SentenceTransformer使用范例
1使用SentenceTransformers获得句子向量嵌入
from sentence_transformers import SentenceTransformer
#模型下载
model = SentenceTransformer('paraphrase-MiniLM-L6-v2')
# 编码句子
sentences = ['Python is an interpreted high-level general-purpose programming language.',
'Python is dynamically-typed and garbage-collected.',
'The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog.']
# 获得句子嵌入向量
embeddings = model.encode(sentences)
# 打印嵌入向量
for sentence, embedding in zip(sentences, embeddings):
print("Sentence:", sentence)
print("Embedding:", embedding)
print("")
# Sentence: Python is an interpreted high-level general-purpose programming language.
# Embedding: [-1.17965914e-01 -4.57159936e-01 -5.87313235e-01 -2.72477478e-01 ...
# ...
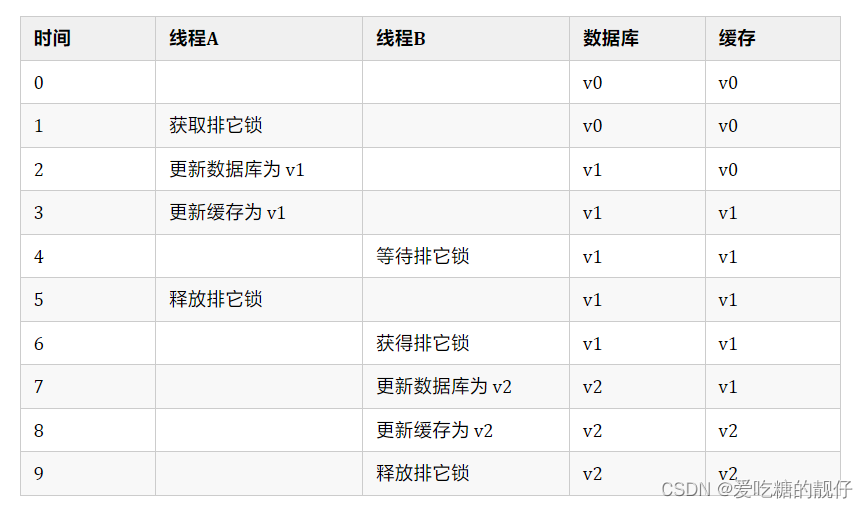
2计算句子或者词语的余弦相似度
- 余弦相似度(Cosine Similarity)是n维空间中两个n维向量之间角度的余弦。它等于两个向量的点积(向量积)除以两个向量长度(或大小)的乘积。
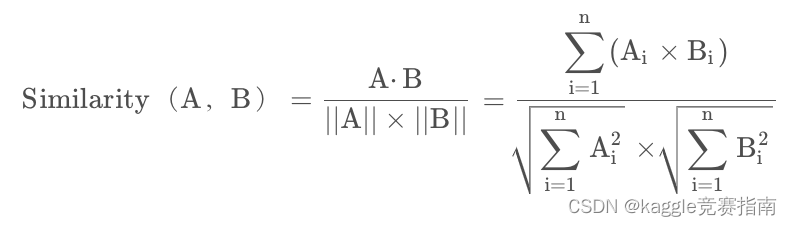
取值范围为[-1:1],取值为-1表示完全不相似,取值为1表示完全相似
from sentence_transformers import SentenceTransformer, util
# 加载模型
model = SentenceTransformer('paraphrase-MiniLM-L6-v2')
# 句子
sentences = ['Python is an interpreted high-level general-purpose programming language.',
'Python is dynamically-typed and garbage-collected.',
'The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog.']
# 讲语句进行向量编码
embeddings = model.encode(sentences)
# 计算相似度
sim = util.cos_sim(embeddings[0], embeddings[1])
print("{0:.4f}".format(sim.tolist()[0][0])) # 0.6445
sim = util.cos_sim(embeddings[0], embeddings[2])
print("{0:.4f}".format(sim.tolist()[0][0])) # 0.0365
3语义搜索
语义搜索通过理解搜索查询的内容来提高搜索的准确性,而不是仅仅依赖于词汇匹配。这是利用嵌入之间的相似性完成的。
语义搜索是将语料库中的所有条目嵌入到向量空间中。在搜索时,查询也会被嵌入到相同的向量空间中,并从语料库中找到最接近的嵌入。
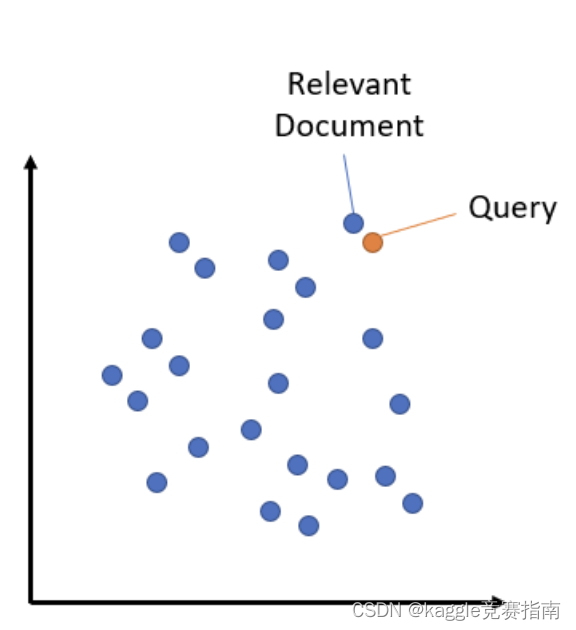
语料库中文档的插入和查询的嵌入
# 下载模型
model = SentenceTransformer('paraphrase-MiniLM-L6-v2')
# Corpus of documents and their embeddings
corpus = ['Python is an interpreted high-level general-purpose programming language.',
'Python is dynamically-typed and garbage-collected.',
'The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog.']
corpus_embeddings = model.encode(corpus)
# Queries and their embeddings
queries = ["What is Python?", "What did the fox do?"]
queries_embeddings = model.encode(queries)
# Find the top-2 corpus documents matching each query
hits = util.semantic_search(queries_embeddings, corpus_embeddings, top_k=2)
# Print results of first query
print(f"Query: {queries[0]}")
for hit in hits[0]:
print(corpus[hit['corpus_id']], "(Score: {:.4f})".format(hit['score']))
# Query: What is Python?
# Python is an interpreted high-level general-purpose programming language. (Score: 0.6759)
# Python is dynamically-typed and garbage-collected. (Score: 0.6219)
# Print results of second query
print(f"Query: {queries[1]}")
for hit in hits[1]:
print(corpus[hit['corpus_id']], "(Score: {:.4f})".format(hit['score']))
# Query: What did the fox do?
# The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog. (Score: 0.3816)
# Python is dynamically-typed and garbage-collected. (Score: 0.0713)
为了充分利用语义搜索,必须区分对称和非对称语义搜索,因为它会严重影响要使用的模型的选择。
文章参考:
5分钟 NLP系列 — SentenceTransformers 库介绍
Sentence Transformer官网