1、整个 Spring5 框架的代码基于 Java8,运行时兼容 JDK9,许多不建议使用的类和方 法在代码库中删除
日志框架
2、Spring 5.0 框架自带了通用的日志封装
(1)Spring5 已经移除 Log4jConfigListener,官方建议使用 Log4j2
(2)Spring5 框架整合 Log4j2
第一步 引入 jar 包
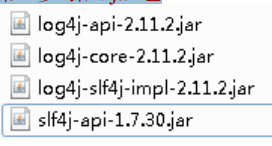
log4j有安全问题,需要下载2.15版本以上的
第二步 创建 log4j2.xml 配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!--日志级别以及优先级排序: OFF > FATAL > ERROR > WARN > INFO > DEBUG > TRACE >
ALL -->
<!--Configuration 后面的 status 用于设置 log4j2 自身内部的信息输出,可以不设置,
当设置成 trace 时,可以看到 log4j2 内部各种详细输出-->
<configuration status="INFO">
<!--先定义所有的 appender-->
<appenders>
<!--输出日志信息到控制台-->
<console name="Console" target="SYSTEM_OUT">
<!--控制日志输出的格式-->
<PatternLayout pattern="%d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS} [%t] %-
5level %logger{36} - %msg%n"/>
</console>
</appenders> <!--然后定义 logger,只有定义 logger 并引入的 appender,appender 才会生效-->
<!--root:用于指定项目的根日志,如果没有单独指定 Logger,则会使用 root 作为
默认的日志输出-->
<loggers>
<root level="info">
<appender-ref ref="Console"/>
</root>
</loggers>
</configuration>

@Nullable
(1)@Nullable 注解可以使用在方法上面,属性上面,参数上面,表示方法返回可以为空,属性值可以 为空,参数值可以为空
(2)注解用在方法上面,方法返回值可以为空

(3)注解使用在方法参数里面,方法参数可以为空

(4)注解使用在属性上面,属性值可以为空

函数式风格
//函数式风格创建对象,交给 spring 进行管理
@Test
public void testGenericApplicationContext() {
//1 创建 GenericApplicationContext 对象
GenericApplicationContext context = new GenericApplicationContext();
//2 调用 context 的方法对象注册
context.refresh();
context.registerBean("user1",User.class,() -> new User());
//3 获取在 spring 注册的对象
// User user = (User)context.getBean("com.atguigu.spring5.test.User");
User user = (User)context.getBean("user1");
System.out.println(user);
}
JUnit5
@ExtendWith(SpringExtension.class)
@ContextConfiguration("classpath:bean1.xml")
public class JTest5 {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
@Test
public void test1() {
userService.accountMoney();
}
}
或者
@SpringJUnitConfig(locations = "classpath:bean1.xml")
public class JTest5 {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
@Test
public void test1() {
userService.accountMoney();
}
}





![3.crypto-config.yaml配置文件分析和cryptogen工具使用[fabric2.2]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/632b626448e6412c8a6e2f3bd6929bae.png)