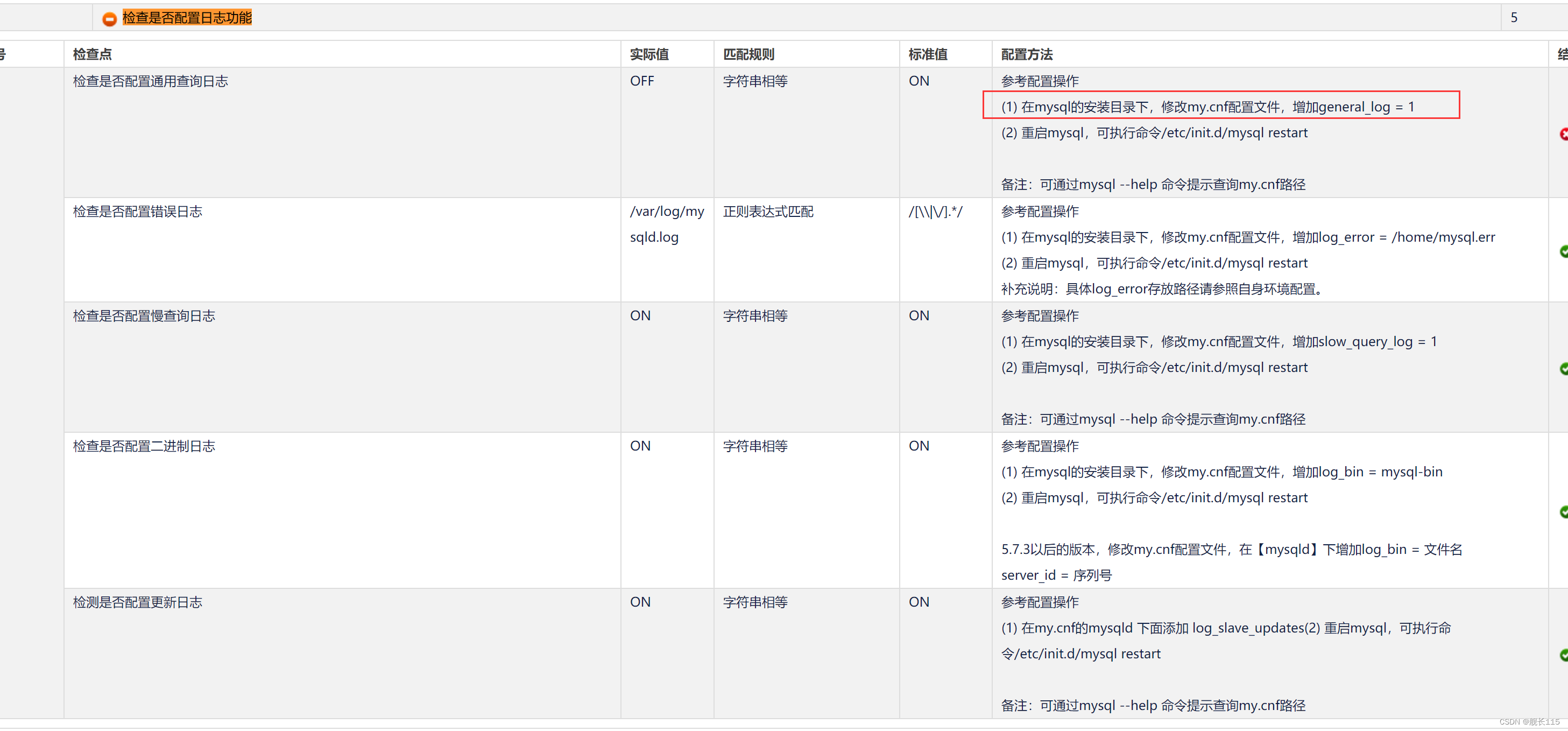
Platform Driver (1)
Linux kernel中大部分设备可以归结为平台设备,因此大部分的驱动是平台驱动(patform driver)
什么是平台设备
平台设备是linux的设备模型中一类设备的抽象。 内核中的描述:
Platform devices are devices that typically appear as autonomous entities in the system. This includes legacy port-based devices and host bridges to peripheral buses, and most controllers integrated into system-on-chip platforms. What they usually have in common is direct addressing from a CPU bus. Rarely, a platform_device will be connected through a segment of some other kind of bus; but its registers will still be directly addressable.
一句话来描述就是: CPU能够直接寻址的SOC上的外设
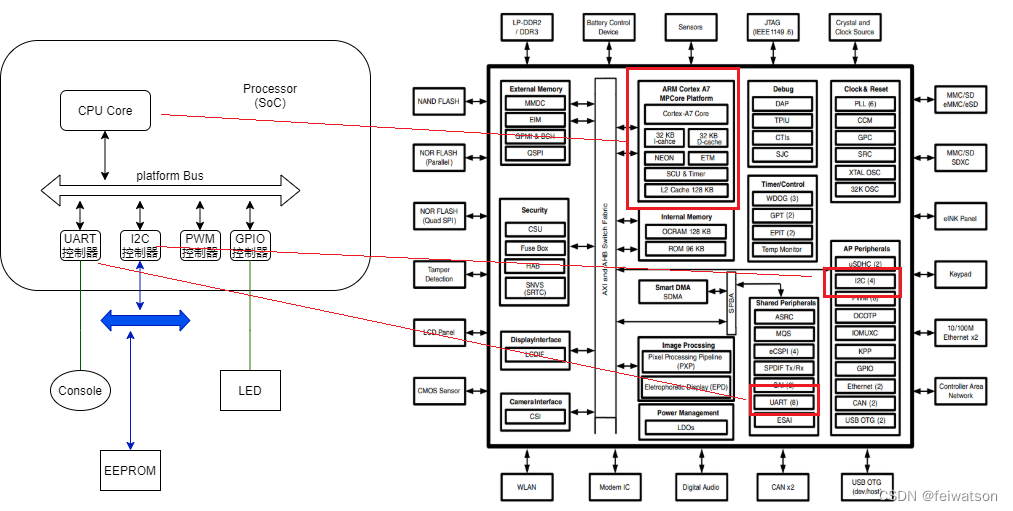
图1:Platform设备
图1中的uart控制器,I2C控制器,GPIO控制器等,都是平台设备。
可以说,paltform设备对Linux驱动工程师是非常重要的,因为我们编写的大多数设备驱动,都是为了驱动plaftom设备。
Platform设备在内核中的实现主要包括三个部分:
- Platform Bus,基于底层bus模块,抽象出一个虚拟的Platform bus,用于挂载Platform设备;
- Platform Device,基于底层device模块,抽象出Platform Device,用于表示Platform设备;
- Platform Driver,基于底层device_driver模块,抽象出Platform Driver,用于驱动Platform设备
对于图1中的I2C控制器挂载在platform Bus上,因此我们在linux kernel中常说的I2C driver,都是指I2C controller driver,都是以platform driver的形式存在,当然,对应的控制器是platform device。
与此同时,kernel抽象出I2C bus(/sys/bus/i2c),用于挂载和I2C controller通过I2C总线连接的各个I2C slave device。
串口驱动开发
驱动开发框架
得益于设备模型,Linux kernel平台驱动的开发有了一套非常固定的框架
1)模块的入口和出口
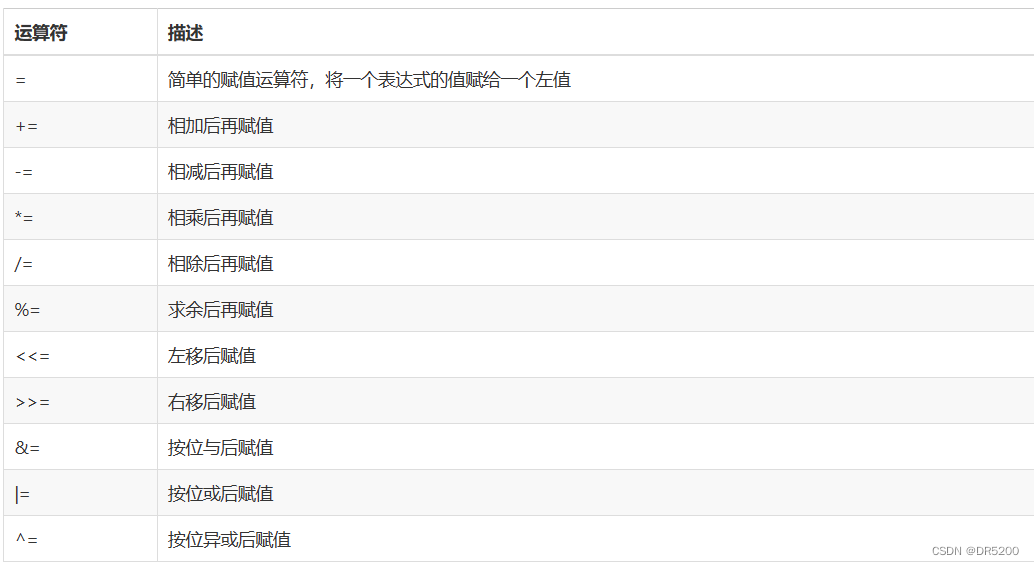
用于注册/注销platform driver,这一部分的代码基本固定,包括函数和变量的命名方式也可固定,如下:
/* 驱动模块加载 */
static int __init xxxdriver_init(void)
{
return platform_driver_register(&xxx_driver);
}
/* 驱动模块卸载 */
static void __exit xxxdriver_exit(void)
{
platform_driver_unregister(&xxx_driver);
}
module_init(xxxdriver_init);
module_exit(xxxdriver_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL V2");
MODULE_AUTHOR("QianRuShi-ABC");
2)platform driver
基本的platform driver包含三要素:struct platform_driver变量、probe/remove函数、用于和device tree匹配的match table,如下:
/*
* platform 平台驱动结构体
*/
static struct platform_driver xxx_driver = {
.driver = {
.name = "xxx",
.of_match_table = xxx_of_match,
},
.probe = xxx_probe,
.remove = xxx_remove,
};
/*
* platform 驱动的 probe 函数
* 驱动与设备匹配成功以后此函数就会执行
*/
static int xxx_probe(struct platform_device *dev)
{
match = of_match_device(xxx_of_match, &pdev->dev);
if (!match) {
dev_err(&pdev->dev, "Error: No device match found\n");
return -ENODEV;
}
return 0;
}
static int xxx_remove(struct platform_device *dev)
{
......
/* 函数具体内容 */
return 0;
}
/* 匹配列表 */
static const struct of_device_id xxx_of_match[] = {
{ .compatible = "xxx-xxx" },
{ /* Sentinel */ }
};
注意,xxx_of_match中的.compatible需要和DTS文件中的compatible对应,一般格式是“厂商名称,芯片系列-模块名”,例如“actions,s900-serial”
##串口驱动
串口设备(serial or uart,后面不再区分)是TTY设备的一种,Linux kernel为了方便串口驱动的开发,在TTY framework的基础上,封装了一层串口框架(serial framework)。该框架尽可能的屏蔽了TTY有关的技术细节(比较难懂),驱动工程师在编写串口驱动的时候,只需要把精力放在串口以及串口控制器本身即可。
Linux kernel serial framework位于“drivers/tty/serial”目录中,其软件架构(如下面图2所示)比较简单:
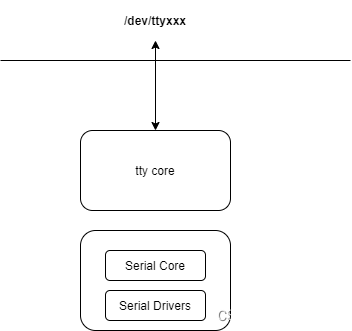
图2: serialFramework
Serial core是Serial framework的核心实现,对上封装、屏蔽TTY的技术细节,对下为具体的串口驱动提供简单、统一的编程API。
Serial drivers就是具体的串口驱动。
Serial Core
serial core主要实现如下三类功能
1)将串口设备有关的物理对象(及其操作方法)封装成一个一个的数据结构,以达到用软件语言描述硬件的目的。
2)向底层driver提供串口驱动的编程接口。
3)基于TTY framework所提供的TTY driver的编写规则,将底层driver看到的serial driver,转换为TTY driver,并将所有的serial操作,转换为对应的tty操作。
关键数据结构
struct uart_port
struct uart_state
struct uart_ops
struct uart_driver
API:
int uart_register_driver(struct uart_driver *uart);
void uart_unregister_driver(struct uart_driver *uart);
int uart_add_one_port(struct uart_driver *reg, struct uart_port *port);
int uart_remove_one_port(struct uart_driver *reg, struct uart_port *port);
int uart_match_port(struct uart_port *port1, struct uart_port *port2);
int uart_suspend_port(struct uart_driver *reg, struct uart_port *port);
int uart_resume_port(struct uart_driver *reg, struct uart_port *port);
static inline int uart_tx_stopped(struct uart_port *port)
extern void uart_insert_char(struct uart_port *port, unsigned int status,
unsigned int overrun, unsigned int ch, unsigned int flag);
串口驱动的移植步骤
- 定义并注册uart driver
- 注册uart port
- 定义并实现uart ops
定义并注册uart driver
static struct uart_driver imx_reg = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.driver_name = DRIVER_NAME,
.dev_name = DEV_NAME,
.major = SERIAL_IMX_MAJOR,
.minor = MINOR_START,
.nr = ARRAY_SIZE(imx_ports),
.cons = IMX_CONSOLE,
};
注册uart port
platform device代表uart控制器,是实体抽象。对应的,uart port代表“串口”. 因此,我们需要在platform device probe的时候(platform driver的probe接口),动态分配并注册一个uart port(struct uart_port)。在后续的串口操作中,都是以uart port指针为对象. 见下一章节代码中i.mx6的驱动代码。
定义并实现uart ops
struct uart_ops结构包含了各式各样的uart端口的操作函数,需要在添加uart port的时候提供.见下一章节代码中i.mx6的驱动代码
完整代码
对应驱动开发框架中,1)模块的入口和出口
static int __init imx_serial_init(void)
{
int ret = uart_register_driver(&imx_reg);
if (ret)
return ret;
ret = platform_driver_register(&serial_imx_driver);
if (ret != 0)
uart_unregister_driver(&imx_reg);
return ret;
}
static void __exit imx_serial_exit(void)
{
platform_driver_unregister(&serial_imx_driver);
uart_unregister_driver(&imx_reg);
}
module_init(imx_serial_init);
module_exit(imx_serial_exit);
MODULE_AUTHOR("Sascha Hauer");
MODULE_DESCRIPTION("IMX generic serial port driver");
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
MODULE_ALIAS("platform:imx-uart");
对应驱动开发框架中,2)platform driver
基本的platform driver包含三要素:struct platform_driver变量、probe/remove函数、用于和device tree匹配的match table
- struct platform_driver变量
static struct platform_driver serial_imx_driver = {
.probe = serial_imx_probe,
.remove = serial_imx_remove,
.suspend = serial_imx_suspend,
.resume = serial_imx_resume,
.id_table = imx_uart_devtype,
.driver = {
.name = "imx-uart",
.of_match_table = imx_uart_dt_ids,
},
};
- robe/remove函数
static int serial_imx_probe(struct platform_device *pdev) { struct imx_port *sport; void __iomem *base; int ret = 0; struct resource *res; int txirq, rxirq, rtsirq; sport = devm_kzalloc(&pdev->dev, sizeof(*sport), GFP_KERNEL); if (!sport) return -ENOMEM; ret = serial_imx_probe_dt(sport, pdev); if (ret > 0) serial_imx_probe_pdata(sport, pdev); else if (ret < 0) return ret;res = platform_get_resource(pdev, IORESOURCE_MEM, 0); base = devm_ioremap_resource(&pdev->dev, res); if (IS_ERR(base)) return PTR_ERR(base); rxirq = platform_get_irq(pdev, 0); txirq = platform_get_irq(pdev, 1); rtsirq = platform_get_irq(pdev, 2); sport->port.dev = &pdev->dev; sport->port.mapbase = res->start; sport->port.membase = base; sport->port.type = PORT_IMX, sport->port.iotype = UPIO_MEM; sport->port.irq = rxirq; sport->port.fifosize = 32; sport->port.ops = &imx_pops; sport->port.rs485_config = imx_rs485_config; sport->port.rs485.flags = SER_RS485_RTS_ON_SEND | SER_RS485_RX_DURING_TX; sport->port.flags = UPF_BOOT_AUTOCONF; init_timer(&sport->timer); sport->timer.function = imx_timeout; sport->timer.data = (unsigned long)sport; sport->clk_ipg = devm_clk_get(&pdev->dev, "ipg"); if (IS_ERR(sport->clk_ipg)) { ret = PTR_ERR(sport->clk_ipg); dev_err(&pdev->dev, "failed to get ipg clk: %d\n", ret); return ret; } sport->clk_per = devm_clk_get(&pdev->dev, "per"); if (IS_ERR(sport->clk_per)) { ret = PTR_ERR(sport->clk_per); dev_err(&pdev->dev, "failed to get per clk: %d\n", ret); return ret; } sport->port.uartclk = clk_get_rate(sport->clk_per); if (sport->port.uartclk > IMX_MODULE_MAX_CLK_RATE) { ret = clk_set_rate(sport->clk_per, IMX_MODULE_MAX_CLK_RATE); if (ret < 0) { dev_err(&pdev->dev, "clk_set_rate() failed\n"); return ret; } } sport->port.uartclk = clk_get_rate(sport->clk_per); /* * Allocate the IRQ(s) i.MX1 has three interrupts whereas later * chips only have one interrupt. */ if (txirq > 0) { ret = devm_request_irq(&pdev->dev, rxirq, imx_rxint, 0, dev_name(&pdev->dev), sport); if (ret) return ret; ret = devm_request_irq(&pdev->dev, txirq, imx_txint, 0, dev_name(&pdev->dev), sport); if (ret) return ret; } else { ret = devm_request_irq(&pdev->dev, rxirq, imx_int, 0, dev_name(&pdev->dev), sport); if (ret) return ret; } imx_ports[sport->port.line] = sport; platform_set_drvdata(pdev, sport); return uart_add_one_port(&imx_reg, &sport->port);
}
static int serial_imx_remove(struct platform_device *pdev)
{
struct imx_port *sport = platform_get_drvdata(pdev);
return uart_remove_one_port(&imx_reg, &sport->port);
}
- 用于和device tree匹配的match table
static const struct of_device_id imx_uart_dt_ids[] = {
{ .compatible = "fsl,imx6q-uart", .data = &imx_uart_devdata[IMX6Q_UART], },
{ .compatible = "fsl,imx1-uart", .data = &imx_uart_devdata[IMX1_UART], },
{ .compatible = "fsl,imx21-uart", .data = &imx_uart_devdata[IMX21_UART], },
{ /* sentinel */ }
};
MODULE_DEVICE_TABLE(of, imx_uart_dt_ids);
对应串口驱动的移植步骤中,定义并注册uart driver
在驱动init函数中注册了uart driver
int ret = uart_register_driver(&imx_reg);
在linux serial framework中,uart driver是一个平行于platform driver的概念,用于驱动“虚拟”的“串口”设备。
#define DRIVER_NAME "IMX-uart"
static struct uart_driver imx_reg = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.driver_name = DRIVER_NAME,
.dev_name = DEV_NAME,
.major = SERIAL_IMX_MAJOR,
.minor = MINOR_START,
.nr = ARRAY_SIZE(imx_ports),
.cons = IMX_CONSOLE,
};
对应串口驱动的移植步骤中,注册uart port
假如一个soc中有5个串口控制器(也可称作uart控制器,后面我们不再区分),每个uart控制器都可引出一个串口(uart port)。那么:
每个uart控制器,都是一个platform device,由dts文件的一个node描述。而这5个platform device,可由同一个driver驱动,即platform driver。
相对于uart控制器实实在在的存在,我们更为熟悉的串口(uart port),则是虚拟的设备,它们由“struct uart_port”描述(后面会介绍),并在platform driver的probe接口中,注册到kernel。它们可由同一个driver驱动,即这里所说的uart driver。
struct imx_port {
struct uart_port port;
struct timer_list timer;
unsigned int old_status;
unsigned int have_rtscts:1;
unsigned int dte_mode:1;
unsigned int irda_inv_rx:1;
unsigned int irda_inv_tx:1;
unsigned short trcv_delay; /* transceiver delay */
struct clk *clk_ipg;
struct clk *clk_per;
const struct imx_uart_data *devdata;
/* DMA fields */
unsigned int dma_is_inited:1;
unsigned int dma_is_enabled:1;
unsigned int dma_is_rxing:1;
unsigned int dma_is_txing:1;
struct dma_chan *dma_chan_rx, *dma_chan_tx;
struct scatterlist tx_sgl[2];
struct imx_dma_rxbuf rx_buf;
unsigned int tx_bytes;
unsigned int dma_tx_nents;
struct delayed_work tsk_dma_tx;
wait_queue_head_t dma_wait;
unsigned int saved_reg[10];
#define DMA_TX_IS_WORKING 1
unsigned long flags;
};
在platform driver的probe函数中会动态分配并注册一个uart port(struct uart_port)然后初始化并注册其中的port变量。初始化完之后,直接调用uart_add_one_port接口,将该port添加到kernel serial core
再返回上面的static int serial_imx_probe(struct platform_device *pdev)展开看到
//分配struct xxx_port类型的指针
struct imx_port *sport;
sport = devm_kzalloc(&pdev->dev, sizeof(*sport), GFP_KERNEL);
//获取中断号,该串口对应的中断号, 一般是从DTS中解析得到的;
rxirq = platform_get_irq(pdev, 0);
txirq = platform_get_irq(pdev, 1);
rtsirq = platform_get_irq(pdev, 2);
//初始化并注册其中的port变量
sport->port.dev = &pdev->dev;
sport->port.mapbase = res->start;
sport->port.membase = base;
sport->port.type = PORT_IMX,
sport->port.iotype = UPIO_MEM;
sport->port.irq = rxirq;
sport->port.fifosize = 32;
sport->port.ops = &imx_pops;
sport->port.rs485_config = imx_rs485_config;
sport->port.rs485.flags =
SER_RS485_RTS_ON_SEND | SER_RS485_RX_DURING_TX;
sport->port.flags = UPF_BOOT_AUTOCONF;
init_timer(&sport->timer);
sport->timer.function = imx_timeout;
sport->timer.data = (unsigned long)sport;
在proble函数的最后,调用uart_add_one_port接口,将该port添加到kernel serial core
return uart_add_one_port(&imx_reg, &sport->port);
对应串口驱动的移植步骤中,定义并实现uart ops
上面platform driver的probe函数serial_imx_probe,展开中看到
sport->port.ops = &imx_pops;
struct uart_ops结构包含了各式各样的uart端口的操作函数,需要在添加uart port的时候提供。
static struct uart_ops imx_pops = {
.tx_empty = imx_tx_empty,
.set_mctrl = imx_set_mctrl,
.get_mctrl = imx_get_mctrl,
.stop_tx = imx_stop_tx,
.start_tx = imx_start_tx,
.stop_rx = imx_stop_rx,
.enable_ms = imx_enable_ms,
.break_ctl = imx_break_ctl,
.startup = imx_startup,
.shutdown = imx_shutdown,
.flush_buffer = imx_flush_buffer,
.set_termios = imx_set_termios,
.type = imx_type,
.config_port = imx_config_port,
.verify_port = imx_verify_port,
#if defined(CONFIG_CONSOLE_POLL)
.poll_init = imx_poll_init,
.poll_get_char = imx_poll_get_char,
.poll_put_char = imx_poll_put_char,
#endif
};
个人公众号交流

#参考
http://www.wowotech.net/x_project/serial_driver_porting_1.html
http://www.wowotech.net/x_project/serial_driver_porting_2.html
http://www.wowotech.net/x_project/serial_driver_porting_3.html
http://www.wowotech.net/x_project/serial_driver_porting_4.html
http://www.wowotech.net/comm/serial_overview.html