我们都知道,路由指的是组件和路径的一种映射关系。Router-view也被称为路由的出口,今天我们就探讨下如何去使用路由出口。
也就是:
路径--------------------------------------------------------------->页面
可以把router-view理解成一类代码存放的位置。
一.基本的路由配置(没用子集)
我们都知道所有的组成注册最终在app.vue注册完毕。
通过代码来分析:
import Vue from 'vue'
import VueRouter from 'vue-router'
Vue.use(VueRouter)
const routes = [
{
path: '/',
name: '首页',
// route level code-splitting
// this generates a separate chunk (about.[hash].js) for this route
// which is lazy-loaded when the route is visited.
component: () =>
import(/* webpackChunkName: "about" */ '../views/shouye.vue')
},
{
path: '/1',
name: 'About1',
// route level code-splitting
// this generates a separate chunk (about.[hash].js) for this route
// which is lazy-loaded when the route is visited.
component: () =>
import(/* webpackChunkName: "about" */ '../views/About.vue')
},
{
path: '/2',
name: 'About2',
// route level code-splitting
// this generates a separate chunk (about.[hash].js) for this route
// which is lazy-loaded when the route is visited.
component: () =>
import(/* webpackChunkName: "about" */ '../views/About1.vue')
},
{
path: '/3',
name: 'About3',
// route level code-splitting
// this generates a separate chunk (about.[hash].js) for this route
// which is lazy-loaded when the route is visited.
component: () =>
import(/* webpackChunkName: "about" */ '../views/About2.vue')
},
{
path: '/4',
name: 'About4',
// route level code-splitting
// this generates a separate chunk (about.[hash].js) for this route
// which is lazy-loaded when the route is visited.
component: () =>
import(/* webpackChunkName: "about" */ '../views/Aboutf.vue')
}
]
const router = new VueRouter({
mode: 'history',
base: process.env.BASE_URL,
routes
})
export default router在这里通过path路径来匹配组件。
打开页面之后。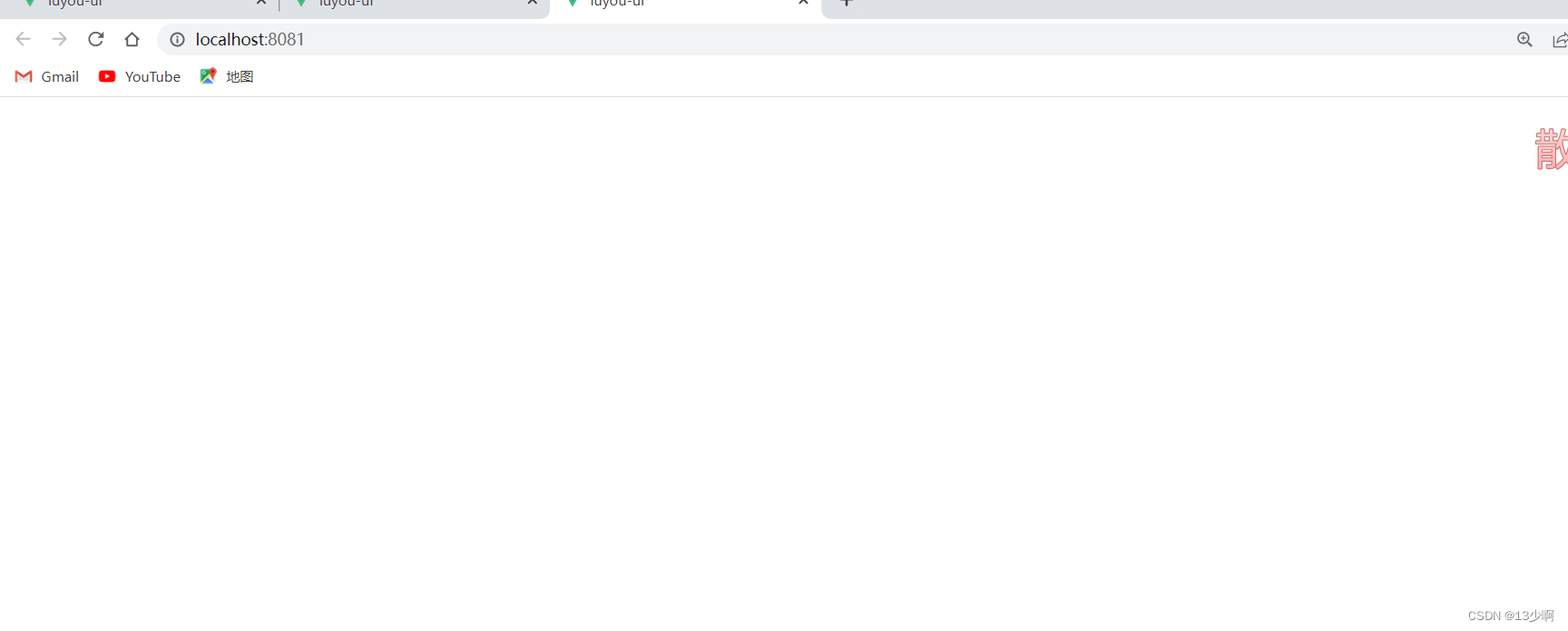
页面是空白的什么都没有。
为什么会出现这种状况呢?这里就和router-view有关了。
原因很简单,所对应的组件没有位置可放。
解决方法:
<template>
<div class="">
<router-view></router-view>
</div>
</template>
在App.vue加个路由组件存放的位置即可。
为什么不在其它的组件里面放router-view?
因为App.vue是根组件,最开始的页面就显示在这里。
加完之后
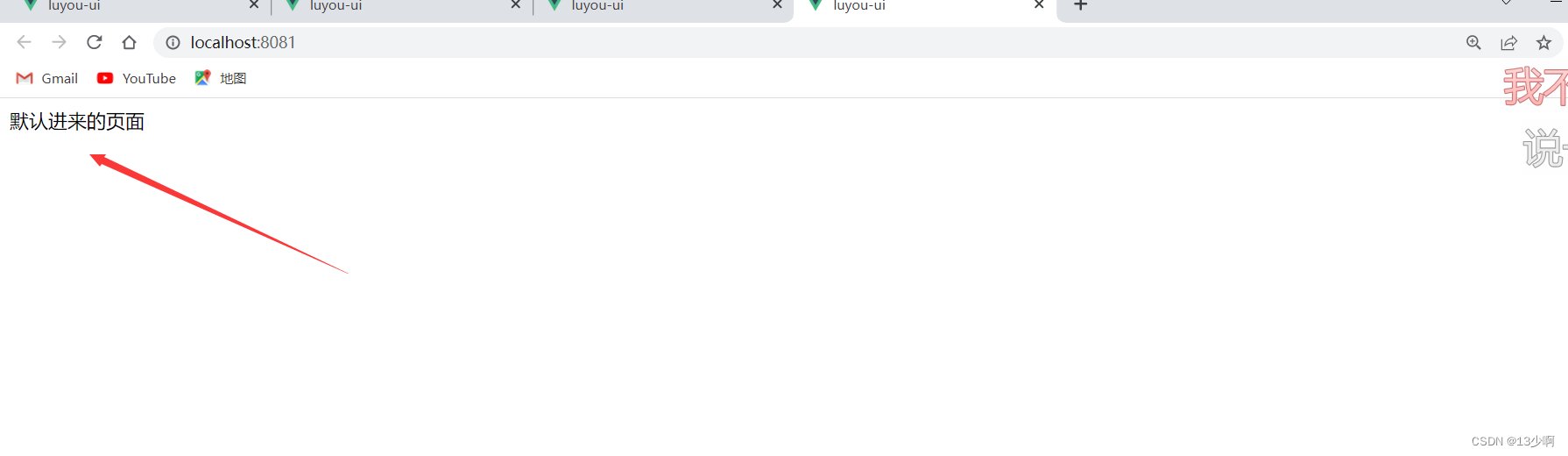
默认根组件显示的内容就显示出来了。
我们在换个路径/1
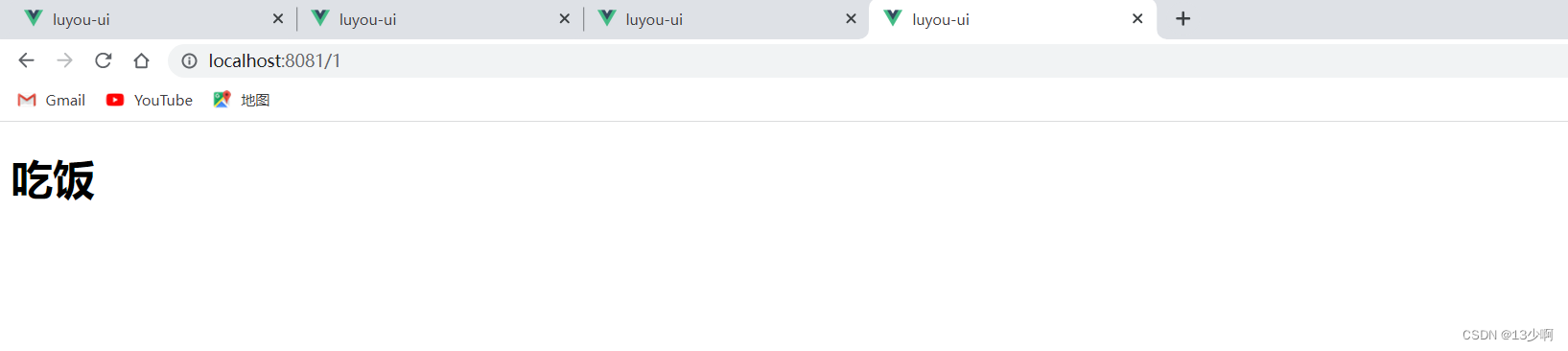
也是可以正常显示的。
二.有子集的路由配置
代码:
import Vue from 'vue'
import VueRouter from 'vue-router'
import a from '@/views/a.vue'
Vue.use(VueRouter)
const routes = [
{
path: '/',
name: '首页',
// route level code-splitting
// this generates a separate chunk (about.[hash].js) for this route
// which is lazy-loaded when the route is visited.
component: () =>
import(/* webpackChunkName: "about" */ '../views/shouye.vue'),
children: [
{
path: 'a',
component: a
}
]
},
{
path: '/1',
name: 'About1',
// route level code-splitting
// this generates a separate chunk (about.[hash].js) for this route
// which is lazy-loaded when the route is visited.
component: () =>
import(/* webpackChunkName: "about" */ '../views/About.vue')
},
{
path: '/2',
name: 'About2',
// route level code-splitting
// this generates a separate chunk (about.[hash].js) for this route
// which is lazy-loaded when the route is visited.
component: () =>
import(/* webpackChunkName: "about" */ '../views/About1.vue')
},
{
path: '/3',
name: 'About3',
// route level code-splitting
// this generates a separate chunk (about.[hash].js) for this route
// which is lazy-loaded when the route is visited.
component: () =>
import(/* webpackChunkName: "about" */ '../views/About2.vue')
},
{
path: '/4',
name: 'About4',
// route level code-splitting
// this generates a separate chunk (about.[hash].js) for this route
// which is lazy-loaded when the route is visited.
component: () =>
import(/* webpackChunkName: "about" */ '../views/Aboutf.vue')
}
]
const router = new VueRouter({
mode: 'history',
base: process.env.BASE_URL,
routes
})
export default router
可以看出在首页下,又放了一个a页面。
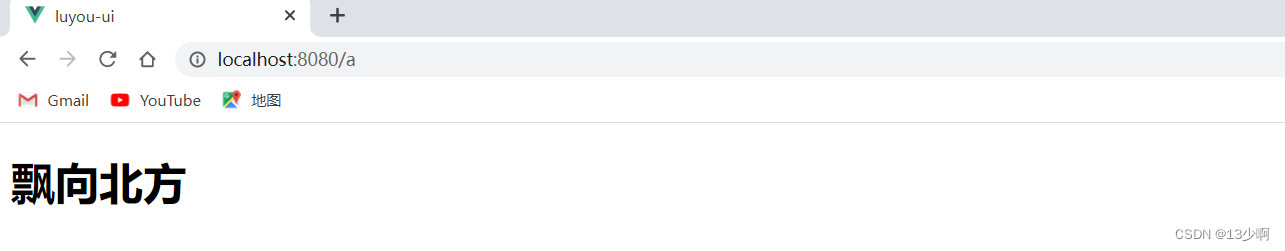
可以看出是无法访问的。
原因还是没有router-view,此时的router-view加在哪里呢?
加在当前一级路由里面。
代码:
<template>
<div class="">
<!-- 默认进来的页面 -->
<h1>飘向北方</h1>
<router-view></router-view>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: '',
methods: {}
}
</script>
<style scoped></style>
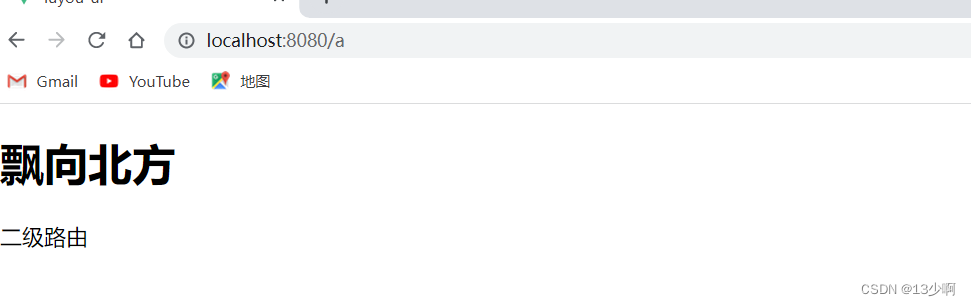
可以访问了
我们在再一级路由shouye下在加上一个二级路由。
代码:
import Vue from 'vue'
import VueRouter from 'vue-router'
import a from '@/views/a.vue'
import aa from '@/views/aa.vue'
Vue.use(VueRouter)
const routes = [
{
path: '/',
name: '首页',
// route level code-splitting
// this generates a separate chunk (about.[hash].js) for this route
// which is lazy-loaded when the route is visited.
component: () =>
import(/* webpackChunkName: "about" */ '../views/shouye.vue'),
children: [
{
path: 'a',
component: a
},
{
path: 'aa',
component: aa
}
]
},
{
path: '/1',
name: 'About1',
// route level code-splitting
// this generates a separate chunk (about.[hash].js) for this route
// which is lazy-loaded when the route is visited.
component: () =>
import(/* webpackChunkName: "about" */ '../views/About.vue')
},
{
path: '/2',
name: 'About2',
// route level code-splitting
// this generates a separate chunk (about.[hash].js) for this route
// which is lazy-loaded when the route is visited.
component: () =>
import(/* webpackChunkName: "about" */ '../views/About1.vue')
},
{
path: '/3',
name: 'About3',
// route level code-splitting
// this generates a separate chunk (about.[hash].js) for this route
// which is lazy-loaded when the route is visited.
component: () =>
import(/* webpackChunkName: "about" */ '../views/About2.vue')
},
{
path: '/4',
name: 'About4',
// route level code-splitting
// this generates a separate chunk (about.[hash].js) for this route
// which is lazy-loaded when the route is visited.
component: () =>
import(/* webpackChunkName: "about" */ '../views/Aboutf.vue')
}
]
const router = new VueRouter({
mode: 'history',
base: process.env.BASE_URL,
routes
})
export default router
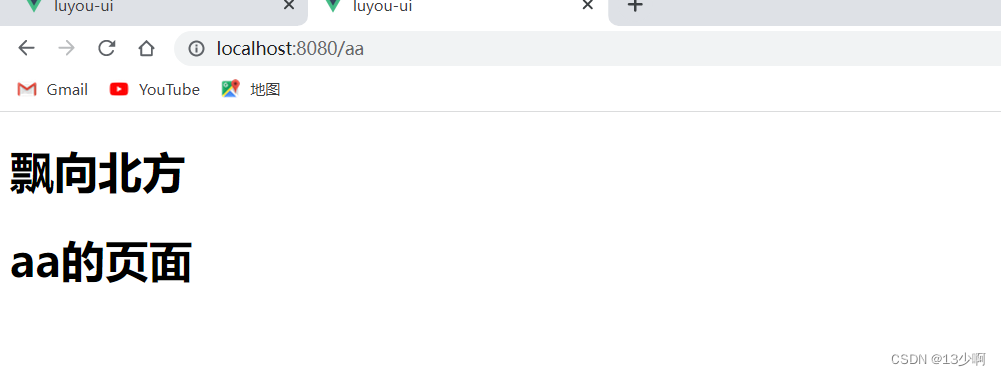
此时a页面消失了,但是aa页面是可以访问到的。
三.实战练习
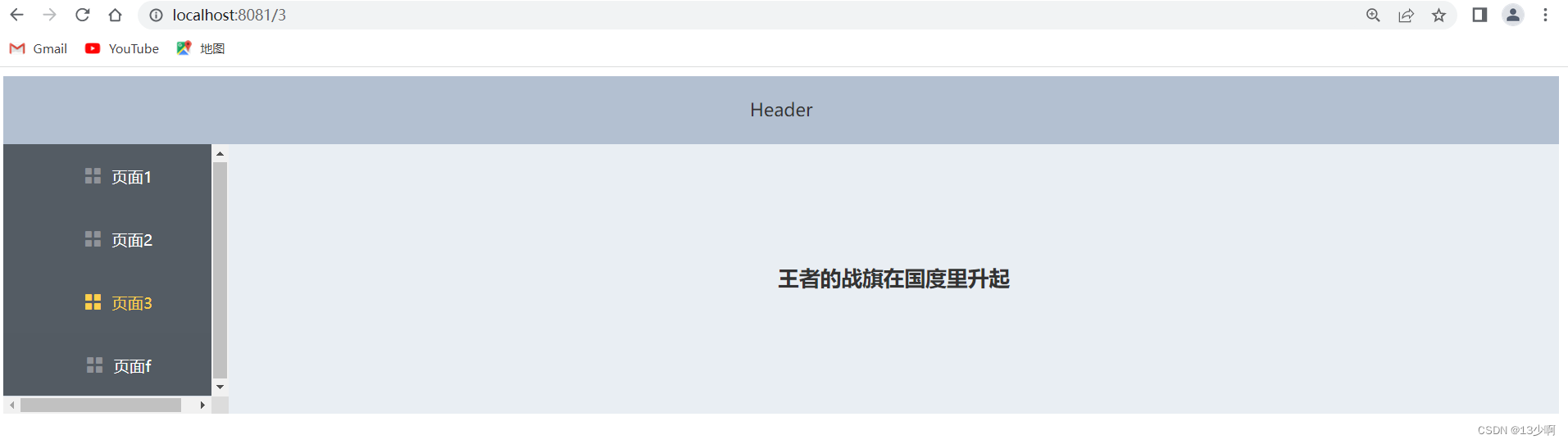
需求:左侧是侧边栏,右面是显示的内容。
代码:
router/index.js路由的配置
import Vue from 'vue'
import VueRouter from 'vue-router'
import a from '@/views/a.vue'
import aa from '@/views/aa.vue'
import a3 from '@/views/a3.vue'
import af from '@/views/af.vue'
Vue.use(VueRouter)
const routes = [
{
path: '/',
name: '首页',
// route level code-splitting
// this generates a separate chunk (about.[hash].js) for this route
// which is lazy-loaded when the route is visited.
component: () =>
import(/* webpackChunkName: "about" */ '../views/shouye.vue'),
children: [
{
path: '1',
component: a
},
{
path: '2',
component: aa
},
{
path: '3',
component: a3
},
{
path: 'f',
component: af
}
]
}
]
const router = new VueRouter({
mode: 'history',
base: process.env.BASE_URL,
routes
})
export default router
shouye.vue
<template>
<div class="">
<el-container>
<el-header>Header</el-header>
<el-container>
<el-aside width="200px">
<sideBar />
</el-aside>
<el-main>
<!-- 二级路的出口 -->
<router-view></router-view>
</el-main>
</el-container>
</el-container>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import sideBar from '@/views/sideBar/index.vue'
export default {
components: {
sideBar
},
name: '',
methods: {}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
.el-header,
.el-footer {
background-color: #b3c0d1;
color: #333;
text-align: center;
line-height: 60px;
}
.el-aside {
background-color: #d3dce6;
color: #333;
text-align: center;
line-height: 200px;
}
.el-main {
background-color: #e9eef3;
color: #333;
text-align: center;
line-height: 160px;
}
body > .el-container {
margin-bottom: 40px;
}
.el-container:nth-child(5) .el-aside,
.el-container:nth-child(6) .el-aside {
line-height: 260px;
}
.el-container:nth-child(7) .el-aside {
line-height: 320px;
}
</style>
sideBar/index
<template>
<div class="">
<el-row class="tac">
<el-col :span="12">
<el-menu
default-active="2"
class="el-menu-vertical-demo"
@open="handleOpen"
router
@close="handleClose"
background-color="#545c64"
text-color="#fff"
active-text-color="#ffd04b"
>
<el-menu-item index="1" class="aa">
<i class="el-icon-menu"></i>
<span slot="title">页面1</span>
</el-menu-item>
<el-menu-item index="2" class="aa">
<i class="el-icon-menu"></i>
<span slot="title">页面2</span>
</el-menu-item>
<el-menu-item index="3" class="aa">
<i class="el-icon-menu"></i>
<span slot="title">页面3</span>
</el-menu-item>
<el-menu-item index="f" class="aa">
<i class="el-icon-menu"></i>
<span slot="title">页面f</span>
</el-menu-item>
</el-menu>
</el-col>
</el-row>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
methods: {
handleOpen (key, keyPath) {
console.log(key, keyPath)
},
handleClose (key, keyPath) {
console.log(key, keyPath)
}
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
.aa {
width: 200px;
}
</style>
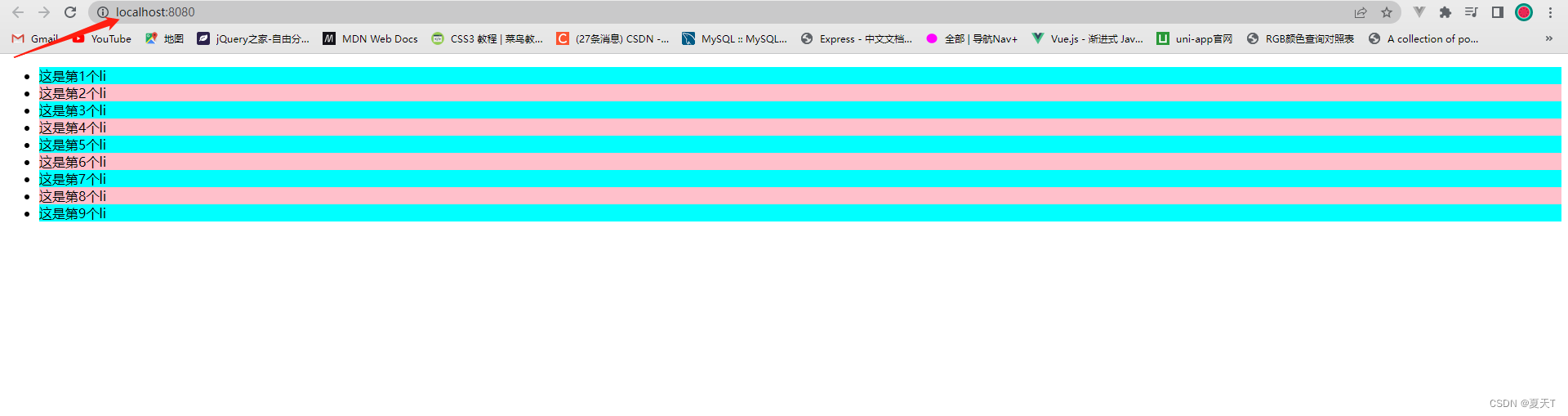
效果:

四.路由的懒加载
通过上述导入组件的过程你会发现,导入组件的方式有两种。
第一种:
import Vue from 'vue'
import VueRouter from 'vue-router'
import a from '@/views/a.vue'
import aa from '@/views/aa.vue'
import a3 from '@/views/a3.vue'
import af from '@/views/af.vue'
Vue.use(VueRouter)
const routes = [
{
path: '/',
name: '首页',
// route level code-splitting
// this generates a separate chunk (about.[hash].js) for this route
// which is lazy-loaded when the route is visited.
component: () =>
import(/* webpackChunkName: "about" */ '../views/shouye.vue'),
children: [
{
path: '1',
component: a
},
{
path: '2',
component: aa
},
{
path: '3',
component: a3
},
{
path: 'f',
component: af
}
]
}
]一级路由的导入方式:
import(/* webpackChunkName: "about" */ '../views/shouye.vue'),二级路由的导入方式:
import af from '@/views/af.vue'在性能方面,懒加载会更好一些。
五.总结
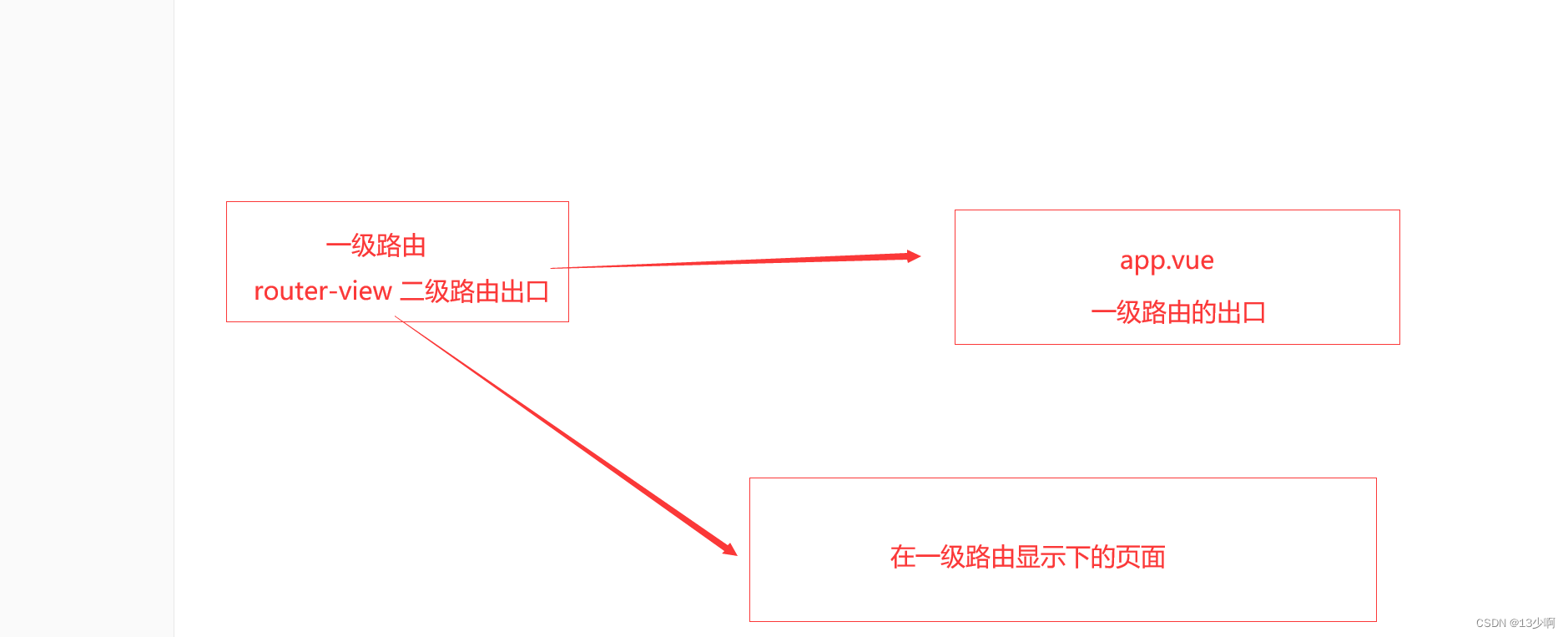
1.router-view是路由的出口,没有它页面则没法进行显示。
2.二级路由的出口对应在一级路由里面进行配置。
3.一个router-view只能存储一个组件,当路径发生改变,之前的会消失。
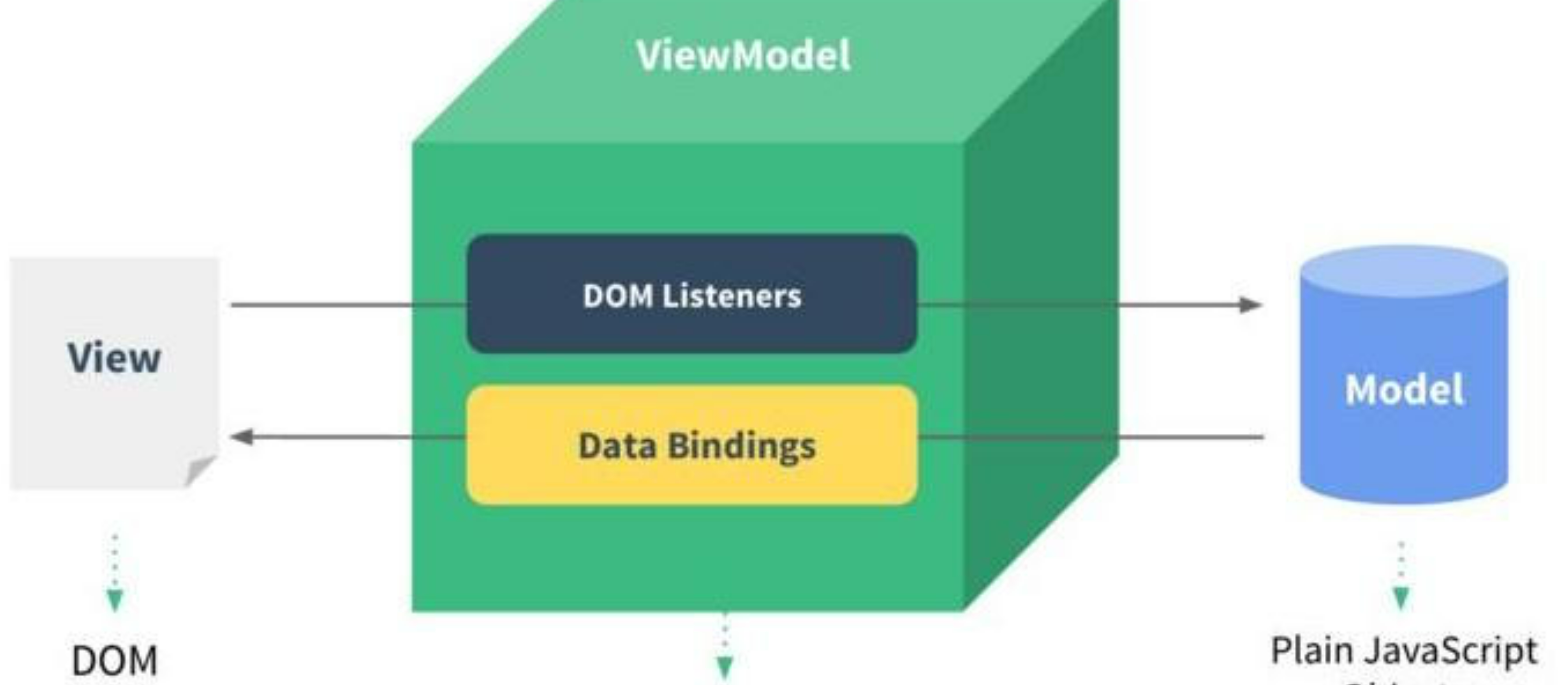
4.图示
觉得有帮助的三连哦。