4.Elasticsearch深入了解
[toc]
1.Elasticsearch架构原理
Elasticsearch的节点类型
在Elasticsearch主要分成两类节点,一类是Master,一类是DataNode。
Master节点
在Elasticsearch启动时,会选举出来一个Master节点。当某个节点启动后,然后使用Zen Discovery机制找到集群中的其他节点,并建立连接。
discovery.seed_hosts: ["192.168.21.130", "192.168.21.131", "192.168.21.132"]并从候选主节点中选举出一个主节点。
cluster.initial_master_nodes: ["node1", "node2","node3"]master节点主要负责
管理索引(创建索引、删除索引)、分配分片
维护元数据
管理集群节点状态
不负责数据写入和查询,比较轻量级
一个Elasticsearch集群中,只有一个Master节点。在生产环境中,内存可以相对小一点,但机器要稳定。
DataNote节点
在Elasticsearch集群中,会有N个DataNode节点。DataNode节点主要负责:
数据写入、数据检索,大部分Elasticsearch的压力都在DataNode节点上
在生产环境中,内存最好配置大一些
2.分片和副本机制
分片-shard
Elasticsearch是一个分布式的搜索引擎,索引的数据也是分成若干部分,分布在不同的服务器节点中
分布在不同服务器节点中的索引数据,就是分片(Shard)。Elasticsearch会自动管理分片,如果发现分片分布不均衡,就会自动迁移
一个索引(index)由多个shard(分片)组成,而分片是分布在不同的服务器上的
副本
为了对Elasticsearch的分片进行容错,假设某个节点不可用,会导致整个索引库都将不可用。所以,需要对分片进行副本容错。每一个分片都会有对应的副本。
在Elasticsearch中,默认创建的索引为1个分片、每个分片有1个主分片和1个副本分片。
每个分片都会有一个Primary Shard(主分片),也会有若干个Replica Shard(副本分片)
Primary Shard和Replica Shard不在同一个节点上
指定分片,副本数量
# 创建指定分片数量、副本数量的索引
PUT /job_idx_shard_temp
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"id": {
"type": "long",
"store": true
},
"area": {
"type": "keyword",
"store": true
},
"exp": {
"type": "keyword",
"store": true
},
"edu": {
"type": "keyword",
"store": true
},
"salary": {
"type": "keyword",
"store": true
},
"job_type": {
"type": "keyword",
"store": true
},
"cmp": {
"type": "keyword",
"store": true
},
"pv": {
"type": "keyword",
"store": true
},
"title": {
"type": "text",
"store": true
},
"jd": {
"type": "text"
}
}
},
"settings": {
"number_of_shards": 3,
"number_of_replicas": 2
}
}
# 查看分片、主分片、副本分片
GET /_cat/indices?v执行结果
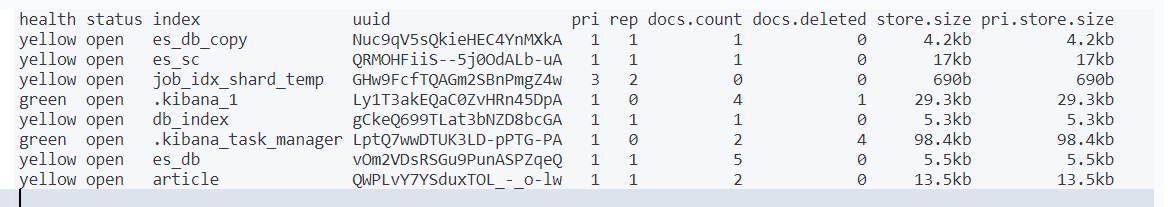
3.Elasticsearch重要工作流程
Elasticsearch文档写入原理
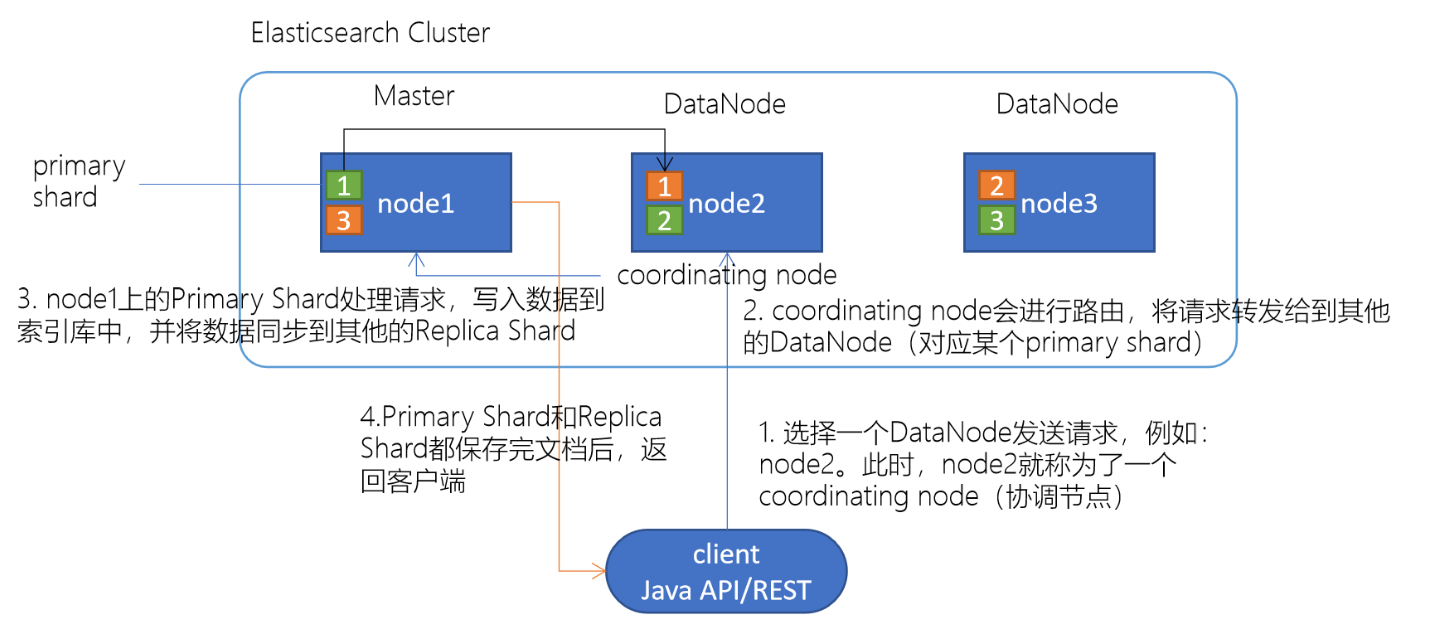
选择任意一个DataNode发送请求,例如:node2。此时,node2就成为一个coordinating node(协调节点)
计算得到文档要写入的分片
shard = hash(routing) % number_of_primary_shards
routing 是一个可变值,默认是文档的 _idcoordinating node会进行路由,将请求转发给对应的primary shard所在的DataNode(假设primary shard在node1、replica shard在node2)
node1节点上的Primary Shard处理请求,写入数据到索引库中,并将数据同步到Replica shard
Primary Shard和Replica Shard都保存好了文档,返回client
Elasticsearch检索原理
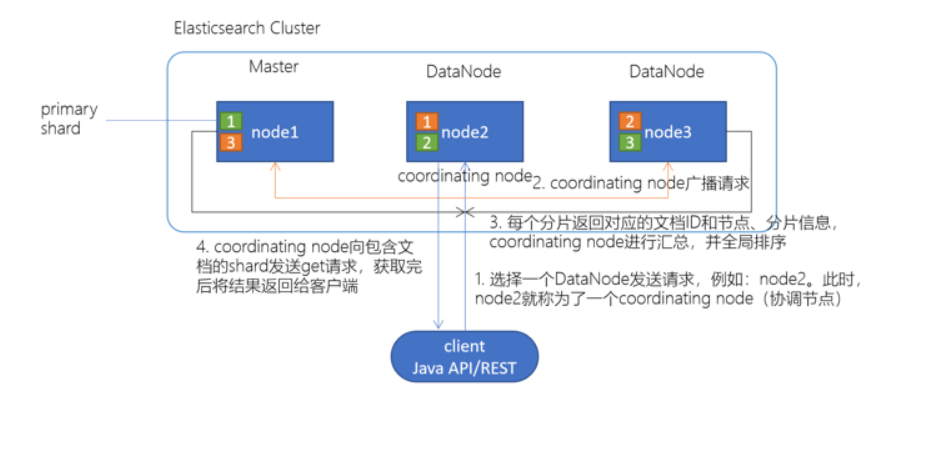
client发起查询请求,某个DataNode接收到请求,该DataNode就会成为协调节点(Coordinating Node)
协调节点(Coordinating Node)将查询请求广播到每一个数据节点,这些数据节点的分片会处理该查询请求
每个分片进行数据查询,将符合条件的数据放在一个优先队列中,并将这些数据的文档ID、节点信息、分片信息返回给协调节点
协调节点将所有的结果进行汇总,并进行全局排序
协调节点向包含这些文档ID的分片发送get请求,对应的分片将文档数据返回给协调节点,最后协调节点将数据返回给客户端
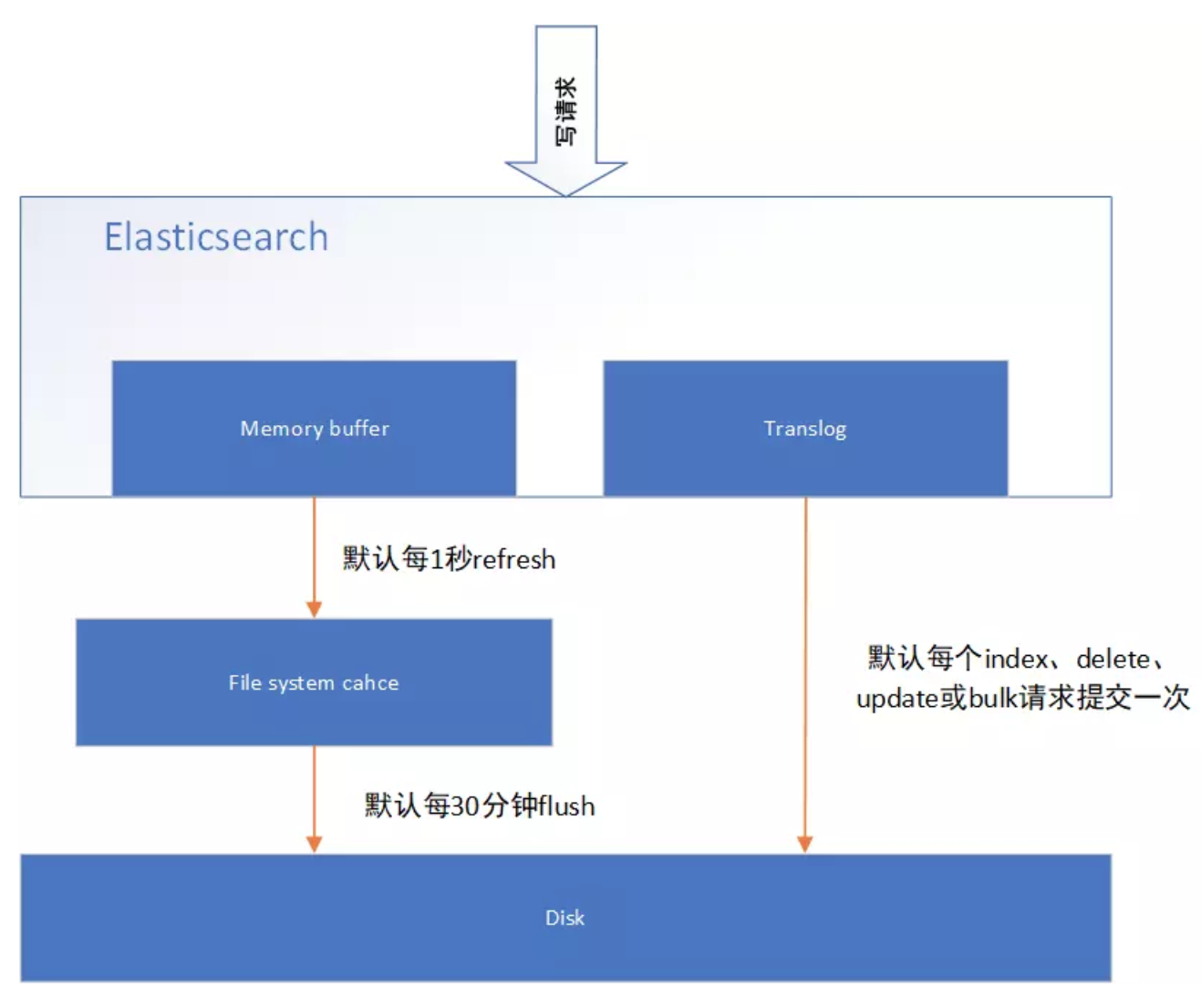
4.Elasticsearch准实时索引实现
溢写到文件系统缓存
当数据写入到ES分片时,会首先写入到内存中,然后通过内存的buffer生成一个segment,并刷到 文件系统缓存中,数据可以被检索(注意不是直接刷到磁盘)
ES中默认1秒,refresh一次
写translog保障容错
在写入到内存中的同时,也会记录translog日志,在refresh期间出现异常,会根据translog来进行数据恢复
等到文件系统缓存中的segment数据都刷到磁盘中,清空translog文件
flush到磁盘
ES默认每隔30分钟会将文件系统缓存的数据刷入到磁盘
segment合并
Segment太多时,ES定期会将多个segment合并成为大的segment,减少索引查询时IO开销,此阶段ES会真正的物理删除(之前执行过的delete的数据)
5.手工控制搜索结果精准度
下述搜索中,如果document中的remark字段包含java或developer词组,都符合搜索条件。
# 手工控制搜索精准度
GET /es_db/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"remark": "java developer"
}
}
}执行结果
{
"took" : 2,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 1,
"successful" : 1,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : {
"value" : 4,
"relation" : "eq"
},
"max_score" : 1.4691012,
"hits" : [
{
"_index" : "es_db",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "1",
"_score" : 1.4691012,
"_source" : {
"name" : "张三",
"sex" : 1,
"age" : 25,
"address" : "广州天河公园",
"remark" : "java developer"
}
},
{
"_index" : "es_db",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "3",
"_score" : 0.9092851,
"_source" : {
"name" : "rod",
"sex" : 0,
"age" : 26,
"address" : "广州白云山公园",
"remark" : "php developer"
}
},
{
"_index" : "es_db",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "2",
"_score" : 0.5598161,
"_source" : {
"name" : "李四",
"sex" : 1,
"age" : 28,
"address" : "上海金融大厦",
"remark" : "java assistant"
}
},
{
"_index" : "es_db",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "5",
"_score" : 0.46919838,
"_source" : {
"name" : "小明",
"sex" : 0,
"age" : 19,
"address" : "长沙岳麓山",
"remark" : "java architect assistant"
}
}
]
}
}如果需要搜索的document中的remark字段,包含java和developer词组,则需要使用下述语法:
# 查询的字段都要包含
GET /es_db/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"remark": {
"query": "java developer",
"operator": "and"
}
}
}
}执行结果
{
"took" : 2,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 1,
"successful" : 1,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : {
"value" : 1,
"relation" : "eq"
},
"max_score" : 1.4691012,
"hits" : [
{
"_index" : "es_db",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "1",
"_score" : 1.4691012,
"_source" : {
"name" : "张三",
"sex" : 1,
"age" : 25,
"address" : "广州天河公园",
"remark" : "java developer"
}
}
]
}
}上述语法中,如果将operator的值改为or。则与第一个案例搜索语法效果一致。默认的ES执行搜索的时候,operator就是or。
如果在搜索的结果document中,需要remark字段中包含多个搜索词条中的一定比例,可以使用下述语法实现搜索。其中minimum_should_match可以使用百分比或固定数字。百分比代表query搜索条件中词条百分比,如果无法整除,向下匹配(如,query条件有3个单词,如果使用百分比提供精准度计算,那么是无法除尽的,如果需要至少匹配两个单词,则需要用67%来进行描述。如果使用66%描述,ES则认为匹配一个单词即可。)。固定数字代表query搜索条件中的词条,至少需要匹配多少个。
# 按一定比例
GET /es_db/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"remark": {
"query": "java architect assistant",
"minimum_should_match": "68%"
}
}
}
}执行结果
{
"took" : 3,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 1,
"successful" : 1,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : {
"value" : 2,
"relation" : "eq"
},
"max_score" : 2.145171,
"hits" : [
{
"_index" : "es_db",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "5",
"_score" : 2.145171,
"_source" : {
"name" : "小明",
"sex" : 0,
"age" : 19,
"address" : "长沙岳麓山",
"remark" : "java architect assistant"
}
},
{
"_index" : "es_db",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "2",
"_score" : 1.1196322,
"_source" : {
"name" : "李四",
"sex" : 1,
"age" : 28,
"address" : "上海金融大厦",
"remark" : "java assistant"
}
}
]
}
}如果使用should+bool搜索的话,也可以控制搜索条件的匹配度。具体如下:下述案例代表搜索的document中的remark字段中,必须匹配java、developer、assistant三个词条中的至少2个。
# 至少两个
GET /es_db/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"should": [
{
"match": {
"remark": "java"
}
},
{
"match": {
"remark": "developer"
}
},
{
"match": {
"remark": "assistant"
}
}
],
"minimum_should_match": 2
}
}
}执行结果
{
"took" : 2,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 1,
"successful" : 1,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : {
"value" : 3,
"relation" : "eq"
},
"max_score" : 1.4691012,
"hits" : [
{
"_index" : "es_db",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "1",
"_score" : 1.4691012,
"_source" : {
"name" : "张三",
"sex" : 1,
"age" : 25,
"address" : "广州天河公园",
"remark" : "java developer"
}
},
{
"_index" : "es_db",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "2",
"_score" : 1.1196322,
"_source" : {
"name" : "李四",
"sex" : 1,
"age" : 28,
"address" : "上海金融大厦",
"remark" : "java assistant"
}
},
{
"_index" : "es_db",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "5",
"_score" : 0.93839675,
"_source" : {
"name" : "小明",
"sex" : 0,
"age" : 19,
"address" : "长沙岳麓山",
"remark" : "java architect assistant"
}
}
]
}
}match的底层转换
其实在ES中,执行match搜索的时候,ES底层通常都会对搜索条件进行底层转换,来实现最终的搜索结果。如:
# 转换前
GET /es_db/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"remark": "java developer"
}
}
}
# 转换后
GET /es_db/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"should": [
{
"term": {
"remark": "java"
}
},
{
"term": {
"remark": {
"value": "developer"
}
}
}
]
}
}
}执行结果
{
"took" : 1,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 1,
"successful" : 1,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : {
"value" : 4,
"relation" : "eq"
},
"max_score" : 1.4691012,
"hits" : [
{
"_index" : "es_db",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "1",
"_score" : 1.4691012,
"_source" : {
"name" : "张三",
"sex" : 1,
"age" : 25,
"address" : "广州天河公园",
"remark" : "java developer"
}
},
{
"_index" : "es_db",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "3",
"_score" : 0.9092851,
"_source" : {
"name" : "rod",
"sex" : 0,
"age" : 26,
"address" : "广州白云山公园",
"remark" : "php developer"
}
},
{
"_index" : "es_db",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "2",
"_score" : 0.5598161,
"_source" : {
"name" : "李四",
"sex" : 1,
"age" : 28,
"address" : "上海金融大厦",
"remark" : "java assistant"
}
},
{
"_index" : "es_db",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "5",
"_score" : 0.46919838,
"_source" : {
"name" : "小明",
"sex" : 0,
"age" : 19,
"address" : "长沙岳麓山",
"remark" : "java architect assistant"
}
}
]
}
}# 转换前
GET /es_db/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"remark": {
"query": "java developer",
"operator": "and"
}
}
}
}
# 转换后
GET /es_db/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{
"term": {
"remark": "java"
}
},
{
"term": {
"remark": {
"value": "developer"
}
}
}
]
}
}
}执行结果
{
"took" : 1,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 1,
"successful" : 1,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : {
"value" : 1,
"relation" : "eq"
},
"max_score" : 1.4691012,
"hits" : [
{
"_index" : "es_db",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "1",
"_score" : 1.4691012,
"_source" : {
"name" : "张三",
"sex" : 1,
"age" : 25,
"address" : "广州天河公园",
"remark" : "java developer"
}
}
]
}
}# 转换前
GET /es_db/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"remark": {
"query": "java architect assistant",
"minimum_should_match": "68%"
}
}
}
}
# 转换后
GET /es_db/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"should": [
{
"term": {
"remark": "java"
}
},
{
"term": {
"remark": "architect"
}
},
{
"term": {
"remark": "assistant"
}
}
],
"minimum_should_match": 2
}
}
}{
"took" : 1,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 1,
"successful" : 1,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : {
"value" : 2,
"relation" : "eq"
},
"max_score" : 2.145171,
"hits" : [
{
"_index" : "es_db",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "5",
"_score" : 2.145171,
"_source" : {
"name" : "小明",
"sex" : 0,
"age" : 19,
"address" : "长沙岳麓山",
"remark" : "java architect assistant"
}
},
{
"_index" : "es_db",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "2",
"_score" : 1.1196322,
"_source" : {
"name" : "李四",
"sex" : 1,
"age" : 28,
"address" : "上海金融大厦",
"remark" : "java assistant"
}
}
]
}
}建议,如果不怕麻烦,尽量使用转换后的语法执行搜索,效率更高。
如果开发周期短,工作量大,使用简化的写法。
boost权重控制
搜索document中remark字段中包含java的数据,如果remark中包含developer或architect,则包含architect的document优先显示。(就是将architect数据匹配时的相关度分数增加)。
一般用于搜索时相关度排序使用。如:电商中的综合排序。将一个商品的销量,广告投放,评价值,库存,单价比较综合排序。在上述的排序元素中,广告投放权重最高,库存权重最低。
# 权重
GET /es_db/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{
"match": {
"remark": "java"
}
}
],
"should": [
{
"match": {
"remark": {
"query": "developer",
"boost": 1
}
}
},
{
"match": {
"remark": {
"query": "architect",
"boost": 3
}
}
}
]
}
}
}执行结果
{
"took" : 3,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 1,
"successful" : 1,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : {
"value" : 3,
"relation" : "eq"
},
"max_score" : 4.0895214,
"hits" : [
{
"_index" : "es_db",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "5",
"_score" : 4.0895214,
"_source" : {
"name" : "小明",
"sex" : 0,
"age" : 19,
"address" : "长沙岳麓山",
"remark" : "java architect assistant"
}
},
{
"_index" : "es_db",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "1",
"_score" : 1.4691012,
"_source" : {
"name" : "张三",
"sex" : 1,
"age" : 25,
"address" : "广州天河公园",
"remark" : "java developer"
}
},
{
"_index" : "es_db",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "2",
"_score" : 0.5598161,
"_source" : {
"name" : "李四",
"sex" : 1,
"age" : 28,
"address" : "上海金融大厦",
"remark" : "java assistant"
}
}
]
}
}基于dis_max实现best fields策略进行多字段搜索
best fields策略: 搜索的document中的某一个field,尽可能多的匹配搜索条件。与之相反的是,尽可能多的字段匹配到搜索条件(most fields策略)。如百度搜索使用这种策略。
优点:精确匹配的数据可以尽可能的排列在最前端,且可以通过minimum_should_match来去除长尾数据,避免长尾数据字段对排序结果的影响。
缺点:相对排序不均匀
dis_max语法: 直接获取搜索的多条件中的,单条件query相关度分数最高的数据,以这个数据做相关度排序
下述的案例中,就是找name字段中rod匹配相关度分数或remark字段中java developer匹配相关度分数,哪个高,就使用哪一个相关度分数进行结果排序。
# 搜索策略
GET /es_db/_search
{
"query": {
"dis_max": {
"queries": [
{
"match": {
"name": "rod"
}
},
{
"match": {
"remark": "java developer"
}
}
]
}
}
}执行结果
{
"took" : 5,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 1,
"successful" : 1,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : {
"value" : 4,
"relation" : "eq"
},
"max_score" : 1.4691012,
"hits" : [
{
"_index" : "es_db",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "1",
"_score" : 1.4691012,
"_source" : {
"name" : "张三",
"sex" : 1,
"age" : 25,
"address" : "广州天河公园",
"remark" : "java developer"
}
},
{
"_index" : "es_db",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "3",
"_score" : 1.3862944,
"_source" : {
"name" : "rod",
"sex" : 0,
"age" : 26,
"address" : "广州白云山公园",
"remark" : "php developer"
}
},
{
"_index" : "es_db",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "2",
"_score" : 0.5598161,
"_source" : {
"name" : "李四",
"sex" : 1,
"age" : 28,
"address" : "上海金融大厦",
"remark" : "java assistant"
}
},
{
"_index" : "es_db",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "5",
"_score" : 0.46919838,
"_source" : {
"name" : "小明",
"sex" : 0,
"age" : 19,
"address" : "长沙岳麓山",
"remark" : "java architect assistant"
}
}
]
}
}基于tie_breaker参数优化dis_max搜索效果
dis_max是将多个搜索query条件中相关度分数最高的用于结果排序,忽略其他query分数,在某些情况下,可能还需要其他query条件中的相关度介入最终的结果排序,这个时候可以使用tie_breaker参数来优化dis_max搜索。tie_breaker参数代表的含义是:将其他query搜索条件的相关度分数乘以参数值,再参与到结果排序中。如果不定义此参数,相当于参数值为0。所以其他query条件的相关度分数被忽略。
GET /es_db/_search
{
"query": {
"dis_max": {
"queries": [
{
"match": {
"name": "rod"
}
},
{
"match": {
"remark": "java developer"
}
}
],
"tie_breaker": 0.5
}
}
}执行结果
{
"took" : 3,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 1,
"successful" : 1,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : {
"value" : 4,
"relation" : "eq"
},
"max_score" : 1.8409369,
"hits" : [
{
"_index" : "es_db",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "3",
"_score" : 1.8409369,
"_source" : {
"name" : "rod",
"sex" : 0,
"age" : 26,
"address" : "广州白云山公园",
"remark" : "php developer"
}
},
{
"_index" : "es_db",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "1",
"_score" : 1.4691012,
"_source" : {
"name" : "张三",
"sex" : 1,
"age" : 25,
"address" : "广州天河公园",
"remark" : "java developer"
}
},
{
"_index" : "es_db",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "2",
"_score" : 0.5598161,
"_source" : {
"name" : "李四",
"sex" : 1,
"age" : 28,
"address" : "上海金融大厦",
"remark" : "java assistant"
}
},
{
"_index" : "es_db",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "5",
"_score" : 0.46919838,
"_source" : {
"name" : "小明",
"sex" : 0,
"age" : 19,
"address" : "长沙岳麓山",
"remark" : "java architect assistant"
}
}
]
}
}使用multi_match简化dis_max+tie_breaker
ES中相同结果的搜索也可以使用不同的语法语句来实现。不需要特别关注,只要能够实现搜索,就是完成任务!
# 优化
GET /es_db/_search
{
"query": {
"dis_max": {
"queries": [
{
"match": {
"name": "rod"
}
},
{
"match": {
"remark": {
"query": "java developer",
"boost": 2,
"minimum_should_match": 2
}
}
}
],
"tie_breaker": 0.5
}
}
}
#使用multi_match语法为:其中type常用的有best_fields和most_fields。^n代表权重,相当于"boost":n。
GET /es_db/_search
{
"query": {
"multi_match": {
"query": "rod java developer",
"fields": [
"name",
"remark^2"
],
"type": "best_fields",
"tie_breaker": 0.5,
"minimum_should_match": "50%"
}
}
}执行结果
{
"took" : 1,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 1,
"successful" : 1,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : {
"value" : 2,
"relation" : "eq"
},
"max_score" : 2.9382024,
"hits" : [
{
"_index" : "es_db",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "1",
"_score" : 2.9382024,
"_source" : {
"name" : "张三",
"sex" : 1,
"age" : 25,
"address" : "广州天河公园",
"remark" : "java developer"
}
},
{
"_index" : "es_db",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "3",
"_score" : 1.3862944,
"_source" : {
"name" : "rod",
"sex" : 0,
"age" : 26,
"address" : "广州白云山公园",
"remark" : "php developer"
}
}
]
}
}cross fields搜索
cross fields : 一个唯一的标识,分部在多个fields中,使用这种唯一标识搜索数据就称为cross fields搜索。如:人名可以分为姓和名,地址可以分为省、市、区县、街道等。那么使用人名或地址来搜索document,就称为cross fields搜索。
实现这种搜索,一般都是使用most fields搜索策略。因为这就不是一个field的问题
Cross fields搜索策略,是从多个字段中搜索条件数据。默认情况下,和most fields搜索的逻辑是一致的,计算相关度分数是和best fields策略一致的。一般来说,如果使用cross fields搜索策略,那么都会携带一个额外的参数operator。用来标记搜索条件如何在多个字段中匹配。
当然,在ES中也有cross fields搜索策略。具体语法如下:
# cross fields
GET /es_db/_search
{
"query": {
"multi_match": {
"query": "java developer",
"fields": [
"name",
"remark"
],
"type": "cross_fields",
"operator": "and"
}
}
}执行结果
{
"took" : 1,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 1,
"successful" : 1,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : {
"value" : 1,
"relation" : "eq"
},
"max_score" : 1.4691012,
"hits" : [
{
"_index" : "es_db",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "1",
"_score" : 1.4691012,
"_source" : {
"name" : "张三",
"sex" : 1,
"age" : 25,
"address" : "广州天河公园",
"remark" : "java developer"
}
}
]
}
}上述语法代表的是,搜索条件中的java必须在name或remark字段中匹配,developer也必须在name或remark字段中匹配。
most field策略问题:most fields策略是尽可能匹配更多的字段,所以会导致精确搜索结果排序问题。又因为cross fields搜索,不能使用minimum_should_match来去除长尾数据
所以在使用most fields和cross fields策略搜索数据的时候,都有不同的缺陷。所以商业项目开发中,都推荐使用best fields策略实现搜索
copy_to组合fields
京东中,如果在搜索框中输入“手机”,点击搜索,那么是在商品的类型名称、商品的名称、商品的卖点、商品的描述等字段中,哪一个字段内进行数据的匹配?如果使用某一个字段做搜索不合适,那么使用_all做搜索是否合适?也不合适,因为_all字段中可能包含图片,价格等字段。
假设,有一个字段,其中的内容包括(但不限于):商品类型名称、商品名称、商品卖点等字段的数据内容。是否可以在这个特殊的字段上进行数据搜索匹配?
{
"category_name": "手机",
"product_name": "一加6T手机",
"price": 568800,
"sell_point": "国产最好的Android手机",
"tags": [
"8G+128G",
"256G可扩展"
],
"color": "红色",
"keyword": "手机一加6T手机国产最好的Android手机"
}copy_to : 就是将多个字段,复制到一个字段中,实现一个多字段组合。copy_to可以解决cross fields搜索问题,在商业项目中,也用于解决搜索条件默认字段问题。
如果需要使用copy_to语法,则需要在定义index的时候,手工指定mapping映射策略。
copy_to语法:
DELETE /es_db
PUT /es_db
# 创建新的映射
PUT /es_db/_mapping
{
"properties": {
"provice": {
"type": "text",
"analyzer": "standard",
"copy_to": "address"
},
"city": {
"type": "text",
"analyzer": "standard",
"copy_to": "address"
},
"street": {
"type": "text",
"analyzer": "standard",
"copy_to": "address"
},
"address": {
"type": "text",
"analyzer": "standard"
}
}
}上述的mapping定义中,是新增了4个字段,分别是provice、city、street、address,其中provice、city、street三个字段的值,会自动复制到address字段中,实现一个字段的组合。那么在搜索地址的时候,就可以在address字段中做条件匹配,从而避免most fields策略导致的问题。在维护数据的时候,不需对address字段特殊的维护。因为address字段是一个组合字段,是由ES自动维护的。类似java代码中的推导属性。在存储的时候,未必存在,但是在逻辑上是一定存在的,因为address是由3个物理存在的属性province、city、street组成的。
近似匹配
前文都是精确匹配。如doc中有数据java assistant,那么搜索jave是搜索不到数据的。因为jave单词在doc中是不存在的。
如果语句是这样
GET _search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"name": "jave"
}
}
}执行结果
{
"took" : 1,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 10,
"successful" : 10,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : {
"value" : 0,
"relation" : "eq"
},
"max_score" : null,
"hits" : [ ]
}
}如果需要的结果是有特殊要求,如:hello world必须是一个完整的短语,不可分割;或document中的field内,包含的hello和world单词,且两个单词之间离的越近,相关度分数越高。那么这种特殊要求的搜索就是近似搜索。包括hell搜索条件在hello world数据中搜索,包括h搜索提示等都数据近似搜索的一部分。
如上述特殊要求的搜索,使用match搜索语法就无法实现了。
match phrase
短语搜索。就是搜索条件不分词。代表搜索条件不可分割。
如果hello world是一个不可分割的短语,我们可以使用前文学过的短语搜索match phrase来实现。语法如下:
# 短句搜索
GET _search
{
"query": {
"match_phrase": {
"remark": "java assistant"
}
}
}执行结果
{
"took" : 9,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 10,
"successful" : 10,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : {
"value" : 1,
"relation" : "eq"
},
"max_score" : 1.1196322,
"hits" : [
{
"_index" : "es_db",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "2",
"_score" : 1.1196322,
"_source" : {
"name" : "李四",
"sex" : 1,
"age" : 28,
"address" : "上海金融大厦",
"remark" : "java assistant"
}
}
]
}
}match phrase原理 --term position
这里涉及到了倒排索引的建立过程。在倒排索引建立的时候,ES会先对document数据进行分词,如:
# 分词
GET _analyze
{
"text": "hello world, java spark",
"analyzer": "standard"
}自行结果
{
"tokens" : [
{
"token" : "hello",
"start_offset" : 0,
"end_offset" : 5,
"type" : "<ALPHANUM>",
"position" : 0
},
{
"token" : "world",
"start_offset" : 6,
"end_offset" : 11,
"type" : "<ALPHANUM>",
"position" : 1
},
{
"token" : "java",
"start_offset" : 13,
"end_offset" : 17,
"type" : "<ALPHANUM>",
"position" : 2
},
{
"token" : "spark",
"start_offset" : 18,
"end_offset" : 23,
"type" : "<ALPHANUM>",
"position" : 3
}
]
}从上述结果中,可以看到。ES在做分词的时候,除了将数据切分外,还会保留一个position。position代表的是这个词在整个数据中的下标。当ES执行match phrase搜索的时候,首先将搜索条件hello world分词为hello和world。然后在倒排索引中检索数据,如果hello和world都在某个document的某个field出现时,那么检查这两个匹配到的单词的position是否是连续的,如果是连续的,代表匹配成功,如果是不连续的,则匹配失败。
match phrase搜索参数 --slop
在做搜索操作的是,如果搜索参数是hello spark。而ES中存储的数据是hello world, java spark。那么使用match phrase则无法搜索到。在这个时候,可以使用match来解决这个问题。但是,当我们需要在搜索的结果中,做一个特殊的要求:hello和spark两个单词距离越近,document在结果集合中排序越靠前,这个时候再使用match则未必能得到想要的结果。
ES的搜索中,对match phrase提供了参数slop。slop代表match phrase短语搜索的时候,单词最多移动多少次,可以实现数据匹配。在所有匹配结果中,多个单词距离越近,相关度评分越高,排序越靠前。
这种使用slop参数的match phrase搜索,就称为近似匹配(proximity search)
示例
数据为: hello world, java spark
搜索为:match phrase : hello spark
slop为:3
执行短语搜索的时候,将条件hello spark分词为hello和spark两个单词。并且连续。
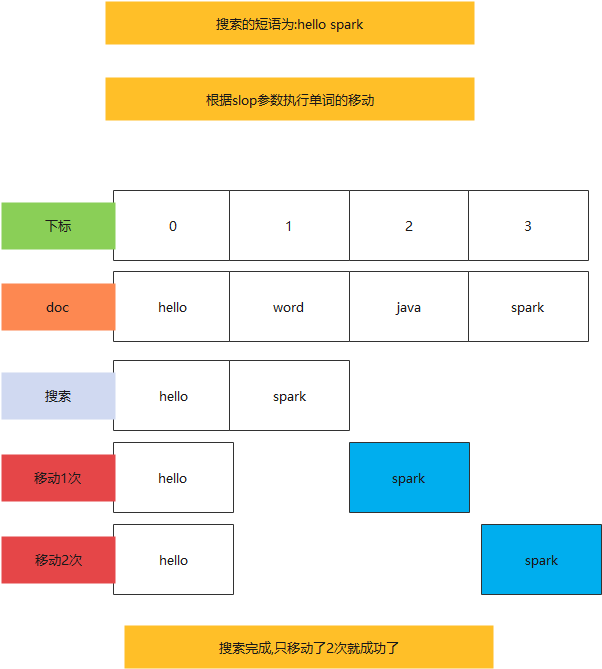
如果当slop移动次数使用完毕,还没有匹配成功,则无搜索结果。如果使用中文分词,则移动次数更加复杂,因为中文词语有重叠情况,很难计算具体次数,需要多次尝试才行。
测试案例:英文
# 英文
GET _analyze
{
"text": "hello world, java spark",
"analyzer": "standard"
}分词结果
{
"tokens" : [
{
"token" : "hello",
"start_offset" : 0,
"end_offset" : 5,
"type" : "<ALPHANUM>",
"position" : 0
},
{
"token" : "world",
"start_offset" : 6,
"end_offset" : 11,
"type" : "<ALPHANUM>",
"position" : 1
},
{
"token" : "java",
"start_offset" : 13,
"end_offset" : 17,
"type" : "<ALPHANUM>",
"position" : 2
},
{
"token" : "spark",
"start_offset" : 18,
"end_offset" : 23,
"type" : "<ALPHANUM>",
"position" : 3
}
]
}# 添加文档
POST /test_a/_doc/3
{
"f": "hello world, java spark"
}执行结果
{
"_index" : "test_a",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "3",
"_version" : 1,
"result" : "created",
"_shards" : {
"total" : 2,
"successful" : 1,
"failed" : 0
},
"_seq_no" : 0,
"_primary_term" : 1
}# 查询
GET /test_a/_search
{
"query": {
"match_phrase": {
"f": {
"query": "hello spark",
"slop": 2
}
}
}
}查询结果
{
"took" : 2,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 1,
"successful" : 1,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : {
"value" : 1,
"relation" : "eq"
},
"max_score" : 0.27517417,
"hits" : [
{
"_index" : "test_a",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "3",
"_score" : 0.27517417,
"_source" : {
"f" : "hello world, java spark"
}
}
]
}
}# 指定slop次数
GET /test_a/_search
{
"query": {
"match_phrase": {
"f": {
"query": "spark hello",
"slop": 4
}
}
}
}执行结果
{
"took" : 0,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 1,
"successful" : 1,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : {
"value" : 1,
"relation" : "eq"
},
"max_score" : 0.18082874,
"hits" : [
{
"_index" : "test_a",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "3",
"_score" : 0.18082874,
"_source" : {
"f" : "hello world, java spark"
}
}
]
}
}测试案例:中文
# 中文
GET _analyze
{
"text": "中国,一个世界上最强的国家",
"analyzer": "ik_max_word"
}分词结果
{
"tokens" : [
{
"token" : "中国",
"start_offset" : 0,
"end_offset" : 2,
"type" : "CN_WORD",
"position" : 0
},
{
"token" : "一个",
"start_offset" : 3,
"end_offset" : 5,
"type" : "CN_WORD",
"position" : 1
},
{
"token" : "一",
"start_offset" : 3,
"end_offset" : 4,
"type" : "TYPE_CNUM",
"position" : 2
},
{
"token" : "个",
"start_offset" : 4,
"end_offset" : 5,
"type" : "COUNT",
"position" : 3
},
{
"token" : "世界上",
"start_offset" : 5,
"end_offset" : 8,
"type" : "CN_WORD",
"position" : 4
},
{
"token" : "世界",
"start_offset" : 5,
"end_offset" : 7,
"type" : "CN_WORD",
"position" : 5
},
{
"token" : "上",
"start_offset" : 7,
"end_offset" : 8,
"type" : "CN_CHAR",
"position" : 6
},
{
"token" : "最强",
"start_offset" : 8,
"end_offset" : 10,
"type" : "CN_WORD",
"position" : 7
},
{
"token" : "的",
"start_offset" : 10,
"end_offset" : 11,
"type" : "CN_CHAR",
"position" : 8
},
{
"token" : "国家",
"start_offset" : 11,
"end_offset" : 13,
"type" : "CN_WORD",
"position" : 9
}
]
}# 添加文档
POST /test_a/_doc/1
{
"f": "中国,一个世界上最强的国家"
}执行结果
{
"_index" : "test_a",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "1",
"_version" : 1,
"result" : "created",
"_shards" : {
"total" : 2,
"successful" : 1,
"failed" : 0
},
"_seq_no" : 1,
"_primary_term" : 1
}# 查询
GET /test_a/_search
{
"query": {
"match_phrase": {
"f": {
"query": "中国最强",
"slop": 5
}
}
}
}执行结果
{
"took" : 104,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 1,
"successful" : 1,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : {
"value" : 1,
"relation" : "eq"
},
"max_score" : 0.55960506,
"hits" : [
{
"_index" : "test_a",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "1",
"_score" : 0.55960506,
"_source" : {
"f" : "中国,一个世界上最强的国家"
}
}
]
}
}GET /test_a/_search
{
"query": {
"match_phrase": {
"f": {
"query": "最强中国",
"slop": 9
}
}
}
}执行结果
{
"took" : 0,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 1,
"successful" : 1,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : {
"value" : 1,
"relation" : "eq"
},
"max_score" : 0.348554,
"hits" : [
{
"_index" : "test_a",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "1",
"_score" : 0.348554,
"_source" : {
"f" : "中国,一个世界上最强的国家"
}
}
]
}
}6.经验分享
使用match和proximity search实现召回率和精准度平衡。
召回率:召回率就是搜索结果比率,如:索引A中有100个document,搜索时返回多少个document,就是召回率(recall)。
精准度:就是搜索结果的准确率,如:搜索条件为hello java,在搜索结果中尽可能让短语匹配和hello java离的近的结果排序靠前,就是精准度(precision)。
如果在搜索的时候,只使用match phrase语法,会导致召回率底下,因为搜索结果中必须包含短语(包括proximity search)。
如果在搜索的时候,只使用match语法,会导致精准度底下,因为搜索结果排序是根据相关度分数算法计算得到。
那么如果需要在结果中兼顾召回率和精准度的时候,就需要将match和proximity search混合使用,来得到搜索结果。
测试案例
# 测试案例
POST /test_a/_doc/3
{
"f": "hello, java is very good, spark is also very good"
}
POST /test_a/_doc/4
{
"f": "java and spark, development language "
}
POST /test_a/_doc/5
{
"f": "Java Spark is a fast and general-purpose cluster computing system. It provides high-level APIs in Java, Scala, Python and R, and an optimized engine that supports general execution graphs."
}
POST /test_a/_doc/6
{
"f": "java spark and, development language "
}
# 查询
GET /test_a/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"f": "java spark"
}
}
}
GET /test_a/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{
"match": {
"f": "java spark"
}
}
],
"should": [
{
"match_phrase": {
"f": {
"query": "java spark",
"slop": 50
}
}
}
]
}
}
}7.前缀搜索 prefix search
使用前缀匹配实现搜索能力。通常针对keyword类型字段,也就是不分词的字段。
# 前缀搜索
GET /test_a/_search
{
"query": {
"prefix": {
"f.keyword": {
"value": "J"
}
}
}
}注意:针对前缀搜索,是对keyword类型字段而言。而keyword类型字段数据大小写敏感
前缀搜索效率比较低。前缀搜索不会计算相关度分数。前缀越短,效率越低。如果使用前缀搜索,建议使用长前缀。因为前缀搜索需要扫描完整的索引内容,所以前缀越长,相对效率越高。
8.通配符搜索
ES中也有通配符。但是和java还有数据库不太一样。通配符可以在倒排索引中使用,也可以在keyword类型字段中使用。
常用通配符
? : 一个任意字符* : 0~n个任意字符# 正则表达式
GET /test_a/_search
{
"query": {
"wildcard": {
"f.keyword": {
"value": "?e*o*"
}
}
}
}性能也很低,也是需要扫描完整的索引。不推荐使用。
9.正则搜索
ES支持正则表达式。可以在倒排索引或keyword类型字段中使用。
常用符号:
[] 范围,如: [0-9]是0~9的范围数字. 一个字符+ 前面的表达式可以出现多次。GET /test_a/_search
{
"query": {
"regexp": {
"f.keyword": "[A-z].+"
}
}
}性能也很低,需要扫描完整索引。
10.搜索推荐
搜索推荐: search as your type, 搜索提示。如:索引中有若干数据以“hello”开头,那么在输入hello的时候,推荐相关信息。(类似百度输入框)
GET /test_a/_search
{
"query": {
"match_phrase_prefix": {
"f": {
"query": "java s",
"slop": 10,
"max_expansions": 10
}
}
}
}其原理和match phrase类似,是先使用match匹配term数据(java),然后在指定的slop移动次数范围内,前缀匹配(s),max_expansions是用于指定prefix最多匹配多少个term(单词),超过这个数量就不再匹配了。
这种语法的限制是,只有最后一个term会执行前缀搜索。
执行性能很差,毕竟最后一个term是需要扫描所有符合slop要求的倒排索引的term。
因为效率较低,如果必须使用,则一定要使用参数max_expansions。
11.fuzzy模糊搜素技术
搜索的时候,可能搜索条件文本输入错误,如:hello world -> hello word。这种拼写错误还是很常见的。fuzzy技术就是用于解决错误拼写的(在英文中很有效,在中文中几乎无效。)。其中fuzziness代表value的值word可以修改多少个字母来进行拼写错误的纠正(修改字母的数量包含字母变更,增加或减少字母。)。f代表要搜索的字段名称。
GET /test_a/_search
{
"query": {
"fuzzy": {
"f": {
"value": "word",
"fuzziness": 2
}
}
}
}