Sping MVC 源码解析——HandlerMapping处理器映射器
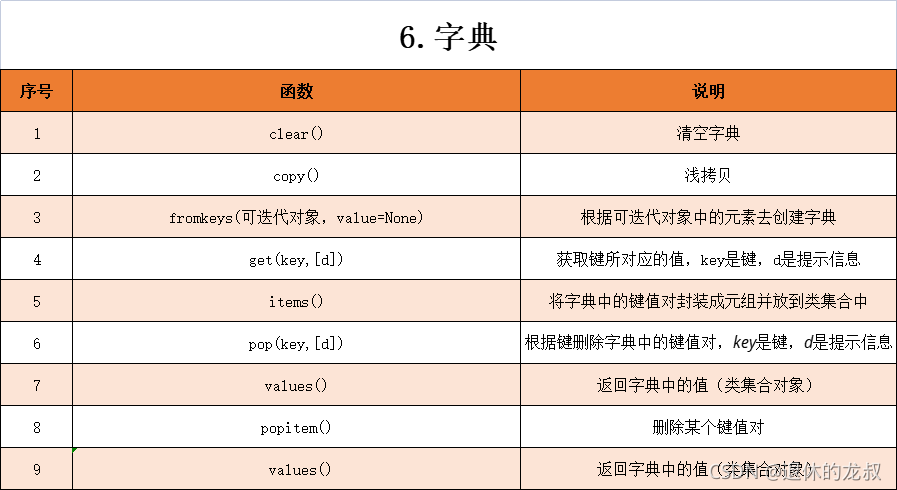
- 1. 什么是HandlerMapping
- 2. HandlerMapping
- 2.1 HandlerMapping初始化
- 2.2 getHandler解析
- 3. getHandlerInternal()子类实现
- 3.1 AbstractUrlHandlerMapping与AbstractHandlerMethodMapping的区别
- 3.2 AbstractUrlHandlerMapping
- 3.3 AbstractHandlerMethodMapping
- 4. RequestMappingHandlerMapping
- 4.1 加载过程
- 5. SimpleUrlHandlerMapping
- 6. 使用HandlerMapping
- 6.1 如何选择合适的HandlerMapping
- 7. 总结
- 8. 参考文章
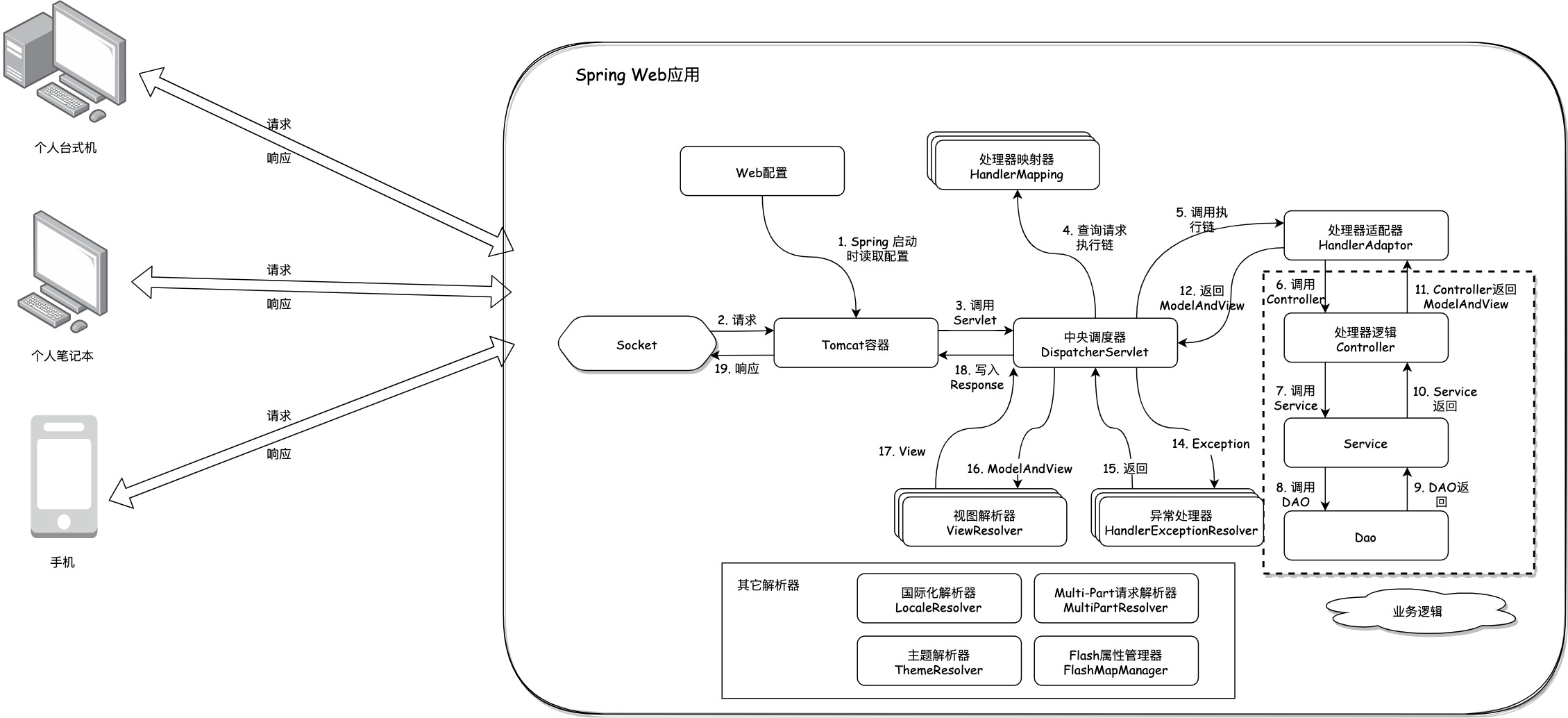
注:图片引用自SpringMVC 解析(一)概览 - 御狐神 - 博客园 (cnblogs.com)
1. 什么是HandlerMapping
在Spring MVC中,HandlerMapping(处理器映射器)用于确定请求处理器对象。请求处理器可以是任何对象,只要它们使用了@Controller注解或注解@RequestMapping。HandlerMapping负责将请求(url)映射到适当的处理器对象(Controller)。
注:Handler即绑定了注解@RequestMapping或@Controller的类
HandlerMapping接口定义了一个方法:
public interface HandlerMapping {
HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception;
}
getHandler方法用于查找处理器对象并返回处理程序的执行链,HandlerExecutionChain包含了处理器对象和一系列拦截器,这些拦截器可以在处理程序执行之前和之后执行一些操作。
HandlerMapping接口继承结构体系
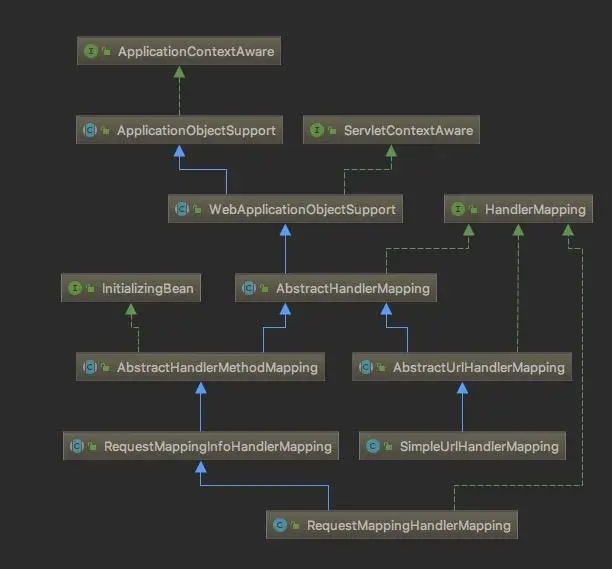
2. HandlerMapping
2.1 HandlerMapping初始化
Http请求由servlet容器分发到DispatcherServlet,在其中会进行九大核心组件的初始化
protected void initStrategies(ApplicationContext context) {
this.initMultipartResolver(context);
this.initLocaleResolver(context);
this.initThemeResolver(context);
this.initHandlerMappings(context);
this.initHandlerAdapters(context);
this.initHandlerExceptionResolvers(context);
this.initRequestToViewNameTranslator(context);
this.initViewResolvers(context);
this.initFlashMapManager(context);
}
这里我们主要关注
initHandlerMappings
public class DispatcherServlet extends FrameworkServlet {
private void initHandlerMappings(ApplicationContext context) {...}
}
private void initHandlerMappings(ApplicationContext context) {
this.handlerMappings = null;
//private boolean detectAllHandlerMappings = true;
//该值默认为 true,查询所有的handlerMapping
// 如果设置为 false , Spring MVC就只会查找名为“handlerMapping”的bean,并作为当前系统的唯一的HandlerMapping
if (this.detectAllHandlerMappings) {
//在ApplicationContext中查找所有handler映射,包括父类上下文。
Map<String, HandlerMapping> matchingBeans = BeanFactoryUtils.beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors(context, HandlerMapping.class, true, false);
//存在Handler
if (!matchingBeans.isEmpty()) {
//将获取的 HandlerMapping 转换成集合并排序
this.handlerMappings = new ArrayList(matchingBeans.values());
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(this.handlerMappings);
}
} else {
//没有找到
try {
//查找名为“handlerMapping”的bean,并作为当前系统的唯一的HandlerMapping,确保至少有一个HandlerMapping
HandlerMapping hm = (HandlerMapping)context.getBean("handlerMapping", HandlerMapping.class);
this.handlerMappings = Collections.singletonList(hm);
} catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException var4) {
}
}
this.handlerMappings = this.getDefaultStrategies(context, HandlerMapping.class);
}
Iterator var6 = this.handlerMappings.iterator();
//迭代HandlerMapping
while(var6.hasNext()) {
HandlerMapping mapping = (HandlerMapping)var6.next();
//判断HandlerMapping实例是否启用了解析的PathPatterns
//如果启用则DispatcherServlet会自动解析RequestPath,以便在HandlerMappings,HandlerInterceptors和其他组件中访问
if (mapping.usesPathPatterns()) {
this.parseRequestPath = true;
break;
}
}
}
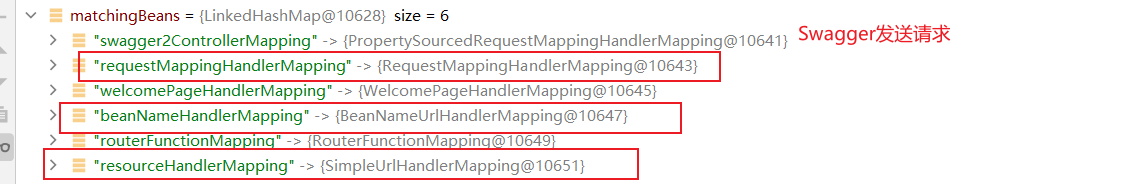
Spring MVC框架中有多个HandlerMapping实现,每个实现都可以使用不同的策略来确定请求处理器对象。最常见的HandlerMapping实现是RequestMappingHandlerMapping和SimpleUrlHandlerMapping。
2.2 getHandler解析
getHandler方法根据请求找到对应的处理器对象, 在
DispatcherServlet类中,doDispatch()方法调用getHandler()方法得到HandlerExecutionChain对象。
注:
HandlerExecutionChain是一个类,用于封装处理器对象和拦截器列表。它是HandlerMapping的getHandler方法的返回值。
HandlerExecutionChain的作用是在请求处理流程中,提供一种责任链模式(看图),让拦截器可以在处理器执行前后进行一些额外的操作,例如验证、日志、事务等。拿到这个对象后,DispatcherServlet会调用它的applyPreHandle方法,执行所有拦截器的preHandle方法。如果都返回true,则继续调用处理器的方法;否则,返回响应或者跳转到其他页面。
处理器执行完毕后,DispatcherServlet会调用它的applyPostHandle方法,执行所有拦截器的postHandle方法。这些方法可以对模型和视图进行修改或增强。
最后,在渲染视图之后,DispatcherServlet会调用它的triggerAfterCompletion方法,执行所有拦截器的afterCompletion方法。这些方法可以进行一些清理工作或异常处理
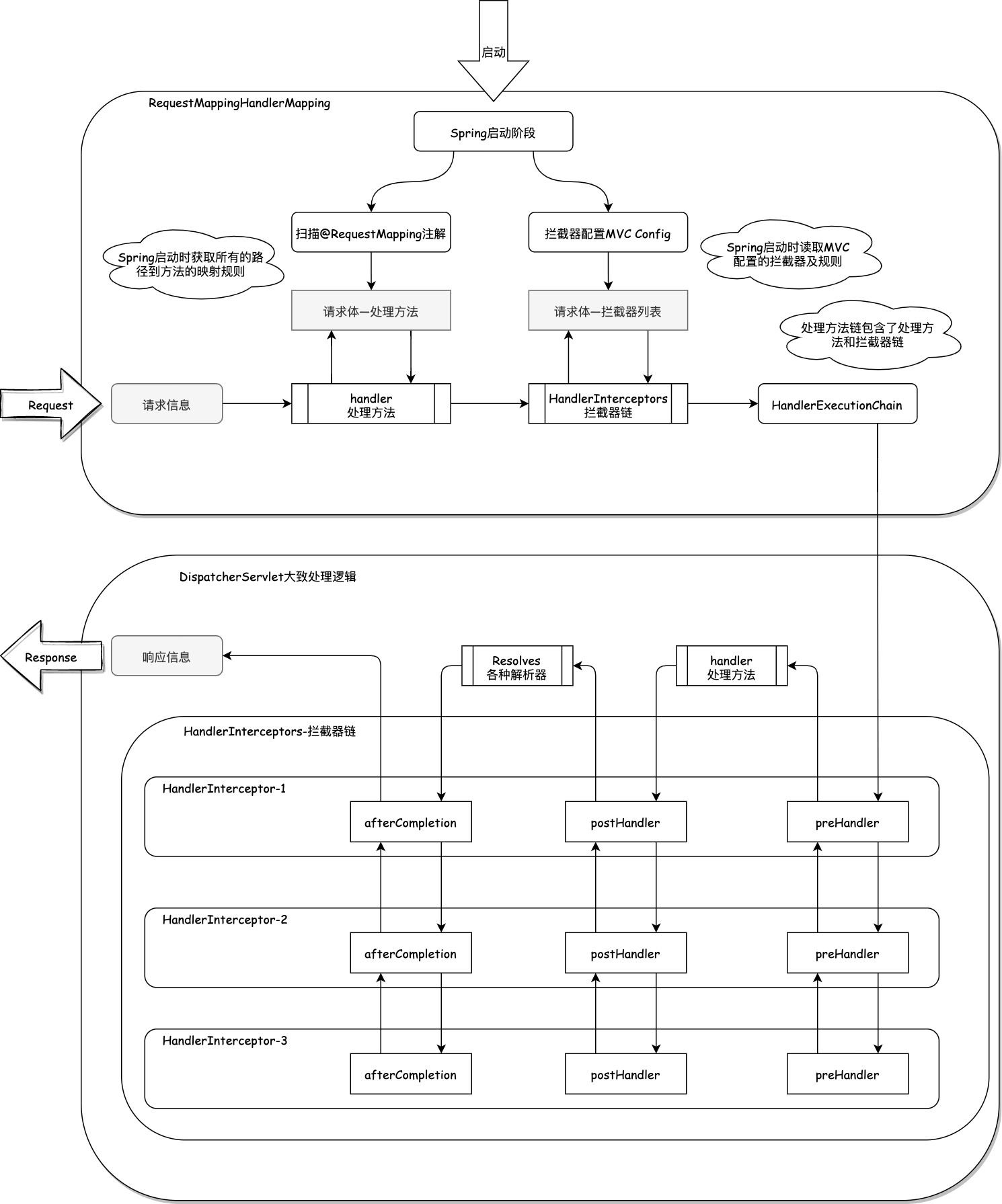
注:图片引用自SpringMVC 解析(一)概览 - 御狐神 - 博客园 (cnblogs.com)
源码解析:
protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
mappedHandler = this.getHandler(processedRequest);
}
//返回一个HandlerExecutionChain对象
@Nullable
protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
if (this.handlerMappings != null) {
Iterator var2 = this.handlerMappings.iterator();
//遍历所有的初始化的HandlerMapping列表
while(var2.hasNext()) {
HandlerMapping mapping = (HandlerMapping)var2.next();
//获取一个HandlerExecutionChain对象,它包含了处理请求的handler对象和任何配置的拦截器
//接口方法
HandlerExecutionChain handler = mapping.getHandler(request);
//匹配到就进行返回
if (handler != null) {
return handler;
}
}
}
return null;
}
实现类为
AbstractHandlerMapping
public abstract class AbstractHandlerMapping extends WebApplicationObjectSupport implements HandlerMapping, Ordered, BeanNameAware {
public final HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {……};
}
@Nullable
public final HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
// 根据请求从缓存中查找handler,如果没有则调用子类实现的getHandlerInternal()方法
该方法在本类中有定义,是一个protected型的抽象方法
Object handler = this.getHandlerInternal(request);
// 没有找到,则会使用getDefaultHandler()方法获取默认的处理器
if (handler == null) {
handler = this.getDefaultHandler();
}
if (handler == null) {
return null;
} else {
//检查handler对象是否是一个字符串类型。如果是的话,就从应用上下文中根据字符串名称获取对应的bean作为handler对象
if (handler instanceof String) {
String handlerName = (String)handler;
handler = this.obtainApplicationContext().getBean(handlerName);
}
//如果请求对象中没有缓存的路径信息,就调用initLookupPath方法来解析请求的路径信息,并且保存在请求对象的一个属性中
if (!ServletRequestPathUtils.hasCachedPath(request)) {
this.initLookupPath(request);
}
//根据handler对象和请求创建一个HandlerExecutionChain对象,包含处理器对象和拦截器列表
HandlerExecutionChain executionChain = this.getHandlerExecutionChain(handler, request);
return executionChain;
}
}
到此为止就获得了executionChain对象实例了,也就是第一张图的第4步。
3. getHandlerInternal()子类实现
getHandlerInternal()方法在AbstractUrlHandlerMapping类和AbstractHandlerMethodMapping类中均有实现, 均继承于AbstractHandlerMapping类
3.1 AbstractUrlHandlerMapping与AbstractHandlerMethodMapping的区别
AbstractUrlHandlerMapping是基于URL映射的HandlerMapping,它支持字面匹配和模式匹配,如"/test/*“,”/test/"等, 它返回的Handler是一个类级别的对象**,例如一个Controller类或一个Bean对象
AbstractHandlerMethodMapping是基于方法级别的HandlerMapping,它支持使用@RequestMapping注解来指定请求路径和方法。它返回的Handler是一个方法级别的对象,例如一个Controller类中的某个方法或一个Bean对象中的某个方法
示例:
AbstractUrlHandlerMapping的一个子类是SimpleUrlHandlerMapping,它可以在XML配置文件中定义URL和Handler的映射关系
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.SimpleUrlHandlerMapping">
<property name="mappings">
<props>
<prop key="/test.do">testController</prop>
</props>
</property>
</bean>
<bean id="testController" class="com.example.TestController"/>
AbstractHandlerMethodMapping的一个子类是RequestMappingHandlerMapping,它可以在Java类中使用@RequestMapping注解来定义URL和方法的映射关系
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/test")
public class TestController {
@RequestMapping("/do")
public String doSomething() {
// ...
}
}
这两种方式都可以实现URL和Handler的绑定,但是后者更灵活和简洁
3.2 AbstractUrlHandlerMapping
//根据用户请求信息中的URL查找handler
protected Object getHandlerInternal(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
//初始化请求的查找路径,也就是去掉上下文路径和后缀名的URL路径
String lookupPath = this.initLookupPath(request);
Object handler;
//是否使用路径模式来选择不同的查找handler的方法
//
if (this.usesPathPatterns()) {
//获取请求的RequestPath对象,它封装了请求的URL路径、上下文路径、后缀名等信息。
RequestPath path = ServletRequestPathUtils.getParsedRequestPath(request);
//根据RequestPath对象、查找路径和请求对象,调用lookupHandler()方法来查找匹配的handler
handler = this.lookupHandler(path, lookupPath, request);
} else {
handler = this.lookupHandler(lookupPath, request);
}
//没有找到匹配的handler时,尝试获取根handler或者默认handler,并进行验证和包装。
if (handler == null) {
Object rawHandler = null;
if (StringUtils.matchesCharacter(lookupPath, '/')) {
rawHandler = this.getRootHandler();
}
if (rawHandler == null) {
rawHandler = this.getDefaultHandler();
}
if (rawHandler != null) {
if (rawHandler instanceof String) {
String handlerName = (String)rawHandler;
rawHandler = this.obtainApplicationContext().getBean(handlerName);
}
this.validateHandler(rawHandler, request);
handler = this.buildPathExposingHandler(rawHandler, lookupPath, lookupPath, (Map)null);
}
}
//返回获取到的handler对象
return handler;
}
3.3 AbstractHandlerMethodMapping
protected HandlerMethod getHandlerInternal(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
//初始化请求的查找路径,也就是去掉上下文路径和后缀名的URL路径
String lookupPath = this.initLookupPath(request);
//获取映射注册表的读锁,以保证线程安全
this.mappingRegistry.acquireReadLock();
HandlerMethod var4;
//获取读锁后,尝试查找匹配的handler方法,并在最后释放读锁
try {
//根据查找路径和请求对象,在映射注册表中查找匹配的handler方法
HandlerMethod handlerMethod = this.lookupHandlerMethod(lookupPath, request);
//判断是否找到了handler方法
//如果找到了,则调用createWithResolvedBean()方法来创建一个新的HandlerMethod实例,并解析其关联的bean对象;
//如果没有找到,则返回null。
var4 = handlerMethod != null ? handlerMethod.createWithResolvedBean() : null;
} finally {
this.mappingRegistry.releaseReadLock();
}
//返回获取到的handler对象
return var4;
}
下面简单介绍一下AbstractUrlHandlerMapping与AbstractHandlerMethodMapping的常用子类实现
4. RequestMappingHandlerMapping
RequestMappingHandlerMapping是Spring MVC中最常用的HandlerMapping实现之一。它使用@RequestMapping注解来确定请求处理器对象。
下面是一个简单的控制器示例:
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/user")
public class UserController {
@GetMapping("/{id}")
public String getUser(@PathVariable int id, Model model) {
User user = userRepository.findById(id);
model.addAttribute("user", user);
return "user";
}
}
在这个示例中,
UserController类被@Controller注解标记为一个控制器,并且所有请求路径以/user开头。@GetMapping注解用于处理HTTP GET请求,{id}是一个路径变量,它将匹配任何非空字符串,并将其解析为一个整数。getUser方法将通过id获取用户对象并将其添加到模型中,最后返回一个视图名为"user"的字符串。
RequestMappingHandlerMapping会扫描所有@Controller注解标记的类,并将所有带有@RequestMapping注解的方法添加到HandlerMapping中。在请求到达服务器时,RequestMappingHandlerMapping将匹配请求路径和请求方法,并将请求映射到适当的处理器方法。
4.1 加载过程
RequestMappingHandlerMapping实现了接口InitializingBean,在bean加载完成后会自动调用afterPropertiesSet方法,在此方法中调用了initHandlerMethods()来实现初始化initHandlerMethods()会遍历所有bean,如果bean实现带有注解@Controller或者@RequestMapping 则进一步调用detectHandlerMethods处理,处理逻辑大致就是根据@RequestMapping配置的信息,把解析结果封装成RequestMappingInfo对象,也就是说RequestMappingInfo对象是用来装载方法的匹配相关信息,每个匹配的方法都会对应一个RequestMappingInfo对象,然后注册到MappingRegistry中
具体流程:
- 当Spring容器启动时,它会扫描所有带有@Controller或@RestController注解的类,并将它们作为处理器对象注册到
RequestMappingHandlerMapping中。RequestMappingHandlerMapping会遍历每个处理器对象中的所有方法,并使用getMappingForMethod()方法来获取每个方法上定义或继承的@RequestMapping注解,然后将这些注解转换为RequestMappingInfo对象,包含了请求路径、请求方法、请求参数、请求头等信息。RequestMappingHandlerMapping会将每个RequestMappingInfo对象和对应的处理器方法封装成一个HandlerMethod对象,并将这些对象存储在一个Map结构中,以便于后续查找。- 当一个HTTP请求到达
DispatcherServlet时,它会调用RequestMappingHandlerMapping的getHandler()方法来根据请求URI找到匹配的处理器方法。RequestMappingHandlerMapping会遍历Map中的所有键值对(即每个RequestMappingInfo和HandlerMethod),并使用PathMatcher或PathPatternParser来判断请求URI是否与RequestMappingInfo中定义的路径匹配。如果匹配,就返回对应的HandlerMethod;如果不匹配,就继续查找下一个键值对。- 如果找到了匹配的
HandlerMethod,DispatcherServlet就会根据其类型选择合适的HandlerAdapter来执行它,并返回响应结果;如果没有找到匹配的HandlerMethod,DispatcherServlet就会抛出异常或者返回404错误页面。
步骤1的注册过程
public void afterPropertiesSet() {
//……
super.afterPropertiesSet();
}
//父类AbstractHandlerMethodMapping 的方法
public void afterPropertiesSet() {
this.initHandlerMethods();
}
//扫描容器中的bean,检测和注册handler方法
protected void initHandlerMethods() {
//获取候选的bean名称数组
String[] var1 = this.getCandidateBeanNames();
int var2 = var1.length;
//遍历
for(int var3 = 0; var3 < var2; ++var3) {
String beanName = var1[var3];
//用于过滤掉以"scopedTarget."开头的bean名称的。
//这些bean名称是由Spring创建的代理对象,用于支持不同作用域的bean
//例如session或request。这些代理对象不是真正的handler,所以要排除掉。
if (!beanName.startsWith("scopedTarget.")) {
//处理候选的bean,判断候选的bean是否是一个handler,也就是是否有@Controller注解或者@RequestMapping注解
//如果是的话,就调用detectHandlerMethods方法,用于检测和注册handler方法
this.processCandidateBean(beanName);
}
}
//初始化handler方法, 对所有handler方法进行排序和日志输出
this.handlerMethodsInitialized(this.getHandlerMethods());
}
//检测和注册handler方法
protected void detectHandlerMethods(Object handler) {
//存储handler对象的类信息
//如果handler是一个字符串,那么就使用应用程序上下文来获取对应的类类型;否则就直接使用handler.getClass()方法来获取类类型。
Class<?> handlerType = handler instanceof String ? this.obtainApplicationContext().getType((String)handler) : handler.getClass();
if (handlerType != null) {
//存储handlerType去除代理和增强后的原始类类型。这是为了避免AOP对方法检测造成干扰。
Class<?> userType = ClassUtils.getUserClass(handlerType);
//存储userType中所有带有映射注解(如@RequestMapping)的方法及其对应的映射信息
Map<Method, T> methods = MethodIntrospector.selectMethods(userType, (method) -> {
try {
//获取每个方法上定义或继承的映射信息
return this.getMappingForMethod(method, userType);
} catch (Throwable var4) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Invalid mapping on handler class [" + userType.getName() + "]: " + method, var4);
}
});
//遍历methods中每个键值对(即每个方法及其映射信息)
methods.forEach((method, mapping) -> {
//存储经过AopUtils.selectInvocableMethod()方法处理后可以被调用(即没有被final修饰)
//且与userType匹配(即没有被覆盖) 的原始或桥接(即泛型擦除后生成) 方法
Method invocableMethod = AopUtils.selectInvocableMethod(method, userType);
//注册到处理器映射
this.registerHandlerMethod(handler, invocableMethod, mapping);
});
}
}
注:
RequestMappingInfo类,主要用来记录方法上@RequestMapping()注解里面的参数,针对RequestMappingHandlerMapping映射器来使用。
步骤2:
RequestMappingHandlerMapping会遍历每个处理器对象中的所有方法,并使用getMappingForMethod()方法来获取每个方法上定义或继承的@RequestMapping注解,然后将这些注解转换为RequestMappingInfo对象,包含了请求路径、请求方法、请求参数、请求头等信息。
//根据处理器类和方法上的@RequestMapping注解来创建一个RequestMappingInfo对象(封装了请求映射的信息,如请求路径、请求方法、请求参数、请求头等)
protected RequestMappingInfo getMappingForMethod(Method method, Class<?> handlerType) {
//获取方法上定义或继承的@RequestMapping注解,并将其转换为一个RequestMappingInfo对象
RequestMappingInfo info = this.createRequestMappingInfo(method);
if (info != null) {
//获取处理器类上定义或继承的@RequestMapping注解,并将其转换为另一个RequestMappingInfo对象
RequestMappingInfo typeInfo = this.createRequestMappingInfo(handlerType);
if (typeInfo != null) {
//合并两个RequestMappingInfo对象
info = typeInfo.combine(info);
}
//获取处理器类上定义或继承的@PathPrefix注解,并将其转换为一个字符串前缀
String prefix = this.getPathPrefix(handlerType);
if (prefix != null) {
//根据指定的路径前缀和配置选项来构建一个新的请求映射信息,并且与原有信息进行合并
info = RequestMappingInfo.paths(new String[]{prefix}).options(this.config).build().combine(info);
}
}
return info;
}
步骤3:
RequestMappingHandlerMapping会将每个RequestMappingInfo对象和对应的处理器方法封装成一个HandlerMethod对象,并将这些对象存储在一个Map结构中,以便于后续查找。
protected void registerHandlerMethod(Object handler, Method method, RequestMappingInfo mapping) {
super.registerHandlerMethod(handler, method, mapping);
this.updateConsumesCondition(mapping, method);
}
//AbstractHandlerMethodMapping类中的方法
protected void registerHandlerMethod(Object handler, Method method, T mapping) {
this.mappingRegistry.register(mapping, handler, method);
}
public void register(T mapping, Object handler, Method method) {
try {
// 创建HandlerMethod对象
HandlerMethod handlerMethod = AbstractHandlerMethodMapping.this.createHandlerMethod(handler, method);
this.validateMethodMapping(handlerMethod, mapping);
//获取匹配条件对应的直接路径,添加到pathLookup中
Set<String> directPaths = AbstractHandlerMethodMapping.this.getDirectPaths(mapping);
Iterator var6 = directPaths.iterator();
while(var6.hasNext()) {
String path = (String)var6.next();
this.pathLookup.add(path, mapping);
}
//如果有命名策略,获取handler方法的名称,添加到nameLookup中
String name = null;
if (AbstractHandlerMethodMapping.this.getNamingStrategy() != null) {
name = AbstractHandlerMethodMapping.this.getNamingStrategy().getName(handlerMethod, mapping);
this.addMappingName(name, handlerMethod);
}
//将匹配条件和MappingRegistration对象(封装了handler方法、直接路径、名称、跨域配置等信息)添加到registry中
this.registry.put(mapping, new AbstractHandlerMethodMapping.MappingRegistration(mapping, handlerMethod, directPaths, name, corsConfig != null));
} finally {
}
}
步骤4:当一个HTTP请求到达
DispatcherServlet时,它会调用RequestMappingHandlerMapping的getHandler()方法来根据请求URI找到匹配的处理器方法。(即3.3节提到的AbstractHandlerMethodMapping父类中的getHandler()方法)
步骤5:
RequestMappingHandlerMapping会遍历Map中的所有键值对(即每个RequestMappingInfo和HandlerMethod),并使用PathMatcher或PathPatternParser来判断请求URI是否与RequestMappingInfo中定义的路径匹配。如果匹配,就返回对应的HandlerMethod;如果不匹配,就继续查找下一个键值对。
protected HandlerMethod lookupHandlerMethod(String lookupPath, HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
// 创建一个空的Match列表,用来存放匹配的RequestMappingInfo和HandlerMethod对象
List<AbstractHandlerMethodMapping<T>.Match> matches = new ArrayList();
// 从mappingRegistry中获取直接路径匹配(即没有通配符或变量)的RequestMappingInfo列表
List<T> directPathMatches = this.mappingRegistry.getMappingsByDirectPath(lookupPath);
if (directPathMatches != null) {
// 调用addMatchingMappings方法,判断直接路径匹配的RequestMappingInfo是否与请求条件匹配
//如果匹配,就添加到matches列表中
this.addMatchingMappings(directPathMatches, matches, request);
}
if (matches.isEmpty()) {
// 如果matches列表为空,说明没有直接路径匹配的RequestMappingInfo与请求条件匹配
//那么就从mappingRegistry中获取所有注册过的RequestMappingInfo,
//并调用addMatchingMappings方法判断是否与请求条件匹配
//如果匹配,就添加到matches列表中
this.addMatchingMappings(this.mappingRegistry.getRegistrations().keySet(), matches, request);
}
if (matches.isEmpty()) {
// 如果matches列表仍然为空,说明没有任何一个RequestMappingInfo与请求条件匹配
//那么就调用handleNoMatch方法处理没有匹配结果的情况,并返回null或抛出异常
return this.handleNoMatch(this.mappingRegistry.getRegistrations().keySet(), lookupPath, request);
} else {
// 如果matches列表不为空,说明至少有一个RequestMappingInfo与请求条件匹配
// 那么就从matches列表中获取第一个Match对象(即最先添加进去的),作为最佳匹配结果
AbstractHandlerMethodMapping<T>.Match bestMatch = (AbstractHandlerMethodMapping.Match)matches.get(0);
if (matches.size() > 1) {
// 如果matches列表中有多个Match对象(即有多个RequestMappingInfo与请求条件匹配)
//那么就需要进行排序和筛选
// 首先创建一个比较器comparator,根据getMappingComparator方法返回的比较器对每个Match对象进行比较(主要比较它们包含的RequestMappingInfo)
Comparator<AbstractHandlerMethodMapping<T>.Match> comparator = new AbstractHandlerMethodMapping.MatchComparator(this.getMappingComparator(request));
// 然后对matches列表进行排序,根据comparator比较器确定每个Match对象之间的优先级和顺序
matches.sort(comparator);
// 再次从matches列表中获取第一个Match对象(即排序后最优先级最高、顺序最靠前、
//最符合请求条件、最具体化、最少参数化等等)作为最佳匹配结果
bestMatch = (AbstractHandlerMethodMapping.Match)matches.get(0);
}
}
request.setAttribute(BEST_MATCHING_HANDLER_ATTRIBUTE, bestMatch.getHandlerMethod());
this.handleMatch(bestMatch.mapping, lookupPath, request);
return bestMatch.getHandlerMethod();
}
}
步骤6:如果找到了匹配的
HandlerMethod,DispatcherServlet就会根据其类型选择合适的HandlerAdapter来执行它,并返回响应结果;如果没有找到匹配的HandlerMethod,DispatcherServlet就会抛出异常或者返回404错误页面。
5. SimpleUrlHandlerMapping
SimpleUrlHandlerMapping是另一个常用的HandlerMapping实现。它允许指定URL模式和Handler的映射关系。

下面是一个简单的SimpleUrlHandlerMapping示例:
public class MySimpleUrlHandlerMapping extends SimpleUrlHandlerMapping {
public MySimpleUrlHandlerMapping() {
Properties mappings = new Properties();
mappings.setProperty("/hello", "helloController");
setMappings(mappings);
}
}
在这个示例中,我们创建了一个名为
MySimpleUrlHandlerMapping的自定义HandlerMapping类。我们通过创建一个Properties对象并将请求路径"/hello"映射到控制器名为"helloController"来设置URL映射。当请求到达服务器时,
SimpleUrlHandlerMapping将查找请求路径并将其与已注册的URL模式进行匹配。如果找到匹配项,则返回关联的处理程序对象。
下面是一个使用SimpleUrlHandlerMapping的控制器示例:
public class HelloController implements Controller {
@Override
public ModelAndView handleRequest(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
ModelAndView mav = new ModelAndView("hello");
mav.addObject("message", "Hello, World!");
return mav;
}
}
在这个示例中,我们创建了一个名为HelloController的控制器类,并实现了Controller接口。handleRequest方法将返回一个名为"hello"的视图,并将一个名为"message"的字符串添加到模型中。
我们将HelloController添加到MySimpleUrlHandlerMapping中:
MySimpleUrlHandlerMapping handlerMapping = new MySimpleUrlHandlerMapping();
Map<String, Object> urlMap = new HashMap<>();
urlMap.put("/hello", new HelloController());
handlerMapping.setUrlMap(urlMap);
在这个示例中,我们将HelloController添加到MySimpleUrlHandlerMapping的URL映射中,并将其注册到Spring MVC应用程序上下文中。
介绍一下这个类中的一个重要方法
registerHandlers(), 这个方法是在Spring框架中用来注册URL映射器的,它可以将URL模式和请求处理器(handler)关联起来
protected void registerHandlers(Map<String, Object> urlMap) throws BeansException {
if (urlMap.isEmpty()) {
//不作操作
} else {
//遍历urlMap中的每一对键值对,键是URL模式,值是handler对象
urlMap.forEach((url, handler) -> {
//对于每一个URL模式,如果它没有以斜杠(/)开头,则在前面加上一个斜杠
if (!url.startsWith("/")) {
url = "/" + url;
}
//对于每一个handler对象,如果它是一个字符串,则去掉字符串两端的空白字符
if (handler instanceof String) {
handler = ((String)handler).trim();
}
//调用父类AbstractUrlHandlerMapping的registerHandler方法,将URL模式和handler对象注册到内部的handlerMap中
this.registerHandler(url, handler);
});
}
}
6. 使用HandlerMapping
在Spring MVC中,使用HandlerMapping非常简单。在控制器中,您可以使用@Autowired注解来注入HandlerMapping实现,并使用它来查找适当的处理程序对象。
@Controller
public class MyController {
@Autowired
private HandlerMapping handlerMapping;
@RequestMapping("/my/path")
public String handleRequest(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
HandlerExecutionChain chain = handlerMapping.getHandler(request);
Object handler = chain.getHandler();
// ...
}
}
在这个示例中,我们使用@Autowired注解将HandlerMapping注入到控制器中。在handleRequest方法中,我们使用HandlerMapping的getHandler方法来获取请求的处理程序对象。我们可以进一步操作处理程序对象,例如调用其方法或检查其注解。
6.1 如何选择合适的HandlerMapping
SpringMVC提供了多种HandlerMapping实现类,你可以根据不同的方式来配置URL和Handler的映射关系,例如:
- 使用XML配置文件来定义
SimpleUrlHandlerMapping或BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping,这种方式比较传统,但是可以集中管理所有的映射关系,也可以自定义拦截器。 - 使用@RequestMapping注解来定义
RequestMappingHandlerMapping,这种方式比较流行,但是需要在每个Controller类或方法上添加注解,也可以使用@PathVariable或@RequestParam等注解来获取请求参数。 - 使用@ControllerAdvice注解来定义
ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver,这种方式可以用来统一处理异常情况,也可以使用@ExceptionHandler或@ResponseStatus等注解来自定义异常处理逻辑。
你可以根据你的喜好和需求来选择一种或多种HandlerMapping实现类,并且可以通过设置order属性来调整它们的优先级
7. 总结
HandlerMapping是Spring MVC中非常重要的一个组件,它负责将请求映射到适当的处理程序对象。RequestMappingHandlerMapping和SimpleUrlHandlerMapping是两个常用的HandlerMapping实现。RequestMappingHandlerMapping使用@RequestMapping注解来确定处理程序对象,而SimpleUrlHandlerMapping使用URL模式来确定处理程序对象。
8. 参考文章
SpringMVC 解析(一)概览 - 御狐神 - 博客园 (cnblogs.com)
RequestMappingHandlerMapping详解 - 朱子威 - 博客园 (cnblogs.com)
SpringMVC工作原理之处理映射HandlerMapping] - 简书 (jianshu.com)
越看越糊涂,打算停一停准备找实习了,希望大家都能有个好结果!!!








![[1.3_3]计算机系统概述——系统调用](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/caf7058e90fe1b17e2978a4d6c45ec83.png)