什么是SpringIOC?
答:IOC即控制反转,就是我们不在手动的去new一个对象,而是将创建对象的权力交给Spring去管理,我们想要一个User类型的对象,就只需要定义一个User类型的变量user1,然后让Spring去给我们创建对象,然后将创建的对象注入到user1中。
什么是依赖注入?
答:DI机制(DependencyInjection),依赖注入,上面提到的Spring将它创建的对象交给我们创建的变量的过程。依赖注入的方式有三种(set方法注入、构造器注入、注解注入)。下面我们简答的实现注解注入,了解IOC原理。
第一步,创建注解
创建的注解其实没有太大的作用,就是用来标记哪个类需要Spring帮我们去管理,哪个成员变量需要Spring去给我们注入。
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
/**
*创建注解文件Component.java
*标记需要IOC的类
**/
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface Component {
}
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
/**
*创建注解文件Autowired.java
*标记需要Spring帮忙DI的成员变量
**/
@Target(ElementType.FIELD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface Autowired {
}
第二部,创建两个需要注解的类
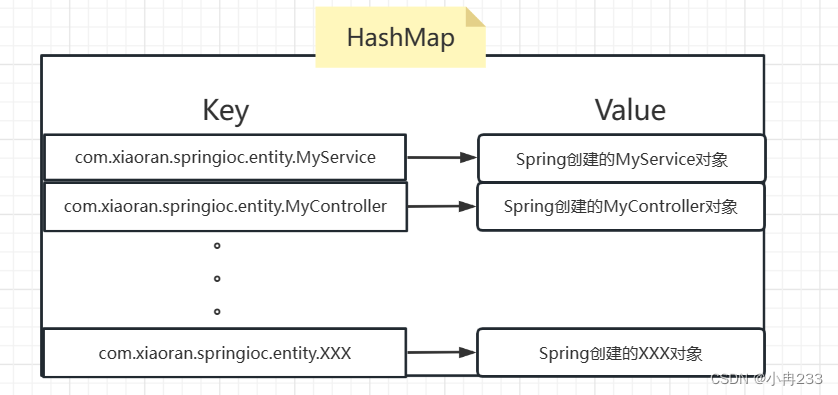
我们想要将MyService和MyController都交给Spring管理(项目启动后将这两个类实例化,然后放入一个HashMap中,等待调用)
import com.xiaoran.springioc.annotation.Component;
@Component
public class MyService {
private int id;
private String name;
private int age;
public void speck(String name,int age) {
System.out.println("大家好,我叫"+name+"今年"+age+"岁了,请多多关照!");
}
}
import com.xiaoran.springioc.annotation.Autowired;
import com.xiaoran.springioc.annotation.Component;
@Component
public class MyController {
@Autowired
private MyService myService;
public void test(){
myService.speck("moss",67);
}
}
第三步,IOC过程
创建MyIOC类,用于IOC过程
- 在项目启动时,实例化MyIOC,加载MyIOC的无参构造器时,对项目下所有的文件进行扫描,调用实例化方法完成被注释类的实例化和依赖注入。
private String basePath="D:\\Project\\XiaoRanIOC\\src\\main\\java\\com\\xiaoran\\springioc\\"; //项目路径
private String basePackage="com.xiaoran.springioc"; //包路径
private List<String> filePaths;//所有文件的路径
private List<String> beanNames;//所有.java文件的全限定名
private Map<String, Object> beans = new HashMap<>();
/**
* 实例化MyIOC时,让IOC进程伴随无参构造器加载启动
*/
public MyIOC() throws FileNotFoundException, IllegalAccessException {
//扫描路径下所有文件
scan();
beanNames = new ArrayList<>();
initBeanNames();
initBeans();
}
- 扫描项目下所有文件,将所有文件的路径存入filePaths中
/**
* 扫描项目下所有文件,将所有文件的路径存入filePaths中
*/
public void scan() throws FileNotFoundException {
File file = new File(basePath);
filePaths=new ArrayList<>();
if (file.exists()) {
//将file放入列,出队后判断,如果是路径那就继续入队,如果是文件,就将文件路径放入filePaths中
Queue<File> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(file);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
File poll = queue.poll();
if(poll==null){
continue;
}
if (poll.isDirectory()){
File[] files = poll.listFiles();
for (File f :
files) {
queue.add(f);
}
}else{
filePaths.add(poll.getPath());
}
}
}else {
throw new FileNotFoundException(basePath + "不存在");
}
}
- 将所有的.java文件的全限定名放入beanNames中
/**
*将所有的.java文件的全限定名放入beanNames中
*/
public void initBeanNames(){
for (String string :
filePaths) {
String replace = string.replace(basePath, "");
if (replace.endsWith(".java")) {
replace = replace.substring(0, replace.length() - 5);
}
char[] chars = replace.toCharArray();
for (int i = 0; i < chars.length; i++) {
if(chars[i]=='\\'){
chars[i] = '.';
}
}
beanNames.add(basePackage+"."+new String(chars));
}
}
- 核心代码:将被@Component注解的类实例化放入beans(HashMap)中,等待调用
/**
*核心代码:将被@Component注解的类实例化放入beans(HashMap)中,等待调用
*/
public void initBeans() throws IllegalAccessException {
//遍历包路径下所有类,是否被@Component注解,如果被注解就将其实例化放入beans
for (String beanName :
beanNames) {
try {
Class<?> aClass = Class.forName(beanName);
//获取类的所有注解
Annotation[] declaredAnnotation = aClass.getDeclaredAnnotations();
//遍历所有注解,是否是@Component注解
for (Annotation annotation :
declaredAnnotation) {
if (annotation instanceof Component){
Object o = aClass.newInstance();
beans.put(beanName, o);
}
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InstantiationException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//遍历所有的beans的成员变量,如果有成员变量被@Autowired修饰,就根据成员变量的类型从beans中查找到对应的对象,用此对象给成员变量注入
//因为是从beans中查找对象,所以被注入的成员变量对应的类一定是已经被实例化放入beans中的
for (Map.Entry<String, Object> entry : beans.entrySet()) {
Object value = entry.getValue();
Field[] fields = value.getClass().getDeclaredFields();
for (Field f :
fields) {
Annotation[] declaredAnnotations = f.getDeclaredAnnotations();
for (Annotation annotation :
declaredAnnotations) {
if (annotation instanceof Autowired){
//获取被@Autowired注解成员变量的类型(全限定名)
String typeName = f.getType().getName();
Object o = beans.get(typeName);
//暴力反射
f.setAccessible(true);
//将从beans中获得的对象o,注入到该属性上
f.set(value,o);
}
}
}
}
}
/**
* 对外提供一个方法:根据全限定名返回对象
*/
public Object getInstance(String beanName){
return beans.get(beanName);
}
第四步,测试
创建测试类IOCTest
import com.xiaoran.springioc.entity.MyController;
import com.xiaoran.springioc.ioc.MyIOC;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
public class IOCTest {
@Test
public void test() throws FileNotFoundException, IllegalAccessException {
MyIOC myIOC = new MyIOC();
MyController myController = (MyController)myIOC.getInstance(MyController.class.getName());
myController.test();
}
}
GitHub
手撕SpringIOC