Python遥感开发之FY的批量处理
- 0 FY遥感数据
- 1 批量提取数据
- 2 批量拼接TIF数据
- 3 批量HAM转WGS投影(重要)
- 4 批量掩膜裁剪
介绍FY数据的格式,以及FY数据的批量提取数据、批量拼接数据、批量投影转换、批量掩膜裁剪等操作。
本博客代码参考《 Hammer坐标系转换到WGS1984,以处理FY3D/MERSI NVI数据为例。FY3D/MERSI NVI空间分辨率250m,全球 10°×10°分幅 》,非常感谢博主公开代码!!!
0 FY遥感数据
- 本博客以《MERSI-II植被指数旬产品(1000M)》数据处理为例子,“FY3D_MERSI_00A0_L3_NVI_MLT_HAM_20191130_AOTD_1000M_MS.HDF”,其中FY3D是卫星名字、MERSI是仪器名称、00A0是数据区域类型(也是该影像的经纬度范围)、L3是数据级别、NVI是数据名称、MLT是通道名称、HAM是投影方式、AOTD是时段类型、1000M是分辨率、HDF是数据名称格式。
- 最核心最难的就是HAM投影如何转换成常见的WGS投影
1 批量提取数据
MERSI-II植被指数旬产品(1000M)数据包含如下波段,根据需要自己取

切记

完整代码如下所示:
import os
from osgeo import gdal
import h5py
def get_data_list(file_path, out = ""):
list1 = [] # 文件的完整路径
if os.path.isdir(file_path):
fileList = os.listdir(file_path)
if out != "":
for f in fileList:
out_data = out + "\\" + f
out_data = out_data.replace(".HDF", "_ndvi.tif")
list1.append(out_data)
else:
for f in fileList:
pre_data = file_path + '\\' + f # 文件的完整路径
list1.append(pre_data)
return list1
import numpy as np
def HDF2Tif(in_file,out_file):
hdf_ds = h5py.File(in_file, "r")
if type(hdf_ds.attrs['Left-Top X']) is np.ndarray:
left_x = hdf_ds.attrs['Left-Top X'][0]
else:
left_x = float(hdf_ds.attrs['Left-Top X'])
if type(hdf_ds.attrs['Left-Top Y']) is np.ndarray:
left_y = hdf_ds.attrs['Left-Top Y'][0]
else:
left_y = float(hdf_ds.attrs['Left-Top Y'])
res_x = hdf_ds.attrs['Resolution X'][0]
res_y = hdf_ds.attrs['Resolution Y'][0]
ndviname = list(hdf_ds.keys())[6] #5是evi 6是ndvi
# print(list(hdf_ds.keys()))
ndvi_ds = hdf_ds[ndviname]
rows = ndvi_ds.shape[0]
cols = ndvi_ds.shape[1]
data = ndvi_ds[()]
driver = gdal.GetDriverByName("GTiff")
outds = driver.Create(out_file, cols, rows, 1, gdal.GDT_Int16)
outds.SetGeoTransform(
(float(left_x) * 1000,#切记250m的分辨率需要除以4
float(res_x) * 1000,
0,
float(left_y) * 1000,#切记250m的分辨率需要除以4
0,
-1 * float(res_y) * 1000)
)
proj = 'PROJCS["World_Hammer",GEOGCS["Unknown datum based upon the custom spheroid",DATUM["Not_specified_based_on_custom_spheroid",SPHEROID["Custom spheroid",6363961,0]],PRIMEM["Greenwich",0],UNIT["Degree",0.0174532925199433]],PROJECTION["Hammer_Aitoff"],PARAMETER["False_Easting",0],PARAMETER["False_Northing",0],PARAMETER["Central_Meridian",0],UNIT["metre",1],AXIS["Easting",EAST],AXIS["Northing",NORTH]]'
outds.SetProjection(proj)
outband = outds.GetRasterBand(1)
outband.WriteArray(data)
pass
if __name__ == '__main__':
infile = r"C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\HDF"
outfile = r"C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\01提取ndvi"
infile_list = get_data_list(infile)
outfile_list = get_data_list(infile,outfile)
for in_file,out_file in zip(infile_list,outfile_list):
print(in_file)
HDF2Tif(in_file,out_file)
2 批量拼接TIF数据
import os
from osgeo import gdal
def get_data_list(file_path, out = ""):
list1 = [] # 文件的完整路径
if os.path.isdir(file_path):
fileList = os.listdir(file_path)
if out != "":
for f in fileList:
out_data = out + "\\" + f
out_data = out_data.replace(".HDF", "_ndvi.tif")
list1.append(out_data)
else:
for f in fileList:
pre_data = file_path + '\\' + f # 文件的完整路径
list1.append(pre_data)
return list1
def get_same_list(image, infile_list):
infile_list02 = []
for data in infile_list:
if image in data:
# print("----", data)
infile_list02.append(data)
return infile_list02
def get_same_image_list(infile_list):
image_list= []
for file in infile_list:
filename = file[-31:-23]
if filename not in image_list:
image_list.append(filename)
return list(set(image_list))
def pinjie(infile_list,outfile):
ds = gdal.Open(infile_list[0])
cols = ds.RasterXSize
rows = ds.RasterYSize
ingeo = ds.GetGeoTransform()
proj = ds.GetProjection()
minx = ingeo[0]
maxy = ingeo[3]
maxx = ingeo[0] + ingeo[1] * cols
miny = ingeo[3] + ingeo[5] * rows
ds = None
for file in infile_list[1:]:
ds = gdal.Open(file)
cols = ds.RasterXSize
rows = ds.RasterYSize
geo = ds.GetGeoTransform()
minx_ = geo[0]
maxy_ = geo[3]
maxx_ = geo[0] + geo[1] * cols
miny_ = geo[3] + geo[5] * rows
minx = min(minx, minx_)
maxy = max(maxy, maxy_)
maxx = max(maxx, maxx_)
miny = min(miny, miny_)
geo = None
ds = None
newcols = int((maxx - minx) / abs(ingeo[1]))
newrows = int((maxy - miny) / abs(ingeo[5]))
driver = gdal.GetDriverByName("GTiff")
outds = driver.Create(outfile, newcols, newrows, 1, gdal.GDT_Int16)
outgeo = (minx, ingeo[1], 0, maxy, 0, ingeo[5])
outds.SetGeoTransform(outgeo)
outds.SetProjection(proj)
outband = outds.GetRasterBand(1)
for file in infile_list:
ds = gdal.Open(file)
data = ds.ReadAsArray()
geo = ds.GetGeoTransform()
x = int(abs((geo[0] - minx) / ingeo[1]))
y = int(abs((geo[3] - maxy) / ingeo[5]))
outband.WriteArray(data, x, y)
ds = None
outband.FlushCache()
pass
if __name__ == '__main__':
infile = r"C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\01提取ndvi"
outfile = r"C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\02拼接"
infile_list = get_data_list(infile)
image_name_list = get_same_image_list(infile_list)
print(image_name_list)
for name in image_name_list:
print(name)
infile_list02 = get_same_list(name, infile_list)
pinjie(infile_list02,outfile+"\\"+name+".tif")

3 批量HAM转WGS投影(重要)
切记:代码中出现的0.01表示1000m分辨率,如果需要换成250m分辨率,请根据代码注释自行更换。

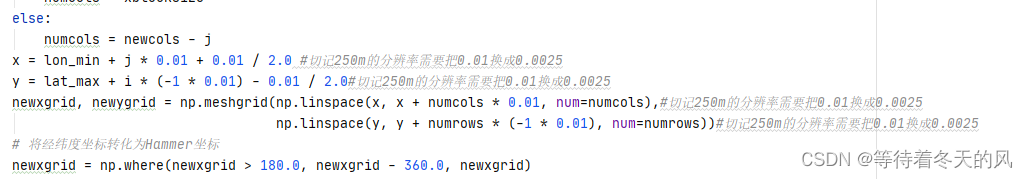
完整代码如下:
import os
from osgeo import gdal
import numpy as np
import math
from osgeo import osr
def get_data_list(file_path, out = ""):
list1 = [] # 文件的完整路径
if os.path.isdir(file_path):
fileList = os.listdir(file_path)
if out != "":
for f in fileList:
out_data = out + "\\" + f
# out_data = out_data.replace(".HDF", "_ndvi.tif")
list1.append(out_data)
else:
for f in fileList:
pre_data = file_path + '\\' + f # 文件的完整路径
list1.append(pre_data)
return list1
def H2W(infile,outfile):
ds = gdal.Open(infile)
ingeo = ds.GetGeoTransform()
cols = ds.RasterXSize
rows = ds.RasterYSize
or_x = ingeo[0]
or_y = ingeo[3]
end_x = ingeo[0] + cols * ingeo[1]
end_y = ingeo[3] + rows * ingeo[5]
# X方向分块
xblocksize = int((cols + 1) / 5)
# Y方向分块
yblocksize = int((rows + 1) / 5)
lon_max = -360
lon_min = 360
lat_max = -90
lat_min = 90
for i in range(0, rows + 1, yblocksize):
if i + yblocksize < rows + 1:
numrows = yblocksize
else:
numrows = rows + 1 - i
for j in range(0, cols + 1, xblocksize):
if j + xblocksize < cols + 1:
numcols = xblocksize
else:
numcols = cols + 1 - j
# 计算所有点的Hammer坐标系下X方向坐标数组
x = ingeo[0] + j * ingeo[1]
y = ingeo[3] + i * ingeo[5]
xgrid, ygrid = np.meshgrid(np.linspace(x, x + numcols * ingeo[1], num=numcols),
np.linspace(y, y + numrows * ingeo[5], num=numrows))
# 将hammer坐标转化为经纬度坐标
# 首先将Hammer转化为-1到1
xgrid = np.where(xgrid > (18000.0 * 1000.0), (18000.0 * 1000.0) - xgrid, xgrid)
xgrid = xgrid / (18000.0 * 1000.0)
ygrid = np.where(ygrid > (9000.0 * 1000.0), (9000.0 * 1000.0) - ygrid, ygrid)
ygrid = ygrid / (9000.0 * 1000.0)
z = np.sqrt(1 - np.square(xgrid) / 2.0 - np.square(ygrid) / 2.0)
lon = 2 * np.arctan(np.sqrt(2) * xgrid * z / (2.0 * (np.square(z)) - 1))
xgrid = None
lat = np.arcsin(np.sqrt(2) * ygrid * z)
ygrid = None
z = None
lon = lon / math.pi * 180.0
lat = lat / math.pi * 180.0
lon[lon < 0] = lon[lon < 0] + 360.0
# lat[lat<0]=lat[lat<0]+180
lon_max = max(lon_max, np.max(lon))
lon_min = min(lon_min, np.min(lon))
lon = None
lat_max = max(lat_max, np.max(lat))
lat_min = min(lat_min, np.min(lat))
lat = None
newcols = math.ceil((lon_max - lon_min) / 0.01)#切记250m的分辨率需要把0.01换成0.0025
newrows = math.ceil((lat_max - lat_min) / 0.01)#切记250m的分辨率需要把0.01换成0.0025
driver = gdal.GetDriverByName("GTiff")
outds = driver.Create(outfile, newcols, newrows, 1, gdal.GDT_Int16)
geo2 = (lon_min, 0.01, 0, lat_max, 0, -1 * 0.01)#切记250m的分辨率需要把0.01换成0.0025
oproj_srs = osr.SpatialReference()
proj_4 = "+proj=longlat +datum=WGS84 +no_defs"
oproj_srs.ImportFromProj4(proj_4)
outds.SetGeoTransform(geo2)
outds.SetProjection(oproj_srs.ExportToWkt())
outband = outds.GetRasterBand(1)
datav = ds.ReadAsArray()
data = np.full((datav.shape[0] + 1, datav.shape[1] + 1), -32750, dtype=int)
data[0:datav.shape[0], 0:datav.shape[1]] = datav
xblocksize = int(newcols / 5)
yblocksize = int(newrows / 5)
for i in range(0, newrows, yblocksize):
if i + yblocksize < newrows:
numrows = yblocksize
else:
numrows = newrows - i
for j in range(0, newcols, xblocksize):
if j + xblocksize < newcols:
numcols = xblocksize
else:
numcols = newcols - j
x = lon_min + j * 0.01 + 0.01 / 2.0 #切记250m的分辨率需要把0.01换成0.0025
y = lat_max + i * (-1 * 0.01) - 0.01 / 2.0#切记250m的分辨率需要把0.01换成0.0025
newxgrid, newygrid = np.meshgrid(np.linspace(x, x + numcols * 0.01, num=numcols),#切记250m的分辨率需要把0.01换成0.0025
np.linspace(y, y + numrows * (-1 * 0.01), num=numrows))#切记250m的分辨率需要把0.01换成0.0025
# 将经纬度坐标转化为Hammer坐标
newxgrid = np.where(newxgrid > 180.0, newxgrid - 360.0, newxgrid)
newxgrid = newxgrid / 180.0 * math.pi
newygrid = newygrid / 180.0 * math.pi
newz = np.sqrt(1 + np.cos(newygrid) * np.cos(newxgrid / 2.0))
x = np.cos(newygrid) * np.sin(newxgrid / 2.0) / newz
newxgrid = None
y = np.sin(newygrid) / newz
newygrid = None
newz = None
x = x * (18000.0 * 1000.0)
y = y * (9000.0 * 1000.0)
x_index = (np.floor((x - or_x) / ingeo[1])).astype(int)
x_index = np.where(x_index < 0, data.shape[1] - 1, x_index)
x_index = np.where(x_index >= data.shape[1], data.shape[1] - 1, x_index)
y_index = (np.floor((y - or_y) / ingeo[5])).astype(int)
y_index = np.where(y_index < 0, data.shape[0] - 1, y_index)
y_index = np.where(y_index >= data.shape[0], data.shape[0] - 1, y_index)
newdata = data[y_index, x_index]
outband.WriteArray(newdata, j, i)
outband.SetNoDataValue(-32750)
outband.FlushCache()
if __name__ == '__main__':
infile_path = r"C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\02拼接"
outfile_path = r"C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\03WGS"
infile_list = get_data_list(infile_path)
outfile_list = get_data_list(infile_path,outfile_path)
for infile,outfile in zip(infile_list,outfile_list):
print(infile)
H2W(infile,outfile)
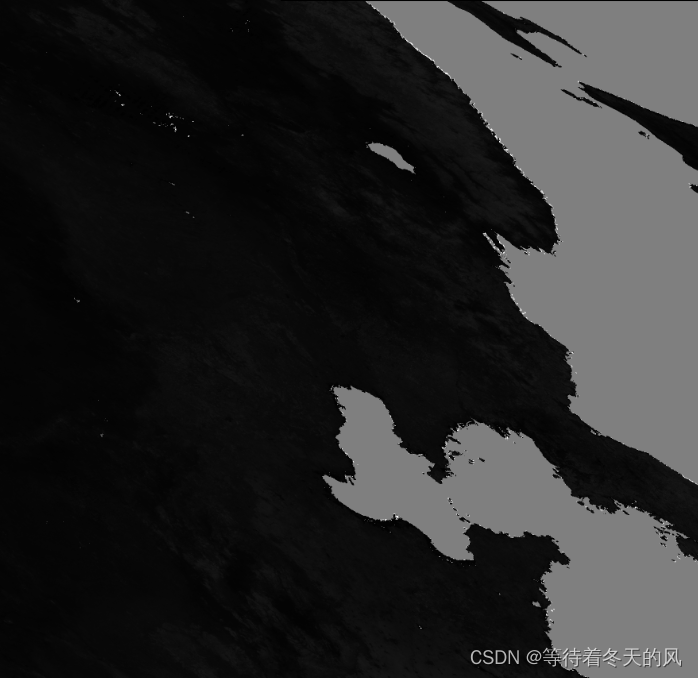

4 批量掩膜裁剪
请参考本人博客《Python遥感开发之批量掩膜和裁剪》