1、背景
在开发过程中很多朋友,由于不会正确使用intern(),导致开发的程序,执行效率比较差。同时最近发现一道非常有意思的关于intern()的面试题,这道面试题还是有不小的难度,相信很多朋友看到以后也不知道怎么解答,所以今天咱们深入详解下intern()。
2、intern()在API中的介绍(jdk1.8)
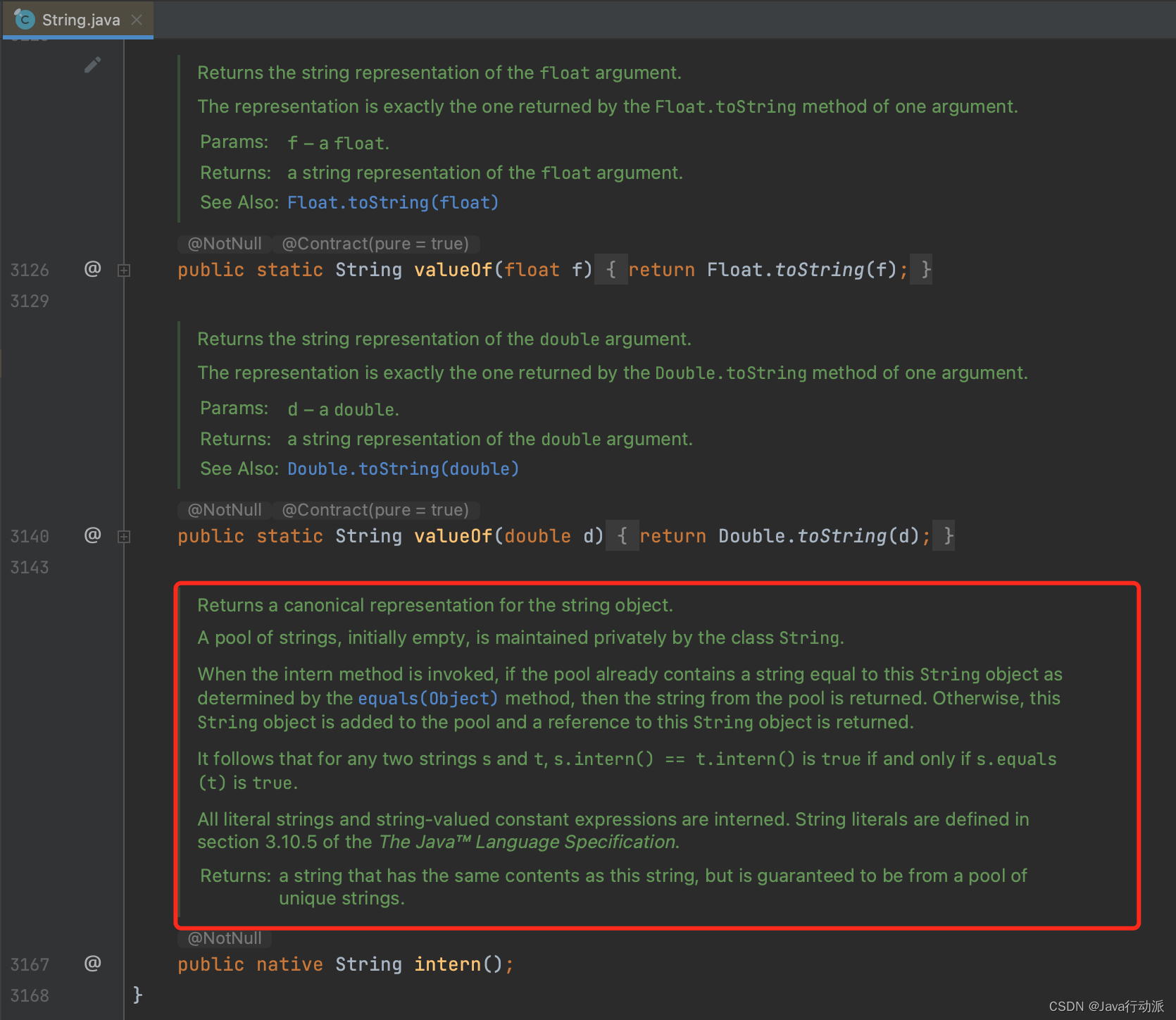
Returns a canonical representation for the string object.
A pool of strings, initially empty, is maintained privately by the class String.
When the intern method is invoked, if the pool already contains a string equal to this String object as determined by the equals(Object) method, then the string from the pool is returned. Otherwise, this String object is added to the pool and a reference to this String object is returned.
It follows that for any two strings s and t, s.intern() == t.intern() is true if and only if s.equals(t) is true.
All literal strings and string-valued constant expressions are interned. String literals are defined in section 3.10.5 of the The Java ™ Language Specification.
翻译:
当调用intern()时,如果池子里已经包含了一个与这个String对象相等的字符串,正如equals(Object)方法所确定的,那么池子里的字符串会被返回。否则,这个String对象被添加到池中,并返回这个String对象的引用。
注意:这里说的池子就是字符串常量池,大白话就是,调用intern()后,如果String对象的值如果在字符串常量池中,直接返回常量池中的地址,否则这个String对象将被添加到字符串常量池中,并返回字符串常量池中的地址。
由此可见,对于任何两个字符串s和t,当且仅当s.equals(t)为真时,s.intern() == t.intern()为真。
所有字面字符串和以字符串为值的常量表达式都是interned。
剖析:
如果不是用双引号声明的String对象,可以使用String提供的intern方法,它会从字符串常量池中查询当前字符串是否存在,若不存在就会将当前字符串放入常量池中。
例如:
String str = new String("hello intern").intern();也就是说,如果在任意字符串上调用String.intern方法,那么其返回结果所指向的那个类实例,必须和直接以常量形式出现的字符串实例完全相同。因此,下列表达式的值必定是true
("a"+"b"+"c").intern() == "abc"通俗点讲,Interned string就是确保字符串在内存里只有一份拷贝,这样可以节约内存空间,加快字符串操作任务的执行速度。注意,这个值会被存放在字符串内部池(String Intern Pool)
3、面试题
面试题:如何保证变量s指向的是字符串常量池中的数据呢?
有两种方式:
①、通过字符串字面量方式什么s变量:String s = "abc";
②、通过intern():String s = new String("abc").intern();
面试题:问一下代码执行结果 jdk6 vs jdk7/jdk8
在看这个面试题之前,的知道 new String 和 new String() + new String() 到底产生了几个对象,如果不清楚的朋友,可以先看这篇文章 https://blog.csdn.net/u011837804/article/details/129307237
@Test
public void test1() {
String str = new String("1");// ”1“被放入了字符串常量池中 ,
// str持有的是new String()后放入堆中的对象地址(非字符串常量池)
str.intern();
String str2 = "1";// str2持有的是字符串常量池中的地址
System.out.println(str == str2);//一个是字符串常量池中的对象一个是堆内对象,所以为false
//str3记录的地址是 堆内对象地址
//注意:执行完此行代码后 字符串常量池中是没有 ”11“的
String str3 = new String("1") + new String("1");
//执行完此行代码后,将”11“ 放入常量池中
//在jdk6中,此行 代码会在常量池中创建一个新的对象,堆内的对象还是存在的 则结果未false
//在jdk7中,此行 代码则会将堆内的对象的地址复制一份,放入常量池,
//然后 堆内对象直接引用的是常量池中对象地址,所以str3就间接引用了常量池中对象的地址 则结果为true
//在jdk8和jdk7一样
str3.intern();
//执行完此行代码后,str4记录的是常量池中已有对象的地址
String str4 = "11";
System.out.println(str3 == str4);//jdk6:false, jdk7/jdk8:true
//jdk6\jdk7及以上 之所以出现不同的结果是因为,在jdk7及以后字符串常量池的实现发生了变化。
//在JDK6及以前的版本中,字符串常量池被存储在永久代中,而在JDK7及以后的版本中,字符串常量池被存储在堆中
}
/**
* 很简单的变化下位置,结果又不一致 为 false
*/
@Test
public void test2() {
String str3 = new String("1") + new String("1");
String str4 = "11";
str3.intern();
System.out.println(str3 == str4);
}4、总结
JDK1.6中,将这个字符串对象尝试放入串池。
如果串池中有,则并不会放入。返回已有的串池中的对象的地址
如果没有,会把此对象复制一份,放入串池,并返回串池中的对象地址
JDK1.7起,将这个字符串对象尝试放入串池。
如果串池中有,则并不会放入。返回已有的串池中的对象的地址
如果没有,则会把对象的引用地址复制一份,放入串池,并返回串池中的引用地址
5、intern的效率测试
5.1、不使用intern()测试
代码:
/**
* @author liuchao
* @date 2023/3/4
*/
public class Test4 {
static final int MAX_COUNT = 1000 * 10000;
/***
* 长度1千万的数组
*/
static final String[] arr = new String[MAX_COUNT];
public static void main(String[] args) {
//填入这些数据
Integer[] data = new Integer[]{1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10};
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_COUNT; i++) {
//直接创建String 对象,填入
arr[i] = new String(String.valueOf(data[i % data.length]));
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("花费的时间为:" + (end - start));
/**
* 暂停一段时间,为了查看内存使用情况
*/
try {
Thread.sleep(1000000);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.getStackTrace();
}
}
}
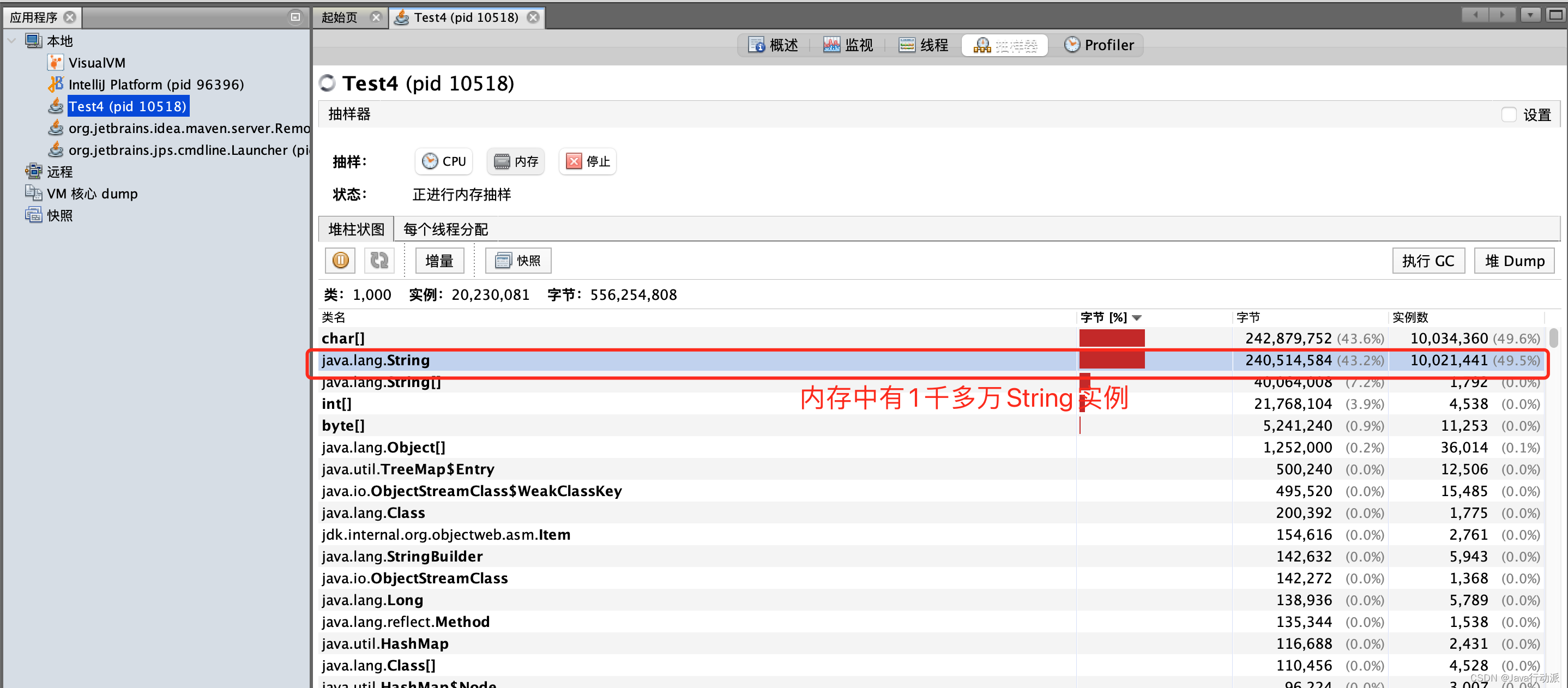
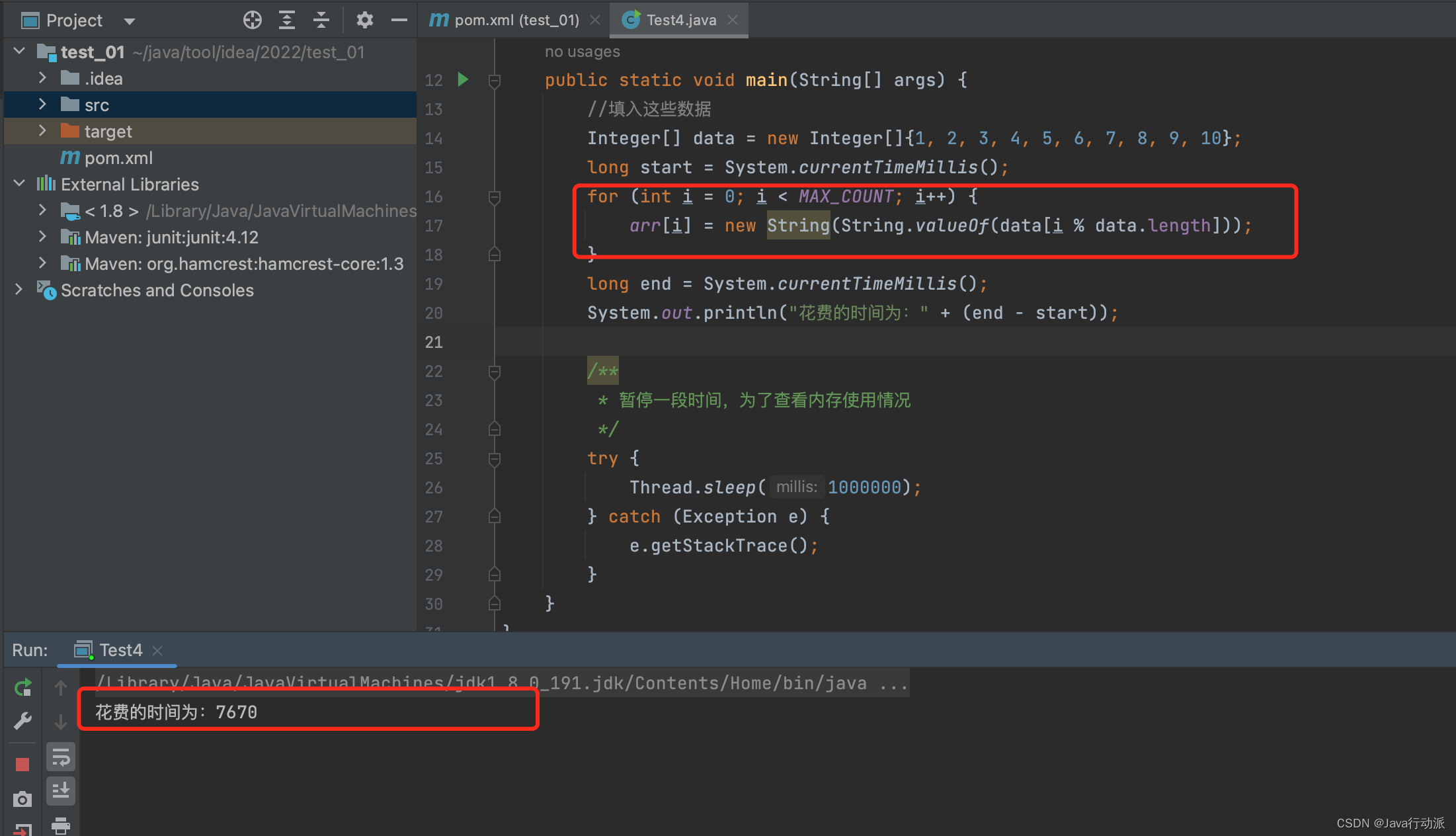
用时7670ms
5.2、使用intern()测试
/**
* @author liuchao
* @date 2023/3/4
*/
public class Test4 {
static final int MAX_COUNT = 1000 * 10000;
/***
* 长度1千万的数组
*/
static final String[] arr = new String[MAX_COUNT];
public static void main(String[] args) {
//填入这些数据
Integer[] data = new Integer[]{1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10};
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_COUNT; i++) {
// 创建String对象后,调用intern()
arr[i] = new String(String.valueOf(data[i % data.length])).intern();
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("花费的时间为:" + (end - start));
/**
* 暂停一段时间,为了查看内存使用情况
*/
try {
Thread.sleep(1000000);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.getStackTrace();
}
}
}
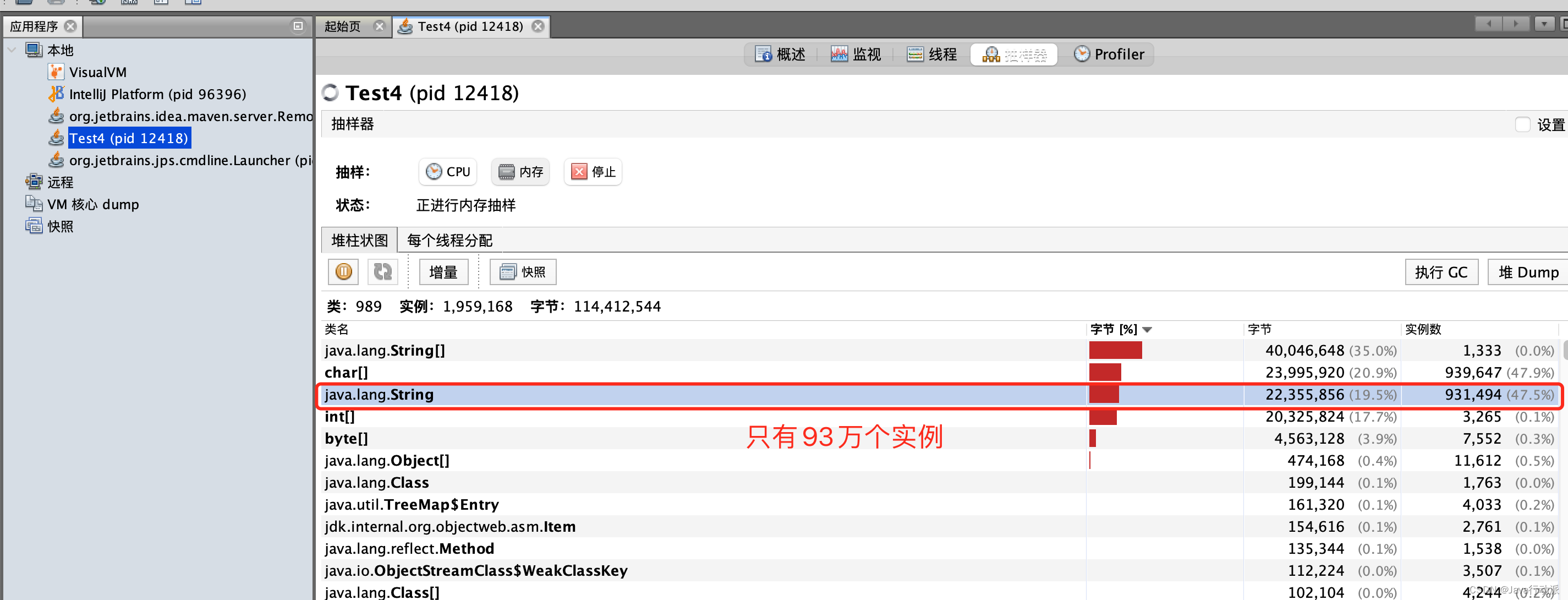
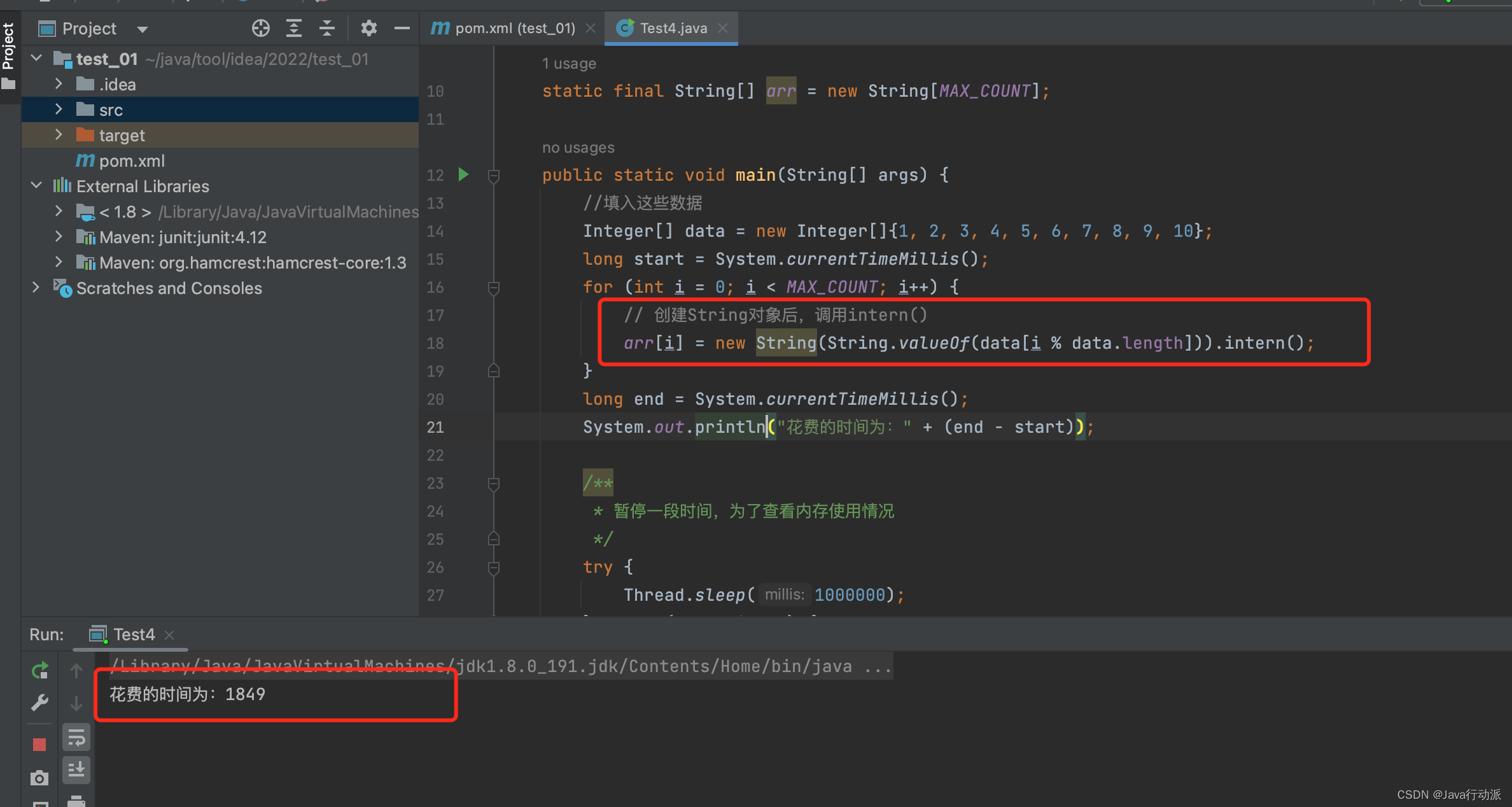
用时只有1849ms
5.3、结论
结论:对于程序中大量使用存在的字符串时,尤其存在很多已经重复的字符串时,使用intern()方法能够节省内存空间。
大的网站平台,需要内存中存储大量的字符串。比如社交网站,很多人都存储:北京市、海淀区等信息。这时候如果字符串都调用intern()方法,就会很明显降低内存的大小。