647. 回文子串:
-
暴力解法:两层for循环,遍历区间起始位置和终止位置,然后判断这个区间是不是回文。时间复杂度:O(n^3). Output Limit Exceeded
class Solution:
#时间复杂度:O(n^3)
def countSubstrings(self, s: str) -> int:
ans = 0
for i in range(len(s)):
for j in range(i+1, len(s)+1):
print('current substring is', s[i:j])
if self.isPalindrome(s, i, j-1):
print('yes')
ans += 1
return ans
def isPalindrome(self, str, start, end):
while start < end:
if str[start] != str[end]:
return False
start += 1
end -= 1
return True-
动态规划:时间复杂度:O(n^2), 空间复杂度:O(n^2)
五部曲:
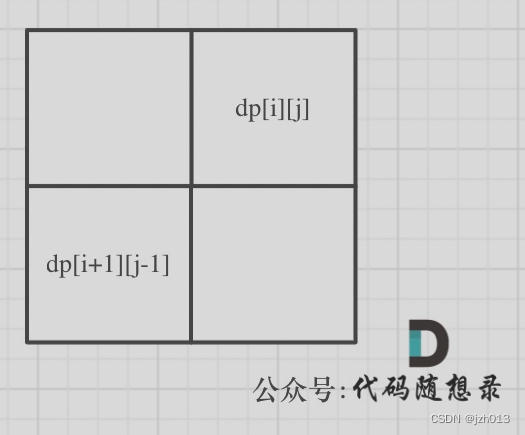
1. 确定dp数组以及下标的含义:布尔类型的dp[i][j]:表示区间范围[i,j] (注意是左闭右闭) 的。子串是否是回文子串,如果是dp[i][j]为true,否则为false。
2. 确定递推公式:分析如下四种情况:
- 当s[i]与s[j]不相等,那没啥好说的了,dp[i][j]一定是false;(情况1)
- 当s[i]与s[j]相等时:
- 下标i 与 j相同,同一个字符例如a,当然是回文子串;(情况2)
- 下标i 与 j相差为1,例如aa,也是回文子串;(情况3)
- 下标:i 与 j相差大于1的时候,例如cabac,此时s[i]与s[j]已经相同了,我们看i到j区间是不是回文子串就看aba是不是回文就可以了,那么aba的区间就是 i+1 与 j-1区间,这个区间是不是回文就看dp[i + 1][j - 1]是否为true。(情况4)
3. dp数组如何初始化:dp[i][j]初始化为false
4. 确定遍历顺序:首先从递推公式中可以看出,情况4是根据dp[i + 1][j - 1]是否为true,再 对dp[i][j]进行赋值true的。如图可以看出,dp[i + 1][j - 1] 在 dp[i][j]的左下角,
如果这矩阵是从上到下,从左到右遍历,那么会用到没有计算过的dp[i + 1][j - 1],也就是根据不确定是不是回文的区间[i+1,j-1],来判断了[i,j]是不是回文,那结果一定是不对的。
所以一定要从下到上,从左到右遍历,这样保证dp[i + 1][j - 1]都是经过计算的。
5. 打印检查
class Solution(object):
def countSubstrings(self, s):
"""
:type s: str
:rtype: int
"""
dp = [[False]*(len(s)+1) for _ in range(len(s)+1)]
ans = 0
for i in range(len(s)-1, -1, -1):
for j in range(i, len(s)):
if s[i] == s[j]:
if j-i <= 1:
ans += 1
dp[i][j] = True
elif dp[i+1][j-1]:
ans += 1
dp[i][j] = True
return ans-
双指针:时间复杂度:O(n^2),空间复杂度:O(1)
- 首先确定回文串,就是找中心然后向两边扩散看是不是对称的就可以了。
- 在遍历中心点的时候,要注意中心点有两种情况:
- 一个元素可以作为中心点,
- 两个元素也可以作为中心点。
class Solution:
def countSubstrings(self, s: str) -> int:
ans = 0
for i in range(len(s)):
ans += self.extendCheck(s, i, i, len(s))
ans += self.extendCheck(s, i, i+1, len(s))
return ans
def extendCheck(self, s, i, j, n):
res = 0
while i >= 0 and j < n and s[i] == s[j]: #由中心向两边扩散
i -= 1
j += 1
res += 1
return res