目录
网络编程阶段项目
项目目标
Web服务器开发准备
Html语言基础
Html简介
Html标签介绍
题目标签
文本标签
列表标签
图片标签
超链接标签
http请求消息
请求类型
http响应消息
http常见状态码
http常见文件类型分类
web服务器开发
基于epoll的web服务器
网页服务器总结:
BS模式示意图
web服务器开发流程
汉字乱码问题
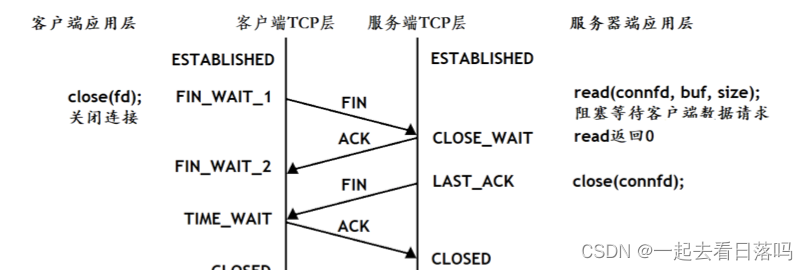
浏览器和web服务器通信模式
完整代码
网络编程阶段项目
项目目标
实现一个web服务器
可以在浏览器页面请求资源页面
Web服务器开发准备
为了编写web服务器,我们需要学会编写html页面,以及掌握部分http协议知识,这两部分内容将在接下来进行介绍。这两个准备工作之后,还需要知道web服务器的通信流程是什么?还需要思考如何支持多浏览器并发访问!
Html语言基础
Html简介
Html(Hyper Texture Markup Language)是超文本标记语言,在计算机中以 .html或者.htm作为扩展名,可以被浏览器识别,就是经常见到的网页.
Html的语法非常简洁,比较松散,以相应的英语单词关键字进行组合,html标签不区分大小写,标签大多数成对出现,有开始,有结束,例如 <html></html>,但是并没有要求必须成对出现.同时也有固定的短标签,例如<br/>,<hr/>.
学习html基本可以认为就是学习各种标签,标签也可以设置属性,例如<font color="red">hello, world</font>,示例中color代表标签的颜色属性,red代表标签是红色字体,hello,world为实际显示的内容.可以新建一个文本文档,然后将后缀名修改.html文件,用代码编辑器打开该html文件可以编辑文件(例如notepad++),将上述内容保存到文件中,双击该文件可以看到如下效果:
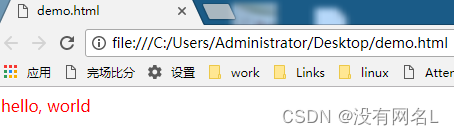
Html的组成可以分为如下部分:
- <!doctype html> 声明文档类型,可以不写
- <html> 开始 和</html> 结束,属于html的根标签
- <head></head> 头部标签,头部标签内一般有 <title></title>
- <body></body> 主体标签,一般用于显示内容
例如
<html>
<head>
<title>这是一个标题</title>
</head>
<body>
<font color="red" size="5">hello, world</font>
</body>
</html>如果想要添加注释,可以使用 <!—我是注释 -->的方式.
也可以指定页面类型和字符编码,下面设置页面类型为html,并且字符编码为utf8
<meta http-equiv="content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf8">
Html标签属性,可以双引号,单引号,或者不写
Html标签介绍
题目标签
共有6种,<h1>,<h2>,…<h6>,其中<h1>最大,<h6>最小
文本标签
<font>标签,可以设置颜色和字体大小属性
颜色表示方法(可以参考网站: RGB颜色对照表):
- 英文单词 red green blue …
- 使用16进制的形式表示颜色:#ffffff
- 使用rgb(255,255,0)
字体大小可以使用size属性,大小范围为1-7,其中7最大,1最小.
有时候需要使用换行标签 ,这是一个短标签 <br/>
与之对应另外还有一个水平线也是短标签, <hr/>,水平线也可以设置颜色和大小
列表标签
列表标签分无序列表和有序列表,分别对应<ul>和<ol>.
无序列表的格式如下:
<ul>
<li>列表内容1</li>
<li>列表内容2</li>
…
</ul>
无序列表可以设置type属性:
实心圆圈:type=disc
空心圆圈:type=circle
小方块: type=square
有序列表的格式如下:
<ol>
<li>列表内容1</li>
<li>列表内容2</li>
…
</ol>
有序列表同样可以设置type属性
数字:type=1,也是默认方式
英文字母:type=a或type=A
罗马数字:type=i或type=I
图片标签
图片标签使用<img>,内部需要设置若干属性,可以不必写结束标签
属性:
- src=”3.gif” 图片来源,必写
- alt=”小岳岳” 图片不显示时,显示的内容
- title=”我的天呐” 鼠标移动到图片上时显示的文字
- width=”600” 图片显示的宽度
- height=”400” 图片显示的高度
例如:
<img src="3.gif" alt="小岳岳" title="我的天呐!" width="300" height="200" />
注意:当图片未定义宽高,图片百分百比例显示,如果只改变图片宽度或者高度,会等比例缩放
超链接标签
超链接标签使用<a>,同样需要设置属性表明要链接到哪里.
属性:
- href=”传智教育【官网】-好口碑IT职业教育,好口碑IT培训机构,一样的教育,不一样的品质”,前往地址,必填,注意要写http://
- title=”前往传智” 鼠标移动到链接上时显示的文字
- target=”_self”或者”_blank”,_self是默认值,在自身页面打开,_blank是新开页面前往连接地址
示例:
<a href=”传智教育【官网】-好口碑IT职业教育,好口碑IT培训机构,一样的教育,不一样的品质” title=”去往传智” target=”_self” >来传智</a>
当我们访问某个网站的时候,当请求的资源不存在,经常会给我们报告一个错误,显示为404错误,一般会给请求用户返回一个错误页,大家可以自行尝试一下编写一个我们自己的错误页.
http超文本传输协议
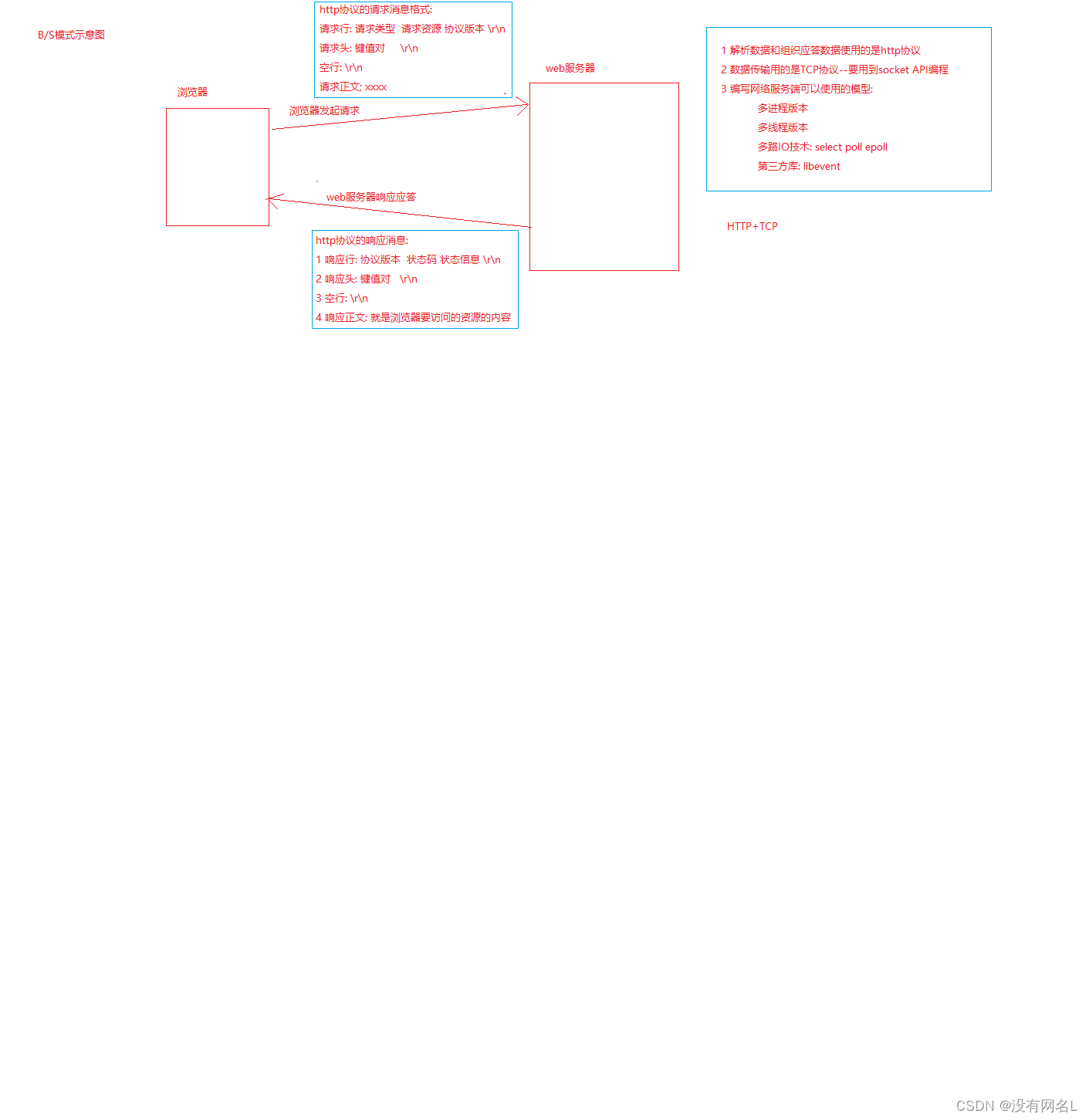
http协议和html前面的ht都是超文本的意思,所以http与html是配合非常紧密的一对,我们可以认为http就是为了传输html这样的文件,http位于应用层,侧重于解释.
http协议对消息区分可以分为请求消息和响应消息.
http请求消息
我们要开发的服务器与浏览器通信采用的就是http协议,在浏览器想访问一个资源的时候,在浏览器输入访问地址(例如http://127.0.0.1:8000),地址输入完成后当敲击回车键的时候,浏览器就将请求消息发送给服务器
我们可以先用测试工具创建一个socket服务器
之后通过浏览器请求地址,就会看到浏览器发送过来的请求消息
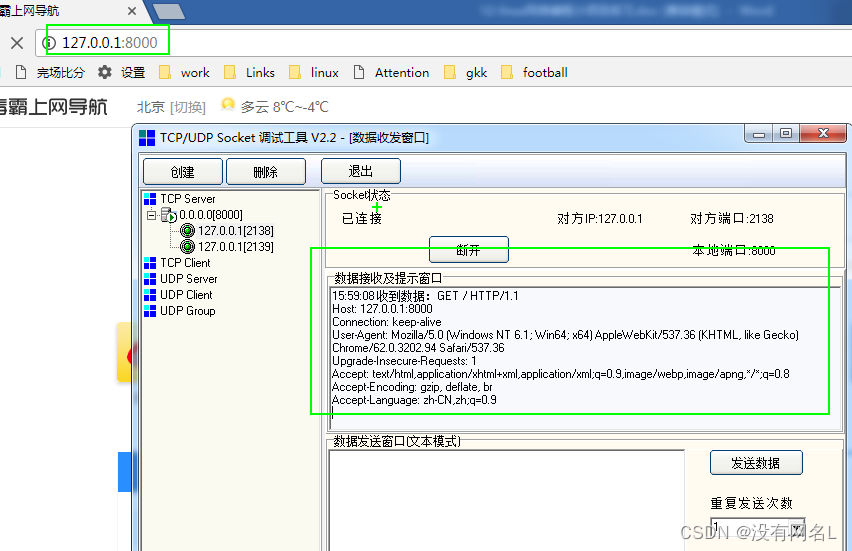
这个消息看起来很乱很复杂,对应的就是我们说的请求消息.
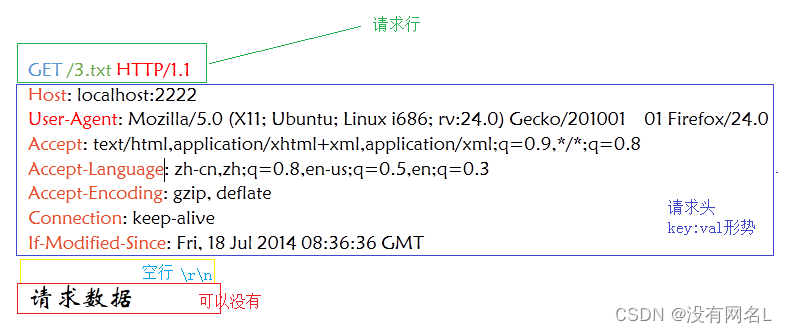
请求消息分为四部分内容:
- 请求行 说明请求类型,要访问的资源,以及使用的http版本
- 请求头 说明服务器使用的附加信息,都是键值对,比如表明浏览器类型
- 空行 不能省略-而且是\r\n,包括请求行和请求头都是以\r\n结尾
- 请求数据 表明请求的特定数据内容,可以省略-如登陆时,会将用户名和密码内容作为请求数据
请求类型
http协议有很多种请求类型,对我们来说常见的用的最多的是get和post请求。常见的请求类型如下:
- Get 请求指定的页面信息,并返回实体主体
- Post 向指定资源提交数据进行处理请求(例如提交表单或者上传文件)。数据被包含在请求体中。POST请求可能会导致新的资源的建立和/或已有资源的修改。
- Head 类似于get请求,但是响应消息没有内容,只是获得报头
- Put 从客户端向浏览器传送的数据取代指定的文档内容
- Delete 请求服务器删除指定的页面
- Connect HTTP/1.1协议中预留给能够将连接改为管道方式的代理服务器
- Options 允许客户端查看浏览器的性能
- Trace 回显服务器收到的请求,主要用于测试和诊断
get 和 post 请求都是请求资源,而且都会提交数据,如果提交密码信息用get请求,就会明文显示,而post则不会显示出涉密信息.
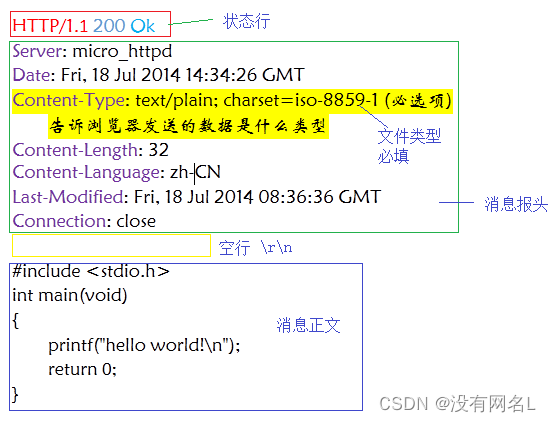
http响应消息
响应消息是代表服务器收到请求消息后,给浏览器做的反馈,所以响应消息是服务器发送给浏览器的,响应消息也分为四部分:
- 状态行 包括http版本号,状态码,状态信息
- 消息报头 说明客户端要使用的一些附加信息,也是键值对
- 空行 \r\n 同样不能省略
- 响应正文 服务器返回给客户端的文本信息
示例:
http常见状态码
http状态码由三位数字组成,第一个数字代表响应的类别,有五种分类:
- 1xx 指示信息--表示请求已接收,继续处理
- 2xx 成功--表示请求已被成功接收、理解、接受
- 3xx 重定向--要完成请求必须进行更进一步的操作
- 4xx 客户端错误--请求有语法错误或请求无法实现
- 5xx 服务器端错误--服务器未能实现合法的请求
常见的状态码如下:
- 200 OK 客户端请求成功
- 301 Moved Permanently 重定向
- 400 Bad Request 客户端请求有语法错误,不能被服务器所理解
- 401 Unauthorized 请求未经授权,这个状态代码必须和WWW-Authenticate报头域一起使用
- 403 Forbidden 服务器收到请求,但是拒绝提供服务
- 404 Not Found 请求资源不存在,eg:输入了错误的URL
- 500 Internal Server Error 服务器发生不可预期的错误
- 503 Server Unavailable 服务器当前不能处理客户端的请求,一段时间后可能恢复正常
http常见文件类型分类
http与浏览器交互时,为使浏览器能够识别文件信息,所以需要传递文件类型,这也是响应消息必填项,常见的类型如下:
- 普通文件: text/plain; charset=utf-8
- *.html: text/html; charset=utf-8
- *.jpg: image/jpeg
- *.gif: image/gif
- *.png: image/png
- *.wav: audio/wav
- *.avi: video/x-msvideo
- *.mov: video/quicktime
- *.mp3: audio/mpeg
特别说明
charset=iso-8859-1 西欧的编码,说明网站采用的编码是英文;
charset=gb2312 说明网站采用的编码是简体中文;
charset=utf-8 代表世界通用的语言编码;可以用到中文、韩文、日文等世界上所有语言编码上
charset=euc-kr 说明网站采用的编码是韩文;
charset=big5 说明网站采用的编码是繁体中文;
web服务器开发
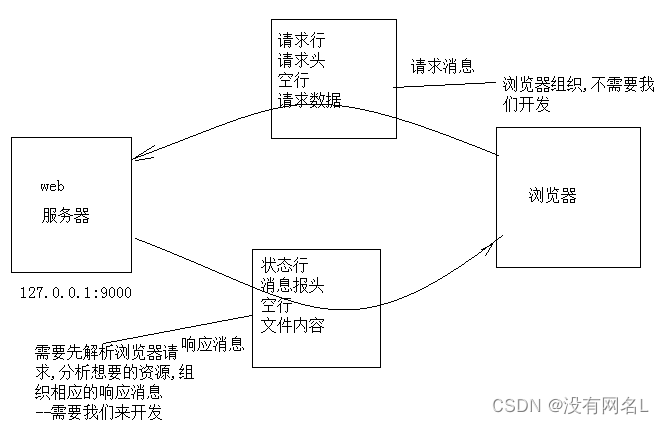
我们要开发web服务器已经明确要使用http协议传送html文件,那么我们如何搭建我们的服务器呢?注意http只是应用层协议,我们仍然需要选择一个传输层的协议来完成我们的传输数据工作,所以开发协议选择是TCP+HTTP,也就是说服务器搭建浏览依照TCP,对数据进行解析和响应工作遵循HTTP的原则.
这样我们的思路很清晰,编写一个TCP并发服务器,只不过收发消息的格式采用的是HTTP协议,如下图:
基于epoll的web服务器
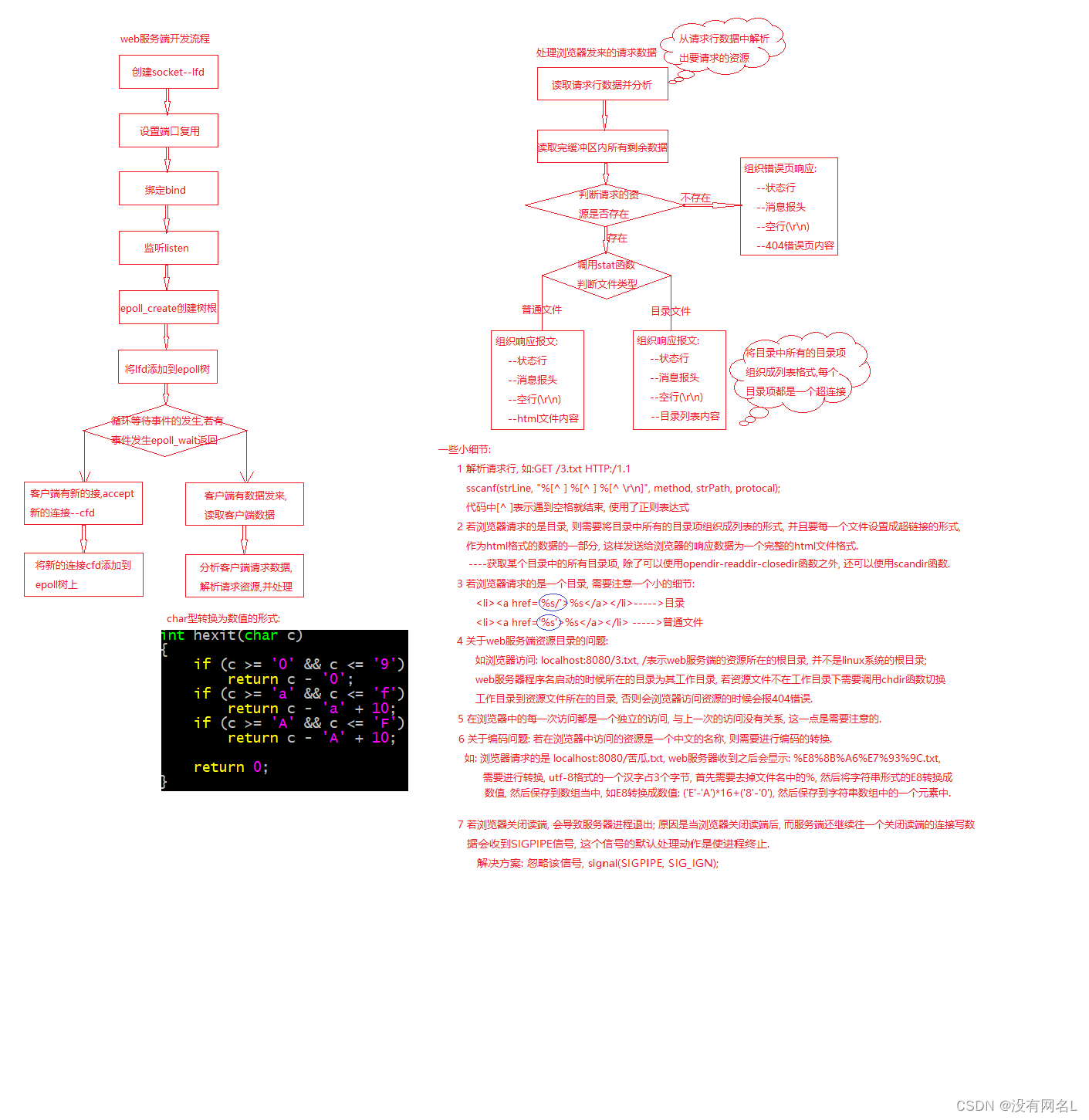
由于我们知道epoll在大量并发少量活跃的情况下效率很高,所以本文以epoll为例,介绍epoll开发的主体流程:
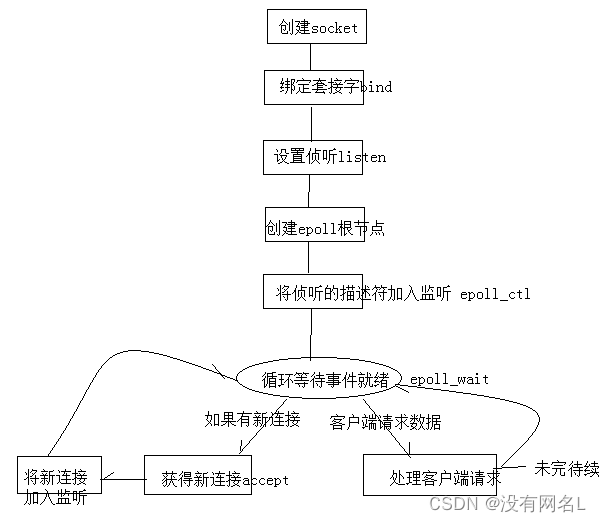
对于我们来说,上述的框架基本没问题,除了处理客户端请求部分,我们可以考虑封装成一个函数,思考:函数参数如何设计?
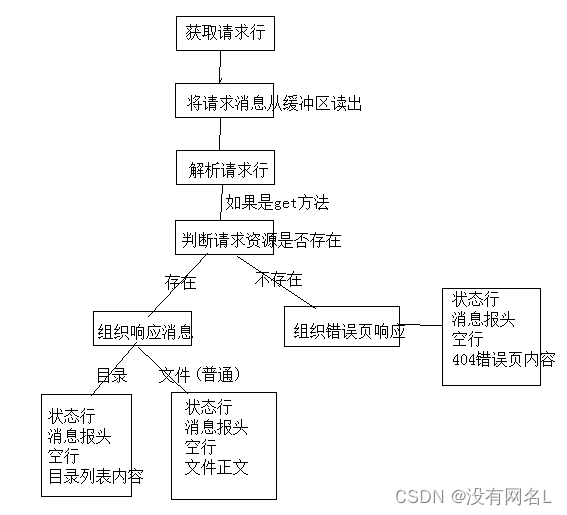
处理客户端请求流程:
思考题:
- 由于每个响应消息都是分为四部分,可以考虑封装为函数,封装几个函数更方便?都分别对应什么功能?
- 目录请求相对复杂,需要遍历目录内的内容,也就是读内容,思考如何做?读到内容形成正文发送的时候,对应的文件类型应该是什么
网页服务器总结:
BS模式示意图
web服务器开发流程
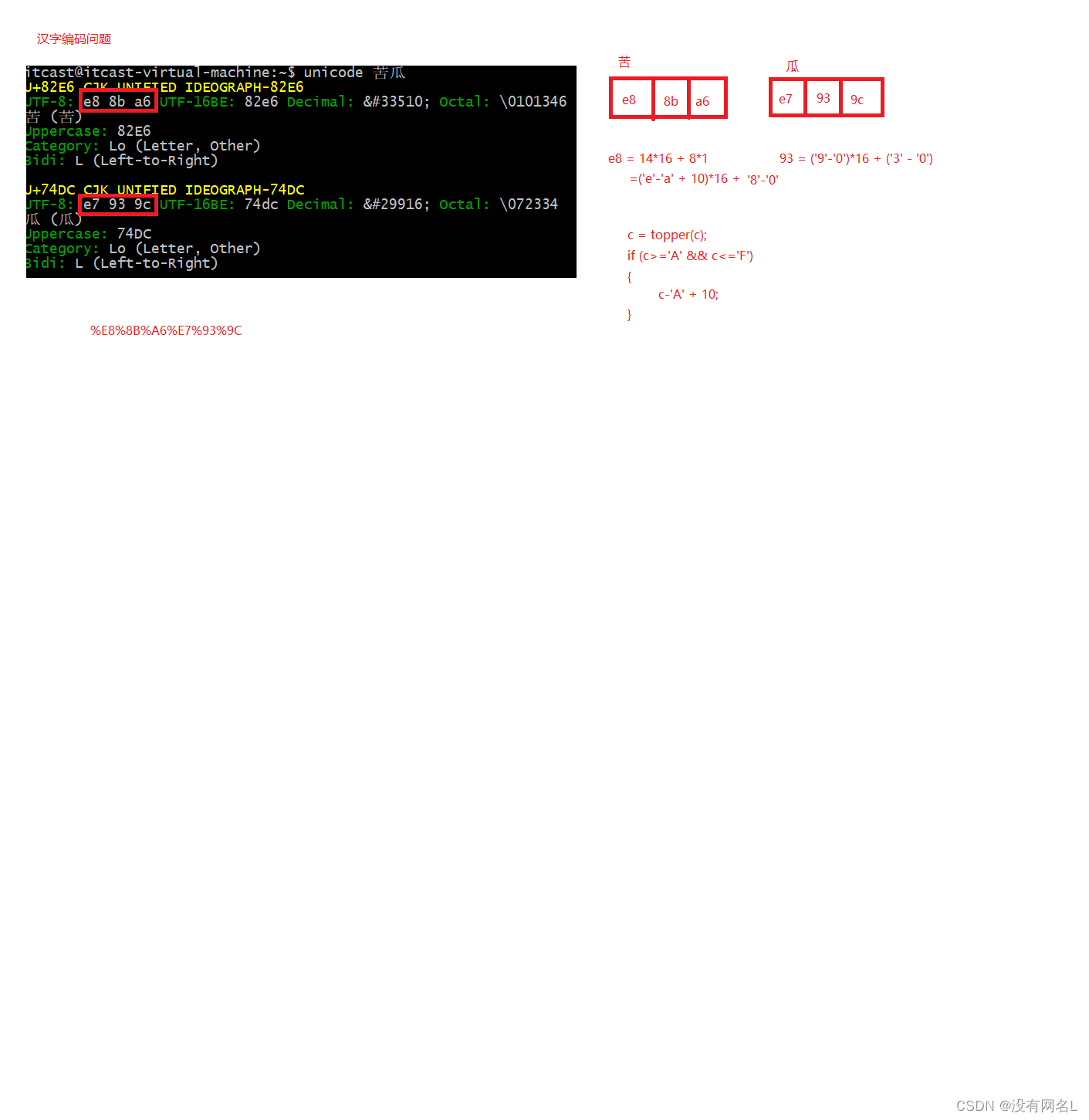
汉字乱码问题
浏览器和web服务器通信模式

网页服务器接收数据可以直接使用epoll模型进行接收数据即可,正常的创建服务器即可,重点在于数据的解析和发送,解析的代码可如下:
//Readline为一行一行读取发送的数据 读取之后读到buf中
// 按行读取数据 读取第一行数据
// 里面调用了read函数对信息继续读取
n = Readline(cfd, buf, sizeof(buf));
if (n < 0)
{
return -1;
}
// 接收第一行请求头信息
// //Get /hanzi.c HTTP/1.1
// %[^ ] %[^ ] %[^/r/n] 截取之后的值分别为 //Get /hanzi.c HTTP/1.1
// sccanf() 第一个参数 原字符串 "%[^ ]" 表示截取第一个出现 的字符串
char reqType[16] = {0};
char filename[256] = {0};
char httppro[16] = {0};
sscanf(buf, "%[^ ] %[^ ] %[^/r/n]", reqType, filename, httppro);
printf("reqType = %s\n", reqType);
printf("filename = %s\n", filename);
printf("httppro = %s\n", httppro);之后根据解析的信息进行处理后,发送浏览器可以解析的头信息和内容信息,头信息如下:
// 发送头部信息函数
/*
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Content-Type:text/plain;charset=iso-8859-1(必选项) 告诉服务器发送的什么类型
Content-Length:32 //要么不传 传了就要传对
*/
int send_header(int cfd, char *code, char *msg, char *fileType, int len)
{
char buf[1024] = {0};
//\r\n换行 HTTP/1.1 200 OK
sprintf(buf, "HTTP/1.1 %s %s\r\n", code, msg);
// Content-Type:text/plain;charset=iso-8859-1
sprintf(buf + strlen(buf), "Content-Type:%s\r\n", fileType);
// Content-Length:32
if (len > 0)
{
sprintf(buf + strlen(buf), "Content-Length:%d\r\n", len);
}
// 追加换行
strcat(buf, "\r\n");
// 发送数据
Write(cfd, buf, strlen(buf));
return 0;
}内容代码如下:
// 发送文件内存函数
int send_file(int cfd, char *fileName)
{
// 打开文件
int fd = open(fileName, O_RDONLY);
if (fd < 0)
{
printf("file open error\n");
return -1;
}
// 循环读取文件
char buf[1024];
int n;
while (1)
{
memset(buf, 0x00, sizeof(buf));
n = read(fd, buf, sizeof(buf));
if (n <= 0)
{
break;
}
else
{
Write(cfd, buf, n);
}
}
}完整代码
如下,封装了pub.c wrap.c两个常用的方法;
pub.h pub. c
//pub.h
#ifndef _PUB_H
#define _PUB_H
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <strings.h>
#include <ctype.h>
char *get_mime_type(char *name);
int get_line(int sock, char *buf, int size);
int hexit(char c); // 16进制转10进制
void strencode(char *to, size_t tosize, const char *from); // 编码
void strdecode(char *to, char *from); // 解码
#endif
//pub.c
#include "pub.h"
// 通过文件名字获得文件类型
char *get_mime_type(char *name)
{
char *dot;
dot = strrchr(name, '.'); // 自右向左查找‘.’字符;如不存在返回NULL
/*
*charset=iso-8859-1 西欧的编码,说明网站采用的编码是英文;
*charset=gb2312 说明网站采用的编码是简体中文;
*charset=utf-8 代表世界通用的语言编码;
* 可以用到中文、韩文、日文等世界上所有语言编码上
*charset=euc-kr 说明网站采用的编码是韩文;
*charset=big5 说明网站采用的编码是繁体中文;
*
*以下是依据传递进来的文件名,使用后缀判断是何种文件类型
*将对应的文件类型按照http定义的关键字发送回去
*/
if (dot == (char *)0)
return "text/plain; charset=utf-8";
if (strcmp(dot, ".html") == 0 || strcmp(dot, ".htm") == 0)
return "text/html; charset=utf-8";
if (strcmp(dot, ".jpg") == 0 || strcmp(dot, ".jpeg") == 0)
return "image/jpeg";
if (strcmp(dot, ".gif") == 0)
return "image/gif";
if (strcmp(dot, ".png") == 0)
return "image/png";
if (strcmp(dot, ".css") == 0)
return "text/css";
if (strcmp(dot, ".au") == 0)
return "audio/basic";
if (strcmp(dot, ".wav") == 0)
return "audio/wav";
if (strcmp(dot, ".avi") == 0)
return "video/x-msvideo";
if (strcmp(dot, ".mov") == 0 || strcmp(dot, ".qt") == 0)
return "video/quicktime";
if (strcmp(dot, ".mpeg") == 0 || strcmp(dot, ".mpe") == 0)
return "video/mpeg";
if (strcmp(dot, ".vrml") == 0 || strcmp(dot, ".wrl") == 0)
return "model/vrml";
if (strcmp(dot, ".midi") == 0 || strcmp(dot, ".mid") == 0)
return "audio/midi";
if (strcmp(dot, ".mp3") == 0)
return "audio/mpeg";
if (strcmp(dot, ".ogg") == 0)
return "application/ogg";
if (strcmp(dot, ".pac") == 0)
return "application/x-ns-proxy-autoconfig";
return "text/plain; charset=utf-8";
}
/**********************************************************************/
/* Get a line from a socket, whether the line ends in a newline,
* carriage return, or a CRLF combination. Terminates the string read
* with a null character. If no newline indicator is found before the
* end of the buffer, the string is terminated with a null. If any of
* the above three line terminators is read, the last character of the
* string will be a linefeed and the string will be terminated with a
* null character.
* Parameters: the socket descriptor
* the buffer to save the data in
* the size of the buffer
* Returns: the number of bytes stored (excluding null) */
/**********************************************************************/
// 获得一行数据,每行以\r\n作为结束标记
int get_line(int sock, char *buf, int size)
{
int i = 0;
char c = '\0';
int n;
while ((i < size - 1) && (c != '\n'))
{
n = recv(sock, &c, 1, 0);
/* DEBUG printf("%02X\n", c); */
if (n > 0)
{
if (c == '\r')
{
n = recv(sock, &c, 1, MSG_PEEK); // MSG_PEEK 从缓冲区读数据,但是数据不从缓冲区清除
/* DEBUG printf("%02X\n", c); */
if ((n > 0) && (c == '\n'))
recv(sock, &c, 1, 0);
else
c = '\n';
}
buf[i] = c;
i++;
}
else
c = '\n';
}
buf[i] = '\0';
return (i);
}
// 下面的函数第二天使用
/*
* 这里的内容是处理%20之类的东西!是"解码"过程。
* %20 URL编码中的‘ ’(space)
* %21 '!' %22 '"' %23 '#' %24 '$'
* %25 '%' %26 '&' %27 ''' %28 '('......
* 相关知识html中的‘ ’(space)是 
*/
void strdecode(char *to, char *from)
{
for (; *from != '\0'; ++to, ++from)
{
if (from[0] == '%' && isxdigit(from[1]) && isxdigit(from[2]))
{ // 依次判断from中 %20 三个字符
*to = hexit(from[1]) * 16 + hexit(from[2]); // 字符串E8变成了真正的16进制的E8
from += 2; // 移过已经处理的两个字符(%21指针指向1),表达式3的++from还会再向后移一个字符
}
else
*to = *from;
}
*to = '\0';
}
// 16进制数转化为10进制, return 0不会出现
int hexit(char c)
{
if (c >= '0' && c <= '9')
return c - '0';
if (c >= 'a' && c <= 'f')
return c - 'a' + 10;
if (c >= 'A' && c <= 'F')
return c - 'A' + 10;
return 0;
}
//"编码",用作回写浏览器的时候,将除字母数字及/_.-~以外的字符转义后回写。
// strencode(encoded_name, sizeof(encoded_name), name);
void strencode(char *to, size_t tosize, const char *from)
{
int tolen;
for (tolen = 0; *from != '\0' && tolen + 4 < tosize; ++from)
{
if (isalnum(*from) || strchr("/_.-~", *from) != (char *)0)
{
*to = *from;
++to;
++tolen;
}
else
{
sprintf(to, "%%%02x", (int)*from & 0xff);
to += 3;
tolen += 3;
}
}
*to = '\0';
}
wrap.h wrap.c
//wrap.h
#ifndef __WRAP_H_
#define __WRAP_H_
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <strings.h>
void perr_exit(const char *s);
int Accept(int fd, struct sockaddr *sa, socklen_t *salenptr);
int Bind(int fd, const struct sockaddr *sa, socklen_t salen);
int Connect(int fd, const struct sockaddr *sa, socklen_t salen);
int Listen(int fd, int backlog);
int Socket(int family, int type, int protocol);
ssize_t Read(int fd, void *ptr, size_t nbytes);
ssize_t Write(int fd, const void *ptr, size_t nbytes);
int Close(int fd);
ssize_t Readn(int fd, void *vptr, size_t n);
ssize_t Writen(int fd, const void *vptr, size_t n);
ssize_t my_read(int fd, char *ptr);
ssize_t Readline(int fd, void *vptr, size_t maxlen);
int tcp4bind(short port, const char *IP);
#endif
//wrap.c
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <strings.h>
// 绑定错误显示和退出
void perr_exit(const char *s)
{
perror(s);
exit(-1);
}
int Accept(int fd, struct sockaddr *sa, socklen_t *salenptr)
{
int n;
again:
if ((n = accept(fd, sa, salenptr)) < 0)
{
if ((errno == ECONNABORTED) || (errno == EINTR)) // ECONNABORTED 代表连接失败 ETINTR 代表被信号打断
goto again;
else
perr_exit("accept error");
}
return n;
}
int Bind(int fd, const struct sockaddr *sa, socklen_t salen)
{
int n;
if ((n = bind(fd, sa, salen)) < 0)
perr_exit("bind error");
return n;
}
int Connect(int fd, const struct sockaddr *sa, socklen_t salen)
{
int n;
if ((n = connect(fd, sa, salen)) < 0)
perr_exit("connect error");
return n;
}
int Listen(int fd, int backlog)
{
int n;
if ((n = listen(fd, backlog)) < 0)
perr_exit("listen error");
return n;
}
int Socket(int family, int type, int protocol)
{
int n;
if ((n = socket(family, type, protocol)) < 0)
perr_exit("socket error");
return n;
}
ssize_t Read(int fd, void *ptr, size_t nbytes)
{
ssize_t n;
again:
if ((n = read(fd, ptr, nbytes)) == -1)
{
if (errno == EINTR) // 被信号打断应该继续读
goto again;
else
return -1;
}
return n;
}
ssize_t Write(int fd, const void *ptr, size_t nbytes)
{
ssize_t n;
again:
if ((n = write(fd, ptr, nbytes)) == -1)
{
if (errno == EINTR)
goto again;
else
return -1;
}
return n;
}
int Close(int fd)
{
int n;
if ((n = close(fd)) == -1)
perr_exit("close error");
return n;
}
/*参三: 应该读取的字节数*/
ssize_t Readn(int fd, void *vptr, size_t n)
{
size_t nleft; // usigned int 剩余未读取的字节数
ssize_t nread; // int 实际读到的字节数
char *ptr;
ptr = vptr;
nleft = n;
while (nleft > 0)
{
if ((nread = read(fd, ptr, nleft)) < 0)
{
if (errno == EINTR)
nread = 0;
else
return -1;
}
else if (nread == 0)
break;
nleft -= nread; // 防止一次数据没有读完
ptr += nread; // 指针需要向后移动
}
return n - nleft;
}
ssize_t Writen(int fd, const void *vptr, size_t n)
{
size_t nleft;
ssize_t nwritten;
const char *ptr;
ptr = vptr;
nleft = n;
while (nleft > 0)
{
if ((nwritten = write(fd, ptr, nleft)) <= 0)
{
if (nwritten < 0 && errno == EINTR)
nwritten = 0;
else
return -1;
}
nleft -= nwritten;
ptr += nwritten;
}
return n;
}
static ssize_t my_read(int fd, char *ptr)
{
static int read_cnt;
static char *read_ptr;
static char read_buf[100]; // 定义了100的缓冲区
if (read_cnt <= 0)
{
again:
// 使用缓冲区可以避免多次从底层缓冲读取数据--为了提高效率
if ((read_cnt = read(fd, read_buf, sizeof(read_buf))) < 0)
{
if (errno == EINTR)
goto again;
return -1;
}
else if (read_cnt == 0)
return 0;
read_ptr = read_buf;
}
read_cnt--;
*ptr = *read_ptr++; // 从缓冲区取数据
return 1;
}
// 读取一行
ssize_t Readline(int fd, void *vptr, size_t maxlen)
{
ssize_t n, rc;
char c, *ptr;
ptr = vptr;
for (n = 1; n < maxlen; n++)
{
if ((rc = my_read(fd, &c)) == 1)
{
*ptr++ = c;
if (c == '\n') // 代表任务完成
break;
}
else if (rc == 0)
{ // 对端关闭
*ptr = 0; // 0 = '\0'
return n - 1;
}
else
return -1;
}
*ptr = 0;
return n;
}
int tcp4bind(short port, const char *IP)
{
struct sockaddr_in serv_addr;
int lfd = Socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0);
bzero(&serv_addr, sizeof(serv_addr)); // 清空serv_addr地址 对比 memset()
if (IP == NULL)
{
// 如果这样使用 0.0.0.0,任意ip将可以连接
serv_addr.sin_addr.s_addr = INADDR_ANY;
}
else
{
if (inet_pton(AF_INET, IP, &serv_addr.sin_addr.s_addr) <= 0)
{
perror(IP); // 转换失败
exit(1);
}
}
serv_addr.sin_family = AF_INET;
serv_addr.sin_port = htons(port);
int opt = 1;
setsockopt(lfd, SOL_SOCKET, SO_REUSEADDR, &opt, sizeof(opt));
Bind(lfd, (struct sockaddr *)&serv_addr, sizeof(serv_addr));
return lfd;
}
服务器代码:
webserver.c
// web服务器使用epoll模型
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/epoll.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <dirent.h>
#include "pub.h"
#include "wrap.h"
// 处理http请求函数
int http_request(int cfd);
// 发送头部信息函数
int send_header(int cfd, char *code, char *msg, char *fileType, int len);
// 发送文件内存函数
int send_file(int cfd, char *fileName);
int main()
{
// 改变文件运行目录 将目录修改为具有文件的目录下
char path[255] = {0};
sprintf(path, "%s/%s", getenv("HOME"), "test3/网络编程/webpath");
chdir(path);
// 创建socket
int lfd = tcp4bind(9999, NULL);
// 设置监听
Listen(lfd, 128);
// 创建epoll树
int epfd = epoll_create(1024);
if (epfd < 0)
{
perror("epoll create error");
close(lfd);
return -1;
}
// 将监听文件描述符上树
struct epoll_event ev;
ev.data.fd = lfd;
ev.events = EPOLLIN;
epoll_ctl(epfd, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, lfd, &ev);
int nready;
struct epoll_event events[1024];
int cfd;
int socketfd;
while (1)
{
nready = epoll_wait(epfd, events, 1024, -1);
printf("nready = %d\n", nready);
if (nready < 0)
{
if (errno == EINTR)
{
continue;
}
break;
}
for (int i = 0; i < nready; i++)
{
socketfd = events[i].data.fd;
// 如果新的客户端到来,那么返回的fd等于监听描述符
if (socketfd == lfd)
{
// 开始接收数据
cfd = Accept(lfd, NULL, NULL);
// 设置cfd为非阻塞
int flag = fcntl(cfd, F_GETFL);
flag |= O_NONBLOCK;
fcntl(cfd, F_SETFL, flag);
// 将描述符上树
ev.data.fd = cfd;
ev.events = EPOLLIN;
epoll_ctl(epfd, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, cfd, &ev);
}
else
{
// 有新的数据过来
http_request(cfd);
}
}
}
}
// 发送头部信息函数
/*
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Content-Type:text/plain;charset=iso-8859-1(必选项) 告诉服务器发送的什么类型
Content-Length:32 //要么不传 传了就要传对
*/
int send_header(int cfd, char *code, char *msg, char *fileType, int len)
{
char buf[1024] = {0};
//\r\n换行 HTTP/1.1 200 OK
sprintf(buf, "HTTP/1.1 %s %s\r\n", code, msg);
// Content-Type:text/plain;charset=iso-8859-1
sprintf(buf + strlen(buf), "Content-Type:%s\r\n", fileType);
// Content-Length:32
if (len > 0)
{
sprintf(buf + strlen(buf), "Content-Length:%d\r\n", len);
}
// 追加换行
strcat(buf, "\r\n");
// 发送数据
Write(cfd, buf, strlen(buf));
return 0;
}
// 发送文件内存函数
int send_file(int cfd, char *fileName)
{
// 打开文件
int fd = open(fileName, O_RDONLY);
if (fd < 0)
{
printf("file open error\n");
return -1;
}
// 循环读取文件
char buf[1024];
int n;
while (1)
{
memset(buf, 0x00, sizeof(buf));
n = read(fd, buf, sizeof(buf));
if (n <= 0)
{
break;
}
else
{
Write(cfd, buf, n);
}
}
}
// 处理http请求函数
int http_request(int cfd)
{
int n;
char buf[1024];
memset(buf, 0x00, sizeof(buf));
// 按行读取数据 读取第一行数据
// 里面调用了read函数对信息继续读取
n = Readline(cfd, buf, sizeof(buf));
if (n < 0)
{
return -1;
}
// 接收第一行请求头信息
// //Get /hanzi.c HTTP/1.1
// %[^ ] %[^ ] %[^/r/n] 截取之后的值分别为 //Get /hanzi.c HTTP/1.1
// sccanf() 第一个参数 原字符串 "%[^ ]" 表示截取第一个出现 的字符串
char reqType[16] = {0};
char filename[256] = {0};
char httppro[16] = {0};
sscanf(buf, "%[^ ] %[^ ] %[^/r/n]", reqType, filename, httppro);
printf("reqType = %s\n", reqType);
printf("filename = %s\n", filename);
printf("httppro = %s\n", httppro);
// 因为上面获取的文件名具有 / 因此需要对/进行去除再访问
char *pFile = filename + 1;
// 将剩下的数据读完
// 因为这里是阻塞函数 所以要将cfd设置为非阻塞状态 否则会阻塞在该处
while (n = Readline(cfd, buf, sizeof(buf)) > 0)
{
};
// 判断文件是否存在
struct stat st;
// 文件不存在
if (stat(pFile, &st) < 0)
{
printf("file is not exit\n");
// 发送头部信息 get_mime_type获取文件类型 error.html为错误文件信息
send_header(cfd, "404", "Not Found", get_mime_type(".html"), 0);
// 发送内容
send_file(cfd, "error.html");
}
else // 文件存在 man 2 stat查看文件的属性 包括文件类型和大小等信息
{
// 普通文件
if (S_ISREG(st.st_mode))
{
printf("file exist\n");
// 发送头部信息
send_header(cfd, "200", "OK", get_mime_type(pFile), st.st_size);
// 发送文件内容
send_file(cfd, pFile);
}
// 目录文件
else if (S_ISDIR(st.st_mode))
{
}
}
}gcc -o web webserver.c wrap.c pub.c编译代码
./web执行即可