【LetMeFly】1599.经营摩天轮的最大利润
力扣题目链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/maximum-profit-of-operating-a-centennial-wheel/
你正在经营一座摩天轮,该摩天轮共有 4 个座舱 ,每个座舱 最多可以容纳 4 位游客 。你可以 逆时针 轮转座舱,但每次轮转都需要支付一定的运行成本 runningCost 。摩天轮每次轮转都恰好转动 1 / 4 周。
给你一个长度为 n 的数组 customers , customers[i] 是在第 i 次轮转(下标从 0 开始)之前到达的新游客的数量。这也意味着你必须在新游客到来前轮转 i 次。每位游客在登上离地面最近的座舱前都会支付登舱成本 boardingCost ,一旦该座舱再次抵达地面,他们就会离开座舱结束游玩。
你可以随时停下摩天轮,即便是 在服务所有游客之前 。如果你决定停止运营摩天轮,为了保证所有游客安全着陆,将免费进行所有后续轮转 。注意,如果有超过 4 位游客在等摩天轮,那么只有 4 位游客可以登上摩天轮,其余的需要等待 下一次轮转 。
返回最大化利润所需执行的 最小轮转次数 。 如果不存在利润为正的方案,则返回 -1 。
示例 1:
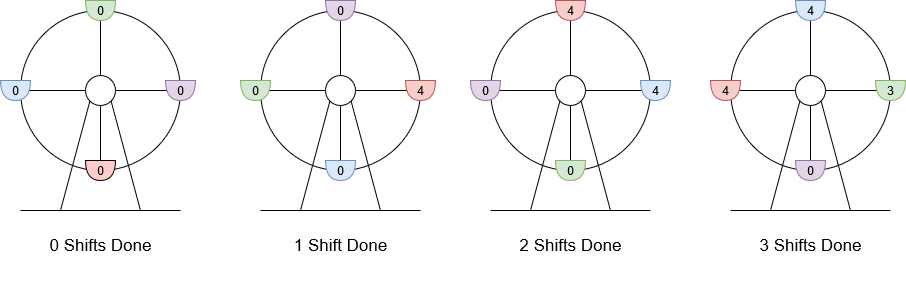
输入:customers = [8,3], boardingCost = 5, runningCost = 6 输出:3 解释:座舱上标注的数字是该座舱的当前游客数。 1. 8 位游客抵达,4 位登舱,4 位等待下一舱,摩天轮轮转。当前利润为 4 * $5 - 1 * $6 = $14 。 2. 3 位游客抵达,4 位在等待的游客登舱,其他 3 位等待,摩天轮轮转。当前利润为 8 * $5 - 2 * $6 = $28 。 3. 最后 3 位游客登舱,摩天轮轮转。当前利润为 11 * $5 - 3 * $6 = $37 。 轮转 3 次得到最大利润,最大利润为 $37 。
示例 2:
输入:customers = [10,9,6], boardingCost = 6, runningCost = 4 输出:7 解释: 1. 10 位游客抵达,4 位登舱,6 位等待下一舱,摩天轮轮转。当前利润为 4 * $6 - 1 * $4 = $20 。 2. 9 位游客抵达,4 位登舱,11 位等待(2 位是先前就在等待的,9 位新加入等待的),摩天轮轮转。当前利润为 8 * $6 - 2 * $4 = $40 。 3. 最后 6 位游客抵达,4 位登舱,13 位等待,摩天轮轮转。当前利润为 12 * $6 - 3 * $4 = $60 。 4. 4 位登舱,9 位等待,摩天轮轮转。当前利润为 * $6 - 4 * $4 = $80 。 5. 4 位登舱,5 位等待,摩天轮轮转。当前利润为 20 * $6 - 5 * $4 = $100 。 6. 4 位登舱,1 位等待,摩天轮轮转。当前利润为 24 * $6 - 6 * $4 = $120 。 7. 1 位登舱,摩天轮轮转。当前利润为 25 * $6 - 7 * $4 = $122 。 轮转 7 次得到最大利润,最大利润为$122 。
示例 3:
输入:customers = [3,4,0,5,1], boardingCost = 1, runningCost = 92 输出:-1 解释: 1. 3 位游客抵达,3 位登舱,0 位等待,摩天轮轮转。当前利润为 3 * $1 - 1 * $92 = -$89 。 2. 4 位游客抵达,4 位登舱,0 位等待,摩天轮轮转。当前利润为 is 7 * $1 - 2 * $92 = -$177 。 3. 0 位游客抵达,0 位登舱,0 位等待,摩天轮轮转。当前利润为 7 * $1 - 3 * $92 = -$269 。 4. 5 位游客抵达,4 位登舱,1 位等待,摩天轮轮转。当前利润为 12 * $1 - 4 * $92 = -$356 。 5. 1 位游客抵达,2 位登舱,0 位等待,摩天轮轮转。当前利润为 13 * $1 - 5 * $92 = -$447 。 利润永不为正,所以返回 -1 。
提示:
n == customers.length1 <= n <= 1050 <= customers[i] <= 501 <= boardingCost, runningCost <= 100
题目描述
首先需要重新描述一下题面(这道题的中文体面翻译得有些抽象)
这道题的意思是:摩天轮每运行一个舱位需要花费成本 r u n n i n g C o s t runningCost runningCost元,每个舱位最多乘坐 4 4 4名乘客,每名乘客收费 b o a r d i n g C o s t boardingCost boardingCost元。
摩天轮匀速运行 i i i个舱位时会有 c u s t o m e r s [ i ] customers[i] customers[i]个新乘客前来排队,乘客左上摩天轮后至少运行一个舱位,然后你可以随时停止摩天轮的运行(管他乘客是否还在半空中)
黑心的商人啊,唯有利益能进入他的视线!
方法一:模拟 + 贪心
使用以下几个变量:
- ans:答案answer的缩写,用于记录答案(运行多少次最佳)
- maxEarn:最多获利多少元
- nowEarn:这次运行后,获利多少元
- customerInLine:到目前为止共有多少乘客在排队
- times:运行了多少次
只需要不断模拟,直到所有乘客都上了🎡
期间记录每次启动摩天轮后的总利润( 原始利润 + 本舱乘客数 × 每位乘客费用 − 🎡转动一个舱位的成本 原始利润 + 本舱乘客数 \times 每位乘客费用 - 🎡转动一个舱位的成本 原始利润+本舱乘客数×每位乘客费用−🎡转动一个舱位的成本)
如果本次利润大于历史最佳利润maxEarn,就更新maxEarn和ans。
为什么我要给这种解法打上一个“贪心”的Tag呢?因为黑心的商人有一个原则:不管乘客之间是否相互认识,尽量把一舱塞满,没有新乘客了不让旧乘客下来就关🎡
- 时间复杂度 O ( l e n ( c u s t o m e r s ) + ∑ i = 0 i < l e n ( c u s t o m e r ) c u s t o m e r s [ i ] ) O(len(customers) + \sum_{i=0}^{i<len(customer)} customers[i]) O(len(customers)+∑i=0i<len(customer)customers[i])。复杂度是乘客列表的长度和乘客数量之和(除以4)
- 空间复杂度 O ( 1 ) O(1) O(1)
AC代码
C++
class Solution {
public:
int minOperationsMaxProfit(vector<int>& customers, int boardingCost, int runningCost) {
int ans = 0;
int maxEarn = 0;
int nowEarn = 0;
int customerInLine = 0;
int times = 0;
while (true) {
if (times < customers.size()) {
customerInLine += customers[times];
}
times++;
int thisCustomer = min(4, customerInLine);
nowEarn += thisCustomer * boardingCost - runningCost;
if (nowEarn > maxEarn) {
maxEarn = nowEarn;
ans = times;
}
customerInLine -= thisCustomer;
if (!customerInLine && times >= customers.size()) {
break;
}
}
return ans ? ans : -1;
}
};
Python
# from typing import List
class Solution:
def minOperationsMaxProfit(self, customers: List[int], boardingCost: int, runningCost: int) -> int:
ans = 0
maxEarn = 0
nowEarn = 0
customerInLine = 0
times = 0
while True:
if times < len(customers):
customerInLine += customers[times]
times += 1
thisCustomer = min(4, customerInLine)
customerInLine -= thisCustomer
nowEarn += thisCustomer * boardingCost - runningCost
if nowEarn > maxEarn:
maxEarn = nowEarn
ans = times
if not customerInLine and times >= len(customers):
break
return ans if ans else -1
同步发文于CSDN,原创不易,转载请附上原文链接哦~
Tisfy:https://letmefly.blog.csdn.net/article/details/129345304