文章目录
- nginx线程池
- 1. 问题
- 2. 解决办法 nginx线程池
- 3. 线程池实现模型
- 4. 线程池实现核心组件
- 5.源码实现
- 测试代码main.c
- 封装互斥锁&条件变量
- 线程池实现
nginx线程池
1. 问题
处理事件过程“阻塞”怎么办?
-
忙于漫长的 CPU 密集型处理
-
读取文件,但文件尚未缓存,从硬盘中读取较为缓慢
-
不得不等待获取某个资源:
网络上的请求和响应,互斥锁,等待同步方式调用的数据库响应
单个进程或线程同时只能处理一个任务,如果有很多请求需要同时处理怎么办?
解决方案: 运用多进程或多线程技术解决
缺 陷:
1. 创建和销毁线程上花费的时间和消耗的系统资源,甚至可能要比花在处理实际的用户请求的时间和资源要多得多
2. 活动的线程需要消耗系统资源,如果启动太多,会导致系统由于过度消耗内存或“切换过度”而导致系统资源不足
2. 解决办法 nginx线程池
线程池简介
- 线程池 - 由一个任务队列和一组处理队列的线程组成。
- 一旦工作进程需要处理某个可能“阻塞”的操作,不用自己操作,将其作为一个任务放到线程池的队列,接着会被某个空闲线程提取处理。
- 任务完成后给进程发信号,我已经处理完了,你可以接着对任务进行处理了.
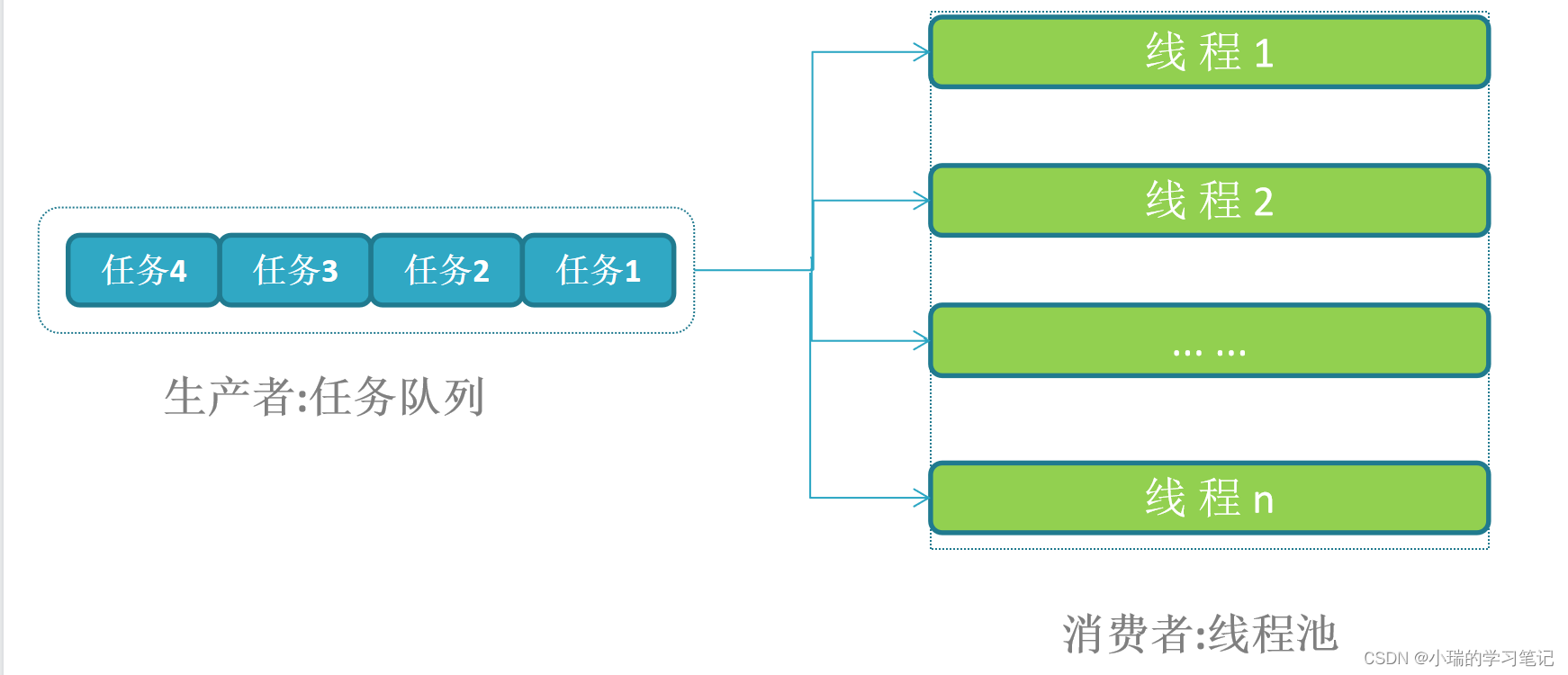
3. 线程池实现模型
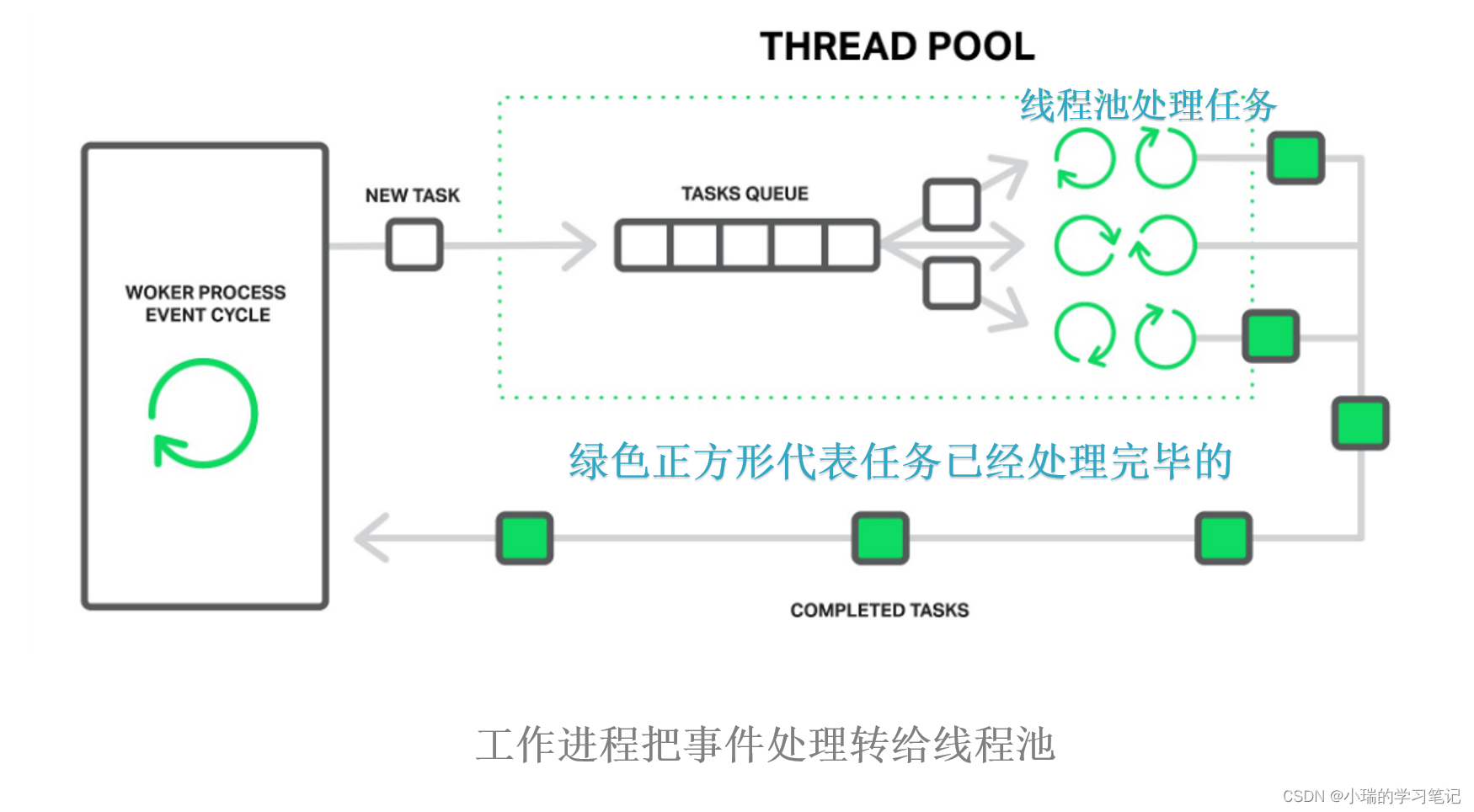
- 工作进程当有任务需要处理的时候 →会封装成一个任务 →然后事件加入任务队列 →线程池中的线程处理任务队列中的任务 →处理完毕后把任务再交给工作进程进行下一步处理
4. 线程池实现核心组件
-
任务 - 待处理的工作,通常由标识、参数和处理函数组成。
-
任务队列 - 按顺序保存待处理的任务序列,等待线程中的线程组处理。
-
线程池 - 由多个已启动的一组线程组成。
-
条件变量 - 一种同步机制,允许线程挂起,直到共享数据上的某些条件得到满足。
-
互斥锁 - 保证在任一时刻,只能有一个线程访问该对象。
5.源码实现
- 下方代码都有详细注释,认真读代码即可
- 阅读顺序,就按照我的排列顺序,这样好理解点
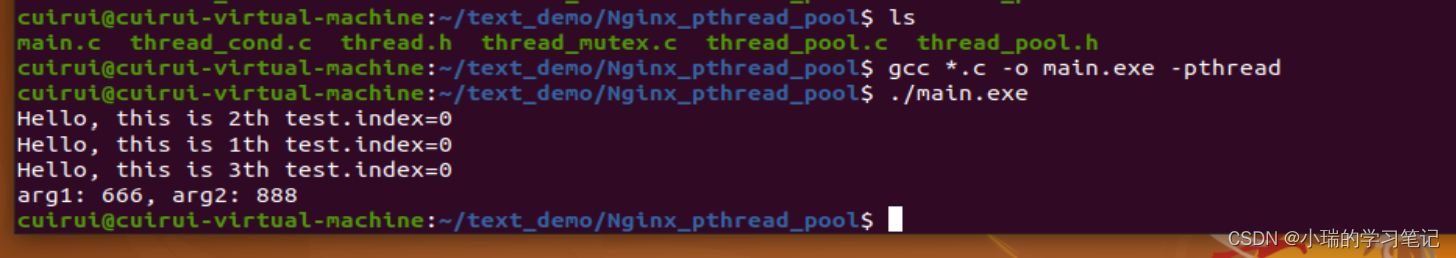
测试代码main.c
- 先上结论
#include "thread_pool.h"
struct test{
int arg1;
int arg2;
};
// 三个处理函数 即回调函数
void task_handler1(void* data){
static int index = 0;
printf("Hello, this is 1th test.index=%d\r\n", index++);
}
void task_handler2(void* data){
static int index = 0;
printf("Hello, this is 2th test.index=%d\r\n", index++);
}
void task_handler3(void* data){
static int index = 0;
struct test *t = (struct test *) data;
printf("Hello, this is 3th test.index=%d\r\n", index++);
printf("arg1: %d, arg2: %d\n", t->arg1, t->arg2);
}
int
main(int argc, char **argv)
{
thread_pool_t* tp = NULL;
int i = 0;
tp = thread_pool_init(); // 创建线程池
// 创建任务 参数为处理任务函数的参数大小,参见thread_task_t中的成员变量
thread_task_t * test1 = thread_task_alloc(0);
thread_task_t * test2 = thread_task_alloc(0);
thread_task_t * test3 = thread_task_alloc(sizeof(struct test));
// 指定任务处理函数
test1->handler = task_handler1;
test2->handler = task_handler2;
test3->handler = task_handler3;
// 设置 task_handler3 的参数
((struct test*)test3->ctx)->arg1 = 666;
((struct test*)test3->ctx)->arg2 = 888;
thread_task_post(tp, test1);
thread_task_post(tp, test2);
thread_task_post(tp, test3);
sleep(5);
thread_pool_destroy(tp); // 销毁线程池
return 0;
}
封装互斥锁&条件变量
thread.h
这个主要对,互斥锁和条件变量进行了一层封装
#ifndef _DEMO_THREAD_H_INCLUDED_
#define _DEMO_THREAD_H_INCLUDED_
// 当C++程序调用这个代码的时候要声明下方的函数都以C语言方式编译
#ifdef __cplusplus
extern "C" {
#endif
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <string.h>
typedef intptr_t int_t;
typedef uintptr_t uint_t;
#define OK 0
#define ERROR -1
// 对互斥量进行了封装 只能有一个线程拿到锁
int thread_mutex_create(pthread_mutex_t *mtx);
int thread_mutex_destroy(pthread_mutex_t *mtx);
int thread_mutex_lock(pthread_mutex_t *mtx);
int thread_mutex_unlock(pthread_mutex_t *mtx);
// 对条件变量进行了封装 上锁后,阻塞等待信号发生,这样就可以触发任务
int thread_cond_create(pthread_cond_t *cond);
int thread_cond_destroy(pthread_cond_t *cond);
int thread_cond_signal(pthread_cond_t *cond);
int thread_cond_wait(pthread_cond_t *cond, pthread_mutex_t *mtx);
#ifdef __cplusplus
}
#endif
#endif /* _DEMO_THREAD_H_INCLUDED_ */
thread_mutex.c
#include "thread.h"
int
thread_mutex_create(pthread_mutex_t *mtx)
{
int err;
pthread_mutexattr_t attr; // 互斥量属性
err = pthread_mutexattr_init(&attr);
if (err != 0) {
// 向标准出错中输入
fprintf(stderr, "pthread_mutexattr_init() failed, reason: %s\n", strerror(errno));
return ERROR;
}
/*
PTHREAD_MUTEX_ERRORCHECK:检测锁 就是防止死锁发生
如果这个线程已经拿到锁了,然后还申请拿锁,如果不做处理就会照成死锁
遇到这个情况设置PTHREAD_MUTEX_ERRORCHECK属性就会报错
*/
err = pthread_mutexattr_settype(&attr, PTHREAD_MUTEX_ERRORCHECK);
if (err != 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "pthread_mutexattr_settype(PTHREAD_MUTEX_ERRORCHECK) failed, reason: %s\n", strerror(errno));
return ERROR;
}
// 使用 attr 初始化mtx锁 初始化后销毁 attr
err = pthread_mutex_init(mtx, &attr);
if (err != 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "pthread_mutex_init() failed, reason: %s\n", strerror(errno));
return ERROR;
}
err = pthread_mutexattr_destroy(&attr);
if (err != 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "pthread_mutexattr_destroy() failed, reason: %s\n", strerror(errno));
}
return OK;
}
// 销毁互斥量
int
thread_mutex_destroy(pthread_mutex_t *mtx)
{
int err;
err = pthread_mutex_destroy(mtx);
if (err != 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "pthread_mutex_destroy() failed, reason: %s\n", strerror(errno));
return ERROR;
}
return OK;
}
// 上锁
int
thread_mutex_lock(pthread_mutex_t *mtx)
{
int err;
err = pthread_mutex_lock(mtx);
if (err == 0) {
return OK;
}
fprintf(stderr, "pthread_mutex_lock() failed, reason: %s\n", strerror(errno));
return ERROR;
}
// 解锁
int
thread_mutex_unlock(pthread_mutex_t *mtx)
{
int err;
err = pthread_mutex_unlock(mtx);
#if 0
ngx_time_update();
#endif
if (err == 0) {
return OK;
}
fprintf(stderr, "pthread_mutex_unlock() failed, reason: %s\n", strerror(errno));
return ERROR;
}
thread_cond.c
#include "thread.h"
// 对条件变量进行了封装
int
thread_cond_create(pthread_cond_t *cond)
{
int err;
// 参数:cond: 条件变量指针 attr:条件变量高级属性
err = pthread_cond_init(cond, NULL);
if (err == 0) {
return OK;
}
fprintf(stderr, "pthread_cond_init() failed, reason: %s\n",strerror(errno));
return ERROR;
}
int
thread_cond_destroy(pthread_cond_t *cond)
{
int err;
err = pthread_cond_destroy(cond);
if (err == 0) {
return OK;
}
fprintf(stderr, "pthread_cond_destroy() failed, reason: %s\n",strerror(errno));
return ERROR;
}
int
thread_cond_signal(pthread_cond_t *cond)
{
int err;
err = pthread_cond_signal(cond);
if (err == 0) {
return OK;
}
fprintf(stderr, "pthread_cond_signal() failed, reason: %s\n",strerror(errno));
return ERROR;
}
int
thread_cond_wait(pthread_cond_t *cond, pthread_mutex_t *mtx)
{
int err;
err = pthread_cond_wait(cond, mtx);
if (err == 0) {
return OK;
}
fprintf(stderr, "pthread_cond_wait() failed, reason: %s\n",strerror(errno));
return ERROR;
}
线程池实现
thread_pool.h
#ifndef _THREAD_POOL_H_INCLUDED_
#define _THREAD_POOL_H_INCLUDED_
// 因为我们执行的是cpp程序,所以要告诉编译器下方的函数都以C语言方式编译
#ifdef __cplusplus
extern "C" {
#endif
#include "thread.h"
/*
1.线程数太多,导致线程切换比较多,所以效率比较低,
但是如果阻塞的任务比较多,那么多开点线程,就会比较快
2.任务队列不可以无限多,因为每一个任务都占有内存,内存不可能无限多
*/
#define DEFAULT_THREADS_NUM 8 // 默认线程数8,因为我电脑核数为8
#define DEFAULT_QUEUE_NUM 65535 // 任务队列最大容量
typedef unsigned long atomic_uint_t;
typedef struct thread_task_s thread_task_t;// 线程任务
typedef struct thread_pool_s thread_pool_t;// 线程池
// 任务结构体
struct thread_task_s {
thread_task_t *next; // 链表的下一个节点
uint_t id; // 每一个任务都有一个id
void *ctx; // 处理函数的参数
void(*handler)(void *data); // 指向任务处理函数
};
typedef struct {
thread_task_t *first;
thread_task_t **last;// 指向最后一个节点,插入的时候直接使用这个
} thread_pool_queue_t;
// thread_pool_queue_init(q); 相当于:(q)->first = NULL;(q)->last = &(q)->first;
// 以后插入任务的时候只需要 last->next = 任务 , 不需要动用first
#define thread_pool_queue_init(q) \
(q)->first = NULL; \
(q)->last = &(q)->first
struct thread_pool_s {
pthread_mutex_t mtx; // 互斥锁
thread_pool_queue_t queue; // 任务队列
int_t waiting;// 没有处理的任务数
pthread_cond_t cond; // 条件变量
char *name; // 线程池的名字
uint_t threads;// 线程池中线程数量
int_t max_queue;// 队列的长度,队列中任务的容纳量
};
thread_task_t *thread_task_alloc(size_t size);// 给任务和处理任务的函数参数分配内存
void thread_task_free(thread_task_t* task);// 释放内存
int_t thread_task_post(thread_pool_t *tp, thread_task_t *task);// 把任务放入线程池
thread_pool_t* thread_pool_init();// 对线程池初始化
void thread_pool_destroy(thread_pool_t *tp);// 销毁线程池
#ifdef __cplusplus
}
#endif
#endif /* _THREAD_POOL_H_INCLUDED_ */
thread_pool.cpp
#include "thread_pool.h"
static void thread_pool_exit_handler(void *data);// 线程自杀
static void *thread_pool_cycle(void *data);//线程池的主循环
static int_t thread_pool_init_default(thread_pool_t *tpp, char *name);// 线程池默认参数
static uint_t thread_pool_task_id;
static int debug = 0;
thread_pool_t* thread_pool_init()
{
int err;
pthread_t tid;
uint_t n;
pthread_attr_t attr;
thread_pool_t *tp=NULL;
// 使用calloc初始化内存,初始内存会置零
tp = (thread_pool_t*)calloc(1,sizeof(thread_pool_t));
if(tp == NULL){
fprintf(stderr, "thread_pool_init: calloc failed!\n");
return NULL;
}
thread_pool_init_default(tp, NULL);// 初始化线程池
thread_pool_queue_init(&tp->queue);// 会使用宏定义替换
// 创建互斥锁和条件变量
if (thread_mutex_create(&tp->mtx) != OK) {
free(tp);
return NULL;
}
if (thread_cond_create(&tp->cond) != OK) {
(void) thread_mutex_destroy(&tp->mtx);
free(tp);
return NULL;
}
err = pthread_attr_init(&attr);// 给线程做初始化
if (err) {
fprintf(stderr, "pthread_attr_init() failed, reason: %s\n",strerror(errno));
free(tp);
return NULL;
}
/*
PTHREAD_CREATE_DETACHED:意思就是和主线程断绝关系,主线程使用pthread_join 无法等待到结束的子进程
*/
err = pthread_attr_setdetachstate(&attr, PTHREAD_CREATE_DETACHED);
if (err) {
fprintf(stderr, "pthread_attr_setdetachstate() failed, reason: %s\n",strerror(errno));
free(tp);
return NULL;
}
/*
原型:int pthread_create (pthread_t *thread,pthread_attr_t *attr,
void *(*start_routine)(void*), void *arg);
参数:thread, 指向新线程的标识符。是一个传出参数
attr, 用来设置新线程的属性。一般取默认属性,即该参数取NULL
start_routine, 该线程的处理函数
该函数的返回类型和参数类型都是void*
arg, 线程处理函数start_routine的参数
*/
for (n = 0; n < tp->threads; n++) {
// 参数:tid , attr , 线程启动后执行函数 , thread_pool_cycle的参数
// thread_pool_cycle:线程池的主循环
err = pthread_create(&tid, &attr, thread_pool_cycle, tp);
if (err) {
fprintf(stderr, "pthread_create() failed, reason: %s\n",strerror(errno));
free(tp);
return NULL;
}
}
(void) pthread_attr_destroy(&attr);// 销毁设置属性
return tp;
}
// 线程池的销毁
void thread_pool_destroy(thread_pool_t *tp)
{
/* 我要干掉你这个线程就让你执行一个自杀函数就行了*/
uint_t n;
thread_task_t task;
volatile uint_t lock; // 无符号整形数
memset(&task,'\0', sizeof(thread_task_t));
task.handler = thread_pool_exit_handler;// 函数执行自杀
task.ctx = (void *) &lock;
// 自杀所有线程
for (n = 0; n < tp->threads; n++) {
lock = 1;
// 向线程池中投递任务
if (thread_task_post(tp, &task) != OK) {
return;
}
while (lock) {
sched_yield();// 线程放弃CPU的优先权
}
// 当自杀任务被执行完毕后,就会把这个任务从线程池中移除,详情参见thread_pool_cycle的源码实现
//task.event.active = 0;
}
(void) thread_cond_destroy(&tp->cond);
(void) thread_mutex_destroy(&tp->mtx);
free(tp);
}
// 函数执行自杀
static void
thread_pool_exit_handler(void *data)
{
uint_t *lock = (uint_t *)data;
*lock = 0;
pthread_exit(0);
}
// size:任务函数所要带的参数大小
thread_task_t *
thread_task_alloc(size_t size)
{
thread_task_t *task;
// 一起分配内存:任务结构体 , 任务大小
task = (thread_task_t *)calloc(1,sizeof(thread_task_t) + size);
if (task == NULL) {
return NULL;
}
// 相当于task移动了sizeof(thread_task_t)个字节
// 即被内存分成两份第一份放thread_task_t,第二份放ctx
task->ctx = task + 1;
return task;
}
void thread_task_free(thread_task_t * task)
{
if (task) {
free(task);
task = NULL;
}
}
// 往线程池中投递任务
int_t
thread_task_post(thread_pool_t *tp, thread_task_t *task)
{
// 上锁 独立占有线程池结构
if (thread_mutex_lock(&tp->mtx) != OK) {
return ERROR;
}
// 不可超过最大队列
if (tp->waiting >= tp->max_queue) {
// 解锁 ,打印队列已经满了
(void) thread_mutex_unlock(&tp->mtx);
fprintf(stderr,"thread pool \"%s\" queue overflow: %ld tasks waiting\n",
tp->name, tp->waiting);
return ERROR;
}
//task->event.active = 1;
// thread_pool_task_id:是一个全局的静态变量
task->id = thread_pool_task_id++;
task->next = NULL;
// 发送信号 唤醒条件变量锁
if (thread_cond_signal(&tp->cond) != OK) {
(void) thread_mutex_unlock(&tp->mtx);
return ERROR;
}
// 向链表尾部插入任务
*tp->queue.last = task;
tp->queue.last = &task->next;
// 等待任务数量 +1
tp->waiting++;
(void) thread_mutex_unlock(&tp->mtx);
if(debug)fprintf(stderr,"task #%lu added to thread pool \"%s\"\n",
task->id, tp->name);
return OK;
}
static void *
thread_pool_cycle(void *data)
{
thread_pool_t *tp = (thread_pool_t *)data; // 拿到线程池结构体
int err;
thread_task_t *task;
if(debug)fprintf(stderr,"thread in pool \"%s\" started\n", tp->name);
for ( ;; ) {
// 上锁 自己独占资源,因为多线程一起访问的话很容易出错,比如多个线程对链表操作
if (thread_mutex_lock(&tp->mtx) != OK) {
return NULL;
}
// 上锁后,线程会拿到一个任务
tp->waiting--;
// 判断池子中有没有任务
while (tp->queue.first == NULL) {
//如果没有任务
// thread_cond_wait :解锁-阻塞等待信号-信号来了-加锁-执行任务
//当有任务来的时候,就会被唤醒 条件锁
if (thread_cond_wait(&tp->cond, &tp->mtx)
!= OK)
{
// 函数执行错误就解锁
(void) thread_mutex_unlock(&tp->mtx);
return NULL;
}
}
// 拿到队列中的任务后,把队列中这个任务去除即first指向下一个任务
task = tp->queue.first;
tp->queue.first = task->next;
if (tp->queue.first == NULL) {
tp->queue.last = &tp->queue.first;
}
//解锁
if (thread_mutex_unlock(&tp->mtx) != OK) {
return NULL;
}
if(debug) fprintf(stderr,"run task #%lu in thread pool \"%s\"\n",
task->id, tp->name);
task->handler(task->ctx);// 处理任务
if(debug) fprintf(stderr,"complete task #%lu in thread pool \"%s\"\n",task->id, tp->name);
task->next = NULL;
//释放task
// free(task); // 一次性把thread_task_t和处理任务的参数一起释放了
thread_task_free(task);
//notify
}
}
// 设置默认属性
static int_t
thread_pool_init_default(thread_pool_t *tpp, char *name)
{
if(tpp)
{
tpp->threads = DEFAULT_THREADS_NUM;// 设置线程数
tpp->max_queue = DEFAULT_QUEUE_NUM;// 最大队列数
tpp->name = strdup(name?name:"default");// 设置线程池名字
if(debug)fprintf(stderr,
"thread_pool_init, name: %s ,threads: %lu max_queue: %ld\n",
tpp->name, tpp->threads, tpp->max_queue);
return OK;
}
return ERROR;
}