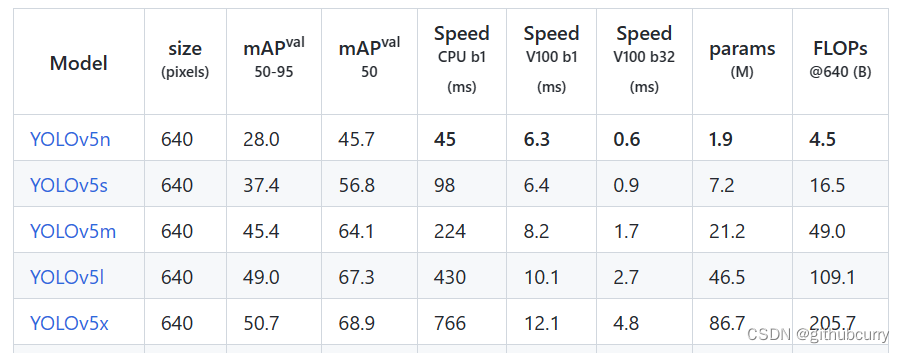
mAP和参数量都上升了不少,具体的感受还是要亲自实践一番。
这篇文章首先对YoloV8做详细的讲解,然后实现对COCO数据集的训练和测试,最后,实现自定义数据集的训练和测试。下图的结果均来自于yolov8的github。
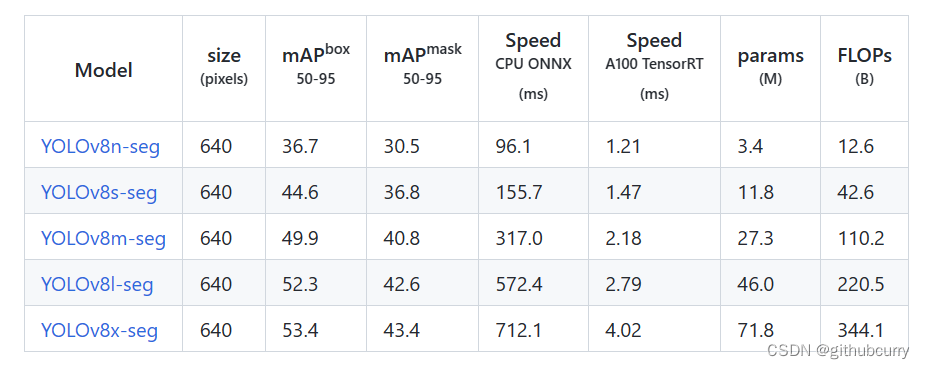
分割的结果(seg):
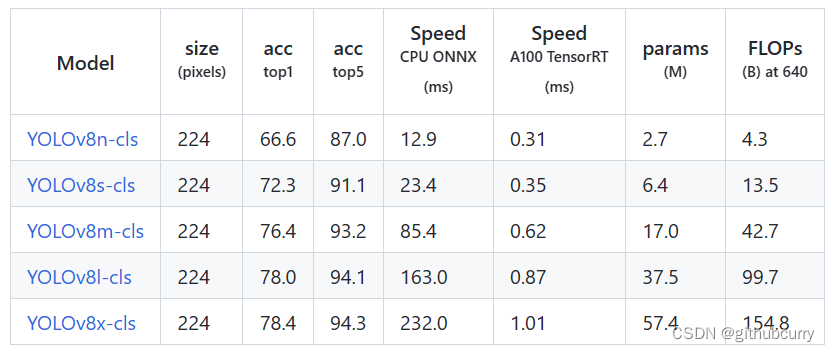
分类的结果(cla):
模型详解
C2F模块
yolov8将yolov5中的C3模块换成了C2F模型,我们先了解一下C3模块,如图:
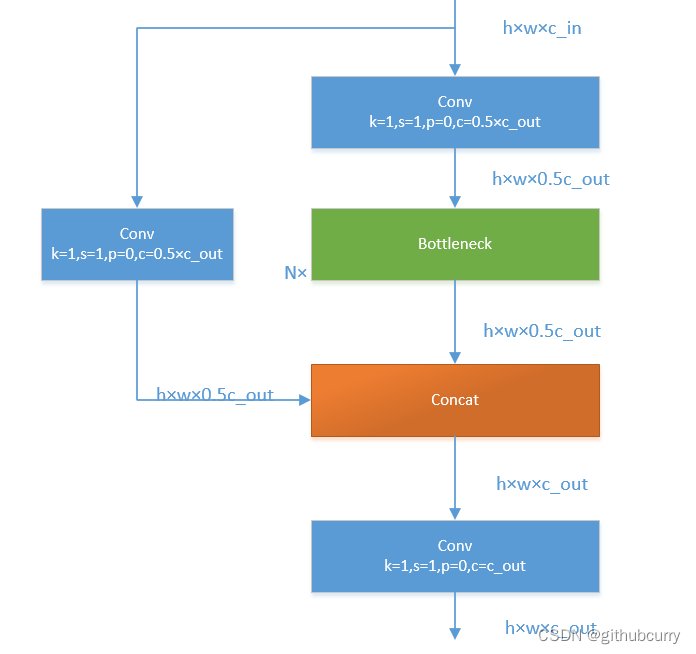
C3模块
C3模块主要是借助CSPNet提取分流的思想,同时结合残差结构的思想,设计了所谓的C3 Block,这里的CSP主分支梯度模块为BottleNeck模块,堆叠的个数由参数n来进行控制,不同的模型,n的个数也不相同。
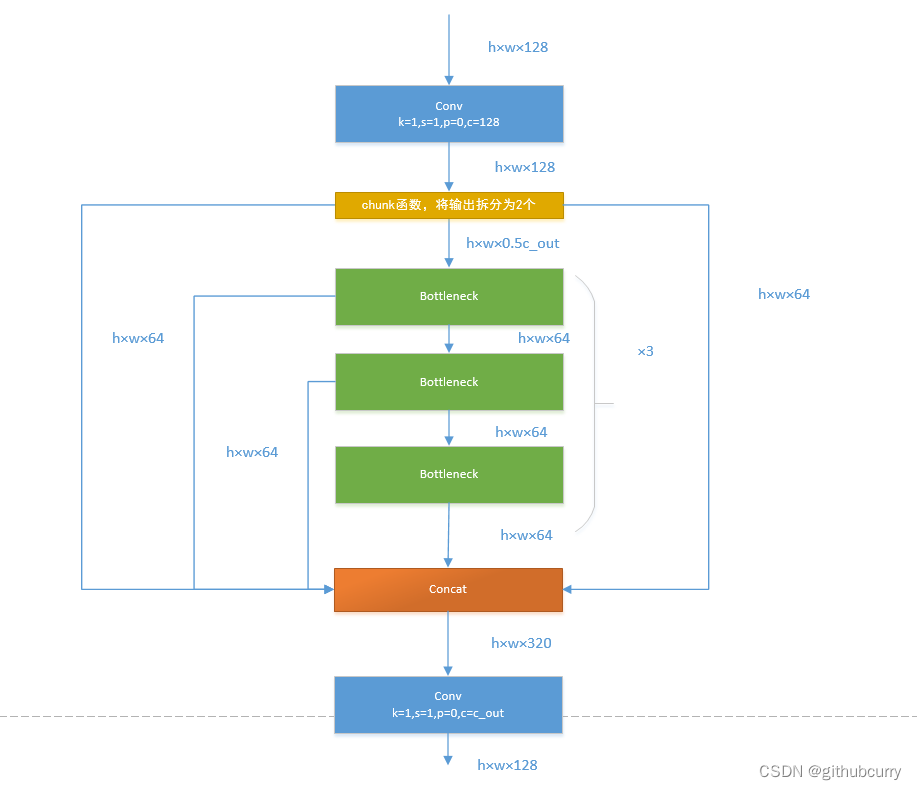
接下来,我们一起学习C2F模块,先经过一个Conv,然后使用chunk函数将out平均拆分成两个向量,然后保存到list中,将后半部分输入到Bottleneck Block里面,Bottleneck Block里面有n个Bottleneck,将每个Bottleneck的输出都追加list中,有n个,所以拼接之后的out等于0.5✖(n+2)。然后经过一个Conv输出,所以输出为h×w×c_out。如下图:
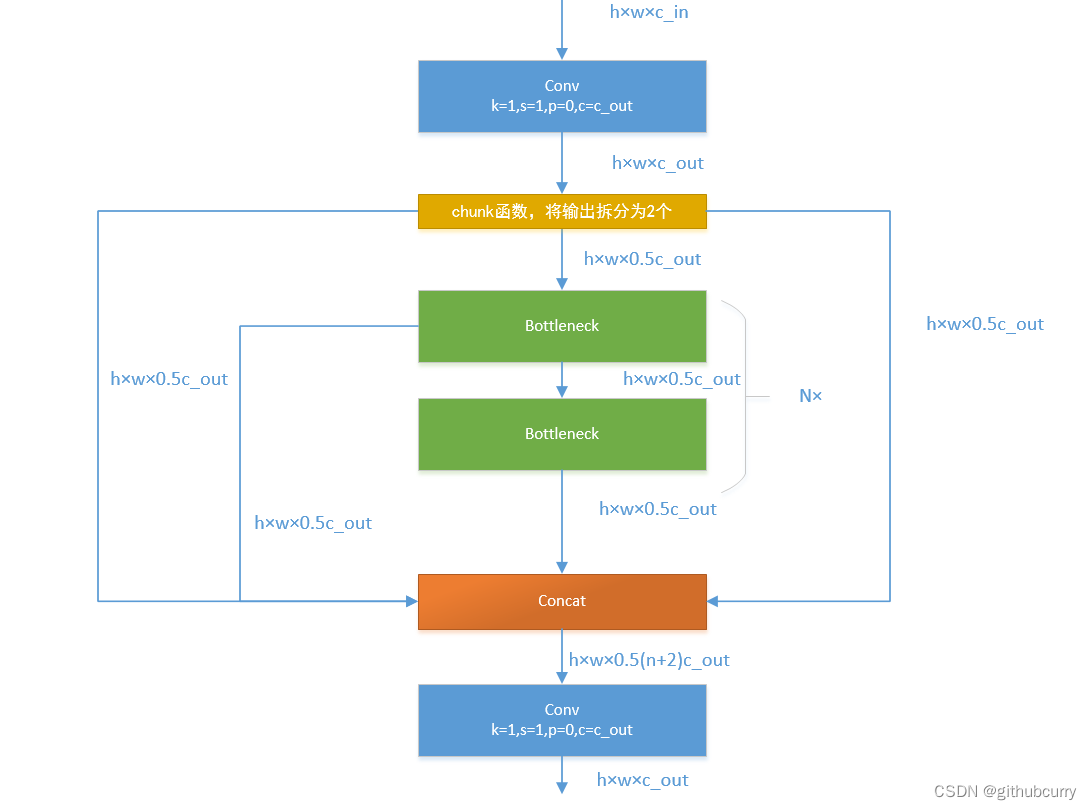
如果还是比较难懂,我将具体的数据代入图中,得出下图:
Loss
对于YOLOv8,其分类损失为VFL Loss,其回归损失为CIOU Loss+DFL的形式,这里Reg_max默认为16。
VFL主要改进是提出了非对称的加权操作,FL和QFL都是对称的。而非对称加权的思想来源于论文PISA,该论文指出首先正负样本有不平衡问题,即使在正样本中也存在不等权问题,因为mAP的计算是主正样本。
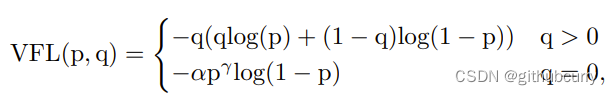
q是label,正样本时候q为bbox和gt的IoU,负样本时候q=0,当为正样本时候其实没有采用FL,而是普通的BCE,只不过多了一个自适应IoU加权,用于突出主样本。而为负样本时候就是标准的FL了。可以明显发现VFL比QFL更加简单,主要特点是正负样本非对称加权、突出正样本为主样本。
针对这里的DFL(Distribution Focal Loss),其主要是将框的位置建模成一个 general distribution,让网络快速的聚焦于和目标位置距离近的位置的分布。
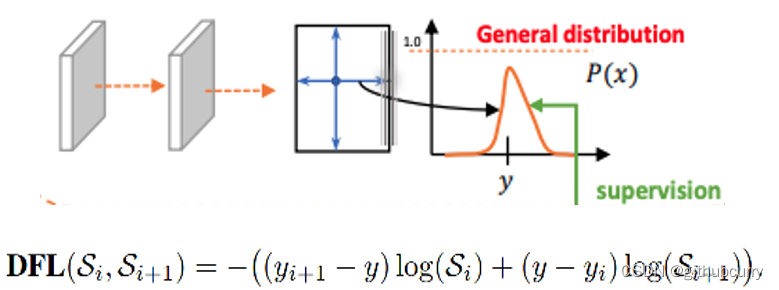
DFL 能够让网络更快地聚焦于目标 y 附近的值,增大它们的概率;
DFL的含义是以交叉熵的形式去优化与标签y最接近的一左一右2个位置的概率,从而让网络更快的聚焦到目标位置的邻近区域的分布;也就是说学出来的分布理论上是在真实浮点坐标的附近,并且以线性插值的模式得到距离左右整数坐标的权重。
head部分
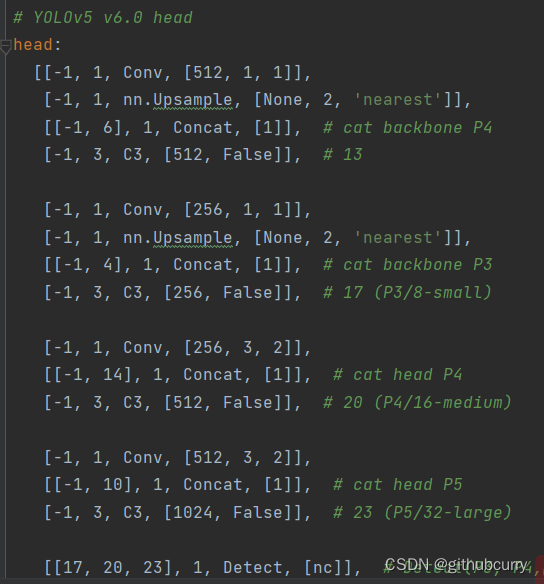
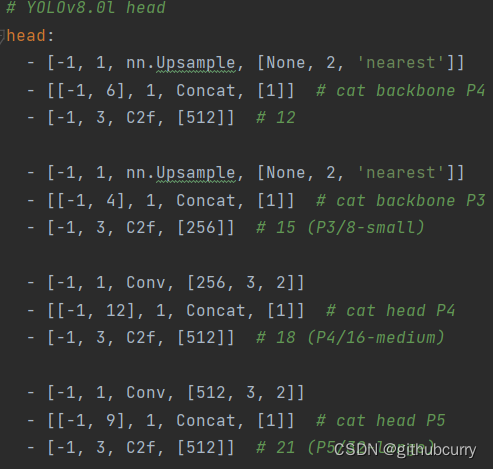
相对于YOLOv5,YOLOv8将Head里面C3模块替换为了C2f,将上采样之前的1×1卷积去除了,将Backbone不同阶段输出的特征直接送入了上采样操作。通过下图对比可以看出差别:
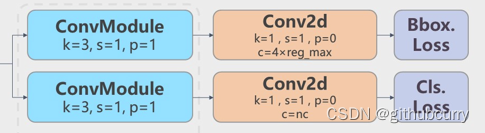
YOLOv8则是使用了Decoupled-Head,同时由于使用了DFL 的思想,因此回归头的通道数也变成了4*reg_max的形式:
模型实战
训练COCO数据集
本次使用2017版本的COCO数据集作为例子,演示如何使用YoloV8训练和预测。
下载数据集
Images:
- 2017 Train images [118K/18GB] :http://images.cocodataset.org/zips/train2017.zip
- 2017 Val images [5K/1GB]:http://images.cocodataset.org/zips/val2017.zip
- 2017 Test images [41K/6GB]:http://images.cocodataset.org/zips/unlabeled2017.zip
Annotations:
- 2017 annotations_trainval2017 [241MB]:http://images.cocodataset.org/annotations/annotations_trainval2017.zip
COCO转yolo格式数据集(适用V4,V5,V6,V7,V8)
最初的研究论文中,COCO中有91个对象类别。然而,在2014年的第一次发布中,仅发布了80个标记和分割图像的对象类别。2014年发布之后,2017年发布了后续版本。部分类别如下:
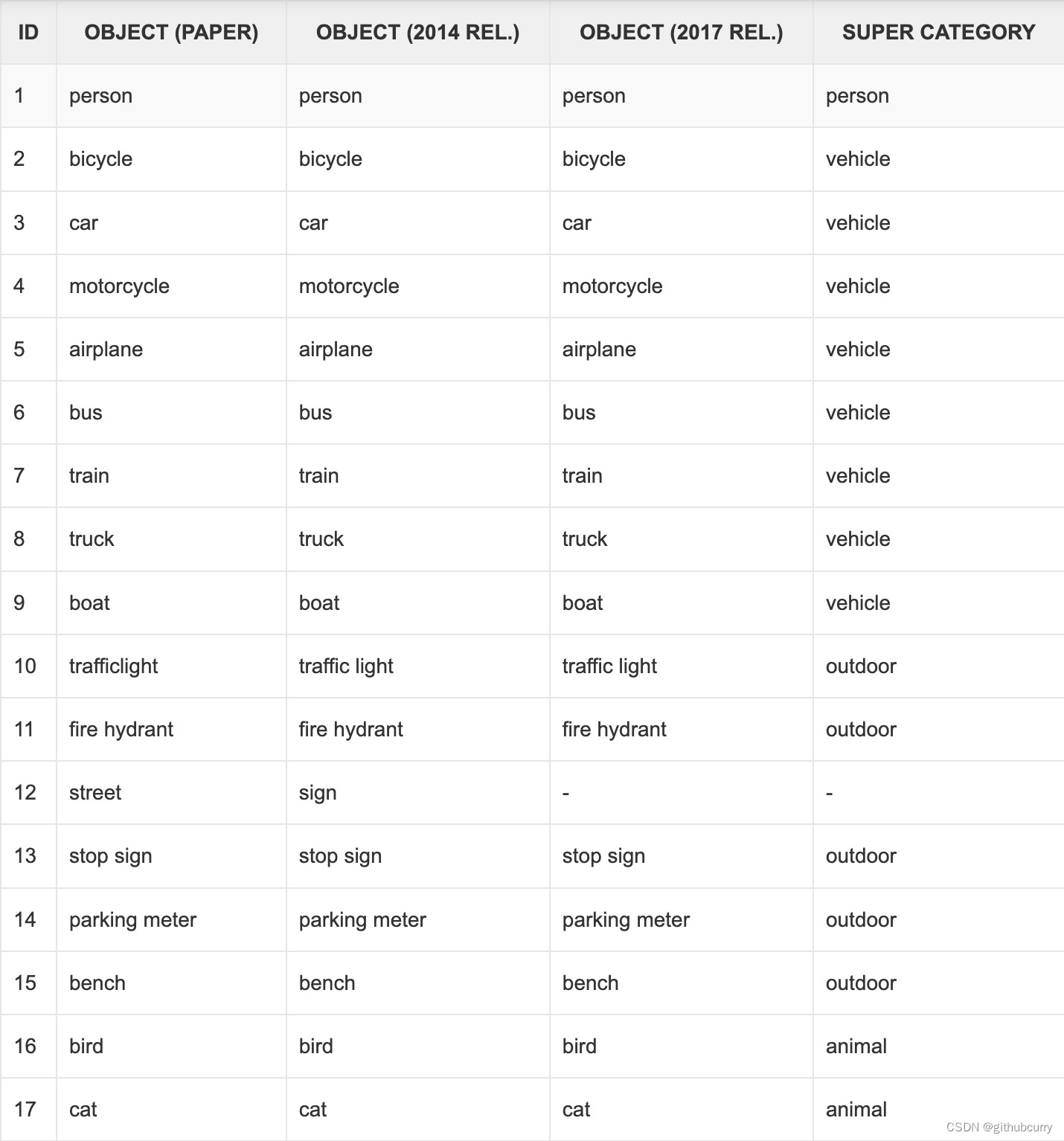
可以看到,2014年和2017年发布的对象列表是相同的,它们是论文中最初91个对象类别中的80个对象。所以在转换的时候,要重新对类别做映射,映射函数如下:
def coco91_to_coco80_class(): # converts 80-index (val2014) to 91-index (paper)# https://tech.amikelive.com/node-718/what-object-categories-labels-are-in-coco-dataset/#
a = np.loadtxt('data/coco.names', dtype='str', delimiter='\n')
b = np.loadtxt('data/coco_paper.names', dtype='str', delimiter='\n')
x1 = [list(a[i] == b).index(True) + 1 for i in range(80)]
x2 = [list(b[i] == a).index(True) if any(b[i] == a) else None for i in range(91)]
coco to darknetx = [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, None, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, None, 24, 25, None,None, 26, 27, 28, 29, 30, 31, 32, 33, 34, 35, 36, 37, 38, 39, None, 40, 41, 42, 43, 44, 45, 46, 47, 48, 49, 50,51, 52, 53, 54, 55, 56, 57, 58, 59, None, 60, None, None, 61, None, 62, 63, 64, 65, 66, 67, 68, 69, 70, 71, 72,None, 73, 74, 75, 76, 77, 78, 79, None]
return x
接下来,开始格式转换,工程的目录如下:
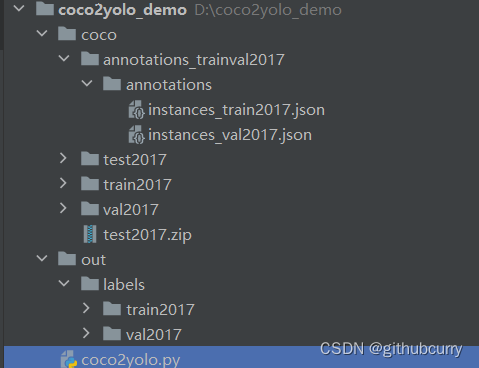
- coco:存放解压后的数据集。
- -out:保存输出结果。
- -coco2yolo.py:转换脚本。
转换代码如下:
import json
import glob
import os
import shutil
from pathlib import Path
import numpy as np
from tqdm import tqdmdef make_folders(path='../out/'):# Create foldersif os.path.exists(path):shutil.rmtree(path) # delete output folderos.makedirs(path) # make new output folderos.makedirs(path + os.sep + 'labels') # make new labels folderos.makedirs(path + os.sep + 'images') # make new labels folderreturn pathdef convert_coco_json(json_dir='./coco/annotations_trainval2017/annotations/'):jsons = glob.glob(json_dir + '*.json')coco80 = coco91_to_coco80_class()# Import jsonfor json_file in sorted(jsons):fn = 'out/labels/%s/' % Path(json_file).stem.replace('instances_', '') # folder namefn_images = 'out/images/%s/' % Path(json_file).stem.replace('instances_', '') # folder nameos.makedirs(fn,exist_ok=True)os.makedirs(fn_images,exist_ok=True)with open(json_file) as f:data = json.load(f)print(fn)# Create image dictimages = {'%g' % x['id']: x for x in data['images']}# Write labels filefor x in tqdm(data['annotations'], desc='Annotations %s' % json_file):if x['iscrowd']:continueimg = images['%g' % x['image_id']]h, w, f = img['height'], img['width'], img['file_name']file_path='coco/'+fn.split('/')[-2]+"/"+f# The Labelbox bounding box format is [top left x, top left y, width, height]box = np.array(x['bbox'], dtype=np.float64)box[:2] += box[2:] / 2 # xy top-left corner to centerbox[[0, 2]] /= w # normalize xbox[[1, 3]] /= h # normalize yif (box[2] > 0.) and (box[3] > 0.): # if w > 0 and h > 0with open(fn + Path(f).stem + '.txt', 'a') as file:file.write('%g %.6f %.6f %.6f %.6f\n' % (coco80[x['category_id'] - 1], *box))file_path_t=fn_images+fprint(file_path,file_path_t)shutil.copy(file_path,file_path_t)def coco91_to_coco80_class(): # converts 80-index (val2014) to 91-index (paper)# https://tech.amikelive.com/node-718/what-object-categories-labels-are-in-coco-dataset/# a = np.loadtxt('data/coco.names', dtype='str', delimiter='\n')# b = np.loadtxt('data/coco_paper.names', dtype='str', delimiter='\n')# x1 = [list(a[i] == b).index(True) + 1 for i in range(80)] # darknet to coco# x2 = [list(b[i] == a).index(True) if any(b[i] == a) else None for i in range(91)] # coco to darknetx = [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, None, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, None, 24, 25, None,None, 26, 27, 28, 29, 30, 31, 32, 33, 34, 35, 36, 37, 38, 39, None, 40, 41, 42, 43, 44, 45, 46, 47, 48, 49, 50,51, 52, 53, 54, 55, 56, 57, 58, 59, None, 60, None, None, 61, None, 62, 63, 64, 65, 66, 67, 68, 69, 70, 71, 72,None, 73, 74, 75, 76, 77, 78, 79, None]return xconvert_coco_json()
开始运行:
转换完成后,验证转换的结果:
import cv2
import osdef draw_box_in_single_image(image_path, txt_path):# 读取图像image = cv2.imread(image_path)# 读取txt文件信息def read_list(txt_path):pos = []with open(txt_path, 'r') as file_to_read:while True:lines = file_to_read.readline() # 整行读取数据if not lines:break# 将整行数据分割处理,如果分割符是空格,括号里就不用传入参数,如果是逗号, 则传入‘,'字符。p_tmp = [float(i) for i in lines.split(' ')]pos.append(p_tmp) # 添加新读取的数据# Efield.append(E_tmp)passreturn pos# txt转换为boxdef convert(size, box):xmin = (box[1]-box[3]/2.)*size[1]xmax = (box[1]+box[3]/2.)*size[1]ymin = (box[2]-box[4]/2.)*size[0]ymax = (box[2]+box[4]/2.)*size[0]box = (int(xmin), int(ymin), int(xmax), int(ymax))return boxpos = read_list(txt_path)print(pos)tl = int((image.shape[0]+image.shape[1])/2)lf = max(tl-1,1)for i in range(len(pos)):label = str(int(pos[i][0]))print('label is '+label)box = convert(image.shape, pos[i])image = cv2.rectangle(image,(box[0], box[1]),(box[2],box[3]),(0,0,255),2)cv2.putText(image,label,(box[0],box[1]-2), 0, 1, [0,0,255], thickness=2, lineType=cv2.LINE_AA)passif pos:cv2.imwrite('./Data/see_images/{}.png'.format(image_path.split('\\')[-1][:-4]), image)else:print('None')img_folder = "./out/images/val2017"
img_list = os.listdir(img_folder)
img_list.sort()label_folder = "./out/labels/val2017"
label_list = os.listdir(label_folder)
label_list.sort()
if not os.path.exists('./Data/see_images'):os.makedirs('./Data/see_images')
for i in range(len(img_list)):image_path = img_folder + "\\" + img_list[i]txt_path = label_folder + "\\" + label_list[i]draw_box_in_single_image(image_path, txt_path)
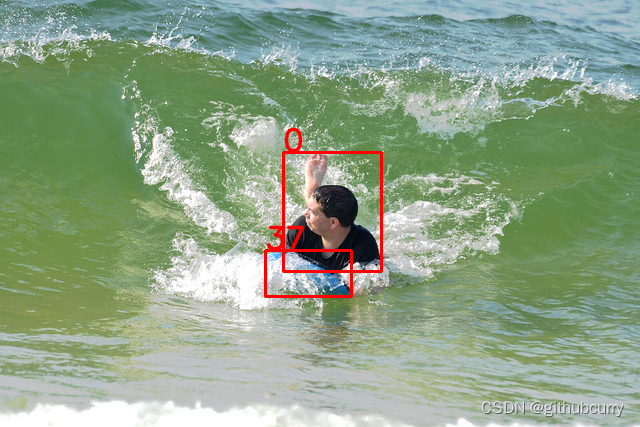
结果展示:

配置yolov8依赖的环境
训练
下载代码:https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics,通过下载的方式可以下载到源码,这样方便修改。
也可以使用命令:
pip install ultralytics
如果仅仅是为了使用yolov8,yolov8还支持使用命令的方式,可以使用这种方式安装。
yolo predict model=yolov8n.pt source="https://ultralytics.com/images/bus.jpg"
接下来,创建训练脚本,可以使用yaml文件创建,例如:
from ultralytics import YOLO# Load a model
model = YOLO("yolov8n.yaml") # build a new model from scratch
模型文件在ultralytics/models/v8下面,如图:
也可以使用预训练模型创建(预训练模型就是官方训练好的模型参数,我们可以直接使用官方给出的.pt文件进行我们的工作)。例如:
model = YOLO("yolov8n.pt") # load a pretrained model (recommended for training)
然后开启训练。
# Use the model
model.train(data="coco128.yaml", epochs=3) # train the model
数据集的配置文件在:ultralytics/datasets/下面,如图:
接下来,我们配置自己的环境。
第一步 找到ultralytics/datasets/coco.yaml文件。
然后将其复制到根目录
将里面的路径修改为:
# Ultralytics YOLO 🚀, GPL-3.0 license
# COCO 2017 dataset http://cocodataset.org by Microsoft
# Example usage: yolo train data=coco.yaml
# parent
# ├── ultralytics
# └── datasets
# └── coco ← downloads here (20.1 GB)# Train/val/test sets as 1) dir: path/to/imgs, 2) file: path/to/imgs.txt, or 3) list: [path/to/imgs1, path/to/imgs2, ..]train: ./coco/images/train2017 # train images (relative to 'path') 118287 images
val: ./coco/images/val2017 # val images (relative to 'path') 5000 images
test: test-dev2017.txt # 20288 of 40670 images, submit to https://competitions.codalab.org/competitions/20794
关于数据集的路径,大家可以自行尝试,我经过多次尝试发现,YoloV8会自行添加datasets这个文件,所以设置./coco/images/train2017,则实际路径是datasets/coco/images/train2017
第二步 新建train.py脚本。
from ultralytics import YOLO# 加载模型
model = YOLO("ultralytics/models/v8/yolov8n.yaml") # 从头开始构建新模型# Use the model
results = model.train(data="coco.yaml", epochs=3,device='3') # 训练模型
然后,点击train.py可以运行了。
如果设置多卡,可以在device中设置,例如我使用四张卡,可以设置为:
results = model.train(data="coco.yaml", epochs=3,device='0,1,2,3') # 训练模型
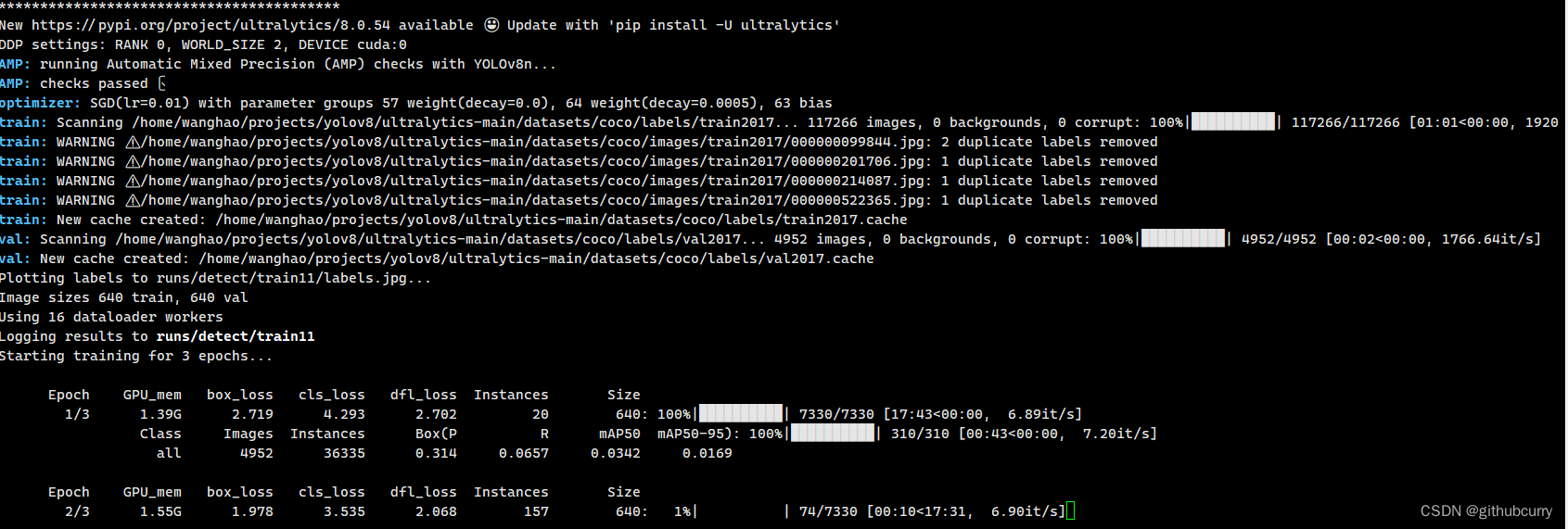
第三步 修改参数,在ultralytics/yolo/cfg/default.yaml文件中查看。例如:
# Train settings ------------------------------------------------------------
model: # path to model file, i.e. yolov8n.pt, yolov8n.yaml
data: # path to data file, i.e. coco128.yaml
epochs: 100 # number of epochs to train for
patience: 50 # epochs to wait for no observable improvement for early stopping of training
batch: 16 # number of images per batch (-1 for AutoBatch)
imgsz: 640 # size of input images as integer or w,h
save: True # save train checkpoints and predict results
save_period: -1 # Save checkpoint every x epochs (disabled if < 1)
cache: False # True/ram, disk or False. Use cache for data loading
device: # device to run on, i.e. cuda device=0 or device=0,1,2,3 or device=cpu
workers: 8 # number of worker threads for data loading (per RANK if DDP)
project: # project name
name: # experiment name, results saved to 'project/name' directory
exist_ok: False # whether to overwrite existing experiment
pretrained: False # whether to use a pretrained model
optimizer: SGD # optimizer to use, choices=['SGD', 'Adam', 'AdamW', 'RMSProp']
verbose: True # whether to print verbose output
seed: 0 # random seed for reproducibility
deterministic: True # whether to enable deterministic mode
single_cls: False # train multi-class data as single-class
image_weights: False # use weighted image selection for training
rect: False # support rectangular training if mode='train', support rectangular evaluation if mode='val'
cos_lr: False # use cosine learning rate scheduler
close_mosaic: 10 # disable mosaic augmentation for final 10 epochs
resume: False # resume training from last checkpoint
上面是训练过程中常用的参数,我们调用yolo函数可以自行修改。
等待测试完成后,就可以看到结果,如下图:
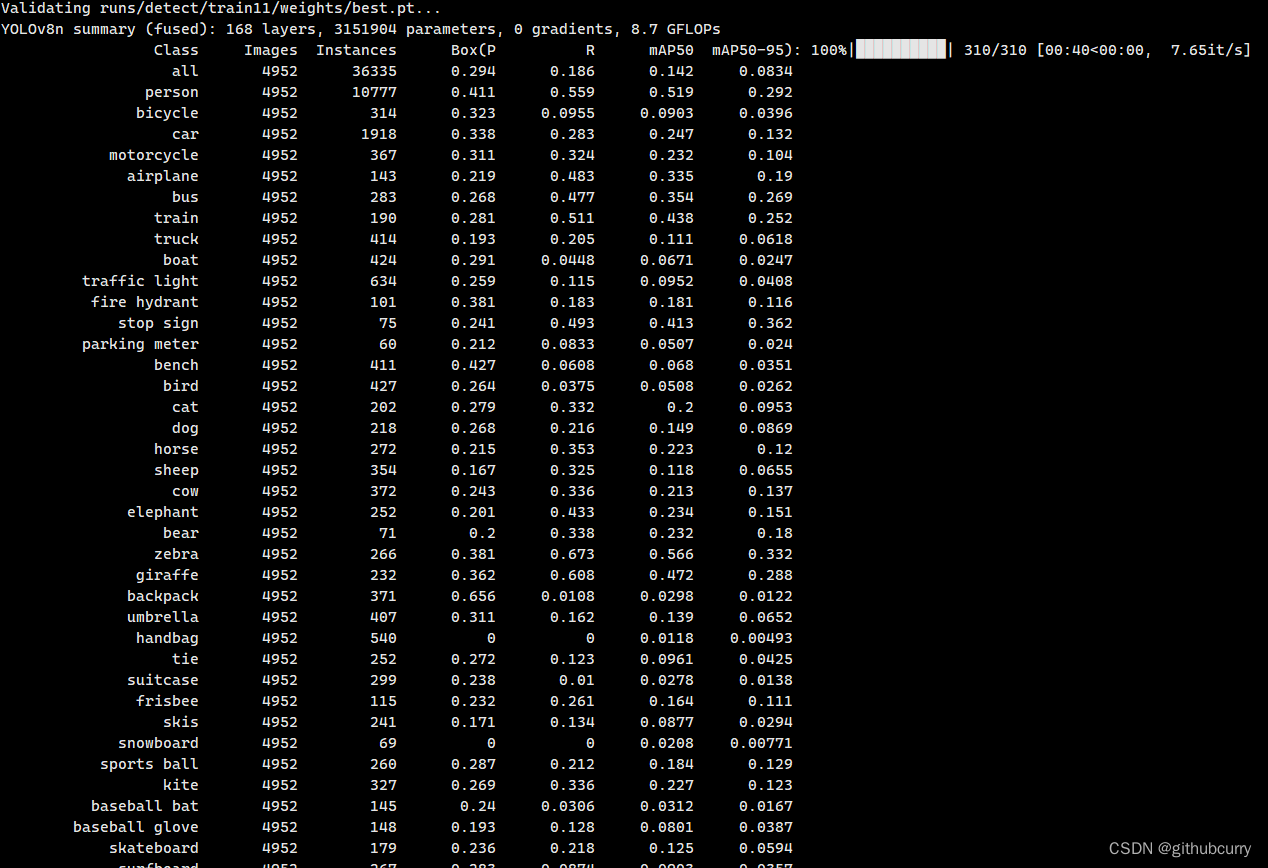
测试
新建测试脚本test.py.
from ultralytics import YOLO# Load a model
model = YOLO("runs/detect/train11/weights/best.pt") # load a pretrained model (recommended for training)results = model.predict(source="ultralytics/assets",device='3') # predict on an image
print(results)
这个results保存了所有的结果。如下图:

predict的参数也可以在ultralytics/yolo/cfg/default.yaml文件中查看。例如:
# Prediction settings ----------------------------------------------------------
source: # source directory for images or videos
show: False # show results if possible
save_txt: False # save results as .txt file
save_conf: False # save results with confidence scores
save_crop: False # save cropped images with results
hide_labels: False # hide labels
hide_conf: False # hide confidence scores
vid_stride: 1 # video frame-rate stride
line_thickness: 3 # bounding box thickness (pixels)
visualize: False # visualize model features
augment: False # apply image augmentation to prediction sources
agnostic_nms: False # class-agnostic NMS
classes: # filter results by class, i.e. class=0, or class=[0,2,3]
retina_masks: False # use high-resolution segmentation masks
boxes: True # Show boxes in segmentation predictions
训练自定义(自己的数据集)数据集,使用Labelme制作数据集
2014-2017转换COCO数据集链接