定义于头文件 <stack>
| template< class T, |
std::stack 类是容器适配器,它给予程序员栈的功能——特别是 FILO (先进后出)数据结构。
该类模板表现为底层容器的包装器——只提供特定函数集合。栈从被称作栈顶的容器尾部推弹元素。
构造 stack
std::stack<T,Container>::stack| stack() : stack(Container()) { } | (1) | (C++11 起) |
| explicit stack( const Container& cont = Container() ); | (2) | (C++11 前) |
| explicit stack( const Container& cont ); | (C++11 起) | |
| explicit stack( Container&& cont ); | (3) | (C++11 起) |
| stack( const stack& other ); | (4) | |
| stack( stack&& other ); | (5) | (C++11 起) |
| template< class Alloc > | (6) | (C++11 起) |
| template< class Alloc > | (7) | (C++11 起) |
| template< class Alloc > | (8) | (C++11 起) |
| template< class Alloc > | (9) | (C++11 起) |
| template< class Alloc > | (10) | (C++11 起) |
从各种数据源构造容器适配器的新底层容器。
1) 默认构造函数。值初始化容器。
2) 以 cont 的内容复制构造底层容器 c 。此亦为默认构造函数。 (C++11 前)
3) 以 std::move(cont) 移动构造底层容器 c 。
4) 复制构造函数。适配器以 other.c 的内容复制构造。(隐式声明)
5) 移动构造函数。适配器以 std::move(other.c) 构造。(隐式声明)
6-10) 仅若 std::uses_allocator<container_type, Alloc>::value == true ,即底层容器是具分配器容器(对所有标准库容器为 true )才定义下列构造函数。
6) 以 alloc 为分配器构造底层容器,如同以 c(alloc) 。
7) 用 cont 的内容,并以 alloc 为分配器构造底层容器,如同以 c(cont, alloc) 。
8) 以 cont 的内容用移动语义,同时以 alloc 为分配器构造底层容器,如同以 c(std::move(cont), alloc) 。
9) 以 other.c 的内容,并以 alloc 为分配器构造适配器,如同以 c(other.c, alloc) 。
10) 以 other 的内容使用移动语义,并以 alloc 为分配器构造适配器,如同以 c(std::move(other.c), alloc) 。
参数
| alloc | - | 用于底层容器所有内存分配的分配器 |
| other | - | 用作源初始化底层容器的另一容器适配器 |
| cont | - | 用作源初始化底层容器的容器 |
| first, last | - | 用以初始化的元素 |
| 类型要求 | ||
- Alloc 必须满足分配器 (Allocator) 的要求。 | ||
- Container 必须满足容器 (Container) 的要求。仅若 Container 满足具分配器容器 (AllocatorAwareContainer) 的要求才定义构造函数 (5-10) | ||
- InputIt 必须满足遗留输入迭代器 (LegacyInputIterator) 的要求。 | ||
复杂度
同被包装容器上的对应操作。
析构 stack
std::stack<T,Container>::~stack| ~stack(); |
销毁容器适配器。调用元素的析构函数,然后解分配所用的存储。注意,若元素是指针,则不销毁所指向的对象。
复杂度
与容器适配器大小成线性。
调用示例
#include <iostream>
#include <forward_list>
#include <string>
#include <iterator>
#include <algorithm>
#include <functional>
#include <stack>
#include <deque>
#include <time.h>
using namespace std;
struct Cell
{
int x;
int y;
Cell() = default;
Cell(int a, int b): x(a), y(b) {}
Cell &operator +=(const Cell &cell)
{
x += cell.x;
y += cell.y;
return *this;
}
Cell &operator +(const Cell &cell)
{
x += cell.x;
y += cell.y;
return *this;
}
Cell &operator *(const Cell &cell)
{
x *= cell.x;
y *= cell.y;
return *this;
}
Cell &operator ++()
{
x += 1;
y += 1;
return *this;
}
bool operator <(const Cell &cell) const
{
if (x == cell.x)
{
return y < cell.y;
}
else
{
return x < cell.x;
}
}
bool operator >(const Cell &cell) const
{
if (x == cell.x)
{
return y > cell.y;
}
else
{
return x > cell.x;
}
}
bool operator ==(const Cell &cell) const
{
return x == cell.x && y == cell.y;
}
};
std::ostream &operator<<(std::ostream &os, const Cell &cell)
{
os << "{" << cell.x << "," << cell.y << "}";
return os;
}
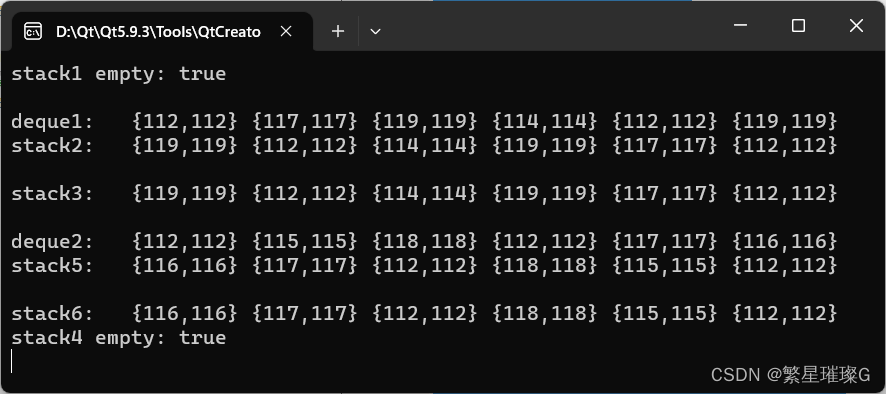
void stackPrint(const std::string &name, std::stack<Cell> &stack)
{
std::cout << name ;
while (stack.size() > 0)
{
std::cout << stack.top() << " ";
stack.pop();
}
std::cout << std::endl;
}
int main()
{
std::cout << std::boolalpha;
std::mt19937 g{std::random_device{}()};
srand((unsigned)time(NULL));
auto generate = []()
{
int n = std::rand() % 10 + 110;
Cell cell{n, n};
return cell;
};
//1) 默认构造函数。值初始化容器。
std::stack<Cell> stack1;
std::cout << "stack1 empty: " << stack1.empty() << std::endl;
std::cout << std::endl;
std::deque<Cell> deque1(6);
std::generate(deque1.begin(), deque1.end(), generate);
std::cout << "deque1: ";
std::copy(deque1.begin(), deque1.end(), std::ostream_iterator<Cell>(std::cout, " "));
std::cout << std::endl;
//2) 以 cont 的内容复制构造底层容器 c 。
std::stack<Cell> stack2(deque1);
stackPrint("stack2: ", stack2);
std::cout << std::endl;
//3) 以 std::move(cont) 移动构造底层容器 c 。
std::stack<Cell> stack3(std::move(deque1));
stackPrint("stack3: ", stack3);
std::cout << std::endl;
std::deque<Cell> deque2(6);
std::generate(deque2.begin(), deque2.end(), generate);
std::cout << "deque2: ";
std::copy(deque2.begin(), deque2.end(), std::ostream_iterator<Cell>(std::cout, " "));
std::cout << std::endl;
std::stack<Cell> stack4(deque2);
//4) 复制构造函数。适配器以 other.c 的内容复制构造。
std::stack<Cell> stack5(stack4);
stackPrint("stack5: ", stack5);
std::cout << std::endl;
//5) 移动构造函数。适配器以 std::move(other.c) 构造。
std::stack<Cell> stack6(std::move(stack4));
stackPrint("stack6: ", stack6);
std::cout << "stack4 empty: " << stack4.empty() << std::endl;
return 0;
}输出