目录
Vue.extend(option)
delimiters
functional
Vue.component(id, Function | Object)
Vue.directive( id, [definition] )
Vue.filter( id, function)
Vue.nextTick()
Vue.set()
Vue.delete(target, index/key)
Vue.compile(template)
Vue.observable(object)
provide/inject
extends、mixins
Vue.extend(option)
作用:返回一个vue子组件的构造函数
参数:创建vue实例的参数
<template>
<div id="home">
<div>home</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import Vue from 'vue'
export default {
name: "",
mounted() {
// 创建子组件构造函数 VueComponent
var VueComponentFun = Vue.extend({
template: "<p>{{firstName}} {{lastName}} aka {{alias}}</p>",
data: function () {
return {
firstName: "Walter",
lastName: "White",
alias: "Heisenberg",
};
},
});
// 挂载到一个元素上。
new VueComponentFun().$mount("#home");
},
};
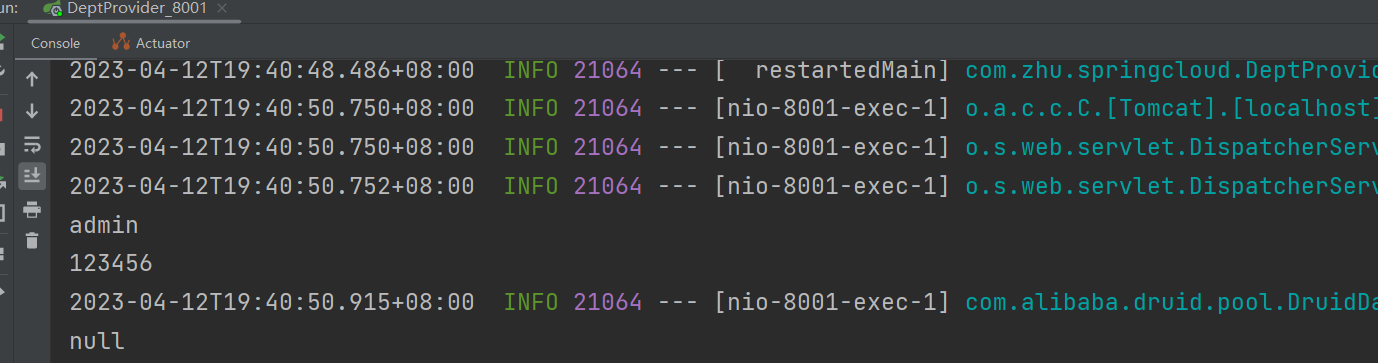
</script>home节点被替换掉,渲染结果如下
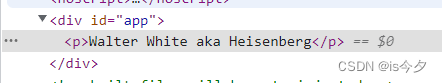
源码:
- 调用Vue.prototype._init()进行数据初始化 - created周期
- 继承原型上的extend、mixin、use、component, directive, filter
Vue.extend = function (extendOptions) {
extendOptions = extendOptions || {};
var Super = this;
......
//创建子类(子组件构造函数),先调用父类的方法进行初始化
var Sub = function VueComponent(options) {
this._init(options);
};
//创建子类的原型对象
Sub.prototype = Object.create(Super.prototype);
Sub.prototype.constructor = Sub;
Sub.options = mergeOptions(Super.options, extendOptions);
Sub['super'] = Super;
//对props属性做set、get拦截
if (Sub.options.props) {
initProps(Sub);
}
if (Sub.options.computed) {
initComputed(Sub);
}
Sub.extend = Super.extend;
Sub.mixin = Super.mixin;
Sub.use = Super.use;
//赋值生命周期
ASSET_TYPES.forEach(function (type) {
Sub[type] = Super[type];
});
......
return Sub;
};delimiters
作用:分隔符,定义 模板字符串的变量标识
上面的代码可改为
template: "<p @click='add'>{firstName} {lastName} aka {num}</p>",
delimiters: ['{', '}'],functional
作用:函数组件,没有响应式数据,也没有实例(this),使用functional:true生命,使用render生成Dom
优点: 1.使用render 函数返回虚拟节点使它们渲染的代价更小;2.不需要实例化
Vue.component('custom-component', Vue.extend({
functional: true,
props: {
params: String,
},
render: function (h, context) {
let props = context.props
return h('div', { class: 'custom' }, [
h('div', {
domProps: {
innerText: props.params,
},
class: ['custom_button'],
on: {
click: () => {
console.log("click")
},
},
})
])
}
}))Vue.component(id, Function | Object)
作用:注册或获取全局组件
有下面两种方法生成组件
// 注册组件,传入一个扩展过的构造器
Vue.component('my-component', Vue.extend({ /* ... */ }))
// 注册组件,传入一个选项对象 (自动调用 Vue.extend)
Vue.component('my-component', { /* ... */ })Vue.directive( id, [definition] )
作用:添加自定义指令,可以在绑定的元素未插入到Dom内时,判断Dom是否存在
参数:指令名称、函数
回调参数:
el:指令绑定到的元素
binding:指令接收的参数
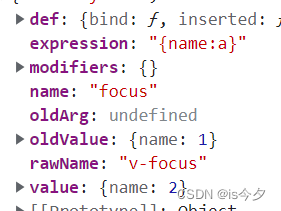
- value:指令绑定的对象
- oldValue:指令绑定的对象修改之前的值
- expression:字符串形式的指令表达式
Vue.directive('focus', {
// 指令与元素成功绑定时调用
bind: function (el, binding) {
},
// 当被绑定的元素插入到 DOM 中时……
inserted: function (el, binding) {
},
// 命令所绑定的dom及数据有变化时,
update: function (el, binding) {
},
// 指令所在组件的 VNode 及其子 VNode 全部更新后调用
componentUpdated: function (el, binding) {
},
// 指令与元素解绑时调用
unbind: function (el, binding) {
}
})
<div v-focus="{name:a}"></div>Vue.filter( id, function)
作用:过滤器
参数:被处理的值、接受的其他传参(多个)
//main.js
Vue.filter('capitalize', function (value, a) {
// 被处理的值、参数...
if (!value) return "";
return value + a;
})
//home.vue
<template>
<div id="home">
<!-- 大括号绑定,页面显示11 -->
<div>{{ a | capitalize(10) }}</div>
<!-- v-bind绑定 -->
<A :pd="b | capitalize"></A>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import A from "./A.vue";
export default {
name: "",
components: {
A,
},
data() {
return {
a: 1,
};
},
};
</script>
源码:['component', 'directive', 'filter'] 直接返回回调函数
function initAssetRegisters(Vue) {
ASSET_TYPES.forEach(function (type) {
// @ts-expect-error function is not exact same type
Vue[type] = function (id, definition) {
if (!definition) {
return this.options[type + 's'][id];
}
else {
......
if (type === 'component' && isPlainObject(definition)) {
// @ts-expect-error
definition.name = definition.name || id;
// this.options._base = Vue构造函数,就是直接调用Vue.extend
definition = this.options._base.extend(definition);
}
if (type === 'directive' && isFunction(definition)) {
definition = { bind: definition, update: definition };
}
// 给当前实例this添加{id: definition}
this.options[type + 's'][id] = definition;
return definition;
}
};
});
}Vue.nextTick()
作用:在 DOM 更新循环结束之后执行延迟回调,vue修改数据时不能及时反映到页面上,需要一轮事务处理,才能获取到页面上修改过的值
参数:callback()、this
用法:
// 修改数据
vm.msg = 'Hello'
// DOM 还没有更新
Vue.nextTick(function () {
// DOM 更新了
})
// 作为一个 Promise 使用 (2.1.0 起新增,详见接下来的提示)
Vue.nextTick()
.then(function () {
// DOM 更新了
})注:使用第二种方法时,需要在支持Promise的环境中(IE不支持)

源码:
如果浏览器支持Promise,则使用Promise.resolve()返回一个Promise 对象(微任务),因为微任务会等待主线程的同步任务执行完毕,再执行微任务队列。微任务队列就是下列callbacks数组,这里面会放入回调函数,如果一次同步任务中有多个nextTick,则callback中会有多个回调函数。这些回调函数会在then()回调中执行。
var p_1 = Promise.resolve();
timerFunc = function () {
p_1.then(flushCallbacks);
if (isIOS)
setTimeout(noop);
};function nextTick(cb, ctx) {
// cb: 回调函数 ctx: this指向
var _resolve;
// 回调函数放入数组,如果短时间内多次调用nextTick,则数组中有多个回调函数
callbacks.push(function () {
if (cb) {
try {
cb.call(ctx);
}
catch (e) {
handleError(e, ctx, 'nextTick');
}
}
else if (_resolve) {
_resolve(ctx);
}
});
// 执行回调函数;
if (!pending) {
pending = true;
timerFunc();
}
// 支持.then写法
if (!cb && typeof Promise !== 'undefined') {
return new Promise(function (resolve) {
_resolve = resolve;
});
}
}
var timerFunc;
// 实现nextTick用了两种方法,Promise.then or MutationObserver
if (typeof Promise !== 'undefined' && isNative(Promise)) {
// 浏览器支持Promise的情况,使用Promise
// 创建微任务,微任务会等到主线程的代码执行完毕,再执行,所以p_1.then实现了nextTick的功能
var p_1 = Promise.resolve();
timerFunc = function () {
p_1.then(flushCallbacks);
if (isIOS)
setTimeout(noop);
};
isUsingMicroTask = true;
}
else if (!isIE &&
typeof MutationObserver !== 'undefined' &&
(isNative(MutationObserver) ||
// PhantomJS and iOS 7.x
MutationObserver.toString() === '[object MutationObserverConstructor]')) {
// Use MutationObserver where native Promise is not available,
// e.g. PhantomJS, iOS7, Android 4.4
var counter_1 = 1;
var observer = new MutationObserver(flushCallbacks);
var textNode_1 = document.createTextNode(String(counter_1));
observer.observe(textNode_1, {
characterData: true
});
timerFunc = function () {
counter_1 = (counter_1 + 1) % 2;
textNode_1.data = String(counter_1);
};
isUsingMicroTask = true;
}
else if (typeof setImmediate !== 'undefined' && isNative(setImmediate)) {
timerFunc = function () {
setImmediate(flushCallbacks);
};
}
else {
timerFunc = function () {
setTimeout(flushCallbacks, 0);
};
}Vue.set()
作用:向具有响应式的对象中添加property,且新的property具有响应式。在创建的过程中对该属性进行依赖收集
<template>
<div id="home">
<div id="customComA">{{ obj }}</div>
<div id="customComB">{{ arr }}</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import Vue from "vue";
export default {
name: "",
data() {
return {
obj: { name: "zz" },
arr: [1, 2]
};
},
mounted() {
// 无效
this.obj.age = 15
this.arr[1] = 10
// Vue.set
Vue.set(this.obj, 'age', 15)
Vue.set(this.obj, 1, 10)
},
};
</script>
源码实现:
- 对Array对象进行修改,对元素进行响应式化
- 对Object类型进行赋值,对赋值的新元素进行响应式
function set(target, key, val) {
// obj|arr , key|index
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && (isUndef(target) || isPrimitive(target))) {
warn$2("Cannot set reactive property on undefined, null, or primitive value: ".concat(target));
}
if (isReadonly(target)) {
process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && warn$2("Set operation on key \"".concat(key, "\" failed: target is readonly."));
return;
}
var ob = target.__ob__;
// 对Array对象进行修改,对元素进行响应式化
if (isArray(target) && isValidArrayIndex(key)) {
target.length = Math.max(target.length, key);
target.splice(key, 1, val);
// when mocking for SSR, array methods are not hijacked
if (ob && !ob.shallow && ob.mock) {
observe(val, false, true);
}
return val;
}
// object修改属性值
if (key in target && !(key in Object.prototype)) {
console.log("obj")
target[key] = val;
return val;
}
if (target._isVue || (ob && ob.vmCount)) {
process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' &&
warn$2('Avoid adding reactive properties to a Vue instance or its root $data ' +
'at runtime - declare it upfront in the data option.');
return val;
}
// 对空值的赋值不做其他处理
if (!ob) {
target[key] = val;
return val;
}
// object对象新增属性值
defineReactive(ob.value, key, val, undefined, ob.shallow, ob.mock);
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
ob.dep.notify({
type: "add" /* TriggerOpTypes.ADD */,
target: target,
key: key,
newValue: val,
oldValue: undefined
});
}
else {
ob.dep.notify();
}
return val;
}Vue.delete(target, index/key)
作用:删除属性,并触发有关dom的改变
对于Array,使用 target.splice(key, 1);
对于Object,使用 delete target[key]; 并触发监听器ob.dep.notify()
源码:
function del(target, key) {
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && (isUndef(target) || isPrimitive(target))) {
warn$2("Cannot delete reactive property on undefined, null, or primitive value: ".concat(target));
}
// 数组类型的直接操作
if (isArray(target) && isValidArrayIndex(key)) {
target.splice(key, 1);
return;
}
var ob = target.__ob__;
......
if (!hasOwn(target, key)) {
return;
}
// Object类型
delete target[key];
if (!ob) {
return;
}
// 通知删除的该元素关联的依赖
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
ob.dep.notify({
type: "delete" /* TriggerOpTypes.DELETE */,
target: target,
key: key
});
}
else {
ob.dep.notify();
}
}Vue.compile(template)
作用:将一个模板字符串编译成 render 函数(VNode)
//把解析的模板渲染,挂载到.home节点上
let res = Vue.compile("<div class='wrapper'>{{ msg }}</div>");
new Vue({
data: {
msg: "hello",
},
render: res.render,
// staticRenderFns: res.staticRenderFns,
}).$mount(".home");源码:
var _a = createCompiler(baseOptions)执行createCompiler函数,即createCompilerCreator函数,即执行 createCompiler函数,同时对baseCompile、compile函数进行缓存;
Vue.compile = compileToFunctions;
Vue.compile("<div class='wrapper'>{{ msg }}</div>");
1.执行createCompileToFunctionFn(compile),即compileToFunctions函数,判断缓存中是否有该模板的编译结果,如果有,取出返回;没有则执行compile函数,之后把获取到的编译结果res.render转化为函数形式,编译结果res写入缓存
2.执行compile函数,先执行baseCompile编译模板template,再在编译结果compiled上添加errors、tips(与options有关,没传入,暂不考虑)
3.执行baseCompile函数,把template模板字符串处理成ast(树状数据结构,未注入真实数据),调用generate把ast转化为render渲染函数字符串形式,返回{ast, render,staticRenderFns)
部分简略源码:
function createCompileToFunctionFn(compile) {
// compile, 一开始就被缓存的参数
var cache = Object.create(null); //对解析的模板进行缓存
return function compileToFunctions(template, options, vm) {
/**
* template: <div class='wrapper'><div>{{ msg }}</div></div>
* option未传
*/
console.log("1----compileToFunctions")
......
var key = template;
if (cache[key]) {
return cache[key];
}
// compile
var compiled = compile(template, options);
......
var res = {};
var fnGenErrors = [];
res.render = createFunction(compiled.render, fnGenErrors);
res.staticRenderFns = compiled.staticRenderFns.map(function (code) {
return createFunction(code, fnGenErrors);
});
......
return (cache[key] = res);
};
}
function createCompilerCreator(baseCompile) {
// baseCompile, 一开始就被缓存的参数
return function createCompiler(baseOptions) {
// 先调用createCompiler,什么都不执行,只返回return {compile, compileToFunctions}
function compile(template, options) {
console.log("2----compile")
var finalOptions = Object.create(baseOptions);
......
var compiled = baseCompile(template.trim(), finalOptions);
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
detectErrors(compiled.ast, warn);
}
compiled.errors = errors;
compiled.tips = tips;
return compiled;
}
return {
compile: compile,
compileToFunctions: createCompileToFunctionFn(compile)
};
};
}
var createCompiler = createCompilerCreator(
function baseCompile(template, options) {
console.log("3----baseCompile")
var ast = parse(template.trim(), options); // 把template字符串处理成树状数据结构,未注入真实数据
var code = generate(ast, options); // code: {render, staticRenderFns}
return {
ast: ast,
render: code.render, // render函数
staticRenderFns: code.staticRenderFns
};
});
//入口
var _a = createCompiler(baseOptions), compileToFunctions = _a.compileToFunctions;
Vue.compile = compileToFunctions;
Vue.observable(object)
作用:让一个对象可响应,返回的对象可以直接用于渲染函数和计算属性内,并且会在发生变更时触发相应的更新。也可以作为最小化的跨组件状态存储器
1.使用计算属性
<template>
<div id="home">
<!-- 点击可改变obj、arr, 并能响应页面 -->
<div @click="changeObj">obj: {{ obj }}</div>
<div @click="changeArr">arr: {{ arr }}</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import Vue from "vue";
// 需要使用computed做中介,供页面使用
const state = Vue.observable({ arr: [1,2,3], obj: {name: 'haha', age: 10} });
console.log("state: ", state); //响应式数据
export default {
name: "",
data() {
return {
};
},
computed: {
obj(){
return state.obj
},
arr(){
return state.arr
}
},
methods: {
changeObj(){
state.obj.age++
},
changeArr(){
state.arr.push(10)
},
pushRouter(){
this.$router.push("/b")
}
},
};
</script>
2.把该步骤单独封装为文件,使用计算属性,可作为跨组件状态存储器使用
// store.js
import Vue from "vue";
const state = Vue.observable({ arr: [1,2,3], obj: {name: 'haha', age: 10} });
export default state
//A页面
<template>
<div>arr: {{ arr }}</div>
</template>
<script>
import state from "@/store/replaceStore.js";
export default {
computed: {
arr() {
return state.arr;
},
},
};
</script>
源码:
function initGlobalAPI(Vue) {
......
Vue.observable = function (obj) {
observe(obj);
return obj;
};
......
}
function observe(value, shallow, ssrMockReactivity) {
// 已经有响应式对象,直接retuen响应式对象
if (value && hasOwn(value, '__ob__') && value.__ob__ instanceof Observer) {
return value.__ob__;
}
......
return new Observer(value, shallow, ssrMockReactivity);
}
function Observer(value, shallow, mock) {
if (shallow === void 0) { shallow = false; }
if (mock === void 0) { mock = false; }
this.value = value;
this.shallow = shallow;
this.mock = mock;
this.dep = mock ? mockDep : new Dep();
this.vmCount = 0;
// 给value添加属性{__ob__: Observer对象}, 表示该数据value已经被响应式
def(value, '__ob__', this);
if (isArray(value)) {
if (!mock) {
if (hasProto) {
value.__proto__ = arrayMethods;
}
else {
// 对数组进行拦截
for (var i = 0, l = arrayKeys.length; i < l; i++) {
var key = arrayKeys[i];
def(value, key, arrayMethods[key]);
}
}
}
if (!shallow) {
this.observeArray(value);
}
}
else {
// 对每个属性进行响应式
var keys = Object.keys(value);
for (var i = 0; i < keys.length; i++) {
var key = keys[i];
defineReactive(value, key, NO_INIITIAL_VALUE, undefined, shallow, mock);
}
}
}provide/inject
作用:祖孙组件通信
provide:返回一个对象,或者一个返回对象的函数
inject:注入的字段名,可重命名
//返回一个对象
//父组件
provide: {
msg: 'haha', //--非响应式
name: this.name, //--简单类型,非响应式
arr: this.arr, //--Array、Object类型,响应式
},
//子组件
inject: ["name"],
//返回一个函数
//父组件
provide: {
name: () => this.subName, //--简单类型,响应式
},
//子组件
<template>
<div>name: {{ name() }}</div>
</template>
inject: ["name"],
v-once
模板只渲染一次,不会根据数据的变化而重新渲染模板
<transition>
vue内部自定义组件,可以设置过渡效果
参数:
- name,会根据name自动生成六个类名,表示不同的过渡阶段
extends、mixins
作用:扩展另一个组件,与minxins原理类似
extends会比mixins先执行。执行顺序:extends > mixins > 组件
<template>
<div id="home">
<div>firstName: {{ firstName }}</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "",
extends: {
data: function () {
return {
firstName: "Walter"
};
},
mounted() {
// console.log("mounted: ", this);
},
},
};
</script>
源码:使用深搜的方法,把extends、mixin的对象扁平化到组件一级
function mergeOptions(parent, child, vm) {
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
checkComponents(child);
}
if (isFunction(child)) {
// @ts-expect-error
child = child.options;
}
normalizeProps(child, vm);
normalizeInject(child, vm);
normalizeDirectives$1(child);
if (!child._base) {
if (child.extends) {
parent = mergeOptions(parent, child.extends, vm);
}
if (child.mixins) {
for (var i = 0, l = child.mixins.length; i < l; i++) {
parent = mergeOptions(parent, child.mixins[i], vm);
}
}
}
var options = {};
var key;
// 映射parent的key到一级
for (key in parent) {
mergeField(key);
}
// 映射child的key(parent没有的)到一级
for (key in child) {
if (!hasOwn(parent, key)) {
mergeField(key);
}
}
function mergeField(key) {
var strat = strats[key] || defaultStrat;
options[key] = strat(parent[key], child[key], vm, key);
}
// 把扁平化的数据返回
return options;
}

![[Java·算法·困难]LeetCode10. 正则表达式匹配](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/326ab5bd23ab4b0bbb50d746414769a2.png)