文件夹操作
OVERVIEW
- 文件夹操作
- 一、文件夹操作
- 1.修改目录chdir
- 2.打开目录opendir
- 3.关闭目录closedir
- 4.读取目录readdir
- 5.文件信息获取stat
- 二、案例使用
- 1.ls实现
- 2.stat文件信息获取
- 3.ls -la主要实现
- 4.ls -la重点修改
- 5.ls -la文件字典序
- 6.ls -la文件颜色显示
- 三、补充操作
- 1.文件定位lseek
- 2.文件控制fcntl
一、文件夹操作
1.修改目录chdir

2.打开目录opendir

3.关闭目录closedir

4.读取目录readdir
NAME
readdir - read a directory
SYNOPSIS
#include <dirent.h>
struct dirent *readdir(DIR *dirp);
DESCRIPTION
The readdir() function returns a pointer to a dirent structure representing the next directory entry in the directory stream pointed to by dirp. It returns NULL on reaching the end of the directory
stream or if an error occurred.
In the glibc implementation, the dirent structure is defined as follows:
struct dirent {
ino_t d_ino; /* Inode number */
off_t d_off; /* Not an offset; see below */
unsigned short d_reclen; /* Length of this record */
unsigned char d_type; /* Type of file; not supported
by all filesystem types */
char d_name[256]; /* Null-terminated filename */
};
The only fields in the dirent structure that are mandated by POSIX.1 are d_name and d_ino. The other fields are
unstandardized, and not present on all systems; see NOTES below for some further details.
The fields of the dirent structure are as follows:
d_ino This is the inode number of the file.
d_off The value returned in d_off is the same as would be returned by calling telldir(3) at the current position in the
directory stream. Be aware that despite its type and name, the d_off field is sel‐dom any kind of directory
offset on modern filesystems. Applications should treat this field as an opaque value, making no assumptions
about its contents; see also telldir(3).
d_reclen
This is the size (in bytes) of the returned record. This may not match the size of the structure definition shown
above; see NOTES.
d_type This field contains a value indicating the file type, making it possible to avoid the expense of calling lstat(2)
if further actions depend on the type of the file.
When a suitable feature test macro is defined (_DEFAULT_SOURCE on glibc versions since 2.19, or _BSD_SOURCE on
glibc versions 2.19 and earlier), glibc defines the following macro constants for the value returned in d_type:
DT_BLK This is a block device.
DT_CHR This is a character device.
DT_DIR This is a directory.
DT_FIFO This is a named pipe (FIFO).
DT_LNK This is a symbolic link.
DT_REG This is a regular file.
DT_SOCK This is a UNIX domain socket.
DT_UNKNOWN The file type could not be determined.
Currently, only some filesystems (among them: Btrfs, ext2, ext3, and ext4) have full support for returning the file type in d_type. All applications must properly handle a return of DT_UNKNOWN.
d_name This field contains the null terminated filename. See NOTES.
The data returned by readdir() may be overwritten by subsequent calls to readdir() for the same directory stream.
RETURN VALUE
On success, readdir() returns a pointer to a dirent structure. (This structure may be statically allocated; do not
attempt to free(3) it.)
If the end of the directory stream is reached, NULL is returned and errno is not changed. If an error occurs, NULL is
returned and errno is set appropriately. To distinguish end of stream and from an error, set errno to zero before
calling readdir() and then check the value of errno if NULL is returned.

5.文件信息获取stat
NAME
stat, fstat, lstat, fstatat - get file status
SYNOPSIS
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int stat(const char *pathname, struct stat *statbuf);
int fstat(int fd, struct stat *statbuf);
int lstat(const char *pathname, struct stat *statbuf);
#include <fcntl.h> /* Definition of AT_* constants */
#include <sys/stat.h>
int fstatat(int dirfd, const char *pathname, struct stat *statbuf,
int flags);
Feature Test Macro Requirements for glibc (see feature_test_macros(7)):
lstat():
/* glibc 2.19 and earlier */ _BSD_SOURCE
|| /* Since glibc 2.20 */ _DEFAULT_SOURCE
|| _XOPEN_SOURCE >= 500
|| /* Since glibc 2.10: */ _POSIX_C_SOURCE >= 200112L
fstatat():
Since glibc 2.10:
_POSIX_C_SOURCE >= 200809L
Before glibc 2.10:
_ATFILE_SOURCE
DESCRIPTION
These functions return information about a file, in the buffer pointed to by statbuf. No permissions are required on
the file itself, but—in the case of stat(), fstatat(), and lstat()—execute (search) permission is required on all of the
directories in pathname that lead to the file.
stat() and fstatat() retrieve information about the file pointed to by pathname; the differences for fstatat() are
described below.
lstat() is identical to stat(), except that if pathname is a symbolic link, then it returns information about the link
itself, not the file that it refers to.
fstat() is identical to stat(), except that the file about which information is to be retrieved is specified by the file
descriptor fd.
The stat structure
All of these system calls return a stat structure, which contains the following fields:
struct stat {
dev_t st_dev; /* ID of device containing file */
ino_t st_ino; /* Inode number */
mode_t st_mode; /* File type and mode */
nlink_t st_nlink; /* Number of hard links */
uid_t st_uid; /* User ID of owner */
gid_t st_gid; /* Group ID of owner */
dev_t st_rdev; /* Device ID (if special file) */
off_t st_size; /* Total size, in bytes */
blksize_t st_blksize; /* Block size for filesystem I/O */
blkcnt_t st_blocks; /* Number of 512B blocks allocated */
/* Since Linux 2.6, the kernel supports nanosecond
precision for the following timestamp fields.
For the details before Linux 2.6, see NOTES. */
struct timespec st_atim; /* Time of last access */
struct timespec st_mtim; /* Time of last modification */
struct timespec st_ctim; /* Time of last status change */
#define st_atime st_atim.tv_sec /* Backward compatibility */
#define st_mtime st_mtim.tv_sec
#define st_ctime st_ctim.tv_sec
};
Note: the order of fields in the stat structure varies somewhat across architectures. In addition, the definition above
does not show the padding bytes that may be present between some fields on various architectures. Consult the glibc and
kernel source code if you need to know the details.
Note: for performance and simplicity reasons, different fields in the stat structure may contain state information from
different moments during the execution of the system call. For example, if st_mode or st_uid is changed by another
process by calling chmod(2) or chown(2), stat() might return the old st_mode together with the new st_uid, or the old
st_uid together with the new st_mode.
The fields in the stat structure are as follows:
st_dev This field describes the device on which this file resides. (The major(3) and minor(3) macros may be useful to
decompose the device ID in this field.)
st_ino This field contains the file's inode number.
st_mode
This field contains the file type and mode. See inode(7) for further information.
st_nlink
This field contains the number of hard links to the file.
st_uid This field contains the user ID of the owner of the file.
st_gid This field contains the ID of the group owner of the file.
st_rdev
This field describes the device that this file (inode) represents.
st_size
This field gives the size of the file (if it is a regular file or a symbolic link) in bytes. The size of a
symbolic link is the length of the pathname it contains, without a terminating null byte.
st_blksize
This field gives the "preferred" block size for efficient filesystem I/O.
st_blocks
This field indicates the number of blocks allocated to the file, in 512-byte units. (This may be smaller than
st_size/512 when the file has holes.)
st_atime
This is the file's last access timestamp.
st_mtime
This is the file's last modification timestamp.
st_ctime
This is the file's last status change timestamp.
For further information on the above fields, see inode(7).
RETURN VALUE
On success, zero is returned. On error, -1 is returned, and errno is set appropriately.
二、案例使用
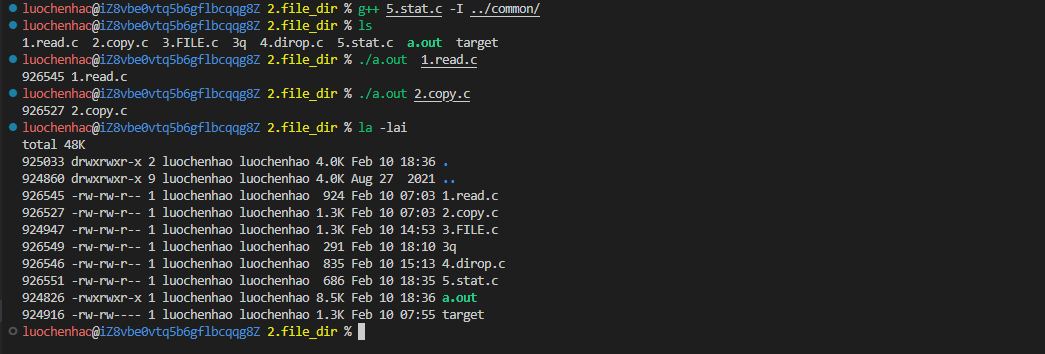
1.ls实现
#include "head.h"
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
char dir_name[256] = {0};
DIR *dir = NULL;
if (argc == 1) {
strcpy(dir_name, ".");//只有命令没有参数 则使用缺省值参数
} else {
strcpy(dir_name, argv[1]);
}
//判定文件夹是否打开成功
if ((dir = opendir(dir_name)) == NULL) {
perror("opendir");
exit(1);
}
//文件夹读取
while (1) {
struct dirent *dir_file;
if ((dir_file = readdir(dir)) == NULL) break;
printf("%s ", dir_file->d_name);//打印文件的名字
}
printf("\n");
closedir(dir);
return 0;
}

2.stat文件信息获取
#include "head.h"
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
char dir_name[50] = {0};//文件名字
if (argc == 1) {
strcpy(dir_name, ".");
} else {
strcpy(dir_name, argv[1]);
}
int stat_num;//返回值情况
struct stat statbuff;//statbuff结构体
if ((stat_num = stat(dir_name, &statbuff)) == -1) {
perror("stat");
exit(1);
}
printf("%ld %s", statbuff.st_ino, dir_name);
printf("\n");
return 0;
}
#include "head.h"
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
char dir_name[256] = {0};
DIR *dir = NULL;
if (argc == 1) {
strcpy(dir_name, ".");
} else {
strcpy(dir_name, argv[1]);
}
if ((dir = opendir(dir_name)) == NULL) {
perror("opendir");
exit(1);
}
//文件夹信息读取
while (1) {
struct stat statbuff;
struct dirent *dir_file;
if ((dir_file = readdir(dir)) == NULL) break;
stat(dir_file->d_name, &statbuff);
char type;
mode_t val = statbuff.st_mode;
switch (val & S_IFMT) {
case S_IFLNK: type = 'l'; break;
case S_IFIFO: type = 'p'; break;
case S_IFREG: type = '-'; break;
case S_IFDIR : type = 'd'; break;
default: break;
}
printf("%ld %c %s\n", statbuff.st_ino, type, dir_file->d_name);
}
printf("\n");
closedir(dir);
return 0;
}
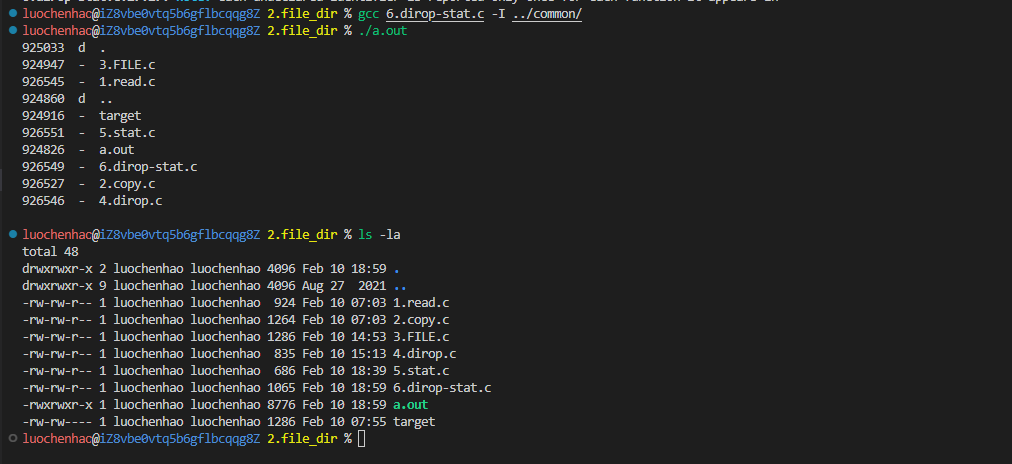
3.ls -la主要实现
#include "head.h"
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
char dir_name[256] = {0};
DIR *dir = NULL;
//1.打开文件夹
if (argc == 1) {
strcpy(dir_name, ".");
} else {
strcpy(dir_name, argv[1]);
}
if ((dir = opendir(dir_name)) == NULL) {
perror("opendir");
exit(1);
}
//2.文件夹信息读取
while (1) {
int stat_num;
struct stat statbuff;
struct dirent *dir_file = NULL;
if ((dir_file = readdir(dir)) == NULL) break;//循环遍历文件夹
//(1)获取statbuff
if (stat_num = lstat(dir_file->d_name, &statbuff) != 0) {
printf("%s\n", dir_file->d_name);
perror("stat");
exit(1);
}
//(2)从statbuff中获取各类信息
char type;
mode_t val = statbuff.st_mode;
switch (val & S_IFMT) {
case S_IFBLK: type = 'b'; break;//printf("block device\n");
case S_IFCHR: type = 'c'; break;//printf("character device\n");
case S_IFDIR: type = 'd'; break;//printf("directory\n");
case S_IFIFO: type = 'p'; break;//printf("FIFO/pipe\n");
case S_IFLNK: type = 'l'; break;//printf("symlink\n");
case S_IFREG: type = '-'; break;//printf("regular file\n");
case S_IFSOCK: type = 's'; break;//printf("socket\n");
default: printf("unknown?\n");break;
}
struct passwd *gpu_passwd;
struct group *ggg_group;
gpu_passwd = getpwuid(statbuff.st_uid);//获取用户uid信息
ggg_group = getgrgid(statbuff.st_gid);//获取用户gid信息
//(3)打印从statbuff中获取的各类信息
printf("%ld ", statbuff.st_ino);
printf("%c", type);
printf("%c", (val & S_IRUSR) ? 'r' : '-');
printf("%c", (val & S_IWUSR) ? 'w' : '-');
printf("%c", (val & S_IXUSR) ? 'x' : '-');
printf("%c", (val & S_IRGRP) ? 'r' : '-');
printf("%c", (val & S_IWGRP) ? 'w' : '-');
printf("%c", (val & S_IXGRP) ? 'x' : '-');
printf("%c", (val & S_IROTH) ? 'r' : '-');
printf("%c", (val & S_IWOTH) ? 'w' : '-');
printf("%c", (val & S_IXOTH) ? 'x' : '-');
printf(" %2ld", statbuff.st_nlink);//链接文件个数
printf(" %-8s", gpu_passwd->pw_name);//uid
printf(" %-8s", ggg_group->gr_name);//gid
printf(" %-8ld", statbuff.st_size);//文件大小
printf("%.12s ",ctime(&statbuff.st_mtime)+4);//文件修改时间
printf(" %s", dir_file->d_name);//文件名
printf("\n");
}
closedir(dir);
return 0;
}
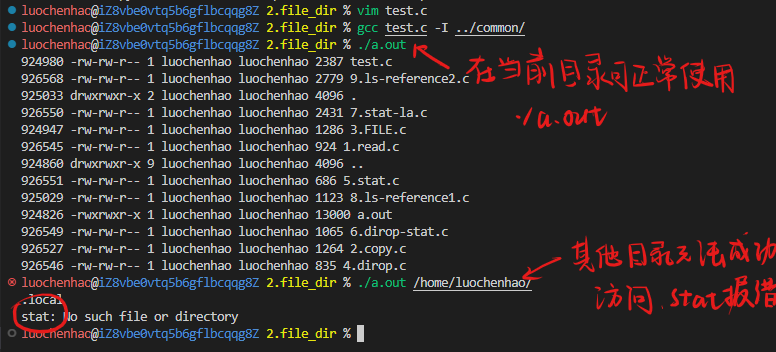
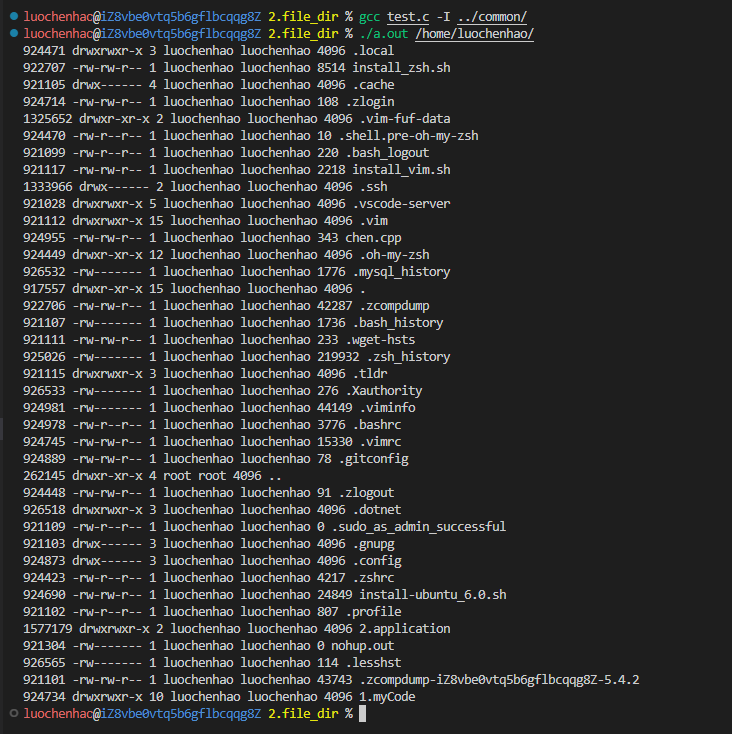
报错原因:
- Linux中的stat函数只能访问用户当前所在的路径下的文件(即pwd命令所提示的目录),该路径下的文件夹无法递归访问。stat函数无法返回文件属性。
- 只有文件为绝对路径的情况下,才能获取到文件的stat状态
- 参见文章Linux中的stat函数只能访问当前用户所在目录。
4.ls -la重点修改
#include "head.h"
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
char dir_name[256] = {0};
DIR *dir = NULL;
//1.打开文件夹
if (argc == 1) {
strcpy(dir_name, ".");
} else {
strcpy(dir_name, argv[1]);
while(--argc) printf("%s:\n",*++argv);//打印目标路径
}
if ((dir = opendir(dir_name)) == NULL) {
perror("opendir");
exit(1);
}
//2.文件夹信息读取
while (1) {
int stat_num;
struct stat statbuff;
struct dirent *dir_file = NULL;
if ((dir_file = readdir(dir)) == NULL) break;//循环遍历文件夹
//(1)获取statbuff
char full_path[512];//为解决stat报错问题 改用full_path绝对路径传入stat函数
sprintf(full_path, "%s/%s", dir_name, dir_file->d_name);
if (stat_num = lstat(full_path, &statbuff) != 0) {
perror("stat");
exit(1);
}
//(2)从statbuff中获取各类信息
char type;
mode_t val = statbuff.st_mode;
switch (val & S_IFMT) {
case S_IFBLK: type = 'b'; break;//printf("block device\n");
case S_IFCHR: type = 'c'; break;//printf("character device\n");
case S_IFDIR: type = 'd'; break;//printf("directory\n");
case S_IFIFO: type = 'p'; break;//printf("FIFO/pipe\n");
case S_IFLNK: type = 'l'; break;//printf("symlink\n");
case S_IFREG: type = '-'; break;//printf("regular file\n");
case S_IFSOCK: type = 's'; break;//printf("socket\n");
default: printf("unknown?\n");break;
}
struct passwd *gpu_passwd;
struct group *ggg_group;
gpu_passwd = getpwuid(statbuff.st_uid);//获取用户uid信息
ggg_group = getgrgid(statbuff.st_gid);//获取用户gid信息
//(3)打印从statbuff中获取的各类信息
printf("%ld ", statbuff.st_ino);
printf("%c", type);
printf("%c", (val & S_IRUSR) ? 'r' : '-');
printf("%c", (val & S_IWUSR) ? 'w' : '-');
printf("%c", (val & S_IXUSR) ? 'x' : '-');
printf("%c", (val & S_IRGRP) ? 'r' : '-');
printf("%c", (val & S_IWGRP) ? 'w' : '-');
printf("%c", (val & S_IXGRP) ? 'x' : '-');
printf("%c", (val & S_IROTH) ? 'r' : '-');
printf("%c", (val & S_IWOTH) ? 'w' : '-');
printf("%c", (val & S_IXOTH) ? 'x' : '-');
printf(" %2ld", statbuff.st_nlink);//链接文件个数
printf(" %-8s", gpu_passwd->pw_name);//uid
printf(" %-8s", ggg_group->gr_name);//gid
printf(" %-8ld", statbuff.st_size);//文件大小
printf("%.12s ",ctime(&statbuff.st_mtime)+4);//文件修改时间
printf(" %s", dir_file->d_name);//文件名
printf("\n");
}
closedir(dir);
return 0;
}
//程序重构
#include "head.h"
void dols(char*);
void printInfo(char*, struct stat);
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
char dir_name[256] = {0};//文件夹名称
if (argc == 1) {
strcpy(dir_name, ".");
} else {
strcpy(dir_name, argv[1]);
while(--argc) printf("%s:\n",*++argv);//打印目标路径
}
dols(dir_name);
return 0;
}
void dols(char *dir_name) {
DIR *dir = NULL;
//1.打开文件夹
if ((dir = opendir(dir_name)) == NULL) {
perror("opendir");
exit(1);
}
//2.获取文件夹信息statbuff
int stat_num;
struct stat statbuff;
struct dirent *dir_file = NULL;
while ((dir_file = readdir(dir)) != NULL) {
char full_path[512];
sprintf(full_path, "%s/%s", dir_name, dir_file->d_name);
if (stat_num = lstat(full_path, &statbuff) != 0) {
perror("stat");
exit(1);
}
//3.打印从statbuff中获取的各类信息
printInfo(dir_file->d_name, statbuff);
}
closedir(dir);
}
void printInfo(char *fileName, struct stat statbuff) {
char type;
mode_t val = statbuff.st_mode;
switch (val & S_IFMT) {
case S_IFBLK: type = 'b'; break;//printf("block device\n");
case S_IFCHR: type = 'c'; break;//printf("character device\n");
case S_IFDIR: type = 'd'; break;//printf("directory\n");
case S_IFIFO: type = 'p'; break;//printf("FIFO/pipe\n");
case S_IFLNK: type = 'l'; break;//printf("symlink\n");
case S_IFREG: type = '-'; break;//printf("regular file\n");
case S_IFSOCK: type = 's'; break;//printf("socket\n");
default: printf("unknown?\n");break;
}
struct passwd *gpu_passwd;
struct group *ggg_group;
gpu_passwd = getpwuid(statbuff.st_uid);//获取用户uid信息
ggg_group = getgrgid(statbuff.st_gid);//获取用户gid信息
printf("%ld ", statbuff.st_ino);
printf("%c", type);
printf("%c", (val & S_IRUSR) ? 'r' : '-');
printf("%c", (val & S_IWUSR) ? 'w' : '-');
printf("%c", (val & S_IXUSR) ? 'x' : '-');
printf("%c", (val & S_IRGRP) ? 'r' : '-');
printf("%c", (val & S_IWGRP) ? 'w' : '-');
printf("%c", (val & S_IXGRP) ? 'x' : '-');
printf("%c", (val & S_IROTH) ? 'r' : '-');
printf("%c", (val & S_IWOTH) ? 'w' : '-');
printf("%c", (val & S_IXOTH) ? 'x' : '-');
printf(" %2ld", statbuff.st_nlink);//链接文件个数
printf(" %-8s", gpu_passwd->pw_name);//uid
printf(" %-8s", ggg_group->gr_name);//gid
printf(" %-8ld", statbuff.st_size);//文件大小
printf("%.12s ",ctime(&statbuff.st_mtime)+4);//文件修改时间
printf(" %s", fileName);//文件名
printf("\n");
}
5.ls -la文件字典序
- 此功能非核心
- 为
ls -la按照文件名称进行字典序排序。 - 对文件大小的显示进行修改
思路:
- 创建一个全局变量的数组filename用于记录所有文件名称,以及全局的计数变量file_cnt
- 先将目录中的文件名存入数组中,然后对文件名进行排序,排完序后再根据已排序的文件名来获取stat数据即可
#include "head.h"
void dols(char*);
void printInfo(char*, struct stat);
char *filenames[4096];//存放数组名的数组
int file_cnt = 0; //目录中文件个数
void errorHandle(char *);
void sort(char** , int , int);
int partition(char** , int , int);
int compare(char* , char*);
void swap(char **, char **);
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
char dir_name[256] = {0};//文件夹名称
if (argc == 1) {
strcpy(dir_name, ".");
} else {
strcpy(dir_name, argv[1]);
while(--argc) printf("%s:\n",*++argv);//打印目标路径
}
dols(dir_name);
return 0;
}
void dols(char *dir_name) {
DIR *dir = NULL;
//1.获取文件名称并对文件名排序 存储在filename数组中
if ((dir = opendir(dir_name)) == NULL) errorHandle("opendir");
struct dirent *dir_file = NULL;
while((dir_file = readdir(dir))) filenames[file_cnt++] = dir_file->d_name;//将目录下的文件名全部存入filename中
sort(filenames, 0, file_cnt-1);//对文件名进行字典序排序
closedir(dir);
//2.获取文件夹信息statbuff
if ((dir = opendir(dir_name)) == NULL) errorHandle("opendir");
int stat_num;
struct stat statbuff;
for (int i = 0; i < file_cnt; ++i) {
char full_path[512];
sprintf(full_path, "%s/%s", dir_name, filenames[i]);
if (stat_num = lstat(full_path, &statbuff) != 0) errorHandle("stat");
//3.打印从statbuff中获取的各类信息
printInfo(filenames[i], statbuff);
}
closedir(dir);
}
void printInfo(char *fileName, struct stat statbuff) {
char type;
mode_t val = statbuff.st_mode;
switch (val & S_IFMT) {
case S_IFBLK: type = 'b'; break;//printf("block device\n");
case S_IFCHR: type = 'c'; break;//printf("character device\n");
case S_IFDIR: type = 'd'; break;//printf("directory\n");
case S_IFIFO: type = 'p'; break;//printf("FIFO/pipe\n");
case S_IFLNK: type = 'l'; break;//printf("symlink\n");
case S_IFREG: type = '-'; break;//printf("regular file\n");
case S_IFSOCK: type = 's'; break;//printf("socket\n");
default: printf("unknown?\n");break;
}
struct passwd *gpu_passwd;
struct group *ggg_group;
gpu_passwd = getpwuid(statbuff.st_uid);//获取用户uid信息
ggg_group = getgrgid(statbuff.st_gid);//获取用户gid信息
printf("%-8ld ", statbuff.st_ino);
printf("%c", type);
printf("%c", (val & S_IRUSR) ? 'r' : '-');
printf("%c", (val & S_IWUSR) ? 'w' : '-');
printf("%c", (val & S_IXUSR) ? 'x' : '-');
printf("%c", (val & S_IRGRP) ? 'r' : '-');
printf("%c", (val & S_IWGRP) ? 'w' : '-');
printf("%c", (val & S_IXGRP) ? 'x' : '-');
printf("%c", (val & S_IROTH) ? 'r' : '-');
printf("%c", (val & S_IWOTH) ? 'w' : '-');
printf("%c", (val & S_IXOTH) ? 'x' : '-');
printf(" %2ld", statbuff.st_nlink);//链接文件个数
printf(" %-10s", gpu_passwd->pw_name);//uid
printf(" %-10s", ggg_group->gr_name);//gid
double size = (double)statbuff.st_size / 1024.00;//文件大小
if (size <= 0) {
printf("%8ld", statbuff.st_size);
} else {
printf("%7.1fK", size);
}
printf("\t%.12s ",ctime(&statbuff.st_mtime)+4);//文件修改时间
printf(" %s", fileName);//文件名
printf("\n");
}
void errorHandle(char *error) {
perror(error);
exit(1);
}
//以下为字典序排序模块
void sort(char** filenames, int start, int end) {
if(start < end) {
int position = partition(filenames, start, end);
sort(filenames, start, position - 1);
sort(filenames, position + 1, end);
}
}
int partition(char** filenames, int start, int end) {
if(!filenames) return -1;
char* privot = filenames[start];
while(start < end) {
while(start < end && compare(privot, filenames[end]) < 0) end--;
swap(&filenames[start], &filenames[end]);
while(start < end && compare(privot, filenames[start]) >= 0) start++;
swap(&filenames[start], &filenames[end]);
}
return start;
}
void swap(char **a, char **b) {
char *temp;
temp = *a;
*a = *b;
*b = temp;
}
int compare(char* s1,char* s2) {
if(*s1=='.') s1++;
if(*s2=='.') s2++;
while(*s1 && *s2 && *s1 == *s2) {
s1++; s2++;
if(*s1=='.') s1++;
if(*s2=='.') s2++;
}
return *s1 - *s2;
}
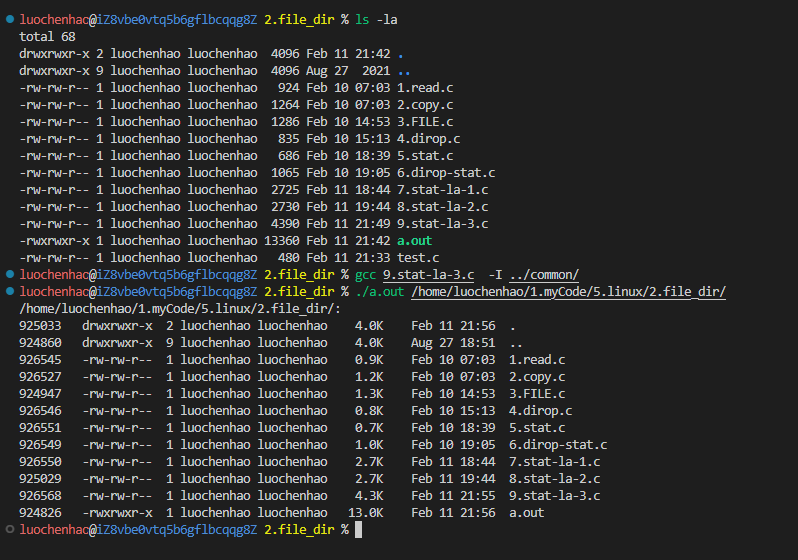
6.ls -la文件颜色显示
不同文件显示出来对应的颜色也是不一样的
- 目录文件是蓝色
- 可执行文件绿色
- 普通文件白色
#include "head.h"
#define WHITE 0
#define BLUE 1
#define GREEN 2
#define RED 3
#define LBLUE 4
#define YELLOW 5
void dols(char*);
void printInfo(char*, struct stat);
char *filenames[4096];//存放数组名的数组
int file_cnt = 0; //目录中文件个数
void errorHandle(char *);
void sort(char** , int , int);
int partition(char** , int , int);
int compare(char* , char*);
void swap(char **, char **);
int getColor(struct stat );
void printfColor(char*, int);
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
char dir_name[256] = {0};//文件夹名称
if (argc == 1) {
strcpy(dir_name, ".");
} else {
strcpy(dir_name, argv[1]);
while(--argc) printf("%s:\n",*++argv);//打印目标路径
}
dols(dir_name);
return 0;
}
void dols(char *dir_name) {
DIR *dir = NULL;
//1.获取文件名称并对文件名排序 存储在filename数组中
if ((dir = opendir(dir_name)) == NULL) errorHandle("opendir");
struct dirent *dir_file = NULL;
while((dir_file = readdir(dir))) filenames[file_cnt++] = dir_file->d_name;//将目录下的文件名全部存入filename中
sort(filenames, 0, file_cnt-1);//对文件名进行字典序排序
closedir(dir);
//2.获取文件夹信息statbuff
if ((dir = opendir(dir_name)) == NULL) errorHandle("opendir");
int stat_num;
struct stat statbuff;
for (int i = 0; i < file_cnt; ++i) {
char full_path[512];
sprintf(full_path, "%s/%s", dir_name, filenames[i]);
if (stat_num = lstat(full_path, &statbuff) != 0) errorHandle("stat");
//3.打印从statbuff中获取的各类信息
printInfo(filenames[i], statbuff);
}
closedir(dir);
}
void printInfo(char *filename, struct stat statbuff) {
char type;
mode_t val = statbuff.st_mode;
switch (val & S_IFMT) {
case S_IFBLK: type = 'b'; break;//printf("block device\n");
case S_IFCHR: type = 'c'; break;//printf("character device\n");
case S_IFDIR: type = 'd'; break;//printf("directory\n");
case S_IFIFO: type = 'p'; break;//printf("FIFO/pipe\n");
case S_IFLNK: type = 'l'; break;//printf("symlink\n");
case S_IFREG: type = '-'; break;//printf("regular file\n");
case S_IFSOCK: type = 's'; break;//printf("socket\n");
default: printf("unknown?\n");break;
}
struct passwd *gpu_passwd;
struct group *ggg_group;
gpu_passwd = getpwuid(statbuff.st_uid);//获取用户uid信息
ggg_group = getgrgid(statbuff.st_gid);//获取用户gid信息
printf("%-8ld ", statbuff.st_ino);
printf("%c", type);
printf("%c", (val & S_IRUSR) ? 'r' : '-');
printf("%c", (val & S_IWUSR) ? 'w' : '-');
printf("%c", (val & S_IXUSR) ? 'x' : '-');
printf("%c", (val & S_IRGRP) ? 'r' : '-');
printf("%c", (val & S_IWGRP) ? 'w' : '-');
printf("%c", (val & S_IXGRP) ? 'x' : '-');
printf("%c", (val & S_IROTH) ? 'r' : '-');
printf("%c", (val & S_IWOTH) ? 'w' : '-');
printf("%c", (val & S_IXOTH) ? 'x' : '-');
printf(" %2ld", statbuff.st_nlink);//链接文件个数
printf(" %-10s", gpu_passwd->pw_name);//uid
printf(" %-10s", ggg_group->gr_name);//gid
double size = (double)statbuff.st_size / 1024.00;//文件大小
if (size < 1) {
printf("%8ld", statbuff.st_size);
} else {
printf("%7.1fK", size);
}
printf("\t%.12s ",ctime(&statbuff.st_mtime)+4);//文件修改时间
int color = getColor(statbuff);//打印文件名
printfColor(filename, color);
printf("\n");
}
void errorHandle(char *error) {
perror(error);
exit(1);
}
//以下为字典序排序模块
void sort(char** filenames, int start, int end) {
if(start < end) {
int position = partition(filenames, start, end);
sort(filenames, start, position - 1);
sort(filenames, position + 1, end);
}
}
int partition(char** filenames, int start, int end) {
if(!filenames) return -1;
char* privot = filenames[start];
while(start < end) {
while(start < end && compare(privot, filenames[end]) < 0) end--;
swap(&filenames[start], &filenames[end]);
while(start < end && compare(privot, filenames[start]) >= 0) start++;
swap(&filenames[start], &filenames[end]);
}
return start;
}
void swap(char **a, char **b) {
char *temp;
temp = *a;
*a = *b;
*b = temp;
}
int compare(char* s1,char* s2) {
if(*s1=='.') s1++;
if(*s2=='.') s2++;
while(*s1 && *s2 && *s1 == *s2) {
s1++; s2++;
if(*s1=='.') s1++;
if(*s2=='.') s2++;
}
return *s1 - *s2;
}
//以下文文件颜色显示模块
int getColor(struct stat buff) {//对不同的文件类型给不同的颜色
int color = 0;
if(S_ISLNK(buff.st_mode)) color = LBLUE;
else if(S_ISDIR(buff.st_mode)) color = BLUE;
else if(S_ISCHR(buff.st_mode) ||S_ISBLK(buff.st_mode)) color = YELLOW;
else if(buff.st_mode & S_IXUSR) color = GREEN;
return color;
}
void printfColor(char *name,int color) {//打印有颜色的文件名
if(color == GREEN) printf("\033[1m\033[32m%-22s\033[0m",name);
else if(color == BLUE) printf("\033[1m\033[34m%-22s\033[0m",name);
else if(color == WHITE) printf("%-22s",name);
else if(color == LBLUE) printf("\033[1m\033[36m%-22s\033[0m",name);
else if(color == YELLOW) printf("\033[1m\033[33m%-22s\033[0m",name);
}
https://developer.aliyun.com/article/899337
https://developer.aliyun.com/article/899338
三、补充操作
1.文件定位lseek
每个打开的文件都会记录当前的读写位置,
- 打开文件时读写位置为0表示文件的开头,通常读写多少字节,文件位置就会向后移动多少字节。
- 以O_APPEND方式打开文件,每次写操作都会在文件末尾追加数据,读写位置移动到新的文件的末尾。

NAME
lseek - reposition read/write file offset
SYNOPSIS
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
off_t lseek(int fd, off_t offset, int whence);
DESCRIPTION
lseek() repositions the file offset of the open file description associated with the file descriptor fd to the
argument offset according to the directive whence as follows:
SEEK_SET
The file offset is set to offset bytes.
SEEK_CUR
The file offset is set to its current location plus offset bytes.
SEEK_END
The file offset is set to the size of the file plus offset bytes.
lseek() allows the file offset to be set beyond the end of the file (but this does not change the size of the file). If data is later written at this point, subsequent reads of the data in the gap (a "hole") return null bytes ('\0')
until data is actually written into the gap.
Seeking file data and holes
Since version 3.1, Linux supports the following additional values for whence:
SEEK_DATA
Adjust the file offset to the next location in the file greater than or equal to offset containing data. If
offset points to data, then the file offset is set to offset.
SEEK_HOLE
Adjust the file offset to the next hole in the file greater than or equal to offset. If offset points into the
middle of a hole, then the file offset is set to offset. If there is no hole past offset, then the file
offset is adjusted to the end of the file (i.e., there is an implicit hole at the end of any file).
In both of the above cases, lseek() fails if offset points past the end of the file.
These operations allow applications to map holes in a sparsely allocated file. This can be useful for applications
such as file backup tools, which can save space when creating backups and preserve holes, if they have a mechanism for
discovering holes.
For the purposes of these operations, a hole is a sequence of zeros that (normally) has not been allocated in the
underlying file storage. However, a filesystem is not obliged to report holes, so these operations are not a guaranteed
mechanism for mapping the storage space actually allocated to a file. (Furthermore, sequence of zeros that actually has
been written to the underlying storage may not be reported as a hole.) In the simplest implementation, a filesystem can
support the operations by making SEEK_HOLE always return the offset of the end of the file, and making SEEK_DATA always
return offset (i.e., even if the location referred to by offset is a hole, it can be considered to consist of data that
is a sequence of zeros).
The _GNU_SOURCE feature test macro must be defined in order to obtain the definitions of SEEK_DATA and SEEK_HOLE from
<unistd.h>.
The SEEK_HOLE and SEEK_DATA operations are supported for the following filesystems:
* Btrfs (since Linux 3.1)
* OCFS (since Linux 3.2)
* XFS (since Linux 3.5)
* ext4 (since Linux 3.8)
* tmpfs(5) (since Linux 3.8)
* NFS (since Linux 3.18)
* FUSE (since Linux 4.5)
RETURN VALUE
Upon successful completion, lseek() returns the resulting offset location as measured in bytes from the beginning of the
file. On error, the value (off_t) -1 is returned and errno is set to indicate the error.
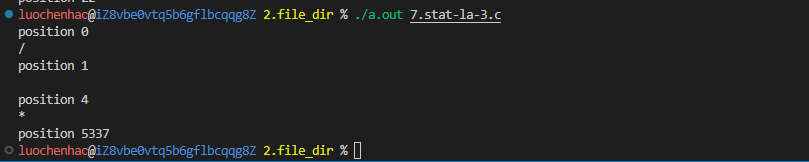
//通过lseek文件定位 确定文件大小
#include"head.h"
int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {
//1.打开一个文件 以只读的方式 并判定是否打开成功
int fd;
if ((fd = open(argv[1], O_RDONLY)) < 0) {
perror("open");
exit(1);
}
//2.读入1个字符 并进行打印操作
printf("position %ld\n", lseek(fd, 0, SEEK_CUR));
char c;
read(fd, &c, 1);
write(STDOUT_FILENO, &c, 1);
//3.通过lseek确定当前指针在文件中的位置
printf("\nposition %ld\n", lseek(fd, 0, SEEK_CUR));
//4.通过lseek移动文件位置
printf("\nposition %ld\n", lseek(fd, 3, SEEK_CUR));
read(fd, &c, 1);
write(STDOUT_FILENO, &c, 1);
//5.通过lseek确定文件的大小
printf("\nposition %ld\n", lseek(fd, 0, SEEK_END));//文件读取的位置直接移动到文件末尾(测量文件大小/字节)
return 0;
}
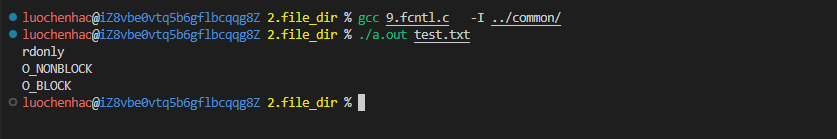
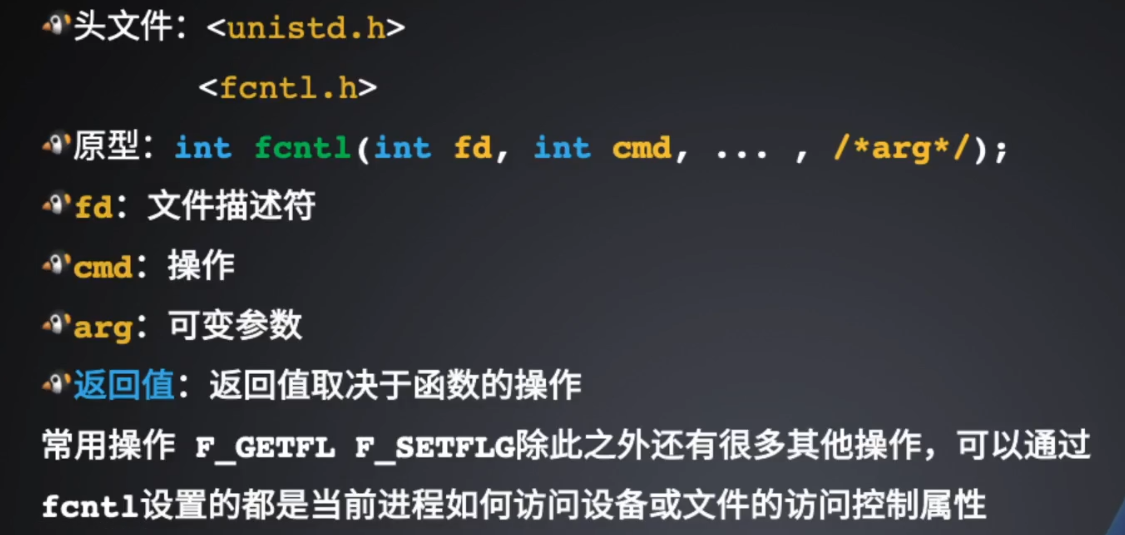
2.文件控制fcntl
fcntl函数用来改变已打开文件的属性,而不必重新open文件,可以重新设置读、写、追加、非阻塞等标志。
#include"head.h"
int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {
//1.打开一个文件 以只读的方式 并判定是否打开成功
int fd;
if ((fd = open(argv[1], O_RDONLY)) < 0) {
perror("open");
exit(1);
}
//2.fcntl设置文件属性
int flag;
flag |= O_NONBLOCK;//利用或等于操作 为文件设置非阻塞属性
fcntl(fd, F_SETFL, flag);
//3.fcntl获取文件属性
if ((flag = fcntl(fd, F_GETFL)) < 0) {
perror("fcntl");
exit(1);
}
switch (flag & O_ACCMODE) {
case O_RDONLY:
printf("rdonly\n");
break;
case O_WRONLY:
printf("wronly\n");
break;
case O_RDWR:
printf("rdwr\n");
break;
default:
printf("no\n");
break;
}
if ((flag & O_NONBLOCK) == O_NONBLOCK) printf("O_NONBLOCK\n");
//printf("O_NONBLOCK = %d = %o\n", flag & O_NONBLOCK, flag & O_NONBLOCK);
//4.fcntl取消文件权限
flag &= ~O_NONBLOCK;
fcntl(fd, F_SETFL, flag);
if ((flag & O_NONBLOCK) != O_NONBLOCK) printf("O_BLOCK\n");
return 0;
}